1.属性动画简介
接下来我们学习Android动画中的第三种动画——属性动画(Property Animation)
Animation一般动画就是我们前面学的帧动画和补间动画!Animator则是本节要讲的属性动画!
1.1为什么要用属性动画
-
补间动画功能比较单调,只有四种动画(透明度,旋转,倾斜和位移)
-
补间动画针对的对象只是UI控件
-
补间动画只是改变View的显示效果,不会去改变View的属性
eg:左边的按钮移到右边,但是此时的按钮其实还停留在左边,假如你去点右面的按钮,是不会触发按钮的点击事件的~
1.2属性动画是什么
-
Andoid 3.0引入,可以说是补间动画的增强版,不止可以实现四种动画效果,可以定义任何属性的变化;
-
执行动画的对象不只是U控件。可以对任何对象执行动画(不管是否显示在屏幕上)
-
属性动画通过对目标对象进行赋值来修改其属性,上面那个按钮问题就不存在了~
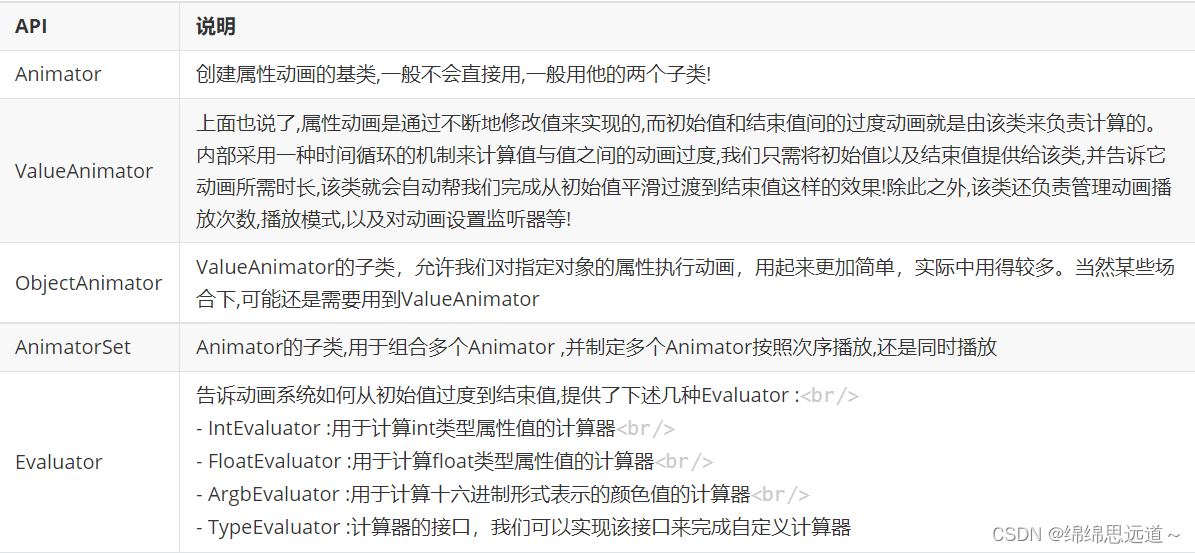
1.3属性动画常用API
见下图:
2.ValueAnimator简单使用
2.1使用流程
-
调用ValueAnimator的ofInt(),ofFloat()或ofObject()静态方法创建ValueAnimator实例
-
调用实例的setXxx方法设置动画持续时间,插值方式,重复次数等
-
调用实例的addUpdateListener添加AnimatorUpdateListener监听器,在该监听器中 可以获得ValueAnimator计算出来的值,你可以值应用到指定对象上
-
调用实例的start()方法开启动画! 另外我们可以看到ofInt和ofFloat都有个这样的参数:float/int... values代表可以多个值!
2.2实例:
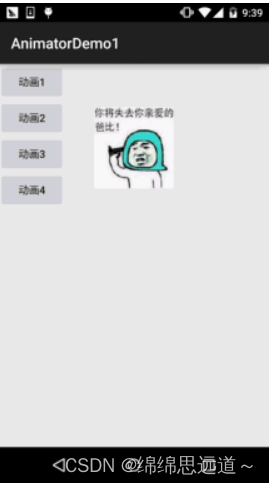
布局文件:activity_main.xml,非常简单,四个按钮,一个ImageView
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"android:id="@+id/ly_root"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"android:orientation="vertical"><Buttonandroid:id="@+id/btn_one"android:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:text="动画1" /><Buttonandroid:id="@+id/btn_two"android:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:text="动画2" /><Buttonandroid:id="@+id/btn_three"android:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:text="动画3" /><Buttonandroid:id="@+id/btn_four"android:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:text="动画4" /><ImageViewandroid:id="@+id/img_babi"android:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:layout_gravity="center"android:background="@mipmap/img_babi" /></LinearLayout>接着到MainActivity.java, 首先需要一个修改View位置的方法,这里调用moveView()设置左边和上边的起始坐标以及宽高!
接着定义了四个动画,分别是:直线移动,缩放,旋转加透明,以及圆形旋转!
然后通过按钮触发对应的动画~
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {private Button btn_one;private Button btn_two;private Button btn_three;private Button btn_four;private ImageView iv_babi;private LinearLayout ly_root;@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);iv_babi = findViewById(R.id.iv_babi);ly_root = findViewById(R.id.ly_root);btn_one = findViewById(R.id.btn_one);btn_two = findViewById(R.id.btn_two);btn_three = findViewById(R.id.btn_three);btn_four = findViewById(R.id.btn_four);btn_one.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {@Overridepublic void onClick(View view) {//获取总布局的宽和高int width = ly_root.getWidth();int height = ly_root.getHeight();ValueAnimator va = ValueAnimator.ofInt(height,0,height/4,height/2,height/4*3,height);va.setDuration(3000l);va.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {@Overridepublic void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator valueAnimator) {int x = width/2;int y = (int) va.getAnimatedValue();moveView(iv_babi,x,y);}});va.setInterpolator(new LinearInterpolator());va.start();}});btn_two.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {@Overridepublic void onClick(View view) {final float scale = 0.5f;AnimatorSet scaleSet = new AnimatorSet();ValueAnimator vaSmall =ValueAnimator.ofFloat(1.0f,scale);vaSmall.setDuration(500);ValueAnimator vaLarge = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(scale,1.0f);vaLarge.setDuration(500);vaSmall.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {@Overridepublic void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator valueAnimator) {float scale = (float) valueAnimator.getAnimatedValue();iv_babi.setScaleX(scale);iv_babi.setScaleY(scale);}});vaLarge.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {@Overridepublic void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator valueAnimator) {float scale = (float) valueAnimator.getAnimatedValue();iv_babi.setScaleX(scale);iv_babi.setScaleY(scale);}});scaleSet.play(vaLarge).after(vaSmall);scaleSet.start();}});btn_three.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {@Overridepublic void onClick(View view) {int width = ly_root.getWidth();int height = ly_root.getHeight();final int R = width/4;ValueAnimator va = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(0,(float) (2.0f*Math.PI));va.setDuration(1000);va.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {@Overridepublic void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator valueAnimator) {float t = (float) valueAnimator.getAnimatedValue();int x =(int) (R* Math.sin(t)+width/2);int y =(int) (R* Math.cos(t)+height/2);moveView(iv_babi,x,y);}});va.setInterpolator(new DecelerateInterpolator());va.start();}});btn_four.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {@Overridepublic void onClick(View view) {ValueAnimator va = ValueAnimator.ofInt(0,360);va.setDuration(1000l);va.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {@Overridepublic void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator valueAnimator) {int rotate = (Integer) valueAnimator.getAnimatedValue();iv_babi.setRotation(rotate);float fractionValue = valueAnimator.getAnimatedFraction();iv_babi.setAlpha(fractionValue);}});va.setInterpolator(new DecelerateInterpolator());va.start();}});}private void moveView(View view,int rawX,int rawY){int left = rawX- view.getWidth()/2;int top = rawY - view.getHeight();int weight = left + view.getWidth();int height = top+ view.getHeight();view.layout(left,top,weight,height);}好的,使用的流程非常简单,先创建ValueAnimator对象,调用ValueAnimator.ofInt/ofFloat 获得,然后设置动画持续时间,addUpdateListener添加AnimatorUpdateListener事件监听, 然后使用参数animation的getAnimatedValue()获得当前的值,然后我们可以拿着这个值 来修改View的一些属性,从而形成所谓的动画效果,接着设置setInterpolator动画渲染模式, 最后调用start()开始动画的播放
3.ObjectAnimator简单使用
比起ValueAnimator,ObjectAnimator显得更为易用,通过该类我们可以直接 对任意对象的任意属性进行动画操作!没错,是任意对象,而不单单只是View对象, 不断地对对象中的某个属性值进行赋值,然后根据对象属性值的改变再来决定如何展现 出来!比如为TextView设置如下动画: ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(textview, "alpha", 1f, 0f); 这里就是不断改变alpha的值,从1f - 0f,然后对象根据属性值的变化来刷新界面显示,从而 展现出淡入淡出的效果,而在TextView类中并没有alpha这个属性,ObjectAnimator内部机制是: 寻找传输的属性名对应的get和set方法~,而非找这个属性值! 不信的话你可以到TextView的源码里找找是否有alpha这个属性! 好的,下面我们利用ObjectAnimator来实现四种补间动画的效果吧~
3.1实例
先看一下效果图:

代码实现如下:
布局直接用的上面那个布局,加了个按钮,把ImageView换成了TextView,这里就不贴代码了, 直接上MainActivity.java部分的代码,其实都是大同小异的~
public class MainActivity3 extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {private Button button1;private Button button2;private Button button3;private Button button4;private Button button5;private LinearLayout ly_root;private TextView tv_show;private int height;private ObjectAnimator animator1;private ObjectAnimator animator2;private ObjectAnimator animator3;private ObjectAnimator animator4;private AnimatorSet animSet;@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.activity_main3);bindViews();initAnimator();}@Overridepublic void onClick(View view) {switch (view.getId()) {case R.id.button1:animator1.setDuration(3000l);animator1.start();break;case R.id.button2:animator2.setDuration(3000l);animator2.start();break;case R.id.button3:animator3.setDuration(3000l);animator3.start();break;case R.id.button4:animator4.setDuration(3000l);animator4.start();break;case R.id.button5://将前面的动画集合到一起~animSet = new AnimatorSet();animSet.play(animator4).with(animator3).with(animator2).after(animator1);animSet.setDuration(5000l);animSet.start();break;case R.id.tv_show:Toast.makeText(MainActivity3.this, "这也可以点???", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();break;}}private void bindViews() {ly_root = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.ly_root);button1 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button1);button2 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button2);button3 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button3);button4 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button4);button5 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button5);tv_show = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv_show);height = ly_root.getHeight();button1.setOnClickListener(this);button2.setOnClickListener(this);button3.setOnClickListener(this);button4.setOnClickListener(this);button5.setOnClickListener(this);tv_show.setOnClickListener(this);}private void initAnimator(){animator1 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(tv_show, "alpha", 1f, 0f, 1f, 0f, 1f);animator2 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(tv_show, "rotation", 0f, 360f, 0f);animator3 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(tv_show, "scaleX", 2f, 4f, 1f, 0.5f, 1f);animator4 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(tv_show, "translationY", height / 8, -100, height / 2);}}
4.使用XML来编写动画
使用XML来编写动画,画的时间可能比Java代码长一点,但是重用起来就轻松很多! 对应的XML标签分别为:<animator><objectAnimator><set> 相关的属性解释如下:
-
android:ordering:指定动画的播放顺序:sequentially(顺序执行),together(同时执行)
-
android:duration:动画的持续时间
-
android:propertyName="x":这里的x,还记得上面的"alpha"吗?加载动画的那个对象里需要 定义getx和setx的方法,objectAnimator就是通过这里来修改对象里的值的!
-
android:valueFrom="1" :动画起始的初始值
-
android:valueTo="0" :动画结束的最终值
-
android:valueType="floatType":变化值的数据类型
4.1实例:
animator/property_animator.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<set xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"android:ordering="together" ><objectAnimatorandroid:duration="3000"android:propertyName="translationX"android:valueFrom="-500"android:valueTo="0"android:valueType="floatType" ></objectAnimator><objectAnimatorandroid:duration="3000"android:propertyName="rotation"android:repeatCount="3"android:valueFrom="0"android:valueTo="360"android:valueType="floatType" ></objectAnimator></set>加载我们的动画文件:
public class MainActivity4 extends AppCompatActivity {private TextView tv_show;private Button btn_start;@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.activity_main4);btn_start = findViewById(R.id.btn_start);tv_show = findViewById(R.id.tv_show);Animator animator = AnimatorInflater.loadAnimator(MainActivity4.this, R.animator.property_animator);animator.setTarget(tv_show);tv_show.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {@Overridepublic void onClick(View view) {Toast.makeText(MainActivity4.this, "没想到吧,我也可以点~~~", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();}});btn_start.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {@Overridepublic void onClick(View view) {animator.start();}});}
}