文章目录
- 应用场景
- N-Queens
- Permutations
- Permutations II
- 参考资料
backtracking(回溯法)是一种算法,主要用来解决带限制条件的计算问题( CSP)。
特点如下:
- 和暴力匹配算法一样,会尝试所有的可能性。
- 比暴力匹配算法好,会在尝试的过程中不断丢弃不正确的解。
应用场景
N-Queens
链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/n-queens/
代码
func solveNQueens(n int) [][]string {board := make([][]int, n)for i := 0; i < n; i++ {board[i] = make([]int, n)}var res [][]stringres = solve(res, board, 0)return res
}// row: 当前行
func solve(res [][]string, board [][]int, row int) [][]string {if row == len(board) {res = append(res, construct(board))return res}for col := 0; col < len(board); col++ {if check(board, row, col) {board[row][col] = 1res = solve(res, board, row+1)board[row][col] = 0}}return res
}func check(board [][]int, row int, col int) bool {for i := 0; i < row; i++ {if board[i][col] == 1 {return false}rowDiff := row - i// 45度if col + rowDiff < len(board) && board[i][col + rowDiff] == 1 {return false}// 135度if col - rowDiff >= 0 && board[i][col - rowDiff] == 1 {return false}}return true
}func construct(board [][]int) []string {var res []stringfor i := 0; i < len(board); i++ {var tmp stringfor j := 0; j < len(board); j++ {if board[i][j] == 1 {tmp += "Q"} else {tmp += "."}}res = append(res, tmp)}return res
}
Permutations
链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/permutations/
代码
func permute(nums []int) [][]int {var res [][]intboard := make([]int, len(nums))for i := 0; i < len(board); i++ {board[i] = math.MinInt32}res = solve(res, board, nums, 0)return res
}func solve(res [][]int, board []int, nums []int, index int) [][]int {if index == len(board) {res = append(res, construct(board))return res}for col := 0; col < len(board); col++ {if check(board, col) {board[col] = nums[index]res = solve(res, board, nums, index+1)board[col] = math.MinInt32}}return res
}func check(board []int, col int) bool {return board[col] == math.MinInt32
}func construct(board []int) []int {res := make([]int, len(board))for i := 0; i < len(board); i++ {res[i] = board[i]}return res
}
同样是回溯,这道题还有另一种解法
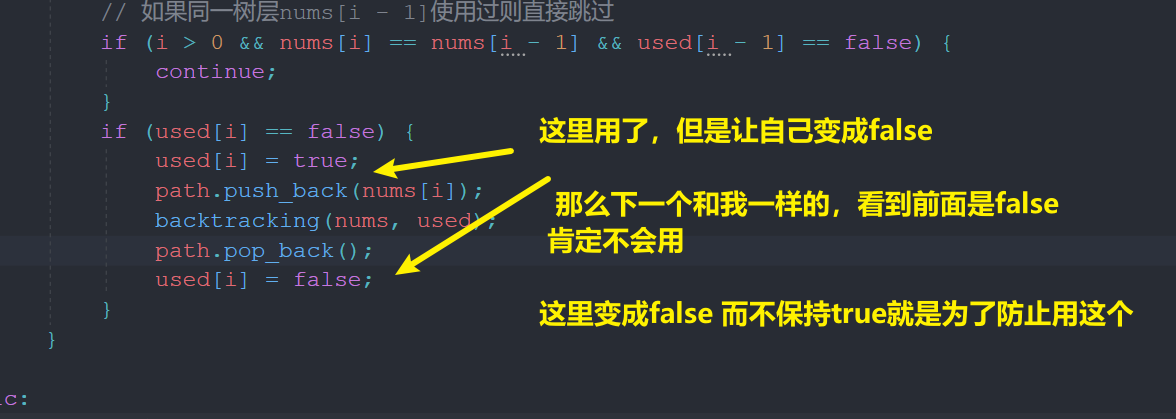
func permute(nums []int) [][]int {var res [][]intused := make([]bool, len(nums))var tmpList []intres = backtrack(res, tmpList, used, nums)return res
}func backtrack(res [][]int, tmpList []int, used []bool, nums []int) [][]int {if len(tmpList) == len(nums) {res = append(res, construct(tmpList))return res}for i := 0; i < len(nums); i++ {if used[i] {continue}used[i] = truetmpList = append(tmpList, nums[i])res = backtrack(res, tmpList, used, nums)tmpList = tmpList[0:len(tmpList)-1]used[i] = false}return res
}func construct(tmpList []int) []int {res := make([]int, len(tmpList))for i := 0; i < len(tmpList); i++ {res[i] = tmpList[i]}return res
}
这里简单说下两者的区别
解法1:
参考N-Queens,题目演化为一个1x3的棋盘,然后将nums中的元素逐个放到棋盘的第一列、第二列、第三列。
解法2:
符合正常思路,遍历nums,将元素逐个放到一个list中。
对于Permutations,我觉得解法1和解法2都是OK的,但是对于Permutations II,解法1扩展起来就比较困难了。
Permutations II
链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/permutations-ii/
代码
【仅贴出和Permutations不同的地方】

参考资料
https://www.interviewbit.com/courses/programming/topics/backtracking/
https://leetcode.com/problems/permutations/discuss/18239/A-general-approach-to-backtracking-questions-in-Java-(Subsets-Permutations-Combination-Sum-Palindrome-Partioning)
https://leetcode.com/problems/permutations-ii/discuss/18594/Really-easy-Java-solution-much-easier-than-the-solutions-with-very-high-vote