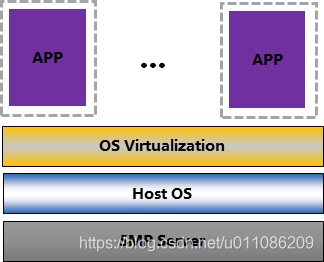
服务器虚拟化目前是IT界的一个热门话题。它的受欢迎程度和使用率一直在增长,尤其是在企业环境中。使虚拟化成为可能的是所谓的hypervisor 管理程序。服务器虚拟化允许不同的操作系统在一台服务器上运行单独的应用程序,同时仍使用相同的物理资源。这些虚拟机使系统和网络管理员可以为需要运行的每个服务拥有专用的计算机。这不仅减少了所需的物理服务器数量,而且还节省了查找问题的时间。
在本文中,我们将讨论什么是虚拟机管理程序(hypervisor ),它们如何工作以及存在的不同类型。
在这里插入图片描述

什么是虚拟机监控程序?
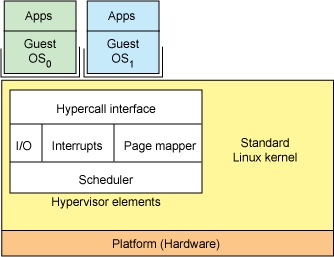
管理程序hypervisor,是使虚拟化成为可能的关键软件。它从实际硬件中提取来宾计算机及其运行的操作系统。
系统管理程序创建一个虚拟化层,该层将CPU /处理器,RAM和其他物理资源与您创建的虚拟机分开。
我们在其上安装虚拟机管理程序的计算机称为主机,而与之相对的是在主机上运行的来宾虚拟机。
虚拟机管理程序模拟可用资源,以便客户机可以使用它们。无论使用虚拟机启动哪种操作系统,被启动的操作系统都会认为实际的物理硬件可供使用。
From a VM’s standpoint, there is no difference between the physical and virtualized environment. Guest machines do not know that the hypervisor created them in a virtual environment. Or that they are sharing available computing power. VMs run simultaneously with the hardware that powers them, and so they are entirely dependent on its stable operation.
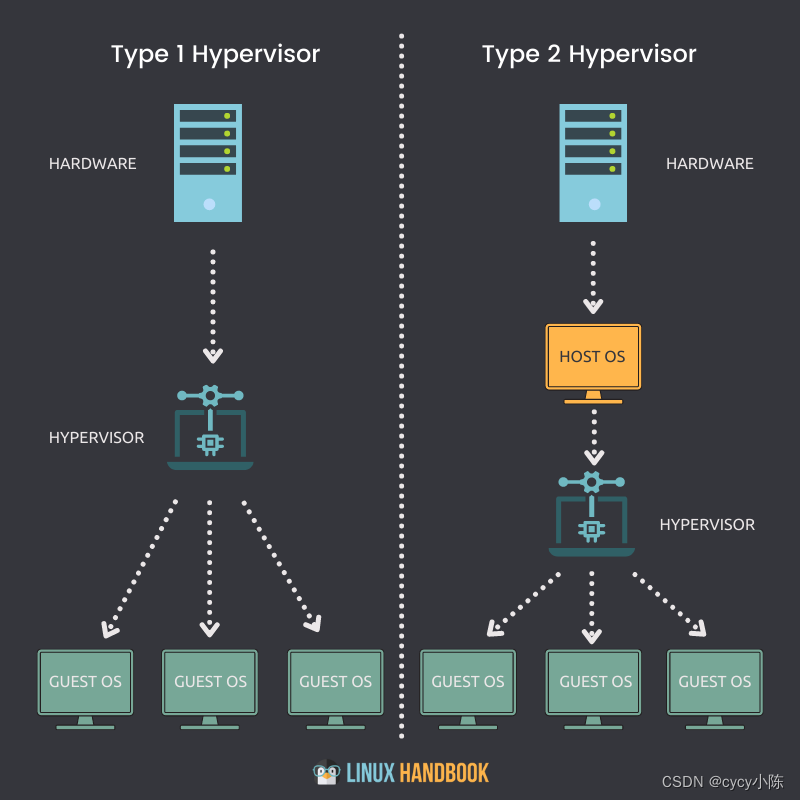
Type 1 Hypervisor (also called bare metal or native)
Type 2 Hypervisor (also known as hosted hypervisors)
Type 1 Hypervisor
A bare-metal hypervisor (Type 1) is a layer of software we install directly on top of a physical server and its underlying hardware.
There is no software or any operating system in between, hence the name bare-metal hypervisor. A Type 1 hypervisor is proven in providing excellent performance and stability since it does not run inside Windows or any other operating system.
Type 1 hypervisors are an OS themselves, a very basic one on top of which you can run virtual machines. The physical machine the hypervisor is running on serves virtualization purposes only. You cannot use it for anything else.
Type 1 hypervisors are mainly found in enterprise environments.

type 1 Hypervisor example with virtual machines and physical server
Hypervisor Type 1 Performance
Given that type 1 hypervisors are relatively simple, they do not offer many functionalities.
Once you boot up a physical server with a bare-metal hypervisor installed, it displays a command prompt-like screen. If you connect a monitor to the server, what you get to see are some of the hardware and network details. This consists of the CPU type, the amount of memory, the IP address and the MAC address.
Below is an example of a VMware type 1 hypervisor’s screen after the server boots up.
 example of VMware hypervisor
example of VMware hypervisor
Another type 1 hypervisor may look quite different but they also only allow for simple server configuration. This consists of changing the date and time, IP address, password, etc. In order to create virtual instances, you need a management console set up on another machine. Using the console, you can connect to the hypervisor on the server, and manage your virtual environment.
A management console can be web-based or a separate software package you install on the machine for which you want remote management. Depending on what functionalities you need, the license cost for management consoles varies substantially.
One action you can perform includes moving virtual machines between physical servers, manually or automatically. This move is based on resource needs of a VM at a given moment and happens without any impact to the end-users. It’s the same process if a piece of hardware or a whole server fails. Properly configured management software moves virtual machines to a working server as soon as an issue arises. The detection and restoration procedure takes place automatically and seamlessly.
One of the best features of type 1 hypervisors is that they allow for over-allocation of physical resources.
With type 1 hypervisors, you can assign more resources to your virtual machines than you have available. For example, if you have 128GB of RAM on your server and eight virtual machines, you can assign 24GB of RAM to each of them. This totals to 192GB of RAM, but VMs themselves will not actually consume all 24GB from the physical server. The VMs think they have 24GB when in reality they only use the amount of RAM they need to perform particular tasks.
The hypervisor allocates only the amount of necessary resources for an instance to be fully functional. This is one of the reasons all modern enterprise data centers, such as phoenixNAP, use type 1 hypervisors.
Type 1 Vendors
There are many different hypervisor vendors available. Most provide trial periods to test out their services before you buy them.
The licensing costs can be high if you want all the bells and whistles they have on offer.
These are the most common type 1 hypervisors:
VMware vSphere with ESX/ESXi
VMware is an industry-leading vendor of virtualization technology, and many large data centers run on their products. It may not be the most cost-effective solution for smaller IT environments. If you do not need all the advanced features VMware vSphere offers, there is a free version of this hypervisor and multiple commercial editions.
KVM (Kernel-Based Virtual Machine)
KVM is built into Linux as an added functionality. It lets you convert the Linux kernel into a hypervisor. It is sometimes confused with a type 2 hypervisor (see definition below). It has direct access to hardware along with virtual machines it hosts. KVM is an open-source hypervisor that contains all the features of Linux with the addition of many other functionalities. This makes it one of the top choices for enterprise environments. Some of the highlights include live migration, scheduling and resource control, alongside higher prioritization.
Microsoft Hyper-V
Despite VMware’s hypervisor being higher on the ladder with its numerous advanced features, Microsoft’s Hyper-V has become a worthy opponent. Microsoft also offers a free edition of their hypervisor, but if you want a GUI and additional functionalities, you will have to go for one of the commercial versions. Hyper-V may not offer as many features as VMware vSphere package, but you still get live migration, replication of virtual machines, dynamic memory and many other features.
Oracle VM
This hypervisor has open-source Xen at its core and is free. Advanced features are only available in paid versions. Even though Oracle VM is essentially a stable product, it is not as robust as vSphere, KVM or Hyper-V.
Citrix Hypervisor (formerly known as Xen Server)
This Server virtualization platform by Citrix is best suited for enterprise environments. It can handle all types of workloads and provides features for the most demanding tasks. Citrix is proud of its proprietary features, such as Intel and NVIDIA enhanced virtualized graphics and workload security with Direct Inspect APIs.
Type 2 Hypervisor
This type of hypervisor runs inside of an operating system of a physical host machine.
This is why we call type 2 hypervisors – hosted hypervisors. As opposed to type 1 hypervisors that run directly on the hardware, hosted hypervisors have one software layer underneath. In this case we have:
A physical machine.
An operating system installed on the hardware (Windows, Linux, macOS).
A type 2 hypervisor software within that operating system.
The actual instances of guest virtual machines.

Type 2 hypervisors are typically found in environments with a small number of servers.
What makes them convenient is that you do not need a management console on another machine to set up and manage virtual machines. You can do all of this on the server where you install the hypervisor. They are not any different from the other applications you have in your operating system.
When you launch a virtual machine, you get another window to perform all tasks.
Hypervisor Type 2 Performance
Hosted hypervisors essentially also act as management consoles for virtual machines, you can perform any task using the built-in functionalities.
There is no need to install separate software on another machine to create and maintain your virtual environment. You simply install and run a type 2 hypervisor as you would any other application within your OS. With it, you can create snapshots or clone your virtual machines, import or export appliances, etc.
Here is one example of a type 2 hypervisor interface (VirtualBox by Oracle):

You do need to be careful when allocating actual resources with this type of hypervisor.
Bare-metal hypervisors can dynamically allocate available resources depending on the current needs of a particular VM. A type 2 hypervisor occupies whatever you allocate to a virtual machine.
When you assign 8GB of RAM to a VM, that amount will be taken up even if the VM is using only a fraction of it. If the host machine has 32GB of RAM and you create three VMs with 8GB each, you are left with 8GB of RAM to keep the physical machine running. Creating another VM with 8GB of ram would bring down your system. This is critical to keep in mind, so as to avoid over-allocating resources and crashing the host machine.
Type 2 hypervisors are convenient for testing new software and research projects.
It is possible to use one physical machine to run multiple instances with different operating systems to test how an application behaves in each environment or to create a specific network environment. You only need to make sure that there are enough physical resources to keep both the host and the virtual machines running.
Type 2 Vendors
As is the case with bare-metal hypervisors, you can choose between numerous vendors and products. Conveniently, many type 2 hypervisors are free in their basic versions and provide sufficient functionalities.
Some even provide advanced features and performance boosts when you install add-on packages, free of charge. We will mention a few of the most used hosted hypervisors:
Oracle VM VirtualBox
A free but stable product with enough features for personal use and most use cases for smaller businesses. VirtualBox is not resource demanding, and it has proven to be a good solution for both desktop and server virtualization. It provides support for guest multiprocessing with up to 32 vCPUs per virtual machine, PXE Network boot, snapshot trees, and much more.
VMware Workstation Pro/VMware Fusion
VMware Workstation Pro is a type 2 hypervisor for Windows OS. It is full of advanced features and has seamless integration with vSphere. This allows you to move your apps between desktop and cloud environments.
It does come with a price tag, as there is no free version. If you want to take a glimpse into VMware hosted hypervisors free of charge, you can try VMware Workstation Player. This is the basic version of the hypervisor suitable for small sandbox environments.
For MacOS users, VMware has developed Fusion that is similar to their Workstation product. It comes with somewhat fewer features, but also carries a smaller price tag.
Windows Virtual PC
It only supports Windows 7 as a host machine and Windows OS on guest machines. This includes multiple versions of Windows 7 and Vista, as well as XP SP3. Virtual PC is completely free.
Parallels Desktop
A competitor to VMware Fusion. It is primarily intended for MacOS users and offers plenty of features depending on the version you purchase. Some of the features are network conditioning, integration with Chef/Ohai/Docker/Vagrant, support for up to 128GB per VM, etc.
Type 1 vs. Type 2 Hypervisor
Choosing the right type of hypervisor strictly depends on your individual needs.
The first thing you need to keep in mind is the size of the virtual environment you intend to run.
For personal use and smaller deployments, you can go for one of the type 2 hypervisors. If budget is not an issue, VMware will provide every feature you need. Otherwise, Oracle VM VirtualBox is a hypervisor that will provide most of the functionalities generally needed.
Enterprise Environments
Even though type 1 hypervisors are the way to go, you do need to take into consideration many factors before making a decision.
The critical factor is usually the licensing cost. This is where you need to pay extra attention since licensing may be per server, per CPU or sometimes even per core. In the current market, there is a battle going on between VMware vSphere and Microsoft Hyper-V. While Hyper-V was falling behind a few years ago, it has now become a valid choice, even for larger deployments. The same argument can be made for KVM.
Many vendors offer multiple products and layers of licenses to accommodate any organization. You may want to create a list of the requirements. Such as, how many VMs you need, maximum allowed resources per VM, nodes per cluster, specific functionalities, and then check which of these products best fits your needs. Note: trial periods can be very useful when testing for which hypervisor to choose.
In Closing
This article has explained what a hypervisor is and the types of hypervisors (type 1 and type 2) you can use.
Hypervisor vendors offer packages that contain multiple products with different licensing agreements. You will need to research the options thoroughly before making a final decision. Even though you can migrate between the hypervisors, this can be a tedious and expensive process. It’s best to get this decision right from the get go.
文章参考:https://phoenixnap.com/kb/what-is-hypervisor-type-1-2