一、缘起
因为springAOP原理其实是使用jdk动态代理和cglib动态代理, 在深入了解springAOP的原理之前,我们需要先补充一点有关动态代理的相关的知识,然后我们对于springAOP的理解才会更透彻。所谓动态代理技术是程序在动态运行期间动态的增强某一方法的功能的技术,举例来说 :
如果你编写了很多的业务代码(仅仅单独的完成了业务逻辑的代码),版本上线后有很多的bug需要进行调试,但是 你发现在写业务代码的时候并没有考虑到用于调试的日志打印,怎么办,重新在所有的业务代码中添加相关的日志打印代码(很多很多的业务代码啊,太痛苦了),但是还有一种更好的办法使用动态代理,你只需要重新编写相关日志操作的代码,通过动态将日志操作代码“加入”业务代码中就ok了,而这里的加入则是使用了动态代理的模式进行实现的。这里我们使用两种方式来实现如上需求,分别是jdk动态代理和cglib动态代理
二、JDK的动态代理
1、demo应用
1.1、实现InvocationHandler接口,并重写其中的invoke()方法,在基于业务接口创建代理对象的时候绑定InvocationHandler接口实现类,则所有的业务接口的方法执行的时候都会执行该invoke() ,所以这里也是我们可以给业务接口动态增加功能的切入点,如下代码例子,给所有的业务接口增加打印日志的功能。
public class LogInvokeHandler implements InvocationHandler {private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LogInvokeHandler.class);//目标对象,业务接口的实现类,放入该对象中,为了能执行业务接口中的方法private Object target;public LogInvokeHandler(Object target) {this.target = target;}public void setTarget(Object target) {this.target = target;}/*** 在基于某个接口产生动态对象的时候绑定该对象,则接口中的所有方法均会执行该invoke 则所有业务接口方法可以在这里进行自定义化的增强* @param proxy 生成的代理对象,* @param method 代理对象中的方法* @param args 方法中的参数* @return* @throws Throwable*/@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {//进行打印日志的相关操作logger.info("执行方法之前执行相关的增强业务逻辑的功能");logger.info("执行的方法信息:class: {},method:{},args:{}",proxy.getClass(),method.getName(), JsonUtil.obj2str(args));//执行方法Object result = method.invoke(target,args);//错误方法 proxy 为代理对象,调用其方法 还是会执行invoke 如此反复循环调用invoke()方法//Object result = method.invoke(proxy,args);logger.info("执行方法之后执行相关的增强业务逻辑的功能");return result;}1.2、业务接口的实现:
/*** author Administrator* date 2018/9/18* 业务代码的接口*/
public class BuninessServiceImpl implements BuninessService{private static List<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();static {students.add(new Student("xieqx","man",24));students.add(new Student("xieqx2","man",25));students.add(new Student("xieqx3","man",26));}@Overridepublic List<Student> findStudentList() {return students;}@Overridepublic Student findStudentByIndex(Integer index) {if(index == null) {return null;}return students.get(index);}@Overridepublic boolean addStudent(Student student) {if(student == null){return false;}students.add(student);return true;}@Overridepublic boolean updateStudent(Student student, Integer index) {if(index == null){return addStudent(student);}Student studentOld = students.get(index);if(studentOld == null){return false;}students.add(index,student);return true;}
}
1.3、 创建相关的对象并进行测试
@Testpublic void testDynamic(){//创建代理对象,需要传递三个参数/*** 第一个参数 该类被加载进入内存的类加载器,* 第二个参数 jdk动态代理是基于接口实现的,所以需要传入需要生成对象的接口信息* 第三个参数 我们上文写的处理器 即实现了InvocationHandler的实现类对象*/BuninessService proxy = (BuninessService) Proxy.newProxyInstance(JdkDynamicTest.class.getClassLoader(),new Class[]{BuninessService.class},new LogInvokeHandler(new BuninessServiceImpl()));System.out.println("酒店信息:"+proxy.findStudentList());//调用业务代码,会自动执行LogInvokeHandler中的invoke()方法proxy.findStudentByIndex(1);
}测试结果如下:
从图中可以看到,在原来的业务代码中添加了日志打印的操作。
2、原理解读
上面的demo使用jdk动态代理实现了一个给所有的业务代码添加日志的操作,相信通过上面的小例子大家对jdk的动态代理有了基础的了解,那么在这里我们先深入了解一下其是如何一步一步帮我们创建代理出来的。
2.1、首先我们需要关注java.lang.reflect.Proxy这个对象的newProxyInstance()方法
public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,Class<?>[] interfaces,InvocationHandler h)throws IllegalArgumentException{//1、InvocationHandler的实现类非空判断Objects.requireNonNull(h);//2、克隆需要动态代理目标对象的接口信息final Class<?>[] intfs = interfaces.clone();//3、获取安全框架(这里不涉及 其实是不懂 哈哈) 安全检查相关final SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();if (sm != null) {checkProxyAccess(Reflection.getCallerClass(), loader, intfs);}/** Look up or generate the designated proxy class.*//*** 4、获取代理对象的字节信息* 这里的逻辑是我们需要关注的重点* 大致的逻辑为 对接口信息进行长度限制的判断* 然后尝试获取对象的class信息 先从缓存中进行获取,如果没有* 则按照业务接口信息和InvocationHandler 尝试com.sun.Proxy#number class信息* 在这里我们可以在运行该程序的时候添加* -Dsun.misc.ProxyGenerator.saveGeneratedFiles=true* 将代理对象的字节码生成出来 查看详情*/Class<?> cl = getProxyClass0(loader, intfs);/** Invoke its constructor with the designated invocation handler.*/try {if (sm != null) {checkNewProxyPermission(Reflection.getCallerClass(), cl);}//5、获取类的构造器信息final Constructor<?> cons = cl.getConstructor(constructorParams);final InvocationHandler ih = h;if (!Modifier.isPublic(cl.getModifiers())) {AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Void>() {public Void run() {cons.setAccessible(true);return null;}});}//6、使用构造器创建代理对象并返回return cons.newInstance(new Object[]{h});} catch (IllegalAccessException|InstantiationException e) {throw new InternalError(e.toString(), e);//抛出异常省略...}}
1、InvocationHandler的实现类非空判断
Objects.requireNonNull(h);
2、克隆需要动态代理目标对象的接口信息
final Class<?>[] intfs = interfaces.clone();
3、获取安全框架(这里不涉及 其实是不懂 哈哈) 安全检查相关
final SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
4、获取代理对象的字节信息 Class<?> cl = getProxyClass0(loader, intfs);
这里的逻辑是我们需要关注的重点大致的逻辑为
(1) 对接口信息进行长度限制的判断
(2)尝试获取对象的class信息 先从缓存中进行获取,如果没有
(3)按照业务接口信息和InvocationHandler 尝试com.sun.Proxy#number class信息 在这里我们可以在运行该程序的时候添加-Dsun.misc.ProxyGenerator.saveGeneratedFiles=true 将代理对象的字节码生成出来 查看详情
5、获取类的构造器信息
final Constructor<?> cons = cl.getConstructor(constructorParams);
6、使用构造器创建代理对象并返回
return cons.newInstance(new Object[]{h});
2.2、查看生成代理类
public final class $Proxy4 extends Proxy implements BuninessService {private static Method m1;private static Method m4;private static Method m5;private static Method m3;private static Method m2;private static Method m0;private static Method m6;public $Proxy4(InvocationHandler var1) throws {super(var1);}public final boolean equals(Object var1) throws {try {return ((Boolean)super.h.invoke(this, m1, new Object[]{var1})).booleanValue();} catch (RuntimeException | Error var3) {throw var3;} catch (Throwable var4) {throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var4);}}public final boolean updateStudent(Student var1, Integer var2) throws {try {return ((Boolean)super.h.invoke(this, m4, new Object[]{var1, var2})).booleanValue();} catch (RuntimeException | Error var4) {throw var4;} catch (Throwable var5) {throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var5);}}public final boolean addStudent(Student var1) throws {try {return ((Boolean)super.h.invoke(this, m5, new Object[]{var1})).booleanValue();} catch (RuntimeException | Error var3) {throw var3;} catch (Throwable var4) {throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var4);}}public final Student findStudentByIndex(Integer var1) throws {try {return (Student)super.h.invoke(this, m3, new Object[]{var1});} catch (RuntimeException | Error var3) {throw var3;} catch (Throwable var4) {throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var4);}}public final String toString() throws {try {return (String)super.h.invoke(this, m2, (Object[])null);} catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) {throw var2;} catch (Throwable var3) {throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3);}}public final int hashCode() throws {try {return ((Integer)super.h.invoke(this, m0, (Object[])null)).intValue();} catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) {throw var2;} catch (Throwable var3) {throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3);}}public final List findStudentList() throws {try {return (List)super.h.invoke(this, m6, (Object[])null);} catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) {throw var2;} catch (Throwable var3) {throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3);}}static {try {m1 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("equals", new Class[]{Class.forName("java.lang.Object")});m4 = Class.forName("com.xiu.sb.aopTest.dynamic.BuninessService").getMethod("updateStudent", new Class[]{Class.forName("com.xiu.sb.aopTest.model.Student"), Class.forName("java.lang.Integer")});m5 = Class.forName("com.xiu.sb.aopTest.dynamic.BuninessService").getMethod("addStudent", new Class[]{Class.forName("com.xiu.sb.aopTest.model.Student")});m3 = Class.forName("com.xiu.sb.aopTest.dynamic.BuninessService").getMethod("findStudentByIndex", new Class[]{Class.forName("java.lang.Integer")});m2 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("toString", new Class[0]);m0 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("hashCode", new Class[0]);m6 = Class.forName("com.xiu.sb.aopTest.dynamic.BuninessService").getMethod("findStudentList", new Class[0]);} catch (NoSuchMethodException var2) {throw new NoSuchMethodError(var2.getMessage());} catch (ClassNotFoundException var3) {throw new NoClassDefFoundError(var3.getMessage());}}
}
从当前代理类中看出其是package java.lang.reflect的子类,并实现了我们的业务接口,同时在其静态代码块中获得所有业务接口方法Method对象(等等 还有三个继承自Object的hashCode() 、equals()、toString() ),并实现了其中的所有方法,所有的方法中都会调用InvoactionHandler 接口实现类(我们自己实现的类),进行处理。所以记住,我们的在调用业务方法和从Object中继承的三个方法 都会走invoke()方法
三、cglib的动态代理
0、cglib介绍
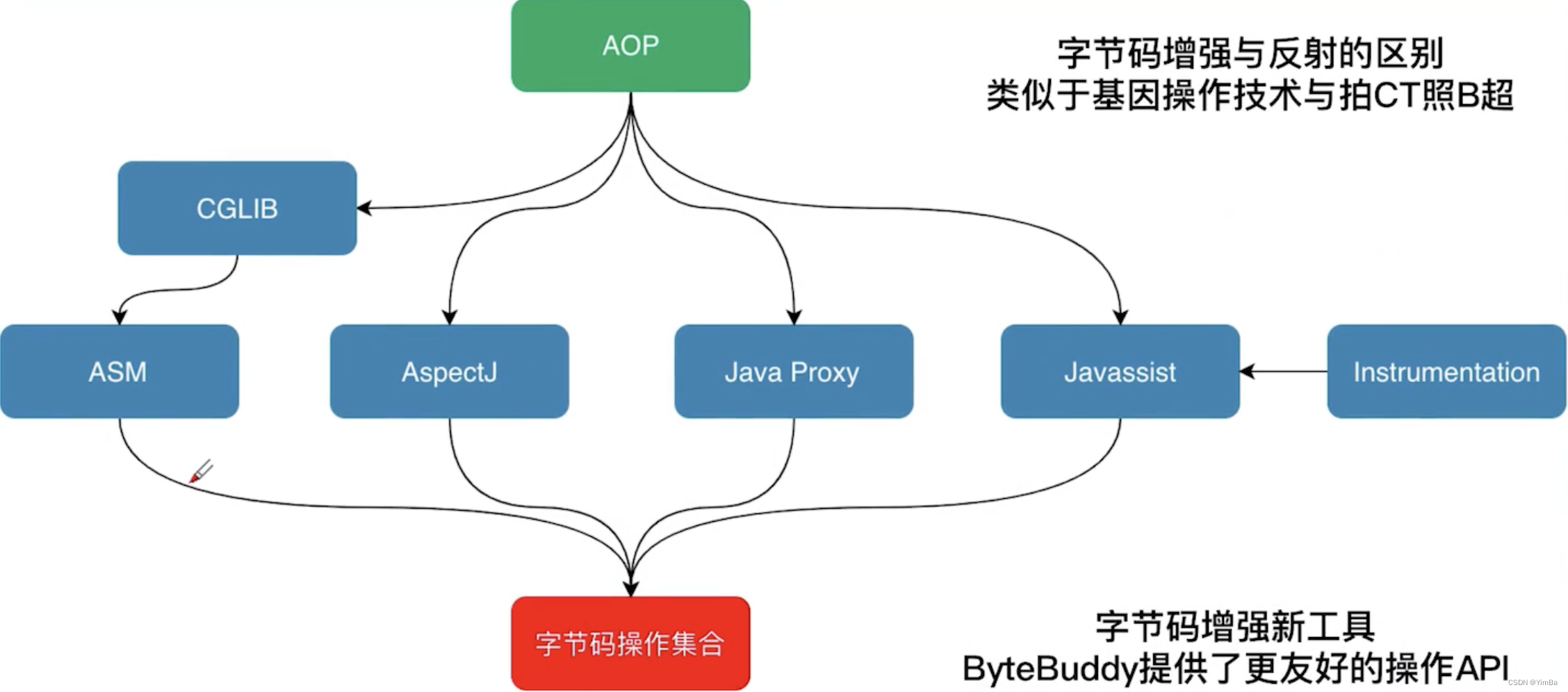
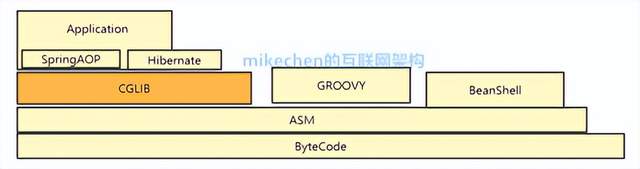
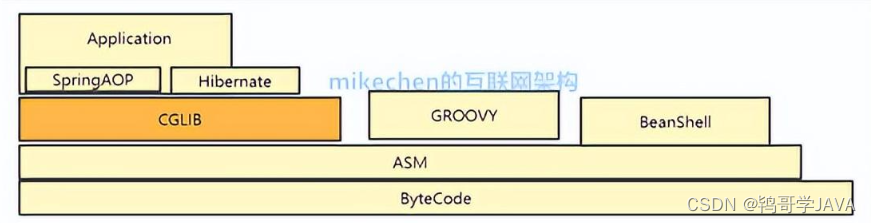
CGLIB是可以看做jdk动态代理的补充,jdk是针对接口进行代理,而cglib 是对于没有实现接口的类生成的代理,而且其不能为final修饰的方法进行代理增强。
CGLIB原理:动态生成一个要代理类的子类,子类重写要代理的类的所有不是final的方法。在子类中采用方法拦截的技术拦截所有父类方法的调用,顺势织入横切逻辑。它比使用java反射的JDK动态代理要快。
CGLIB底层:使用字节码处理框架ASM,来转换字节码并生成新的类。不鼓励直接使用ASM,因为它要求你必须对JVM内部结构包括class文件的格式和指令集都很熟悉。
1、demo应用
1.1、首先定义一个被代理类(目标对象) 该代理类为我们的jdk中1.2所示业务接口实现类相同BuninessServiceImpl类
1.2、定义一个CGLIB的拦截器 来实现自己的代理逻辑
实现CGLIB中的MethodInterceptor(方法拦截器) 并重写其中的intercept()方法,该方法有四个参数
- Object obj为目标对象
- Method method为目标方法
- Object[] params 为参数,
- MethodProxy proxy CGlib方法代理对象
在程序运行期间执行BuninessServiceImpl中的所有非final方法时,都会被该拦截器拦截进行相应的代理增强的处理
/*** 目标对象拦截器,实现MethodInterceptor* @author xieqx**/
public class TargetInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {/*** 重写方法拦截在方法前和方法后加入业务* Object obj为目标对象* Method method为目标方法* Object[] params 为参数,* MethodProxy proxy CGlib方法代理对象*/@Overridepublic Object intercept(Object obj, Method method, Object[] params,MethodProxy proxy) throws Throwable {System.out.println("调用前 打印日志信息 调用的方法: "+proxy.getSignature().getName()+"参数信息:"+params);Object result = proxy.invokeSuper(obj, params);System.out.println(" 调用后"+result);return result;}}
1.3、测试执行
@Testpublic void testCglibDynamic(){//设置将CGLIB的代理类class信息打印到文件System.setProperty(DebuggingClassWriter.DEBUG_LOCATION_PROPERTY, "E:\\class");//cglib 中加强器,用来创建动态代理Enhancer enhancer =new Enhancer();//设置需要代理的目标对象enhancer.setSuperclass(com.xiu.sb.aopTest.cglib.BuninessService.class);//System.setProperty(DebuggingClassWriter.DEBUG_LOCATION_PROPERTY, "com/sun/proxy");//设置代理增强的目标回调(目标代理对象中的所有非final方法)enhancer.setCallback(new TargetInterceptor());//等号右边生成的代理类对象 为目标对象的子类对象,所以可以使用业务对象来进行接收com.xiu.sb.aopTest.cglib.BuninessService buninessService=(com.xiu.sb.aopTest.cglib.BuninessService)enhancer.create();//调用代理信息buninessService.findStudentByIndex(1);}结果
cglib对应的生成的代理对象的字节码信息
public class BuninessService$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$197b44fe extends BuninessService implements Factory {private boolean CGLIB$BOUND;private static final ThreadLocal CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS;private static final Callback[] CGLIB$STATIC_CALLBACKS;private static final Object[] CGLIB$emptyArgs;//业务接口中生成的方法信息和方法对应的代理对象 以及代理增强的拦截器 private MethodInterceptor CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;private static final Method CGLIB$findStudentByIndex$0$Method;private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$findStudentByIndex$0$Proxy;private static final Method CGLIB$addStudent$1$Method;private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$addStudent$1$Proxy;private static final Method CGLIB$updateStudent$2$Method;private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$updateStudent$2$Proxy;private static final Method CGLIB$findStudentList$3$Method;private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$findStudentList$3$Proxy;//因为CGLIB会为所有的公有的非final形式的方法生成代理 所有继承子Object的所有公有方法也会生成对应的方法信息和代理对象private static final Method CGLIB$finalize$4$Method;private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$finalize$4$Proxy;private static final Method CGLIB$equals$5$Method;private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$equals$5$Proxy;private static final Method CGLIB$toString$6$Method;private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$toString$6$Proxy;private static final Method CGLIB$hashCode$7$Method;private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$hashCode$7$Proxy;private static final Method CGLIB$clone$8$Method;private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$clone$8$Proxy;static void CGLIB$STATICHOOK1() {CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS = new ThreadLocal();CGLIB$emptyArgs = new Object[0];Class var0 = Class.forName("com.xiu.sb.aopTest.cglib.BuninessService$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$197b44fe");Class var1;Method[] var10000 = ReflectUtils.findMethods(new String[]{"finalize", "()V", "equals", "(Ljava/lang/Object;)Z", "toString", "()Ljava/lang/String;", "hashCode", "()I", "clone", "()Ljava/lang/Object;"}, (var1 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object")).getDeclaredMethods());CGLIB$finalize$4$Method = var10000[0];CGLIB$finalize$4$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(var1, var0, "()V", "finalize", "CGLIB$finalize$4");CGLIB$equals$5$Method = var10000[1];CGLIB$equals$5$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(var1, var0, "(Ljava/lang/Object;)Z", "equals", "CGLIB$equals$5");CGLIB$toString$6$Method = var10000[2];CGLIB$toString$6$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(var1, var0, "()Ljava/lang/String;", "toString", "CGLIB$toString$6");CGLIB$hashCode$7$Method = var10000[3];CGLIB$hashCode$7$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(var1, var0, "()I", "hashCode", "CGLIB$hashCode$7");CGLIB$clone$8$Method = var10000[4];CGLIB$clone$8$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(var1, var0, "()Ljava/lang/Object;", "clone", "CGLIB$clone$8");var10000 = ReflectUtils.findMethods(new String[]{"findStudentByIndex", "(Ljava/lang/Integer;)Lcom/xiu/sb/aopTest/model/Student;", "addStudent", "(Lcom/xiu/sb/aopTest/model/Student;)Z", "updateStudent", "(Lcom/xiu/sb/aopTest/model/Student;Ljava/lang/Integer;)Z", "findStudentList", "()Ljava/util/List;"}, (var1 = Class.forName("com.xiu.sb.aopTest.cglib.BuninessService")).getDeclaredMethods());CGLIB$findStudentByIndex$0$Method = var10000[0];CGLIB$findStudentByIndex$0$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(var1, var0, "(Ljava/lang/Integer;)Lcom/xiu/sb/aopTest/model/Student;", "findStudentByIndex", "CGLIB$findStudentByIndex$0");CGLIB$addStudent$1$Method = var10000[1];CGLIB$addStudent$1$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(var1, var0, "(Lcom/xiu/sb/aopTest/model/Student;)Z", "addStudent", "CGLIB$addStudent$1");CGLIB$updateStudent$2$Method = var10000[2];CGLIB$updateStudent$2$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(var1, var0, "(Lcom/xiu/sb/aopTest/model/Student;Ljava/lang/Integer;)Z", "updateStudent", "CGLIB$updateStudent$2");CGLIB$findStudentList$3$Method = var10000[3];CGLIB$findStudentList$3$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(var1, var0, "()Ljava/util/List;", "findStudentList", "CGLIB$findStudentList$3");}//其他的代码与如下的代码类似 这里只针对一个业务逻辑进行分析即可//子类的原有方法final Student CGLIB$findStudentByIndex$0(Integer var1) {return super.findStudentByIndex(var1);}public final Student findStudentByIndex(Integer var1) {//获取方法拦截机器 MethodInterceptor var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;if(this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0 == null) {CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;}//判断方法拦截器是否为null 如果不为null 则执行拦截器方法,否则执行父类的原有方法return var10000 != null?(Student)var10000.intercept(this, CGLIB$findStudentByIndex$0$Method, new Object[]{var1}, CGLIB$findStudentByIndex$0$Proxy):super.findStudentByIndex(var1);}}
CGLIB其实是使用ASM框架 来生成新的基于继承的代理类
四、spring AOP的源码解读
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38182963/article/details/78775678
1、有关SpringAOP的应用请参考:https://blog.csdn.net/liushangzaibeijing/article/details/82732535
本次源码解读也是依据该博客中对应的例子来进行处理
2、springAOP的核心处理类AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
其实现的父接口BeanPostProcessor 该接口为spring的后置处理器,其主要作用在spring中对于初始化的bean进行后置处理
(其实该接口既可以做后置处理也可以做前置处理 应该叫做spring的前后置处理器 ,该接口描述如下代码,但是由于在spring中队该接口的实现类都没有进行前置处理的具体实现)
//spring的后置处理器
public interface BeanPostProcessor {//在bean实例化之前执行的方法 spring框架体系中大部分都没有实现@Nullabledefault Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {return bean;}//在bean实例化之后执行的方法@Nullabledefault Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {return bean;}
既然是spring后置处理,我们重点关注AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的postProcessAfterInitialization()方法实现
其具体的实现在AbstractAutoProxyCreator(继承的父类)中
3、AbstractAutoProxyCreator的postProcessAfterInitialization()方法
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {if (bean != null) {//根据class信息从缓存中对应的keyObject cacheKey = this.getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);if (!this.earlyProxyReferences.contains(cacheKey)) {//关键方法,为我们横切进入的业务接口的目标对象生成代理对象return this.wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);}}return bean;}所有由springBoot容器托管的对象,都会被该类的后置处理方法postProcessAfterInitialization()执行相应的后置处理,包括为我们将目标对象包装为代理对象。
4、wrapIfNecessary()方法
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {//非目标对象或者是切面类型的对象,则不进行返回if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {return bean;} else if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {return bean;//isInfrastructureClass判断该bean是否是aop的基础类 如Advice.class,PointCut.class etc//shouldSkip 检查是否应该跳过 } else if (!this.isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) && !this.shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
//下面的代码执行则表明该类是我们需要进行代理对象 Object[] specificInterceptors = this.getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, (TargetSource)null);if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);//关键方法 创建代理对象 jdk动态代理或者cglib代理 Object proxy = this.createProxy(bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());//返回代理对象return proxy;} else {this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);return bean;}} else {this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);return bean;}}5、重点关注createProxy()方法
Object proxy = this.createProxy(bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
protected Object createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory)this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);}//创建代理工厂 并填充相关的代理工厂所需的相关属性,通知器等 ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {if (this.shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);} else {this.evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);}}Advisor[] advisors = this.buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);this.customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);if (this.advisorsPreFiltered()) {proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);}//关键方法,使用代理工厂创建代理对象return proxyFactory.getProxy(this.getProxyClassLoader());}
以上代码主要是创建大力工厂并创建代理对象最终创建AopProxy 获取对象获取的代理有两种实现 一种是JdkDynamicAopProxy的getProxy创建JDK动态代理对象,另一种是CglibAopProxy对象 getProxy 创建Cglib代理对象,另外附上两者实现的相关代码
6、 JdkDynamicAopProxy类
//springAOP的jdk动态代理
final class JdkDynamicAopProxy implements AopProxy, InvocationHandler, Serializable {public Object getProxy() {return this.getProxy(ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());}//获取代理对象public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Creating JDK dynamic proxy: target source is " + this.advised.getTargetSource());}Class<?>[] proxiedInterfaces = AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised, true);this.findDefinedEqualsAndHashCodeMethods(proxiedInterfaces);return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, proxiedInterfaces, this);}private void findDefinedEqualsAndHashCodeMethods(Class<?>[] proxiedInterfaces) {Class[] var2 = proxiedInterfaces;int var3 = proxiedInterfaces.length;for(int var4 = 0; var4 < var3; ++var4) {Class<?> proxiedInterface = var2[var4];Method[] methods = proxiedInterface.getDeclaredMethods();Method[] var7 = methods;int var8 = methods.length;for(int var9 = 0; var9 < var8; ++var9) {Method method = var7[var9];if (AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) {this.equalsDefined = true;}if (AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) {this.hashCodeDefined = true;}if (this.equalsDefined && this.hashCodeDefined) {return;}}
7、CglibAopProxy 类
class CglibAopProxy implements AopProxy, Serializable {public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Creating CGLIB proxy: target source is " + this.advised.getTargetSource());}try {Class<?> rootClass = this.advised.getTargetClass();Assert.state(rootClass != null, "Target class must be available for creating a CGLIB proxy");Class<?> proxySuperClass = rootClass;int x;if (ClassUtils.isCglibProxyClass(rootClass)) {proxySuperClass = rootClass.getSuperclass();Class<?>[] additionalInterfaces = rootClass.getInterfaces();Class[] var5 = additionalInterfaces;int var6 = additionalInterfaces.length;for(x = 0; x < var6; ++x) {Class<?> additionalInterface = var5[x];this.advised.addInterface(additionalInterface);}}this.validateClassIfNecessary(proxySuperClass, classLoader);Enhancer enhancer = this.createEnhancer();if (classLoader != null) {enhancer.setClassLoader(classLoader);if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader && ((SmartClassLoader)classLoader).isClassReloadable(proxySuperClass)) {enhancer.setUseCache(false);}}enhancer.setSuperclass(proxySuperClass);enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised));enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE);enhancer.setStrategy(new CglibAopProxy.ClassLoaderAwareUndeclaredThrowableStrategy(classLoader));Callback[] callbacks = this.getCallbacks(rootClass);Class<?>[] types = new Class[callbacks.length];for(x = 0; x < types.length; ++x) {types[x] = callbacks[x].getClass();}enhancer.setCallbackFilter(new CglibAopProxy.ProxyCallbackFilter(this.advised.getConfigurationOnlyCopy(), this.fixedInterceptorMap, this.fixedInterceptorOffset));enhancer.setCallbackTypes(types);return this.createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks);} catch (IllegalArgumentException | CodeGenerationException var9) {throw new AopConfigException("Could not generate CGLIB subclass of " + this.advised.getTargetClass() + ": Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class", var9);} catch (Throwable var10) {throw new AopConfigException("Unexpected AOP exception", var10);}}}
springAOP的相关原理的解析到此为止,本来觉得自己可以写的更好更深但是写的时候发现自己的理解还是太浅了。不足之处还请各位指正。
分享两篇博客:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38182963/article/details/78775678 (比较深刻,看了几遍还是有不太明白)
https://blog.csdn.net/taotoxht/article/details/54356527