铁子们,快扫码关注啦!或 wx搜索:“聊5毛钱的java”,关注可领取博主的Java学习视频+资料,保证都是干货
上一篇讲了配置文件形式的SpringAOP:Spring中的AOP以及切入点表达式和各种通知
本篇继续看一下注解形式怎么去理解和应用AOP
前几篇已经讲了不少AOP相关的知识,本篇不再赘述,直接用代码写一下注解形式的AOP
举的例子还是前几篇的例子,只不过是用注解的形式去用一下AOP
package com.cj.study.spring.aop.annotation;public interface PersonService {public String savePerson();public void updatePerson();public void deletePerson();}
package com.cj.study.spring.aop.annotation;import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;//目标类
@Repository("personService")
public class PersonServiceImpl implements PersonService{//目标方法public String savePerson() {System.out.println("添加");return "保存成功!";}//目标方法public void updatePerson() {System.out.println("修改");}//目标方法public void deletePerson() {System.out.println("删除");}}
package com.cj.study.spring.aop.annotation;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;/**** @Aspect + @Pointcut()这两个注解就相当于之前配置文件里下边的内容* <aop:config>* <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.cj.study.spring.aop.*.*(..))" id="perform"/>* </aop:config>* * @Before()这个注解就相当于之前配置文件里* <aop:aspect ref="myTransaction">* <aop:before method="beginTransaction" pointcut-ref="perform"/>* </aop:aspect>* * @author caoju**/
//切面类
@Component("myTransaction")
@Aspect
public class MyTransaction {//这个 aaa() 方法没有其他作用,仅仅是用它来标明一下切入点表达式@Pointcut("execution(* com.cj.study.spring.aop..*.*(..))")public void aaa(){}//切面里的通知方法@Before("aaa()")public void beginTransaction(){System.out.println("开启事务 ");}//切面里的通知方法@After("aaa()")public void commit(){System.out.println("提交事务");}}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/aophttp://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/contexthttp://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd"><!-- 配置包扫描器,把目标类和切面类纳入到spring容器中管理 --><context:component-scan base-package="com.cj.study.spring.aop.annotation" /> <!-- 启动aop的注解解析器 --><aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy></beans>
package com.cj.study.spring.aop.annotation;import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;public class AopAnnodationTest {@Testpublic void test(){ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("com/cj/study/spring/aop/annotation/applicationContext.xml");PersonService proxyPersonService = (PersonService) context.getBean("personService");String returnValue = proxyPersonService.savePerson();System.out.println(returnValue);}
}
打断点看下返回的是否是代理类
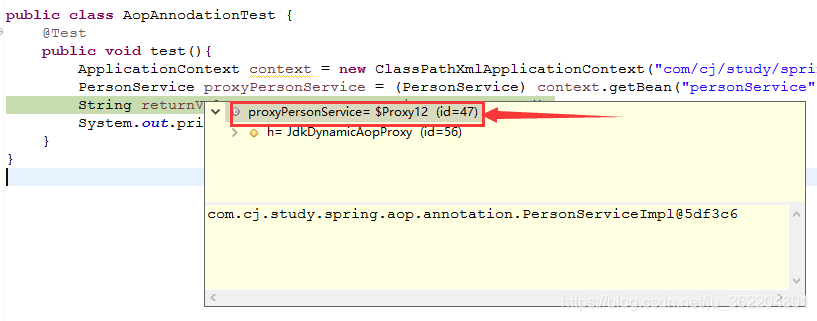
可以看到返回的是$Proxy,说明返回的是代理对象
看下最后的结果
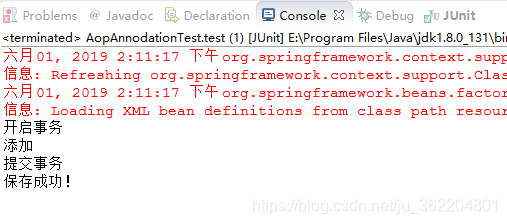
以上就是以注解的形式用了一下AOP
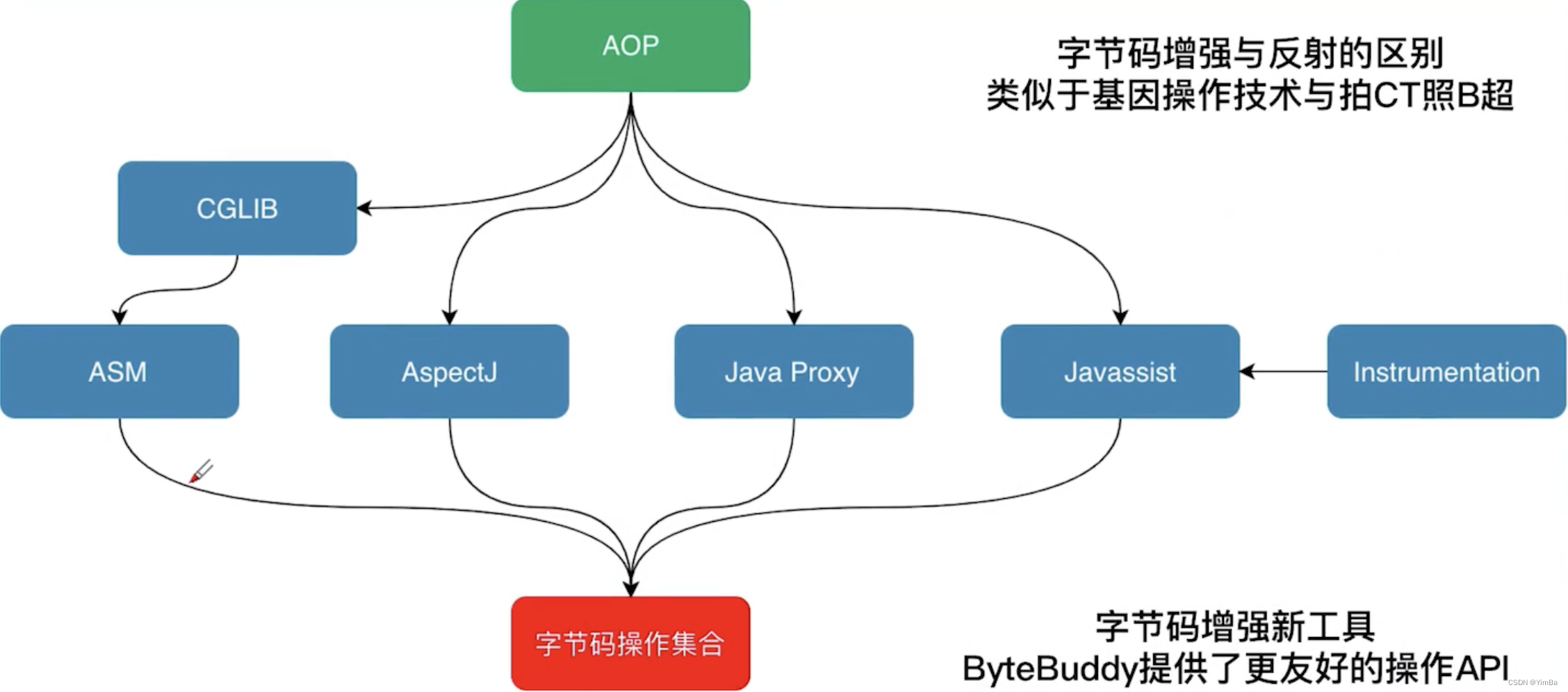
需要知道的是:不管是配置文件的形式还是注解的形式,他们两种实现的功能是一样的
注解形式的可能比配置文件更抽象一点,但是你要清楚它做的事情和配置文件做的是一样的,只是形式上有差别。注解可以对比着配置文件去理解,我已经在代码里进行了注释
不管是配置文件还是注解,最终都要用反射来实现,关于反射和注解,我之前的文章也写过
Java中的反射机制介绍
Java中的注解以及自定义注解
感兴趣的小可爱,可以自行参考
铁子们,如果觉得文章对你有所帮助,可以点关注,点赞
也可以关注下公众号:扫码或 wx搜索:“聊5毛钱的java”,欢迎一起学习交流,关注公众号可领取博主的Java学习视频+资料,保证都是干货

3Q~
纯手敲原创不易,如果觉得对你有帮助,可以打赏支持一下,哈哈,感谢~