概述
在Android中,View的onMeasure()方法用来对控件进行测量,确定控件的宽高。该方法的两个参数widthMeasureSpec和heightMeasureSpec由父View计算后传入子view的measure()方法,再由子view的measure()方法传入onMeasure()方法,本文将介绍MeasureSpec的创建规则
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)LayoutParams
在开始源码分析前,我们要先介绍下LayoutParams,因为子view的MeasureSpec的创建需要用到子view的LayoutParams,LayoutParams有如下三种类型
- FILL_PARENT/MATCH_PARENT:填满父View
- WRAP_CONTENT:包裹内容
- 确定值:确定的值
源码分析
首先我们要先找到父View中调用子view的measure()方法的入口
首先先看View类的onMeasure方法如下,由于View是所有控件的基类,这里只是一个默认实现
我们应该看得是ViewGroup类型的类的onMeasure方法
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));}查看源码后发现ViewGroup.java类中并未重写onMeasure()方法,且ViewGroup类是个抽象类,所以我们应该把目光投向ViewGroup的子类,比如AbsoluteLayout、LinearLayout、FrameLayout等
我们选其中一个看看,查看AbsoluteLayout的onMeasure()方法,可以知道如下的调用栈
可以看到measureChildren()和measureChild()是定义在ViewGroup中的,在子类中可以访问
AbsoluteLayout.onMeasure()->ViewGroup.measureChildren()->ViewGroup.measureChild()
接下来直接看measureChild()的源码
由下面的源码及其注释可以看到,子view的MeasureSpec是交由getChildMeasureSpec()方法来计算,终于是让我们找到了
/*** Ask one of the children of this view to measure itself, taking into* account both the MeasureSpec requirements for this view and its padding.* The heavy lifting is done in getChildMeasureSpec.** @param child The child to measure* @param parentWidthMeasureSpec The width requirements for this view* @param parentHeightMeasureSpec The height requirements for this view*/protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec,int parentHeightMeasureSpec) {final LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams();final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight, lp.width);final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom, lp.height);child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);}接下来我们就看看getChildMeasureSpec()方法的源码,也是本文的重点内容
该方法的功能就是通过父view的MeasureSpec和子View的LayoutParams来计算出子View的MeasureSpec
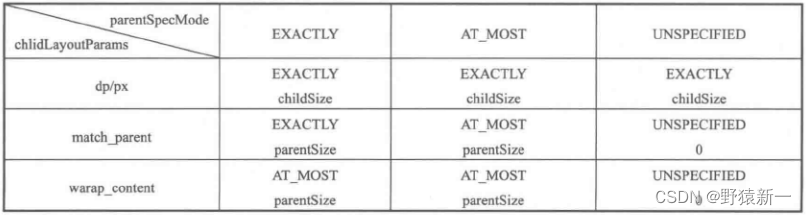
父View的MeasureSpec有MeasureSpec.EXACTLY、MeasureSpec.AT_MOST和MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED三种类型,而子view的LayoutParams也有MATCH_PARENT、WRAP_CONTENT或者确定值三种类型,3*3得出9种情况,如下代码所示
/*** Does the hard part of measureChildren: figuring out the MeasureSpec to* pass to a particular child. This method figures out the right MeasureSpec* for one dimension (height or width) of one child view.** The goal is to combine information from our MeasureSpec with the* LayoutParams of the child to get the best possible results. For example,* if the this view knows its size (because its MeasureSpec has a mode of* EXACTLY), and the child has indicated in its LayoutParams that it wants* to be the same size as the parent, the parent should ask the child to* layout given an exact size.** @param spec The requirements for this view* @param padding The padding of this view for the current dimension and* margins, if applicable* @param childDimension How big the child wants to be in the current* dimension* @return a MeasureSpec integer for the child*/public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec);int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);int resultSize = 0;int resultMode = 0;switch (specMode) {// Parent has imposed an exact size on uscase MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:if (childDimension >= 0) {resultSize = childDimension;resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {// Child wants to be our size. So be it.resultSize = size;resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be// bigger than us.resultSize = size;resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;}break;// Parent has imposed a maximum size on uscase MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:if (childDimension >= 0) {// Child wants a specific size... so be itresultSize = childDimension;resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {// Child wants to be our size, but our size is not fixed.// Constrain child to not be bigger than us.resultSize = size;resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be// bigger than us.resultSize = size;resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;}break;// Parent asked to see how big we want to becase MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:if (childDimension >= 0) {// Child wants a specific size... let him have itresultSize = childDimension;resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {// Child wants to be our size... find out how big it should// beresultSize = 0;resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {// Child wants to determine its own size.... find out how// big it should beresultSize = 0;resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;}break;}return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);}总结
子view的MeasureSpec创建规则如下表所示