Executors框架包含的内容十分的多:看图:

一、各个接口的作用
按照图示关系进行介绍:

Executor
该接口作为顶层接口只有一个execute()方法
execute(Runnable r)
该接口接受一个Runnable实例,即要执行的任务
ExecutorService
该接口继承了Executor接口,增加了非常多的功能
ExecutorService接口提供了很多的方法,比如:
shutdown(); 线程池的关闭
ExecutorService的三种状态:
1.运行
2.关闭
3.终止
-------------------------------------------------
运行状态:只要线程池一直不调用shutdown的话,那么线程池是会一直运行下去的
关闭状态:线程池不再接受新的任务,对于已经提交的任务会处理完毕
终止状态:调用shutdown()方法后已提交的任务处理完之后线程池处于终止状态
ThreadPoolExecutor
线程池的实现类,最常用的类。实现了ExecutorService中所有的方法
ScheduleThreadPoolExecutor
该类继承了ThreadPoolExecutor并实现了ScheduledExecutorService接口
该类主要用来延时执行任务,或定时执行任务。
二、ScheduleThreadPoolExecutor的使用
1.schedule方法
该方法可以用来延迟任务的执行
延迟执行任务一次:public ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable command,long delay, TimeUnit unit)参数:
command:执行的任务
delay:延迟的时间
unit:枚举类,表示时间的单位可以是时分秒……案例:
public class ScheduleThreadPoolExecutorTest {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("当前系统时间"+System.currentTimeMillis());//使用该构造方法默认最大核心线程数为Interger_MaxScheduledThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(5);executor.schedule(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("开始执行时间"+System.currentTimeMillis());}},2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);//延迟两秒再执行executor.shutdown();}
}

运行该程序时,你会发现先打印了当前系统时间,过了两秒后才打印出开始执行
2.固定频率执行任务
scheduleAtFixedRate()方法
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command,long initialDelay,long period,TimeUnit unit);
参数:
command:执行的任务
initialDelay:首次执行的延迟时间
period:表示每次间隔的时间
unit:枚举类是上述两个时间的单位
案例:
import java.sql.SQLOutput;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;public class ScheduleThreadPoolExecutorTest {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("2秒后开始打印当前时间"+getNowTime(System.currentTimeMillis()));ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(100);executor.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("当前时间"+getNowTime(System.currentTimeMillis()));try {//这里休眠是为了和后续的方法做比较Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}},2,1,TimeUnit.SECONDS);}public static String getNowTime(Long time){return new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(time);}
}打印结果:

3.固定的间隔时间执行任务
scheduleWithFixedDelay
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command,long initialDelay,long period,TimeUnit unit);
参数:
command:执行的任务
initialDelay:首次执行的延迟时间
period:表示每次间隔的时间
unit:枚举类是上述两个时间的单位
代码如下(示例):
import java.sql.SQLOutput;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;public class ScheduleThreadPoolExecutorTest {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("2秒后开始打印当前时间"+getNowTime(System.currentTimeMillis()));ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(100);executor.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("当前时间"+getNowTime(System.currentTimeMillis()));try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}},2,1,TimeUnit.SECONDS);}public static String getNowTime(Long time){return new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(time);}
}
scheduleAtFixedRate和scheduleWithFixedDelay两者的区别
scheduleAtFixedRate的下一次执行时间是上一次执行时间+间隔时间
scheduleWithFixedDelay下一次执行时间是上一次执行时间结束时系统时间+间隔时间。
scheduleWithFixedDelay时间不固定但是周期固定
所以第一个案例下一次执行时间间隔了1秒,而第二个案例中每一次任务内部执行了1秒,所以下一次的执行时间就是2秒。
4.定时任务出现异常
如果说scheduleAtFixedRate和scheduleWithFixedDelay在执行时出现异常会怎么样?
案例:
import java.sql.SQLOutput;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;public class ScheduleThreadPoolExecutorTest {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("2秒后开始打印当前时间"+getNowTime(System.currentTimeMillis()));ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(100);ScheduledFuture<?> scheduledFuture = executor.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("当前时间" + getNowTime(System.currentTimeMillis()));try {Thread.sleep(1000);//制造异常int i = 2 / 0;} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}, 2, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);}public static String getNowTime(Long time){return new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(time);}
}我们手动只要了一个异常:看一下结果

程序执行到异常的时候不在执行了。
当我们在使用ScheduledExecutorService接口的实现类处理任务的时候,如果一旦发生异常,就会被ScheduledExecutorService接口内部进行捕获。因此我们在发现程序不正确的时候需要即时查找原因。不然程序停止了也没有异常信息的打印。
5.取消定时任务的执行
我们在使用ScheduleThreadPoolExecutor执行任务时都会返回ScheduledFuture的。我们可以通过方法进行发送中断信号来取消定时任务
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) 试图取消对此任务的执行。 boolean isCancelled() 如果在任务正常完成前将其取消,则返回 true。 boolean isDone() 如果任务已完成,则返回 true。 案例:
5秒后取消定时任务:
import java.sql.SQLOutput;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;public class ScheduleThreadPoolExecutorTest {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("2秒后开始打印当前时间"+getNowTime(System.currentTimeMillis()));ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(100);ScheduledFuture<?> scheduledFuture = executor.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("当前时间" + getNowTime(System.currentTimeMillis()));try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}, 2, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);try {Thread.sleep(5000);//取消定时任务scheduledFuture.cancel(true);if(scheduledFuture.isDone()){System.out.println("任务完成");}if(scheduledFuture.isCancelled()){System.out.println("任务取消");}} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}public static String getNowTime(Long time){return new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(time);}
}结果:

Executors类的使用
Executors类提供一些创建线程池的方法,线程池都实现了ExecutorService接口
newSingleThreadExecutor()
看一下源码
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 0L,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));}
该方法创建单线程的线程池(从源码中可以看到核心线程数是1,最大线程数也是1)!
工作队列采用的是无界的LinkedBlockingQueue阻塞队列。支持先提交的先执行!
如果核心线程异常的话,则创建一个线程去顶替核心线程(但始终保持单线程)
如果阻塞队列中任务太多,单线程处理不完则会引发OOM
newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads)
源码:
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());}
从源码中我们可以看出:该方法会创建一个固定大小的线程池。
核心线程数和最大线程数一致就表明:
当接受一个任务后就创建一个线程直至达到最大线程数。此时会将任务加入工作队列中
工作队列采用的是无界的阻塞队列,支持先提交的先执行。若处理不过来会引发OOM
newCachedThreadPool ()
源码:
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());}
创建一个可缓存的线程池,如果线程池的大小超多处理任务的线程,
那么就会回收空闲线程。当先提交一个线程时便会创建一个线程去处理。
该线程池的最大线程数默认为Integer.MAX_VALUE
内部采用SynchronousQueue队列,该队列要求只有线程获取任务的话才能加入队列中
newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize)
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) {return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize);}//创建源码:super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,new DelayedWorkQueue());
该线程池创建的是支持定时任务的线程池.核心线程数指定,最大线程数为Interger.MAX_VALUE
内部使用的是:DelayedWorkQueue无界优先级阻塞队列。要求元素都实现 Delayed 接口
Future、Callable接口
Future接口提供了一些异步执行的方法:比如:异步获取执行结果、取消任务执行,判断任务是否取消,判断任务是否结束
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) 试图取消对此任务的执行。 V get() 如有必要,等待计算完成,然后获取其结果。 V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) 如有必要,最多等待为使计算完成所给定的时间之后,获取其结果(如果结果可用)。 boolean isCancelled() 如果在任务正常完成前将其取消,则返回 true。 boolean isDone() 如果任务已完成,则返回 true。 Callable接口:返回结果并且可能抛出异常的任务
V call() 计算结果,如果无法计算结果,则抛出一个异常。
注意:返回值类型是一个泛型,若无法计算结果抛出异常。
案例:
import java.util.concurrent.*;public class ExecutorServiceTest {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建一个线程池ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);Future<Integer> future = executorService.submit(new Callable<Integer>() {@Overridepublic Integer call() throws Exception {int j = 0;for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {Thread.sleep(1000);j++;}return j; }});try {System.out.println("获取执行的结果"+future.get());executorService.shutdown();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (ExecutionException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}上述代码中我们使用submit()提交任务,该方法接受一个Callable的实例
返回一个Future的实例。我们可以通过该实例来进行获取结果,取消任务等操作。
结果:

注意:
get()方法会导致当前线程阻塞直至线程计算完结果后,才继续执行。但是我们可以设置超时时间。
get方法设置超时时间:
表明我获取结果只能等待一定的时间

设置等待超时时间的话会抛出TimeOutException异常
FutureTask实现类
FutureTask实现了RunnableFuture接口,而RunnableFuture接口继承了Runnable接口和Callable接口。因此该实现类可以交给Excutor或者直接使用线程的方法执行即可。
线程池的submit方法返回的Future实际类型正是FutureTask对象
FutureTask(Callable<V> callable) 创建一个 FutureTask,一旦运行就执行给定的 Callable。
FutureTask(Runnable runnable, V result) 创建一个 FutureTask,一旦运行就执行给定的 Runnable,并安排成功完成时 get 返回给定的结果 。 案例:
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;public class FutureTaskTest {public static void main(String[] args) {FutureTask<Integer> future = new FutureTask(new Callable<Integer>() {@Overridepublic Integer call() throws Exception {return 10;}});try {new Thread(future).start();System.out.println("获取返回的结果"+future.get());} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (ExecutionException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}问题分析:
获取线程池中最先处理结束的任务
上面我们采用Fucture可能会出现的问题:
import java.util.concurrent.*;public class FutureTaskTest {public static void main(String[] args) {ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);Future<String> future1 = executorService.submit(new Callable<String>() {@Overridepublic String call() throws Exception {Thread.sleep(3000);return "该任务耗时3秒完成";}});Future<String> future2 = executorService.submit(new Callable<String>() {@Overridepublic String call() throws Exception {Thread.sleep(7000);return "该任务耗时7秒完成";}});try {System.out.println(future2.get());long start = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println(future1.get());long end =System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println((end-start)/1000);if(future1.isDone() && future2.isDone()){executorService.shutdown();}} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (ExecutionException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}
调整顺序:
System.out.println(future1.get());long start = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println(future2.get());long end =System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println((end-start)/1000);
结果:

上述问题我们发现顺序不同会导致不一样的结果,为什么会出现这种结果呢?就是因为调用get()方法会一直等到获取结果。因此第一此结果是由于future2任务需要的时间为7秒,而future2的任务处理时间较短3秒。此时先调用future2的get将会导致阻塞。因此start执行的时候几乎适合end一块执行的。而反之,先执行future1的话调用get结束后start就有值了,此时future2还没有执行结束,这样就会导致时间差。我们把耗时较短的放在前边这样就可以尽快的执行后续的代码,而不会因为另外的任务处理较长而等待。
上述案例我们手动设置的,但是实际中我们不知道那个任务处理的时间长,因此需要用到特殊的方法来避免任务等待的耗时。接下的CompletionService就是解决这个问题的。
Future<V> submit(Callable<V> task);用于向服务中提交有返回结果的任务,并返回Future对象Future<V> submit(Runnable task, V result);用户向服务中提交有返回值的任务去执行,并返回Future对象Future<V> take() throws InterruptedException;从服务中返回并移除一个已经完成的任务,如果获取不到,会一致阻塞到有返回值为止。此方法会响应线程中断。Future<V> poll();从服务中返回并移除一个已经完成的任务,如果内部没有已经完成的任务,则返回空,此方法会立即响应。Future<V> poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException;尝试在指定的时间内从服务中返回并移除一个已经完成的任务,等待的时间超时还是没有获取到已完成的任务,则返回空。此方法会响应线程中断
ExecutorCompletionService是CompletionService接口的实现类,创建的时候传递一个线程池
public ExecutorCompletionService(Executor executor) {if (executor == null)throw new NullPointerException();this.executor = executor;this.aes = (executor instanceof AbstractExecutorService) ?(AbstractExecutorService) executor : null;this.completionQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Future<V>>();}
当我们调用submit()方法时会使用传递进来的线程池去处理任务。
他的内部有一个阻塞队列,完成任务的对象会放入该阻塞队列中。
使用take或者poll方法将会取出已经完成的任务对象。因此先完成的先取出
import java.util.concurrent.*;public class FutureTaskTest {public static void main(String[] args) {ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);ExecutorCompletionService<String> executorService = new ExecutorCompletionService<>(executor);Future<String> future1 = executorService.submit(new Callable<String>() {@Overridepublic String call() throws Exception {Thread.sleep(3000);return "该任务耗时3秒完成";}});Future<String> future2 = executorService.submit(new Callable<String>() {@Overridepublic String call() throws Exception {Thread.sleep(7000);return "该任务耗时7秒完成";}});try {for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {//会先获取执行结束的线程System.out.println(executorService.take().get());}if(future1.isDone() && future2.isDone()){executor.shutdown();}} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (ExecutionException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}通过该实例主要可以得知那些任务处理完毕的一个顺序!







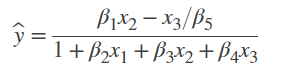




![[MATLAB]非线性回归--自配函数(nlinfit)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20200401160325946.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L20wXzM3MTQ5MDYy,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)

