@Overrideprotected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {int expendSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(Integer.MAX_VALUE >> 2, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, expendSpec);}是不是很熟悉,没错,它就是我们在 ScrollView 嵌套 ListView 的时候,重写 ListView 来处理 ListView 数据显示不全的问题,那么为什么要这么写呢,而 MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(Integer.MAX_VALUE >> 2, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) 又是什么意思呢,别着急,重头戏马上到来。
1. MeasureSpec 是干什么的
2. MeasureSpec 的原理
MeasureSpec 代表一个32为的 int 值,高两位是 SpecMode,低30位是 SpecSize,SpecMode 是指测量模式,而 SpecMode 是指在某种测量模式下的规格大小,下面先看下 MeasureSpec 内部的一些常量的定义,通过下面的代码,应该不难理解 MeasureSpec 的工作原理:
private static final int MODE_SHIFT = 30;private static final int MODE_MASK = 0x3 << MODE_SHIFT;/** @hide */@IntDef({UNSPECIFIED, EXACTLY, AT_MOST})@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)public @interface MeasureSpecMode {}/*** Measure specification mode: The parent has not imposed any constraint* on the child. It can be whatever size it wants.*/public static final int UNSPECIFIED = 0 << MODE_SHIFT;/*** Measure specification mode: The parent has determined an exact size* for the child. The child is going to be given those bounds regardless* of how big it wants to be.*/public static final int EXACTLY = 1 << MODE_SHIFT;/*** Measure specification mode: The child can be as large as it wants up* to the specified size.*/public static final int AT_MOST = 2 << MODE_SHIFT;/*** Creates a measure specification based on the supplied size and mode.** The mode must always be one of the following:* <ul>* <li>{@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#UNSPECIFIED}</li>* <li>{@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#EXACTLY}</li>* <li>{@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#AT_MOST}</li>* </ul>** <p><strong>Note:</strong> On API level 17 and lower, makeMeasureSpec's* implementation was such that the order of arguments did not matter* and overflow in either value could impact the resulting MeasureSpec.* {@link android.widget.RelativeLayout} was affected by this bug.* Apps targeting API levels greater than 17 will get the fixed, more strict* behavior.</p>** @param size the size of the measure specification* @param mode the mode of the measure specification* @return the measure specification based on size and mode*/public static int makeMeasureSpec(@IntRange(from = 0, to = (1 << MeasureSpec.MODE_SHIFT) - 1) int size,@MeasureSpecMode int mode) {if (sUseBrokenMakeMeasureSpec) {return size + mode;} else {return (size & ~MODE_MASK) | (mode & MODE_MASK);}}/*** Like {@link #makeMeasureSpec(int, int)}, but any spec with a mode of UNSPECIFIED* will automatically get a size of 0. Older apps expect this.** @hide internal use only for compatibility with system widgets and older apps*/public static int makeSafeMeasureSpec(int size, int mode) {if (sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec && mode == UNSPECIFIED) {return 0;}return makeMeasureSpec(size, mode);}/*** Extracts the mode from the supplied measure specification.** @param measureSpec the measure specification to extract the mode from* @return {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#UNSPECIFIED},* {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#AT_MOST} or* {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#EXACTLY}*/@MeasureSpecModepublic static int getMode(int measureSpec) {//noinspection ResourceTypereturn (measureSpec & MODE_MASK);}/*** Extracts the size from the supplied measure specification.** @param measureSpec the measure specification to extract the size from* @return the size in pixels defined in the supplied measure specification*/public static int getSize(int measureSpec) {return (measureSpec & ~MODE_MASK);}MeasureSpec 通过将 SpecMode 和 SpecSize 打包成一个 int 值来避免过多的对象内存分配,为了方便操作,其提供了打包和解包的方法。SpecMode 和 SpecSize 也是一个 int 值,一组 SpecMode 和 SpecSize 可以打包成一个 MeasureSpec,而一个 MeasureSpec 可以通过解包的方法来得出原始的 SpecMode 和 SpecSize,需要注意的是这里提到的 MeasureSpec 是值 MeasureSpec 所代表的 int 值,而并非 MeasureSpec 本身。
3. MeasureSpec 的三种模式
(1)UNSPECIFIEND
父容易不对 View 有任何影响,要多大给多大,这种情况一般用于系统内部,表示一种测量模式(我也不是太懂,有懂的大佬指点下)
(2)EXACTLY
父容器已经检测出 View 所需要的精确大小,这个时候 View 的最终大小就是 MeasureSpec 所指定的值,它对应于 LayoutParams 的 match_parent 和具体的数值两种模式。(如果是重写控件,慎用该模式,不然你会发现一件很神奇的事情,想知道的可以自己动手试试)
(3)AT_MOST
父容器指定一个大小即 SpecSize,View 的大小不能大于这个值,具体是什么值要看不同 View 的具体实现,它对应于 LayoutParams 的warp_content。
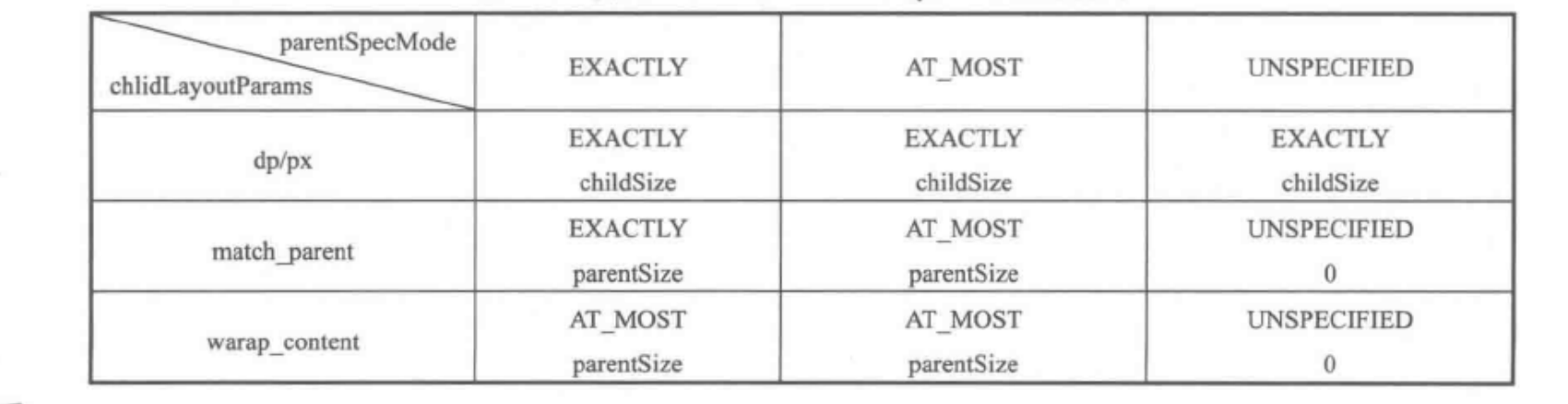
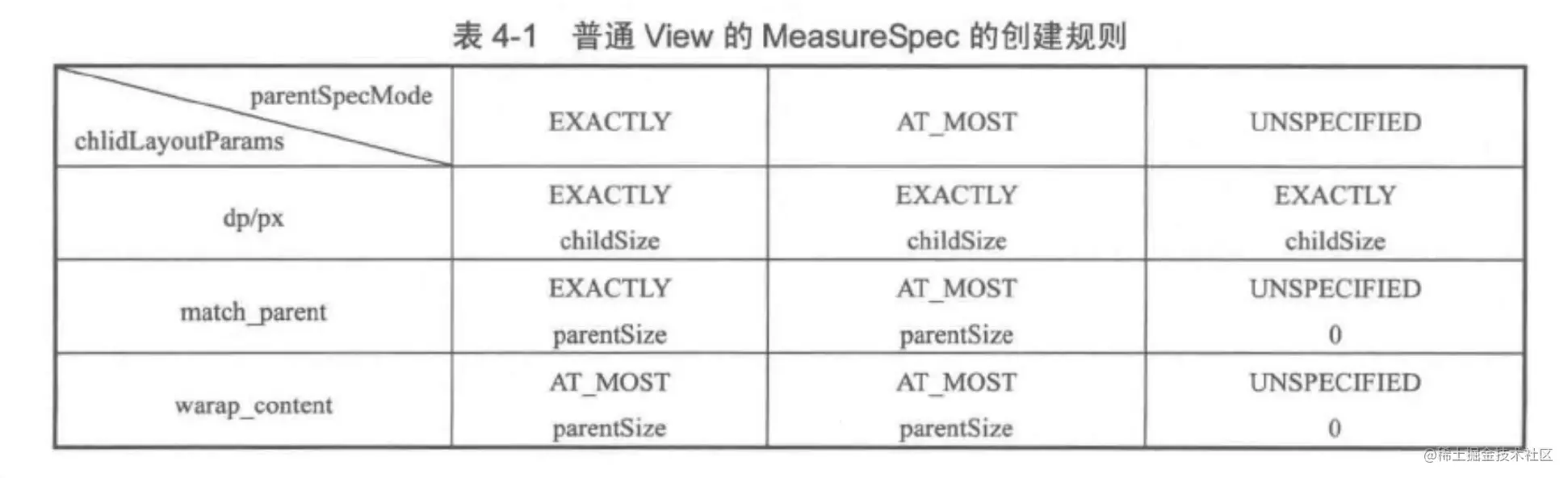
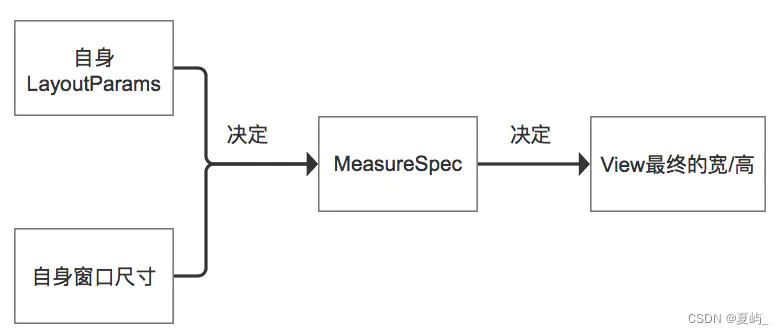
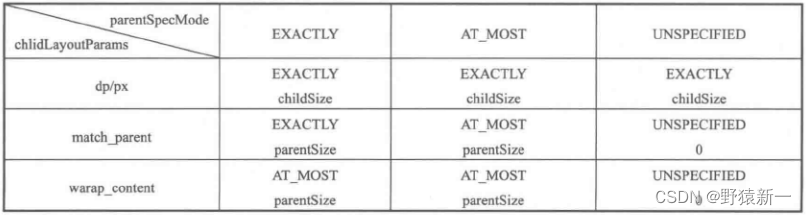
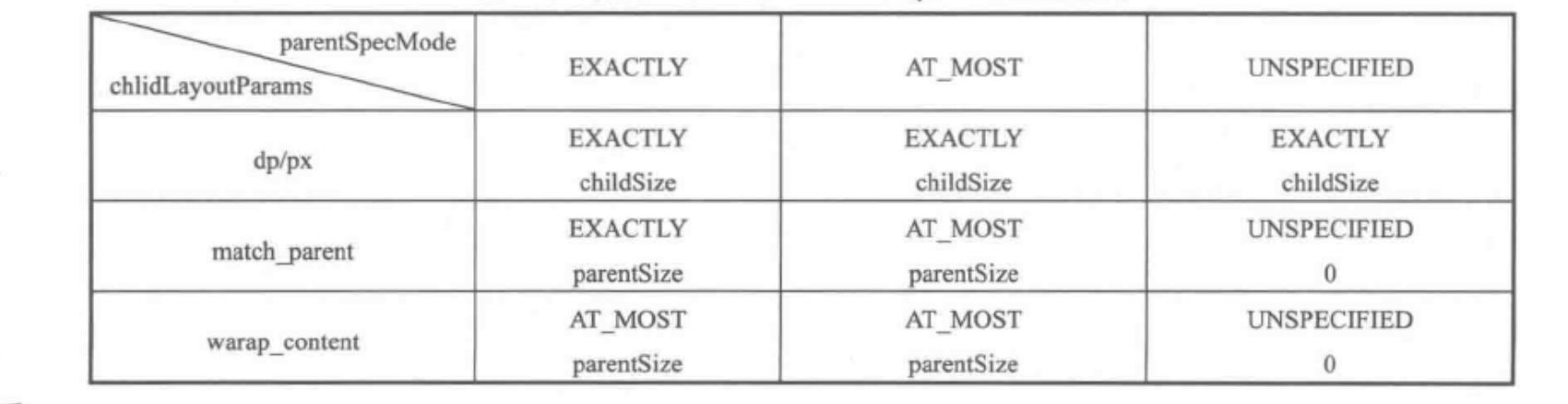
4.MeasureSpec 和 LayoutParams 对应关系
childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(desiredWindowWidth, lp.width);childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(desiredWindowHeight, lp.height);performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);/*** Figures out the measure spec for the root view in a window based on it's* layout params.** @param windowSize* The available width or height of the window** @param rootDimension* The layout params for one dimension (width or height) of the* window.** @return The measure spec to use to measure the root view.*/private static int getRootMeasureSpec(int windowSize, int rootDimension) {int measureSpec;switch (rootDimension) {case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT:// Window can't resize. Force root view to be windowSize.measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);break;case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT:// Window can resize. Set max size for root view.measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);break;default:// Window wants to be an exact size. Force root view to be that size.measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(rootDimension, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);break;}return measureSpec;}
// Note: padding has already been removed from the supplied specsprivate void measureChildWithMargins2(View child, int parentWidthSpec, int parentHeightSpec,int childWidth, int childHeight) {int childWidthSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthSpec,getTotalMargin(child, true), childWidth);int childHeightSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightSpec,getTotalMargin(child, false), childHeight);child.measure(childWidthSpec, childHeightSpec);} /*** Does the hard part of measureChildren: figuring out the MeasureSpec to* pass to a particular child. This method figures out the right MeasureSpec* for one dimension (height or width) of one child view.** The goal is to combine information from our MeasureSpec with the* LayoutParams of the child to get the best possible results. For example,* if the this view knows its size (because its MeasureSpec has a mode of* EXACTLY), and the child has indicated in its LayoutParams that it wants* to be the same size as the parent, the parent should ask the child to* layout given an exact size.** @param spec The requirements for this view* @param padding The padding of this view for the current dimension and* margins, if applicable* @param childDimension How big the child wants to be in the current* dimension* @return a MeasureSpec integer for the child*/public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec);int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);int resultSize = 0;int resultMode = 0;switch (specMode) {// Parent has imposed an exact size on uscase MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:if (childDimension >= 0) {resultSize = childDimension;resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {// Child wants to be our size. So be it.resultSize = size;resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be// bigger than us.resultSize = size;resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;}break;// Parent has imposed a maximum size on uscase MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:if (childDimension >= 0) {// Child wants a specific size... so be itresultSize = childDimension;resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {// Child wants to be our size, but our size is not fixed.// Constrain child to not be bigger than us.resultSize = size;resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be// bigger than us.resultSize = size;resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;}break;// Parent asked to see how big we want to becase MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:if (childDimension >= 0) {// Child wants a specific size... let him have itresultSize = childDimension;resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {// Child wants to be our size... find out how big it should// beresultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {// Child wants to determine its own size.... find out how// big it should beresultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;}break;}//noinspection ResourceTypereturn MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);} int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);