链表
- 一、介绍
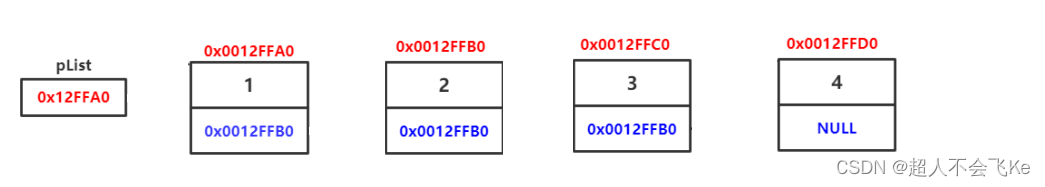
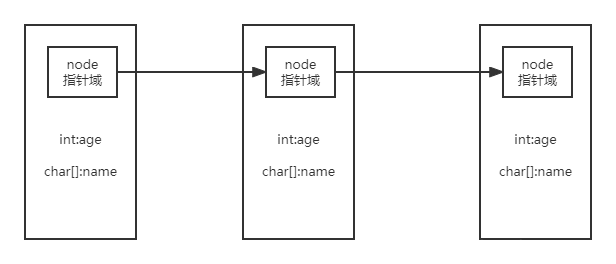
- 1、单链表
- 1、单链表结构体:
- 2、单链表头插法:
- 3、单链表尾插法:
- 二、例题
- 1、双指针(获取倒数第K个元素、获取中间位置的元素、判断链表是否存在环、判断环的长度、查找第一个公共节点、回文链表)
- 1、 判断链表是否存在环
- 1、hot100 - 141. 环形链表(快慢指针)
- 2、hot100 - 142. 环形链表 II(快慢指针)【科大讯飞】
- 2、判断环的长度
- 3、获取倒数第K个元素
- 1、hot100 - 19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点(NC53 删除链表的倒数第n个节点)【蔚来面试】
- 4、查找第一个公共节点
- 1、*hot100 - 160. 相交链表(剑指 Offer 52. 两个链表的第一个公共节点)
- 5、回文链表
- 1、*hot100 - 234. 回文链表
- 6、剑指 Offer II 077. 链表排序【科大讯飞】
- 6.1 自底向上归并排序
- 6.2 自顶向下归并排序
- 2、一般解法
- 1、hot100 - 2. 两数相加
- 2、*hot100 - 206. 反转链表(剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表、NC78 反转链表)
- 3、hot100 - 21. 合并两个有序链表(剑指 Offer 25. 合并两个排序的链表、NC33 合并两个排序的链表)
- 4、NC50 链表中的节点每k个一组翻转(leetcode - 25. K 个一组翻转链表)
- 方法一
- 方法二
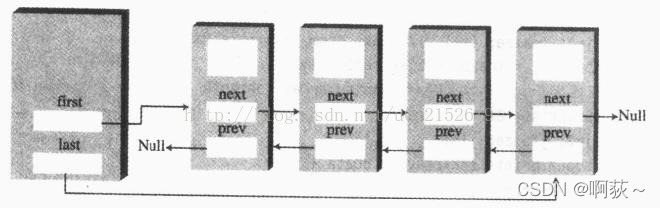
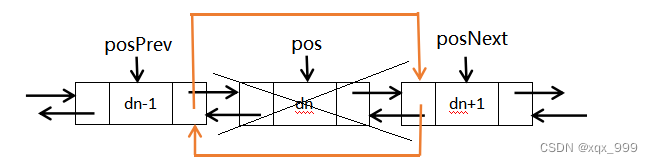
- 3、双链表
- 1、*hot100 - 146. LRU 缓存(NC93 设计LRU缓存结构)
一、介绍
1、单链表
1、单链表结构体:
struct ListNode {int val;ListNode *next;ListNode():val(0), next(nullptr){}ListNode(int x):val(x), next(nullptr){}ListNode(int x, ListNode *next):val(x), next(next){}
};
2、单链表头插法:
ListNode* create(vector<int> &ve){ListNode *head = nullptr;for(int each: ve){if(!head) head = new ListNode(each);else{ListNode *tmp = new ListNode(each);ListNode *p = head->next;head->next = tmp;tmp->next = p;}} return head;
}
3、单链表尾插法:
ListNode* create(vector<int> &ve){ListNode *head = nullptr, *s = nullptr;for(int each: ve){if(!head) head = s = new ListNode(each);else{ListNode *p = new ListNode(each);s->next = p;s = s->next;}} return head;
}
二、例题
1、双指针(获取倒数第K个元素、获取中间位置的元素、判断链表是否存在环、判断环的长度、查找第一个公共节点、回文链表)
1、 判断链表是否存在环
1、hot100 - 141. 环形链表(快慢指针)
题目:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle/
- 判断是否有环:
- 快慢双指针,如果有环两指针肯定会相遇;
- 如果快指针先越界了,无环;
- 证明:慢指针速度为1,快指针速度为2,快慢指针一定能相遇(数学归纳法)
- 快指针与慢指针之间差一步。此时继续往后走,慢指针前进一步,快指针前进两步,二者相遇。
- 快指针与慢指针之间两一步。此时继续往后走,慢指针前进一步,快指针前进两步,两者之间相差一步,转为第一种情况。
- 快指针与慢指针之间差N步。此时继续往后走,慢指针前进一步,快指针前进两步,两者之间相差 N-1步。转化为上一种情况。
- 因此若存在环,快指针必然与慢指针相遇。
- 时间复杂度:O(N)
- 当链表中不存在环时,快指针将先于慢指针到达链表尾部,链表中每个节点至多被访问两次。
- 当链表中存在环时,每一轮移动后,快慢指针的距离将减小一。而初始距离为环的长度,因此至多移动 N 轮。
- 空间复杂度:O(1)。只使用了两个指针的额外空间。
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {if(head == nullptr || head->next==nullptr) return false;ListNode *slow = head, *quick = head->next;while(slow != quick){if(quick == nullptr) return false;slow = slow->next;if(quick->next == nullptr) return false;quick = quick->next->next;}return true;}
};
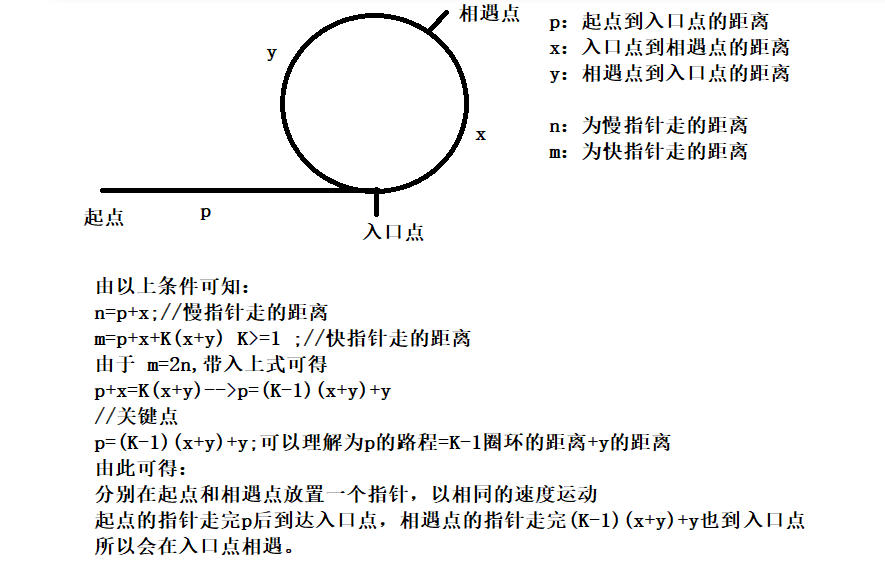
2、hot100 - 142. 环形链表 II(快慢指针)【科大讯飞】
题目:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/
- 思路与算法:
- 使用两个指针,quick与slow。它们起始都位于链表的头部。随后,slow 指针每次向后移动一个位置,而quick指针向后移动两个位置。如果链表中存在环,则quick指针最终将再次与slow 指针在环中相遇。
- 如下图所示,设链表中环外部分的长度为 a。slow 指针进入环后,又走了b的距离与quick相遇。此时,quick指针已经走完了环的n圈,因此它走过的总距离为 a+n(b+c)+b=a+(n+1)b+nc。
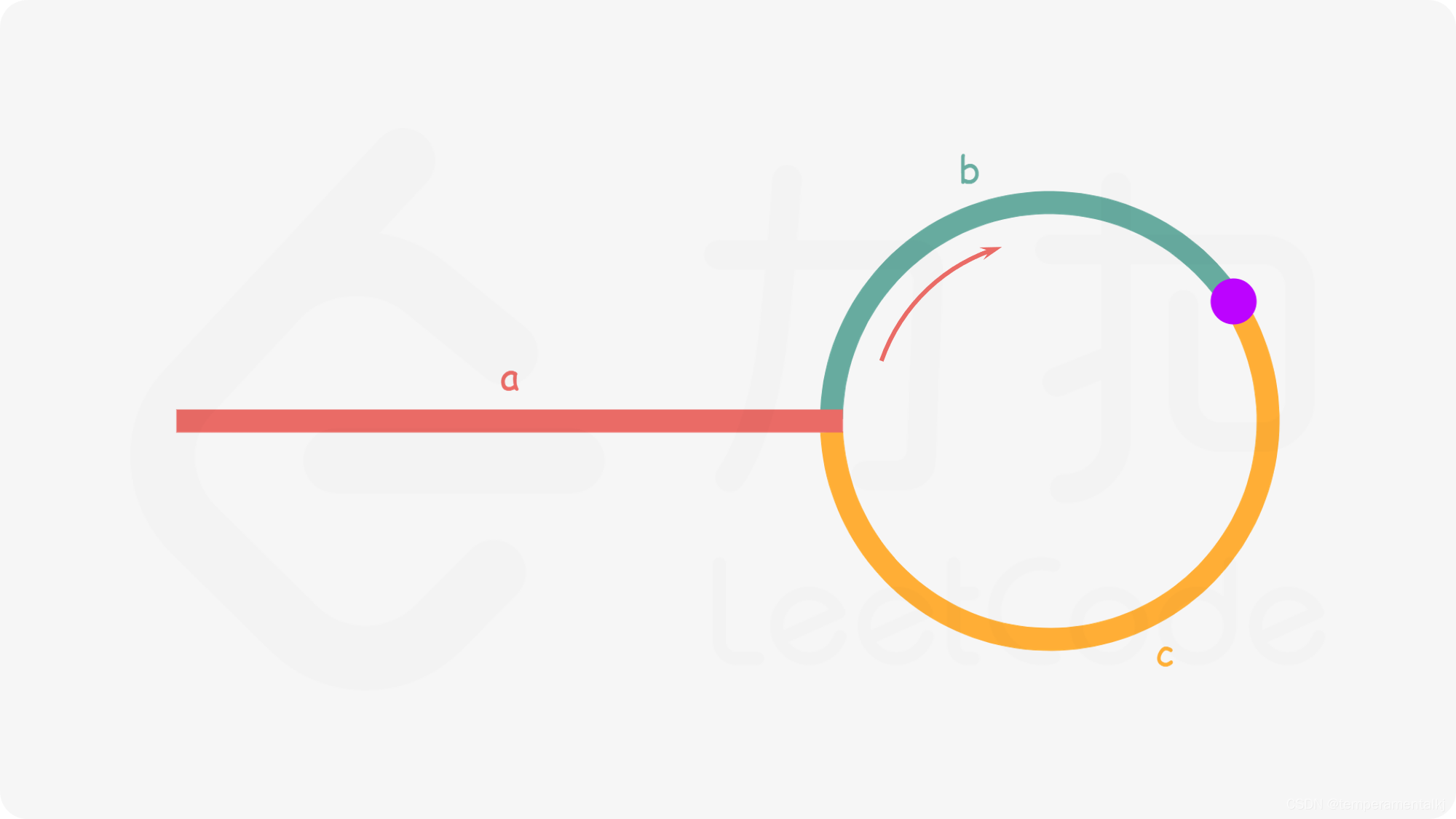
- 根据题意,任意时刻,quick指针走过的距离都为slow 指针的2倍。因此,a+(n+1)b+nc=2(a+b)⟹a=c+(n−1)(b+c)
- 有了 a=c+(n-1)(b+c)a=c+(n−1)(b+c) 的等量关系,我们会发现:从相遇点到入环点的距离加上n−1圈的环长,恰好等于从链表头部到入环点的距离。
- 因此,当发现slow 与quick相遇时,再额外使用一个指针pre。起始,它指向链表头部;随后,它和slow每次向后移动一个位置。最终,它们会在入环点相遇。
- 时间复杂度:O(N)。在最初判断快慢指针是否相遇时,slow 指针走过的距离不会超过链表的总长度;随后寻找入环点时,走过的距离也不会超过链表的总长度。因此,总的执行时间为 O(N)+O(N)=O(N)。
- 空间复杂度:O(1)。只使用了 slow,fast,pre三个指针。
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {ListNode *slow = head, *quick = head;while(quick != nullptr){if(quick->next == nullptr) return nullptr;slow = slow->next;quick = quick->next->next;if(slow == quick){ //慢指针、快指针相遇ListNode *pre = head;while(pre != slow){slow = slow->next;pre = pre->next;}return pre;}}return nullptr;}
};
2、判断环的长度
- 时间复杂度:O(N)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
class Solution {
public:bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {ListNode *slow = head;ListNode *fast = head;while (fast && fast->next) {fast = fast->next->next;slow = slow->next;if (slow == fast) break;}int length = 1;slow = slow->next;while (slow != fast) {slow = slow->next;length++;}return length;}
};
3、获取倒数第K个元素
1、hot100 - 19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点(NC53 删除链表的倒数第n个节点)【蔚来面试】
NC53 删除链表的倒数第n个节点
题目:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/
- 时间复杂度:O(L),L链表长度
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {ListNode *p = head, *pre = head, *n_p = head;int k = 0;while(p!=nullptr){if(k >= n){pre = n_p;n_p = n_p->next;}p = p->next;k++;}if(n_p == pre){head = pre->next;}else{pre->next = n_p->next;}return head;}
};
官网代码:
class Solution {
public:ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0, head);ListNode* first = head;ListNode* second = dummy;for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {first = first->next;}while (first) {first = first->next;second = second->next;}second->next = second->next->next;ListNode* ans = dummy->next;delete dummy;return ans;}
};
4、查找第一个公共节点
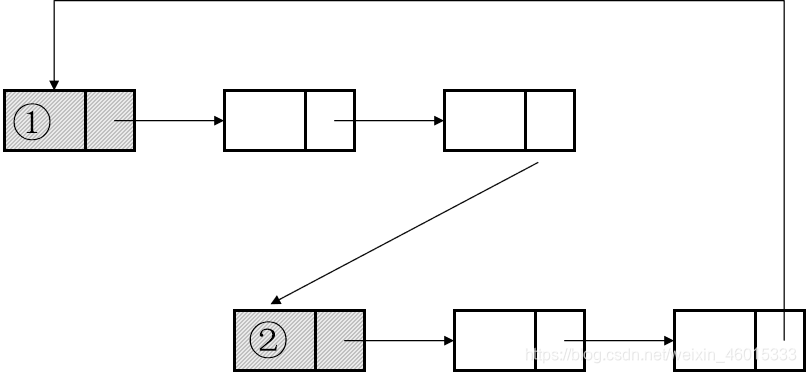
1、*hot100 - 160. 相交链表(剑指 Offer 52. 两个链表的第一个公共节点)
题目:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/
- 解法:
- 首先判断链表headA和headB 是否为空,如果其中至少有一个链表为空,则两个链表一定不相交,返回null
- 当链表headA和headB都不为空时,创建两个指针node1和node2,初始时分别指向两个链表的头节点headA和headB,然后将两个指针依次遍历两个链表的每个节点。具体做法如下:
- 每步操作需要同时更新指针node1和node2。
- 如果指针node1不为空,则将指针node1移到下一个节点;如果指针node2不为空,则将指针node2移到下一个节点。
- 如果指针node1为空,则将指针node1移到链表headB的头节点;如果指针node2为空,则将指针node2移到链表headA的头节点。
- 当指针node1和node2指向同一个节点或者都为空时,返回它们指向的节点或者null。
- 证明:
- 情况一:两个链表相交
- 链表headA和headB的长度分别是m和n。假设链表headA 的不相交部分有a个节点,链表headB的不相交部分有b个节点,两个链表相交的部分有c个节点,则有 a+c=m,b+c=n。
- 如果a=b,则两个指针会同时到达两个链表相交的节点,此时返回相交的节点;
- 如果a!=b,则指针node1会遍历完链表headA,指针node2会遍历完链表headB,两个指针不会同时到达链表的尾节点,然后指针node1移到链表headB的头节点,指针node2 移到链表headA的头节点,然后两个指针继续移动,在指针node1移动了 a+c+b次、指针node2移动了 b+c+a次之后,两个指针会同时到达两个链表相交的节点,该节点也是两个指针第一次同时指向的节点,此时返回相交的节点。
- 情况二:两个链表不相交
- 链表headA和headB的长度分别是m和n。考虑当m=n和m!=n时,两个指针分别会如何移动:
- 如果m=n,则两个指针会同时到达两个链表的尾节点,然后同时变成空值null,此时返回null;
- 如果m!=n,则由于两个链表没有公共节点,两个指针也不会同时到达两个链表的尾节点,因此两个指针都会遍历完两个链表,在指针node1移动了m+n次、指针node2移动了n+m次之后,两个指针会同时变成空值null,此时返回null。
- 时间复杂度:O(m+n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
class Solution {
public:ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {ListNode *node1 = headA;ListNode *node2 = headB;while (node1 != node2) {node1 = node1 != NULL ? node1->next : headB;node2 = node2 != NULL ? node2->next : headA;}return node1;}
};
5、回文链表
1、*hot100 - 234. 回文链表
题目:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/palindrome-linked-list/
- 解法:
- 找到前半部分链表的尾节点(使用快慢双指针);
- 反转后半部分链表(头插法/将当前指针的next指向前一个指针),参见反转链表;
- 判断是否回文(比较前后两部分链表的值,当后半部分达到末尾则比较完成);
- 恢复链表(头插法/将当前指针的next指向前一个指针),参见反转链表;
- 返回结果。
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:void reverseList(ListNode *head){if(!head) return ;ListNode *h_next = head->next;head->next = nullptr;while(h_next){ListNode *p = h_next->next;h_next->next = head->next;head->next = h_next;h_next = p;}}bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {if(!head) return true;//快慢指针找到中间值ListNode *slow = head, *fast = head->next;while(fast && fast->next){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;}ListNode *mid = slow;//翻转后半部分的链表reverseList(mid);//判断是否回文slow = head;fast = mid->next;bool res = true;while(fast){if(slow->val != fast->val){res = false;break;}slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next;}//还原链表reverseList(mid);return res;}
};
6、剑指 Offer II 077. 链表排序【科大讯飞】
题目:https://leetcode.cn/problems/7WHec2/
二路归并排序
- 时间复杂度:O(nlogn)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
6.1 自底向上归并排序

/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {if(head == nullptr) return head;int length = 0;ListNode *p = head;while(p != nullptr){length ++;p = p->next;}ListNode *rehead = new ListNode(0, head);for(int sublength = 1; sublength < length; sublength <<= 1){ListNode *pre = rehead, *cur = rehead->next;while(cur != nullptr){ListNode *head1 = cur;for(int i=1; i<sublength && cur->next!=nullptr; i++){cur = cur->next;}ListNode *head2 = cur->next;cur->next = nullptr; // head1的结尾cur = head2;for(int i=1; i<sublength && cur!=nullptr && cur->next!=nullptr; i++){cur = cur->next;}ListNode *next = nullptr;if(cur != nullptr){next = cur->next;cur->next = nullptr; }ListNode *merged = merge(head1, head2);pre->next = merged;while(pre->next != nullptr){pre = pre->next;}cur = next;}}head = rehead->next;delete rehead;return head; }ListNode *merge(ListNode *head1, ListNode*head2){ListNode *head = new ListNode(0);ListNode *p = head;ListNode *h1 = head1, *h2 = head2;while(h1!=nullptr && h2!=nullptr){if(h1->val <= h2->val){p->next = h1;h1 = h1->next;}else{p->next = h2;h2 = h2->next;}p = p->next;}p->next = h1 != nullptr ? h1 : h2;p = head->next;delete head;return p;}
};
6.2 自顶向下归并排序
- 时间复杂度:O(nlogn)
- 空间复杂度:O(logn)。取决于递归调用的栈空间。
class Solution {
public:ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {return sortList(head, nullptr);}// 区间:前闭后开ListNode *sortList(ListNode *head, ListNode *tail){if(head == nullptr) return head;// 这种情况不需要再找中点if(head->next == tail){ head->next = nullptr;return head;}// 双指针,快慢指针法ListNode *slow = head, *fast = head;while(fast != tail){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next;if(fast != tail) fast = fast->next;}// slow即为中点,区间:前闭后开return merge(sortList(head, slow), sortList(slow, fast));}ListNode *merge(ListNode *head1, ListNode *head2){ListNode *head = new ListNode();ListNode *h = head, *h1 = head1, *h2 = head2;while(h1 != nullptr && h2 != nullptr){if(h1->val <= h2->val){h->next = h1;h1 = h1->next;}else{h->next = h2;h2 = h2->next;}h = h->next;}h->next = h1 != nullptr ? h1 : h2;ListNode *rhead = head->next;delete head;return rhead;}
};2、一般解法
1、hot100 - 2. 两数相加
题目:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/add-two-numbers/
- 时间复杂度:O(max(m,n))
- 空间复杂度:O(1)。注意返回值不计入空间复杂度
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/class Solution {
public:ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {ListNode *head = nullptr, *tail = nullptr;int carry = 0;while (l1 || l2) {int n1 = l1 ? l1->val: 0;int n2 = l2 ? l2->val: 0;int sum = n1 + n2 + carry;if (!head) {head = tail = new ListNode(sum % 10);} else {tail->next = new ListNode(sum % 10);tail = tail->next;}carry = sum / 10;if (l1) {l1 = l1->next;}if (l2) {l2 = l2->next;}}if (carry > 0) {tail->next = new ListNode(carry);}return head;}
};
2、*hot100 - 206. 反转链表(剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表、NC78 反转链表)
题目:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/
-
题解(迭代):
- 在遍历链表时,将当前节点的next 指针改为指向前一个节点。
-
时间复杂度:O(n)
-
空间复杂度:O(1)
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {ListNode *pre = nullptr;ListNode *cur = head;while(cur){ListNode *tmp = cur->next;cur->next = pre;pre = cur;cur = tmp;}return pre;}
};
3、hot100 - 21. 合并两个有序链表(剑指 Offer 25. 合并两个排序的链表、NC33 合并两个排序的链表)
题目:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/
- 时间复杂度:O(m+n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {if(list1==nullptr && list2==nullptr) return nullptr;if(list1!=nullptr && list2==nullptr) return list1;if(list1==nullptr && list2!=nullptr) return list2;ListNode* head = nullptr, *p = nullptr;//尾插法while(list1!=nullptr && list2!=nullptr){if(list1->val < list2->val){if(!head) p = head = list1;ListNode *tmp = list1->next;p->next = list1;p = p->next;list1 = tmp;}else{if(!head) p = head = list2;ListNode *tmp = list2->next;p->next = list2;p = p->next;list2 = tmp;}}p->next = list1==nullptr? list2: list1;return head;}
};创建一个头节点:
class Solution {
public:ListNode* Merge(ListNode* pHead1, ListNode* pHead2) {ListNode *pHead3 = new ListNode(-1);ListNode *p = pHead1, *q = pHead2, *t = pHead3;while(p != nullptr && q != nullptr){ListNode *tmp = nullptr;if(p->val <= q->val){tmp = p;p = p->next;}else{tmp = q;q = q->next;}t->next = tmp;t = t->next;}t->next = p!=nullptr ? p : q;ListNode *tmp = pHead3; pHead3 = pHead3->next;delete tmp;return pHead3;}
};
4、NC50 链表中的节点每k个一组翻转(leetcode - 25. K 个一组翻转链表)
题目:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/b49c3dc907814e9bbfa8437c251b028e?tpId=117&tqId=37746&rp=1&ru=/exam/oj&qru=/exam/oj&sourceUrl=%2Fexam%2Foj%3Fpage%3D1%26tab%3D%25E7%25AE%2597%25E6%25B3%2595%25E7%25AF%2587%26topicId%3D117&difficulty=undefined&judgeStatus=undefined&tags=&title=
方法一
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(n)。O(n/k),最坏情况下k=1。
/*** struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/class Solution {
public:ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {// write code here//找到每次翻转的尾部ListNode *tail = head;//遍历k次到尾部for(int i=0; i<k; i++){//如果不足k到了链表尾,直接返回,不翻转if(tail==nullptr) return head;tail = tail->next;}ListNode *p = head->next, *pre = head;while(p!=tail){ListNode *tmp = p->next;p->next = head;head = p;p = tmp;}//当前尾指向下一段要翻转的链表pre->next = reverseKGroup(tail, k);return head;}
};
方法二
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
class Solution {
public:// 翻转一个子链表,并且返回新的头与尾pair<ListNode*, ListNode*> myReverse(ListNode* head, ListNode* tail) {ListNode* prev = tail->next;ListNode* p = head;while (prev != tail) {ListNode* nex = p->next;p->next = prev;prev = p;p = nex;}return {tail, head};}ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {ListNode* hair = new ListNode(0);hair->next = head;ListNode* pre = hair;while (head) {ListNode* tail = pre;// 查看剩余部分长度是否大于等于 kfor (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {tail = tail->next;if (!tail) {return hair->next;}}ListNode* nex = tail->next;// 这里是 C++17 的写法,也可以写成// pair<ListNode*, ListNode*> result = myReverse(head, tail);// head = result.first;// tail = result.second;tie(head, tail) = myReverse(head, tail);// 把子链表重新接回原链表pre->next = head;tail->next = nex;pre = tail;head = tail->next;}return hair->next;}
};
3、双链表
1、*hot100 - 146. LRU 缓存(NC93 设计LRU缓存结构)
题目: https://leetcode.cn/problems/lru-cache/solution/lruhuan-cun-ji-zhi-by-leetcode-solution/
方法: 哈希表+双向链表
- LRU 缓存机制可以通过哈希表辅以双向链表实现,我们用一个哈希表和一个双向链表维护所有在缓存中的键值对。
- 双向链表按照被使用的顺序存储了这些键值对,靠近头部的键值对是最近使用的,而靠近尾部的键值对是最久未使用的。
- 哈希表即为普通的哈希映射(HashMap),通过缓存数据的键映射到其在双向链表中的位置。
- 这样以来,我们首先使用哈希表进行定位,找出缓存项在双向链表中的位置,随后将其移动到双向链表的头部,即可在 O(1)的时间内完成 get 或者 put 操作。具体的方法如下:
- 对于 get 操作,首先判断 key 是否存在:
- 如果 key 不存在,则返回 -1;
- 如果 key 存在,则 key 对应的节点是最近被使用的节点。通过哈希表定位到该节点在双向链表中的位置,并将其移动到双向链表的头部,最后返回该节点的值。
- 对于 set 操作,首先判断 key 是否存在:
- 如果 key 不存在,使用 key 和 value 创建一个新的节点,在双向链表的头部添加该节点,并将 key 和该节点添加进哈希表中。然后判断双向链表的节点数是否超出容量,如果超出容量,则删除双向链表的尾部节点,并删除哈希表中对应的项;
- 如果 key 存在,则与 get 操作类似,先通过哈希表定位,再将对应的节点的值更新为 value,并将该节点移到双向链表的头部。
- 对于 get 操作,首先判断 key 是否存在:
- 上述各项操作中,访问哈希表的时间复杂度为O(1),在双向链表的头部添加节点、在双向链表的尾部删除节点的复杂度也为O(1)。而将一个节点移到双向链表的头部,可以分成「删除该节点」和「在双向链表的头部添加节点」两步操作,都可以在 O(1)时间内完成。
- 在双向链表的实现中,使用一个伪头部(dummy head)和伪尾部(dummy tail)标记界限,这样在添加节点和删除节点的时候就不需要检查相邻的节点是否存在。
- get和set时间复杂度:O(1)
// get操作:如果key存在,先通过哈希表定位,再移到头部;如果不存在,返回-1
// put操作:
// 1.如果key不存在,创建一个新节点,添加至双链表的头部,如果超出容量,删除双链表的尾部节点
// 2.如果key存在,先通过哈希表定位,再修改value,并移动到头部struct DLinkedNode{int key, value;DLinkedNode *pre, *next;DLinkedNode():key(0), value(0), pre(nullptr), next(nullptr){}DLinkedNode(int _key, int _value):key(_key), value(_value), pre(nullptr), next(nullptr){}
};class Solution {
private:unordered_map<int, DLinkedNode*> cache;DLinkedNode *head;DLinkedNode *tail;int size;int capacity;
public:Solution(int capacity):capacity(capacity), size(0){// 使用伪头部和伪尾部节点head = new DLinkedNode();tail = new DLinkedNode();head->next = tail;tail->pre = head;// write code here}int get(int key) {// write code here// 如果key不存在,返回-1if(!cache.count(key)){return -1;}else{// 如果key存在,先通过哈希表获取key的位置,返回对应的value值,再将key移动到双链表表头. // 如果 key 存在,先通过哈希表定位,再移到头部DLinkedNode *cur = cache[key];moveHead(cur);return cur->value;}}void set(int key, int value){// write code here// 如果缓存中不存在key, 新建一个节点// 判断容器是否装满,如果未装满,直接将新建的节点添加至表头,// 如果装满,将新建节点添加至表头,再删除末尾节点并删除在哈希表中的对应项// 如果 key 不存在,创建一个新的节点if(!cache.count(key)){DLinkedNode *cur = new DLinkedNode(key, value);// 添加进哈希表cache[key] = cur;// 添加至双向链表的头部addToHead(cur);size++;if(size > capacity){// 如果超出容量,删除双向链表的尾部节点DLinkedNode *node = removeTail();// 删除哈希表中对应的项cache.erase(node->key);// 防止内存泄漏delete node;size--;}}else{// 如果 key 存在,先通过哈希表定位,再修改value,并移到头部DLinkedNode *cur = cache[key];cur->value = value;moveHead(cur);}}void addToHead(DLinkedNode *node){node->pre = head;node->next = head->next;head->next->pre = node;head->next = node;}void removeHead(DLinkedNode *node){node->pre->next = node->next;node->next->pre = node->pre;}void moveHead(DLinkedNode *node){removeHead(node);addToHead(node);}DLinkedNode* removeTail(){DLinkedNode *node = tail->pre;removeHead(node);return node;}
};/*** Your Solution object will be instantiated and called as such:* Solution* solution = new Solution(capacity);* int output = solution->get(key);* solution->set(key,value);*/





![[数据结构]链表之单链表(详解)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/f6ed3314eddf8402f6ee6b39edb0f283.png)

![[数据结构] 链表(图文超详解讲解)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/1dce295c1ee04702a5a3fb9bbe74a7ce.png)