本文主要介绍vuex【状态管理模式】,在介绍vuex前,需要重点说下一些概念
vue最大的特点之一。数据驱动视图,可以吧数据理解成状态,视图-view可以理解成用户看到的页面,页面是动态变化的,而这个变化必须是有迹可循的,或是用户操作的(如输入,点击,滑动等),亦或是后台操作数据引起的,不管因为什么引起的,统称他们为状态变化了,他由前一个状态变到了后一个状态,页面也就应该随之变化,可得公式 ===》UI【页面输出】 = render【vue扮演的角色】(state)【输入-用户的,后台的】------最关键的是render,vue怎么知道state变化了,最终反映在了UI上呢?-----vue的变化侦测,js提供的
Object.defineProperty方法(有个set和get后面在补充)
,在vue2中,框架是遵循单向数据流,而vue的特点是组件化开发,即单页面多应用:一个主页面,多个组件,这样做可以提高可维护性,组件化开发可以提高复用性,但是就数据传递而言,动不动就父传子,子传父,还有那啥事件总线,,我子组件数据改了,还得告诉父组件,让他改,虽然说我可以利用漏洞,就是那个js复杂对象的引用地址,我改了可以让原数据也跟着改。对了还有就是数组,能改变原数组的可以省点事,如pop,shift之流,但是其他的就费点劲,还得借助$set唉……
vuex的介绍:
前面说了,父传子,子传父,事件总线,费劲,少点还行,要是项目大,凉凉。
ok,我说说我是怎么理解vuex的吧!如果说父传子,就像是2d平面,跟个送快递一样,一级一级的传递,那么vuex就像3d,上帝视角,开飞机送快递,我直接能联系所有组件,并且数据是响应式的啊,有点双向数据绑定的感觉啊,牛逼。
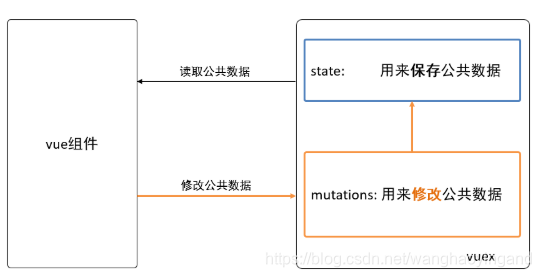

详细的说说他的主要内容--基于vue脚手架安装的--省时省力啊
1.state 保存公共数据的 在组件中通过this.$store.state.name使用 有点像data
<template><div><h2>vuex之 state</h2><div><!-- //如果用脚手架不需要自己导入等操作,真香//可以再任何组件中使用//state的作用是保存公共数据,多组件共用问题1:模板中的可以不加this,其他地方用需要加this,模板底层自动加了this-->在下名叫:{{ $store.state.name }},来自北凉,今年:{{$store.state.age}},早已打遍天下无敌手</div><img :src="this.$store.state.url" alt="" /><button @click="btn">点击修改年龄</button><button @click="btn2">点击切换图片</button><span>{{ this.$store.getters.changeAge }}</span></div>
</template><script>
export default {created () {// 使用mutations进行修改数据,他是入口,只能通过它修改// 固定的方法this.$store.commit('newAge', 1000)console.log(this.$store.getters.changeAge)},methods: {btn () {// 实现的是点击按钮,改变年龄this.$store.commit('newAge', 0.5)},btn2 () {const lj = 'http://s02.mifile.cn/assets/static/image/logo-mi2.png'this.$store.commit('newURL', lj)}}}
</script>2.mutations 用来修改state里面的数据 而且,只有他可以直接修改state里面数据 有点像事件,接下来的几个都将附上两个代码片段,因为他们的使用都是注册和使用,基本都是在store中注册,在组件中使用。组件中使用:this.$store.commit('mutation名',要传入的数据)
//soute注册目录下的代码:
// 提供方法修改数据,他是和其他四个兄弟同级别存在mutations: {// 定义一个mutation来把age改成指定的值,newAge是要传入的数据,也可以不写,而第一个形参是必须的表示当前statesetAge: function(state, newAge) { //注意看他的格式,键值对形式console.log(newAge)state.age = newAge},methods: {hClick() {// 调用mutation来修改年龄,20this.$store.commit('setAge', {newAge: 20, xxx: 100})//this.$store.commit('setAge', 20)}},
//需要提别注意的是:this.$store.commit('mutation名',要传入的数据)3.它的作用是从已有功能数据项中派生出新的数据项,类似于computed (计算属性)
getters:{nickName: function (state) {return state.age > 18 ? '大兄弟' : '小老弟'}},
//就是对state里面的数据进行一些运算,他不能直接修改state,需要借助mutation,调用它修改state的值//在搞这些的时候,多试试,看看log日志打印些啥玩意,然后在应对
<template><div id="app"><NavBar /><div style="display: flex"><SideBar/><div style="flex: 1 1 auto; border:1px solid #ccc;">书目<p v-for="(book, idx) in $store.state.books.list" :key="idx">{{book.name}}, {{book.price}}</p><!-- 共计:{{$store.getters.books.totalPrice}} -->共计:{{ $store.getters['books/totalPrice'] }}</div></div></div>
</template>4.actions 发送异步请求 调用:this.$store.dispatch('actions的名字', 参数)
new Vuex.store({// 省略其他...actions: {// context对象会自动传入,它与store示例具有相同的方法和context对象action的名字: function(context, 载荷) {// 1. 发异步请求, 请求数据// 2. commit调用mutation来修改/保存数据// context.commit('mutation名', 载荷)}}
})5.modules 拆分模板,把复杂的场景按模块来拆开 访问模块中的数据,要加上模块名 {{$store.state.模块名.数据项名}} 在使用modules时,建议都给加上namespaced(命名空间),不写的话不用加模块名
export default new Vuex.Store({// state: 用来保存所有的公共数据state: {},getters: {},mutations: {},actions: {},modules: {模块名1: {// 这个为true,则在使用mutations时,就必须要加上模块名namespaced: true, state: {},getters: {},mutations: {},actions: {},modules: {}},模块名2: {state: {},getters: {},mutations: {},actions: {},modules: {}} }
})
Vuex-辅助函数mapState来使用公共数据
当访问某个数据项嵌套太深了,我们如何
用mapState把公共数据(vuex.store) 映射 到本组件内部的计算属性中
mapState是辅助函数,方便我们使用vuex中的数据;
computed:{ ...mapState() } 这里的...是对象的展开运算符,整体来看是对象的合并。
格式:
// 1. 导入辅助函数mapState,它是在vuex中定义的一个工具函数。
// es6 按需导入 import { mapState } from 'vuex'
import { mapState } from 'vuex'computed: {...mapState(['books'])
}例子:
// 步骤
// 1. 导入辅助函数mapState,它是在vuex中定义的一个工具函数。
// es6 按需导入 import { mapState } from 'vuex'
import { mapState } from 'vuex'// 2. 在computed中使用 ...mapState(['books'])
// const res = mapState(['books'])
// res的结果是一个对象: { books: function() {}}
// console.log('mapState', res)export default {computed: {c1 () {return 'c1'},// books: function() {}// ..res: 把res这个对象合并到computed对象中// ...res...mapState(['books'])}
}
</script>如何使用全局state
直接使用: this.$store.state.;
xxxxxxxxxx computed: { ...mapGetters('模块名', ['xxx']), ...mapGetters('模块名',{'新名字': 'xxx'})}//map辅助函数:参考:---头痛欲裂,抽空好好补上吧!
// 1. 导入vue
import Vue from 'vue'
// 2. 导入 vuex --- 学习的重点
import Vuex from 'vuex'
console.log(Vuex)
// Vue.use 框架中提供的api,用来以vue插件的方式来使用Vuex
// 类似有:Vue.use(vueRouter)
// Vue.use(对象), 对象中会有一个install方法
Vue.use(Vuex)
import axios from 'axios'
// export default: es6的默认导出。
// 这个被导出的对象在main.js中使用.// new Vuex.Store: 实例化一个对象,构造器是Vuex.Store
export default new Vuex.Store({// state: 用来保存所有的公共数据state: {nickName: 'tom',age: 18,url: 'https://img10.360buyimg.com/img/jfs/t1/179086/40/4900/81664/60a47d6bE2bf6455e/208f5820c156d4ab.gif'// url: 'http://s02.mifile.cn/assets/static/image/logo-mi2.png',},// computed// getters的作用是:在state的基础上派生出新的数据项--类似于computedgetters: {gender (state) {return state.age > 18 ? '男人' : '男孩'}},// mutations: 中文是:变化,异动。// 在vuex中,用它提供修改数据的方法。 // 数据不应该在组件内部直接修改,必须在组件内调用mutations来修改mutations: {changeNickName(state, newNickName) {state.nickName = newNickName},changeUrl(state, newUrl) {state.nickName = newNickName}},// modules:用来拆分复杂的业务modules: {book: {// 这个为true,则在使用mutations时,就必须要加上模块名namespaced: true, state: {list: [{name: 'js技术内幕(1)', price: 100}]},mutations: {addBook (state, {name, price}) {state.list.push({name, price})},setBooks(state, books) {state.list = books}},// 发ajax请求,从后端获取数据,再来去修改state中的数据actions: {getBooks (context, params) {console.log('getbooks的查询参数是', params)axios({url: 'https://www.fastmock.site/mock/37d3b9f13a48d528a9339fbed1b81bd5/book/api/books',method: 'GET'}).then(res => {console.log(res)context.commit('setBooks', res.data.data)})}},},skills: {// 这个为false,则在使用mutations时,就必须不需要添加模块名namespaced: false, state: {list: ['手机贴膜']},mutations: {addSkill (state, newSkillName) {state.list.push(newSkillName)}}}}
})




![尚硅谷Vue2.0+Vue3.0全套教程视频笔记 + 代码 [P001-050]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a69aae6ae3a2482aa2d6200037f0434d.png)