基于DeepSpeed训练ChatGPT
最少只需一张32G GPU,自己也可以训练一个ChatGPT!
最近微软发布了一个基于DeepSpeed的训练优化框架来完成ChatGPT类模型的训练,博主对其进行了研究并通过此博文分享相关技术细节。
一、配置预览
1、开源仓库:DeepSpeed-Chat
2、配置要求:
● cuda:11.0以上
● torch:1.12.1+cu113
● deepspeed:0.9.0
● transformers:4.29.0.dev0
3、开源语料(Hugging face Dataset):
● Dahoas/rm-static
● Dahoas/full-hh-rlhf
● Dahoas/synthetic-instruct-gptj-pairwise
● yitingxie/rlhf-reward-datasets
● openai/webgpt_comparisons
● stanfordnlp/SHP
4、数据格式样例:
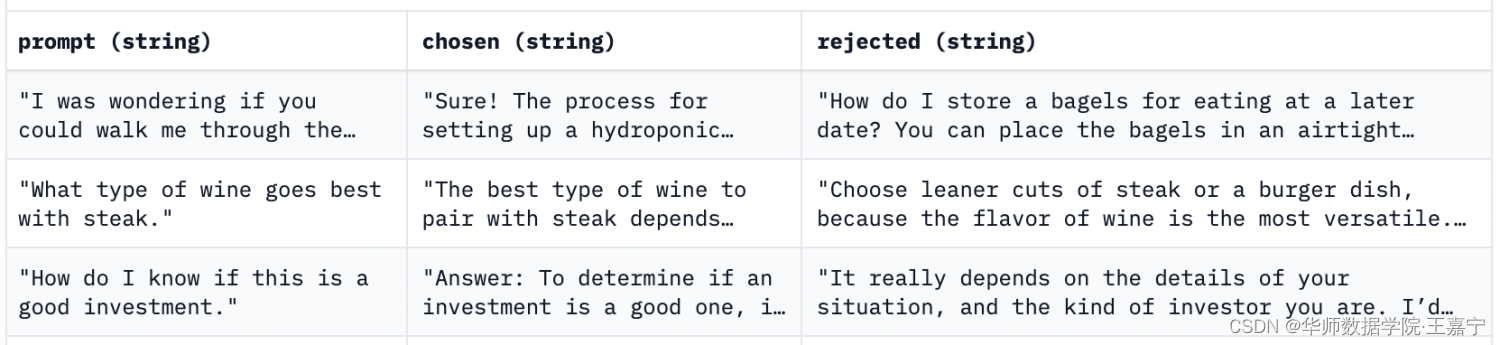
需要包含三个字段,分别为:
● prompt:instruction-prompt,当前的输入;
● chosen:人来反馈选中的回复,或当前pair得分最高的回复;
● rejected:人类反馈未选中的回复,或当前pair得分最低的回复;
个人也可以按照这个格式设计自己的训练数据。
5、数据处理函数(样例):
针对训练数据,可以设计如下几个数据处理函数。
# The prompt should be in the format of: " Human: " + actual_prompt_sentence + " Assistant:"
# 只获取prompt字段的数据
def get_prompt(self, sample):return " Human: " + sample['prompt'] + " Assistant:"# The chosen response should be in the format of: " " + actual_response_sentence
# 只获取chosen字段的数据
def get_chosen(self, sample):return " " + sample['chosen']# The rejected response should be in the format of: " " + actual_response_sentence
# If the dataset does not have rejected response, return None
# 只获取rejected字段的数据
def get_rejected(self, sample):return " " + sample['rejected']
# 同时获取prompt和chosen的数据
# 这两段数据一一拼接后可以训练SFT
def get_prompt_and_chosen(self, sample):return " Human: " + sample['prompt'] + " Assistant: " + sample['chosen']
# 同时获取prompt和rejected数据
def get_prompt_and_rejected(self, sample):return " Human: " + sample['prompt'] + " Assistant: " + sample['rejected']
6、InstructGPT基本流程:
InstructGPT是训练ChatGPT的核心思路,其融入了大量的对话数据,并按照如下三个步骤进行训练,如图所示:
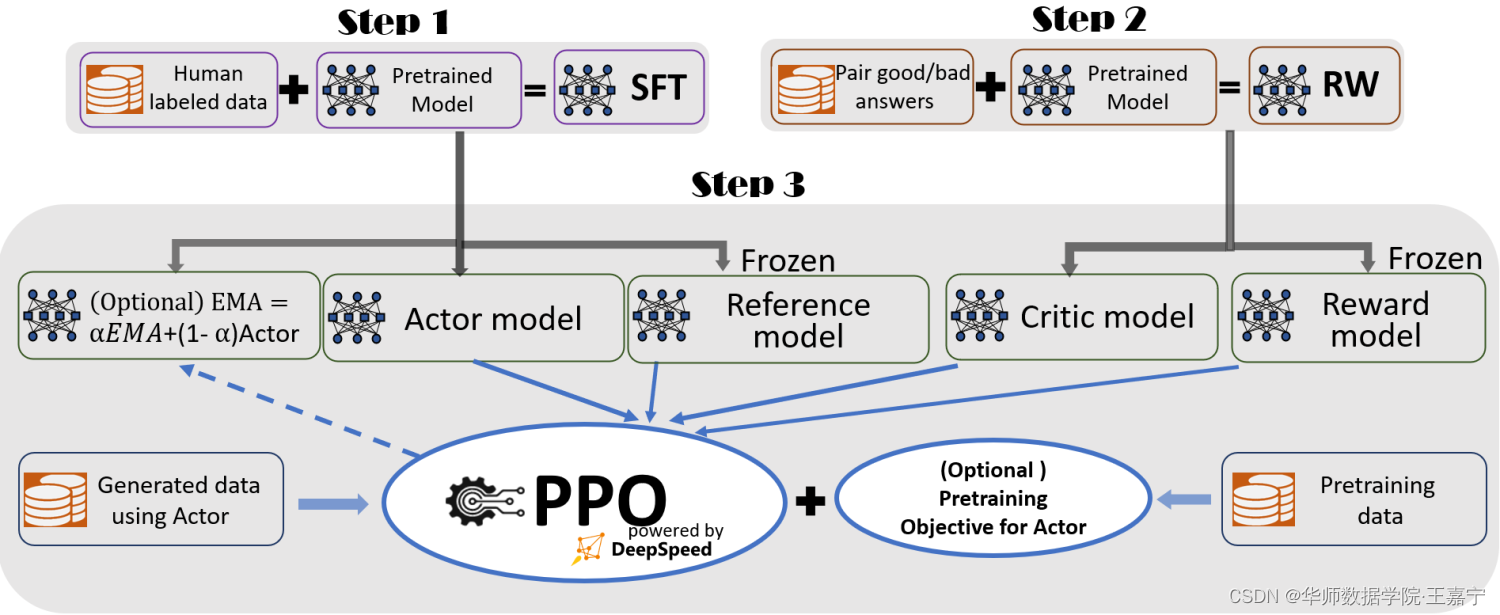
在后面将会结合代码和相关知识介绍这三个步骤。
7、显存优化相关知识:
ZeRo-Stage和ZeRo-offload显存优化:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/619429610
二、Step1: Supervised Fine-tuning(SFT)
第一阶段主要为监督训练。在InstructGPT中,通过设计Instruction Prompt,收集各式各样的数据集,并构建为对话模式,例如下面的就是一个prompt:
Human: How can I find out what types of butterflies are in my area?
Assistant: Which location are you in?
Human: I am in Oregon.
Assistant: There are about 175 species of butterflies in Oregon, of which 100 are long-distance migrants from southern California. Also, some of the common butterflies in Oregon
Human: Great. What are some common species then?
Assistant:
对应人工打标的回复为:
About 150 species of butterflies live in Oregon, with about 100 species are moths, and about 20 species are common here year-round, and another 10 species are seen here year-round. I suggest you keep an eye out for skippers, gossamer wings, and red admirals.
在这一过程,我们可以搜集50万到1000万不等的监督数据来构建此类监督数据。
一般的,这类对话式数据的来源有如下几种:
- 搜集公开的benchmark,通过启发式方法将这些相互独立的样本构建成多轮对话模式;
- 互联网开源的一些对话数据集;
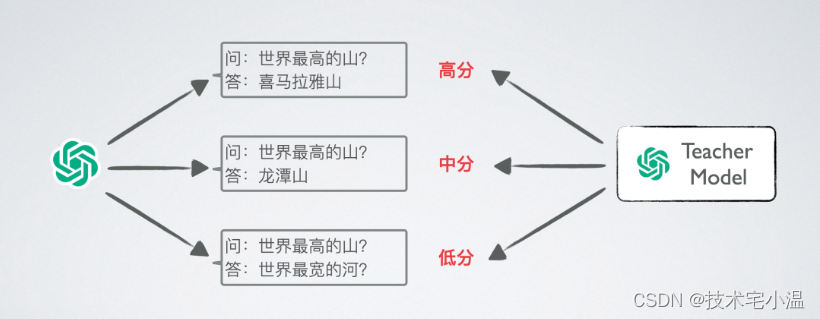
- 自行设计prompt,调用OpenAI gpt3.5-turbo,进行模型蒸馏。目前最近很多大厂或组织发布的ChatGPT类大模型中,在SFT阶段使用的数据大多采用从OpenAI中套取数据的方法来实现的。博主也自行整理了此类数据,详见:[Click Me]
2.1 数据处理:
● 只需要获得训练集和验证集即可,也可以进行采样;
● 接着,读取的数据中,获取prompt和chosen两个字段:
for i, tmp_data in enumerate(current_dataset):# tokenize the textchosen_sentence = raw_dataset.get_prompt_and_chosen(tmp_data) # the accept responseif chosen_sentence is not None:# end_of_conversation_token表示每个对话的终止符,可以用“<|endoftext|>”表示chosen_sentence += end_of_conversation_tokenchosen_token = tokenizer(chosen_sentence,max_length=max_seq_len,padding="max_length",truncation=True,return_tensors="pt")chosen_token["input_ids"] = chosen_token["input_ids"].squeeze(0)chosen_token["attention_mask"] = chosen_token["attention_mask"].squeeze(0)chosen_dataset.append(chosen_token)
● 此时,一条样本可以表示为prompt+chosen,中间会插入一些用于对话的标记,例如“Human: ”、“Assistant: ”、“<|endoftext|>”等。
2.2 模型训练
构建一个用于SFT训练的模型,模型可以指定为AutoModelForCausalLM类
def create_hf_model(model_class,model_name_or_path,tokenizer,ds_config=None,rlhf_training=False):model_config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path)model_config.dropout = 0.0# Note: dschf is defined in function scope to avoid global effects# https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main_classes/deepspeed#nontrainer-deepspeed-integrationif ds_config is not None and ds_config["zero_optimization"]["stage"] == 3:dschf = HfDeepSpeedConfig(ds_config)else:dschf = Noneif rlhf_training:# the weight loading is handled by create critic modelmodel = model_class.from_config(model_config)else:model = model_class.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path,from_tf=bool(".ckpt" in model_name_or_path),config=model_config)model.config.end_token_id = tokenizer.eos_token_idmodel.config.pad_token_id = model.config.eos_token_idmodel.resize_token_embeddings(int(8 * math.ceil(len(tokenizer) / 8.0))) # make the vocab size multiple of 8return model
按照Causal Language Modeling进行训练,例如GPT、OPT、LLaMA、BLOOM等。
三、Step2: Training Pairwise Reward Function(RW)
在此阶段,我们需要训练一个Reward函数,来为模型的输出进行评分。在InstructGPT原文中,采用的方法是对于同一个prompt,让大模型生成4~7个回复,然后让经过培训的标注人员为这些回复进行打分。因而可以得到若干个pair。而此过程需要借助人工标注来完成对齐。
在DeepSpeed-Chat中,我们直接获取已经打标好的开源的Reward训练数据。对于每一条数据,除了prompt以外,包括一对回复:
- chosen:表示较好的回复,可以作为正样本;
- rejected:表示较差的回复,可以作为负样本。
3.1 数据处理:
● 读取训练集和验证集用来训练偏好模型;
● 此时需要读取prompt、chosen和rejected三个字段数据,每一条数据是一个pairwise
for i, tmp_data in enumerate(current_dataset):# tokenize the textchosen_sentence = raw_dataset.get_prompt_and_chosen(tmp_data) # the accept responsereject_sentence = raw_dataset.get_prompt_and_rejected(tmp_data) # the accept responseif chosen_sentence is not None and reject_sentence is not None:chosen_sentence += end_of_conversation_token # the accept responsereject_sentence += end_of_conversation_tokenchosen_token = tokenizer(chosen_sentence,max_length=max_seq_len,padding="max_length",truncation=True,return_tensors="pt")reject_token = tokenizer(reject_sentence,max_length=max_seq_len,padding="max_length",truncation=True,return_tensors="pt")chosen_token["input_ids"] = chosen_token["input_ids"]chosen_token["attention_mask"] = chosen_token["attention_mask"]chosen_dataset.append(chosen_token)reject_token["input_ids"] = reject_token["input_ids"]reject_token["attention_mask"] = reject_token["attention_mask"]reject_dataset.append(reject_token)
3.2 DataCollator
给定一个batch,其包含batch_size个chosen examples和rejected examples,将其进行拆分,具体操作如下:
class DataCollatorReward:def __call__(self, data):batch = {}# f[0]是chosen input ids,f[2]是rrejected input ids# 该操作是指,先给定N个examples,转换为2*N个样本。# 前N个为chosen input ids,后N个为rejected input idsbatch["input_ids"] = torch.cat([f[0] for f in data] + [f[2] for f in data], dim=0)batch["attention_mask"] = torch.cat([f[1] for f in data] + [f[3] for f in data], dim=0)return batch
3.3 定义Reward模型:
定义reward模型:选择OPT-350M模型作为backbone,并定义一个linear层用于分类。
- OPT模型中,需要定义–num_padding_at_beginning=1,OPT默认首个字符为PAD token;
- 对于每个chosen或rejected tokens,取第一个padding token的前一个token的得分作为当前chosen或rejected input的得分
For RW, the training objective is the pairwise ranking score, i.e., for the two query-answer pairs, RM is supposed to give a higher score to the better answer. There are multiple ways to achieve this. In our implementation, we use either the end token of the sequence or the first padding token as the aggregated score and compare them. Others may also use the average score for the entire answer as an alternative.
Reward函数细节详见代码和注释:
# Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation.
# SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0
# DeepSpeed Team
import torch
from torch import nn
## Note that the following code is modified from
## https://github.com/CarperAI/trlx/blob/main/examples/summarize_rlhf/reward_model/reward_model.py
class RewardModel(nn.Module):def __init__(self, base_model, tokenizer, num_padding_at_beginning=0):super().__init__()self.config = base_model.configself.num_padding_at_beginning = num_padding_at_beginningif hasattr(self.config, "word_embed_proj_dim"):# `OPT` models use word_embed_proj_dim as final output# https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/src/transformers/models/opt/modeling_opt.py#L497self.v_head = nn.Linear(self.config.word_embed_proj_dim,1,bias=False)else:# `gpt-neo(x)` models use `hidden_size` attribute names instead of `n_embd``self.config.n_embd = self.config.hidden_size if hasattr(self.config, "hidden_size") else self.config.n_embdself.v_head = nn.Linear(self.config.n_embd, 1, bias=False)self.rwtranrsformer = base_modelself.PAD_ID = tokenizer.pad_token_iddef gradient_checkpointing_enable(self):self.rwtranrsformer.gradient_checkpointing_enable()def gradient_checkpointing_disable(self):self.rwtranrsformer.gradient_checkpointing_disable()def forward(self,input_ids=None,past_key_values=None,attention_mask=None,position_ids=None,head_mask=None,inputs_embeds=None,use_cache=False):"""假设默认设置的batch_size为N,那么len(input_ids)=2*N其中前N个为chosen input ids(正样本),后N个为rejected input ids(负样本)"""loss = Nonetransformer_outputs = self.rwtranrsformer(input_ids,past_key_values=past_key_values,attention_mask=attention_mask,head_mask=head_mask,inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds,use_cache=use_cache)hidden_states = transformer_outputs[0]rewards = self.v_head(hidden_states).squeeze(-1)chosen_mean_scores = []rejected_mean_scores = []# Split the inputs and rewards into two parts, chosen and rejectedassert len(input_ids.shape) == 2bs = input_ids.shape[0] // 2seq_len = input_ids.shape[1]chosen_ids = input_ids[:bs] # N x seq x 1 前N个为正样本rejected_ids = input_ids[bs:] # 后N个为负样本chosen_rewards = rewards[:bs] # 获得前N个正样本的预测的rewardrejected_rewards = rewards[bs:] # 获得后N个负样本的预测的reward# Compute pairwise loss. Only backprop on the different tokens before paddingloss = 0# 遍历每个样本for i in range(bs):# 获得一个chosen样本(正样本)chosen_id = chosen_ids[i] # seq# 获得一个rejected样本(负样本)rejected_id = rejected_ids[i]# 当前正样本的得分chosen_reward = chosen_rewards[i]# 当前负样本的得分rejected_reward = rejected_rewards[i]c_inds = (chosen_id == self.PAD_ID).nonzero() # 获得所有padding token的索引c_ind = c_inds[self.num_padding_at_beginning].item() if len( # 如果是OPT,那么第0个一定是OPT模型默认在input最前面的padding token,不予考虑c_inds) > self.num_padding_at_beginning else seq_len # OPT model pads the first token, so we need to use the second padding token as the end of the sequencecheck_divergence = (chosen_id != rejected_id).nonzero() # [[0, 0], [1, 0], ..., [seq_len, 0]]if len(check_divergence) == 0: # 说明不存在相等的padding tokenend_ind = rejected_reward.size(-1)divergence_ind = end_ind - 1r_ind = c_indelse:# Check if there is any padding otherwise take length of sequencer_inds = (rejected_id == self.PAD_ID).nonzero() # 找出所有与padding token相等的token索引r_ind = r_inds[self.num_padding_at_beginning].item() if len(r_inds) > self.num_padding_at_beginning else seq_lenend_ind = max(c_ind, r_ind)divergence_ind = check_divergence[0]assert divergence_ind > 0c_truncated_reward = chosen_reward[divergence_ind:end_ind]r_truncated_reward = rejected_reward[divergence_ind:end_ind]chosen_mean_scores.append(chosen_reward[c_ind - 1]) #use the end score for referencerejected_mean_scores.append(rejected_reward[r_ind - 1])# pair-wise lossloss += -torch.log(torch.sigmoid(c_truncated_reward - r_truncated_reward)).mean()loss = loss / bschosen_mean_scores = torch.stack(chosen_mean_scores)rejected_mean_scores = torch.stack(rejected_mean_scores)return {"loss": loss,"chosen_mean_scores": chosen_mean_scores,"rejected_mean_scores": rejected_mean_scores,}def forward_value(self,input_ids=None,attention_mask=None,past_key_values=None,position_ids=None,head_mask=None,inputs_embeds=None,return_value_only=False,prompt_length=0,use_cache=False):transformer_outputs = self.rwtranrsformer(input_ids,past_key_values=past_key_values,attention_mask=attention_mask,head_mask=head_mask,inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds,use_cache=use_cache)hidden_states = transformer_outputs[0]values = self.v_head(hidden_states).squeeze(-1)if return_value_only:return valueselse:# [0 0 0 0 prompt, answer, 0 0 0 0 ] for step 3, we have padding at the beginning# [prompt, answer, 0, 0, 0, 0] this is normalassert prompt_length > 1, "prompt_length must be greater than 1 to help select the end score"bs = values.size(0)seq_len = input_ids.shape[1]chosen_end_scores = [] # we use this name for consistency with the original forward functionfor i in range(bs):input_id = input_ids[i]value = values[i]c_inds = (input_id[prompt_length:] == self.PAD_ID).nonzero()# here we only use the answer part of the sequence so we do not need to care about the padding at the beginningc_ind = c_inds[0].item() + prompt_length if len(c_inds) > 0 else seq_lenchosen_end_scores.append(value[c_ind - 1])return {"values": values,"chosen_end_scores": torch.stack(chosen_end_scores),}
上面的Reward函数可以认为是一个分类器,需要基于Causal LM(例如OPT)作为Backbone,获得完整的Reward模型:
def create_critic_model(model_name_or_path,tokenizer,ds_config,num_padding_at_beginning=0,rlhf_training=False):# OPT model family always put a padding token at the beginning of the sequence,# we did not see this in other models but not sure if it is a general rulecritic_model = create_hf_model(AutoModel, model_name_or_path, tokenizer,ds_config, rlhf_training)critic_model = RewardModel(critic_model,tokenizer,num_padding_at_beginning=num_padding_at_beginning)if rlhf_training:# critic model needs to load the weight heremodel_ckpt_path = os.path.join(model_name_or_path, 'pytorch_model.bin')assert os.path.exists(model_ckpt_path), f"Cannot find model checkpoint at {model_ckpt_path}"critic_model.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_ckpt_path, map_location='cpu'))return critic_model
四、Step3:RLHF Tuning——PPO算法
PPO算法是一种Actor-Critic强化学习架构。相关解读如下所示:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/110998399
https://www.zhihu.com/question/56692640/answer/152930557
4.1 数据处理
在第三阶段,可以选择监督训练数据和无监督数据。
● 监督数据:此时只有prompt,没有chosen和rejected input。
for i, tmp_data in enumerate(current_dataset):# tokenize the textprompt = raw_dataset.get_prompt(tmp_data)if prompt is not None:prompt_token = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")prompt_token["input_ids"] = prompt_token["input_ids"]prompt_token["attention_mask"] = prompt_token["attention_mask"]for key_word in ["input_ids", "attention_mask"]:length = prompt_token[key_word].size()[-1]if length > max_seq_len:# 先将正常的token序列的顺序倒序排列,(会在datacollator中再次倒序恢复原始排列)y = prompt_token[key_word].squeeze(0)[length - (max_seq_len - 1):].flip(0)else:# 先将正常的token序列的顺序倒序排列,(会在datacollator中再次倒序恢复原始排列)y = prompt_token[key_word].squeeze(0).flip(0)prompt_token[key_word] = yprompt_dataset.append(prompt_token)
● 无监督数据:只有文本,并进行group:
def get_unsupervised_data(args, tokenizer):unsupervised_raw_datasets = load_dataset(args.unsupervised_dataset_name, args.unsupervised_dataset_config_name)column_names = unsupervised_raw_datasets["train"].column_namestext_column_name = "text" if "text" in column_names else column_names[0]def tokenize_function(examples):return tokenizer(examples[text_column_name])tokenized_datasets = unsupervised_raw_datasets.map(tokenize_function,batched=True,num_proc=args.preprocessing_num_workers,remove_columns=column_names,load_from_cache_file=True,desc="Running tokenizer on dataset",)block_size = args.max_prompt_seq_len + args.max_answer_seq_lendef group_texts(examples):# Concatenate all texts.concatenated_examples = {k: list(chain(*examples[k]))for k in examples.keys()}total_length = len(concatenated_examples[list(examples.keys())[0]])# We drop the small remainder, we could add padding if the model supported it instead of this drop, you can# customize this part to your needs.if total_length >= block_size:total_length = (total_length // block_size) * block_size# Split by chunks of max_len.result = {k:[t[i:i + block_size] for i in range(0, total_length, block_size)]for k, t in concatenated_examples.items()}result["labels"] = result["input_ids"].copy()return resultlm_datasets = tokenized_datasets.map(group_texts,batched=True,num_proc=args.preprocessing_num_workers,load_from_cache_file=True,desc=f"Grouping texts in chunks of {block_size}",)train_dataset = lm_datasets["train"]return train_dataset
4.2 DataCollator
针对监督数据,需要进行处理:
class DataCollatorRLHF:def __init__(self, max_token_len, inference_tp_size):self.max_token_len = max_token_lenself.inference_tp_size = inference_tp_sizedef __call__(self, data):batch = {}pad_token_id = data[-1][-1]prompt = pad_sequence([f[0] for f in data],padding_value=pad_token_id,batch_first=True)prompt_mask = pad_sequence([f[1] for f in data],padding_value=0,batch_first=True)### make sure the final ouput is a seqence of 2**?length = prompt.size()[-1]pad_length = self.max_token_len - lengthif pad_length > 0:batch["prompt"] = F.pad(prompt,pad=(pad_length, 0),mode='constant',value=pad_token_id)batch["prompt_att_mask"] = F.pad(prompt_mask,pad=(pad_length, 0),mode='constant',value=0)else:batch["prompt"] = promptbatch["prompt_att_mask"] = prompt_maskbatch["prompt"] = batch["prompt"].flip(1)batch["prompt_att_mask"] = batch["prompt_att_mask"].flip(1)return batch
4.3 模型
在RLHF阶段,需要加载前两个阶段训练得到的SFT模型和reward,用于初始化RLHF引擎。下面展示具体细节。
4.3.1 初始化DeepSpeedRLHFEngine:
获得一个DeepSpeedRLHFEngine对象,用于初始化一系列模型,包括Actor、Critic、Reference和Reward。
rlhf_engine = DeepSpeedRLHFEngine(actor_model_name_or_path=args.actor_model_name_or_path,critic_model_name_or_path=args.critic_model_name_or_path,tokenizer=tokenizer,num_total_iters=num_total_iters,args=args)
(1)初始化Actor、Reference模型:
● 因为Actor模型是Stage1训练的SFT,其参数量很大,因此需要配置ZeRO-Stage和ZeRO-Offload进行显存优化:
def get_train_ds_config(offload,stage=2,enable_hybrid_engine=False,inference_tp_size=1,release_inference_cache=False,pin_parameters=True,tp_gather_partition_size=8):device = "cpu" if offload else "none"zero_opt_dict = {"stage": stage,"offload_param": {"device": device},"offload_optimizer": {"device": device},"stage3_param_persistence_threshold": 1e4,"stage3_max_live_parameters": 3e7,"stage3_prefetch_bucket_size": 3e7,"memory_efficient_linear": False}return {"train_batch_size": GLOBAL_BATCH_SIZE,"train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu": MICRO_BATCH_SIZE,"steps_per_print": 10,"zero_optimization": zero_opt_dict,"fp16": {"enabled": True,"loss_scale_window": 100},"gradient_clipping": 1.0,"prescale_gradients": False,"wall_clock_breakdown": False,"hybrid_engine": {"enabled": enable_hybrid_engine,"inference_tp_size": inference_tp_size,"release_inference_cache": release_inference_cache,"pin_parameters": pin_parameters,"tp_gather_partition_size": tp_gather_partition_size,}}
ZeRo-stage一共有三个:
如果设置为3,则为最优状态,包括参数、梯度和优化状态全部进行并行化处理。
● 初始化Actor模型,加载预训练SFT的参数(以及LoRA)
● deepspeed engine封装:
actor_engine, *_ = deepspeed.initialize(model=actor_model,optimizer=optim,lr_scheduler=lr_scheduler,config=ds_config)
(2)初始化Critic、Reward模型
● 配置ZeRO-Stage和ZeRO-offload
ds_config = get_train_ds_config(offload=self.args.offload, stage=self.args.critic_zero_stage)
● 用预训练的RW模型,初始化Critic参数;
● 封装DeepSpeed Engine。
4.3.2 PPO训练+无监督预训练
在InstructGPT中,第三阶段的训练通常需要结合无监督的预训练目标和PPO训练目标联合训练,以确保模型在AC框架下强化学习训练过程中不会忘记原始的预训练任务,因此无监督的预训练可以作为一种正则化。
因此定义DeepSpeedPPOTrainerUnsupervised类用于完成PPO+无监督预训练。训练关键细节如下:
(1)Generate Experience
在Actor-Critic框架下,首先需要优化Critic,用于评价在状态 s s s下的得分。因此需要采样一系列的状态-动作序列(即Experience),在GPT模型中,状态 s s s可以视为已经生成的文本。
给定一个prompt(例如in-context examples和query),生成相应的文本,并进行打分。细节如下代码和注释:
def generate_experience(self, prompts):# 给定prompt,生成response textself.eval()# 调用model.generate()生成序列,由actor模型生成。seq = self._generate_sequence(prompts)self.train()pad_token_id = self.tokenizer.pad_token_idattention_mask = seq.not_equal(pad_token_id).long()with torch.no_grad():# 将生成的序列喂入actor模型中,得到输出的概率分布output = self.actor_model(seq, attention_mask=attention_mask)output_ref = self.ref_model(seq, attention_mask=attention_mask)# 将生成的序列喂入critic和reward模型中,获得奖励和状态价值reward_score = self.reward_model.forward_value(seq, attention_mask,prompt_length=self.prompt_length)['chosen_end_scores'].detach()values = self.critic_model.forward_value(seq, attention_mask, return_value_only=True).detach()[:, :-1]logits = output.logitslogits_ref = output_ref.logits# 获得生成的文本seq、以及对应的概率、状态价值和奖励等信息return {'prompts': prompts,'logprobs': gather_log_probs(logits[:, :-1, :], seq[:, 1:]),'ref_logprobs': gather_log_probs(logits_ref[:, :-1, :], seq[:, 1:]),'value': values,'rewards': reward_score,'input_ids': seq,"attention_mask": attention_mask}
(2)保存Experience到经验池
经验池包含一系列根据prompt生成的文本和一系列奖励信息,其可以用于训练Critic模型。
(3)RLHF训练
Actor-Critic的基本流程为:
采样 → 更新Critic参数 → 根据Critic计算Advantage Function → 更新Actor参数
Advantage计算:
Q ^ ( s t , a t ) − V ^ ( s t ) = A ^ ( s t , a t ) \hat{Q}(s_t, a_t) - \hat{V}(s_t) = \hat{A}(s_t, a_t) Q^(st,at)−V^(st)=A^(st,at)
Q ( s t , a t ) = r ( s t , a t ) + ∑ s t + 1 P ( s t + 1 ∣ s t , a t ) [ V ( s t + 1 ) ] Q(s_t, a_t) = r(s_t, a_t) + \sum_{s_{t+1}}P(s_{t+1}|s_t, a_t)[V(s_{t+1})] Q(st,at)=r(st,at)+∑st+1P(st+1∣st,at)[V(st+1)]
我们可以用一个神经网络Critic模型来表示 ∑ s t + 1 P ( s t + 1 ∣ s t , a t ) [ V ( s t + 1 ) ] \sum_{s_{t+1}}P(s_{t+1}|s_t, a_t)[V(s_{t+1})] ∑st+1P(st+1∣st,at)[V(st+1)],即给定一个状态 s s s,可以根据Critic模型预测一个得分 Q ^ \hat{Q} Q^。而 V ^ \hat{V} V^是已知的,所以可以构造监督信号来训练Critic模型。
因此RLHF训练为关键部分,也是InstructGPT第三步的优化过程。细节详见代码和注释:
def train_rlhf(self, inputs):# train the rlhf mode here### process the old outputsprompts = inputs['prompts'] # 输入的prompt(例如in-context exemplar + query)log_probs = inputs['logprobs'] # 根据prompt,actor模型生成的文本的概率ref_log_probs = inputs['ref_logprobs'] # 根据prompt,reference生成模型的文本的概率reward_score = inputs['rewards'] # 根据prompt生成的seq,reward模型得到的奖励values = inputs['value'] # 根据prompt生成的seq,critic模型得到的状态价值函数值attention_mask = inputs['attention_mask'] # actor生成的文本的attention maskseq = inputs['input_ids'] # 根据prompt,actor生成的文本start = prompts.size()[-1] - 1 # 记prompt文本最后一个位置action_mask = attention_mask[:, 1:]old_values = valueswith torch.no_grad():# 获得prompt文本本身的奖励# 由于prompt本身已存在文本,相当于整个决策序列中中已有的状态动作序列,# 因此我们需要计算一下prompt文本对应的奖励old_rewards = self.compute_rewards(prompts, log_probs,ref_log_probs, reward_score,action_mask)"""compute_rewards函数:def compute_rewards(self, prompts, log_probs, ref_log_probs, reward_score,action_mask):kl_divergence_estimate = -self.kl_ctl * (log_probs - ref_log_probs)rewards = kl_divergence_estimatestart = prompts.shape[1] - 1ends = start + action_mask[:, start:].sum(1)reward_clip = torch.clamp(reward_score, -self.clip_reward_value,self.clip_reward_value)batch_size = log_probs.shape[0]for j in range(batch_size):rewards[j, start:ends[j]][-1] += reward_clip[j]return rewards"""# 获得advantage值(v + r - v')advantages, returns = self.get_advantages_and_returns(old_values, old_rewards, start)"""def get_advantages_and_returns(self, values, rewards, start):# Adopted from https://github.com/CarperAI/trlx/blob/main/trlx/models/modeling_ppo.py#L134lastgaelam = 0advantages_reversed = []length = rewards.size()[-1]for t in reversed(range(start, length)):nextvalues = values[:, t + 1] if t < length - 1 else 0.0delta = rewards[:, t] + self.gamma * nextvalues - values[:, t]lastgaelam = delta + self.gamma * self.lam * lastgaelamadvantages_reversed.append(lastgaelam)advantages = torch.stack(advantages_reversed[::-1], dim=1)returns = advantages + values[:, start:]return advantages.detach(), returns"""# 下面则是获得生成部分seq的奖励等信息batch = {'input_ids': seq, "attention_mask": attention_mask}# 获得seq的的概率actor_prob = self.actor_model(**batch, use_cache=False).logitsactor_log_prob = gather_log_probs(actor_prob[:, :-1, :],inputs['input_ids'][:, 1:])# 根据seq的概率logits,advantage作为权重,优化actor模型参数actor_loss = self.actor_loss_fn(actor_log_prob[:, start:],log_probs[:, start:], advantages,action_mask[:, start:])"""def actor_loss_fn(self, logprobs, old_logprobs, advantages, mask):## policy gradient losslog_ratio = (logprobs - old_logprobs) * maskratio = torch.exp(log_ratio)pg_loss1 = -advantages * ratiopg_loss2 = -advantages * torch.clamp(ratio, 1.0 - self.cliprange,1.0 + self.cliprange)pg_loss = torch.sum(torch.max(pg_loss1, pg_loss2) * mask) / mask.sum()return pg_loss"""# 更新actor参数self.actor_model.backward(actor_loss)self.actor_model.step()# 获得seq的critic得分value = self.critic_model.forward_value(**batch,return_value_only=True,use_cache=False)[:, :-1]# 计算Critic losscritic_loss = self.critic_loss_fn(value[:, start:], old_values[:, start:],returns, action_mask[:, start:])"""def critic_loss_fn(self, values, old_values, returns, mask):## value lossvalues_clipped = torch.clamp(values,old_values - self.cliprange_value,old_values + self.cliprange_value,)vf_loss1 = (values - returns)**2vf_loss2 = (values_clipped - returns)**2vf_loss = 0.5 * torch.sum(torch.max(vf_loss1, vf_loss2) * mask) / mask.sum()return vf_loss"""# 更新Critic模型参数self.critic_model.backward(critic_loss)self.critic_model.step()return actor_loss, critic_loss
(4)无监督预训练
在无监督数据集上,按照Causal Language Modeling进行预训练,更新actor模型参数。其为最原始的GPT类模型的预训练目标。
def train_unsupervised(self, inputs, unsup_coef):# Train the unsupervised model hereself._validate_training_mode()outputs = self.actor_model(**inputs, use_cache=False)loss = outputs.lossself.actor_model.backward(unsup_coef * loss)self.actor_model.step()
(5)EMA(指数移动平均)
额外引入EMA优化模型的参数,详见:
def moving_average(model, model_ema, beta=0.992, device=None, zero_stage=0):zero_stage_3 = (zero_stage == 3)with torch.no_grad():for param, param_ema in zip(model.parameters(),model_ema.parameters()):# TODO: use prefiltering for efficiencyparams_to_fetch = _z3_params_to_fetch([param, param_ema]) if zero_stage_3 else []should_gather_param = len(params_to_fetch) > 0with deepspeed.zero.GatheredParameters(params_to_fetch, enabled=should_gather_param):data = param.dataif device is not None:data = data.to(device)param_ema.data.copy_(torch.lerp(data, param_ema.data, beta))
4.3.3 RLHF整体训练过程
下面展示第三步的训练过程:
- for 每一个epoch:
- for 遍历每个batch,得到小批量的prompt和无监督语料:
- 对于所有prompt,调用
trainer.generate_experience(prompts)获得经验数据,包括生成的seq、logits、奖励、状态价值等; - 将这一组prompt的经验数据加入经验池;
- for 每一个ppo_epoch:
- for 遍历经验池中的每一个batch经验数据,以及无监督语料:
- 调用
trainer.train_rlhf(exp_data),更新Actor和Critic模型; - 调用
trainer.train_unsupervised(unsup_data)在无监督语料上预训练,更新Actor模型; - 调用
moving_average()进行指数移动平均
- 调用
- 每一轮ppo_epoch时,打乱经验池和无监督语料的顺序。
- for 遍历经验池中的每一个batch经验数据,以及无监督语料:
- 对于所有prompt,调用
- for 遍历每个batch,得到小批量的prompt和无监督语料:
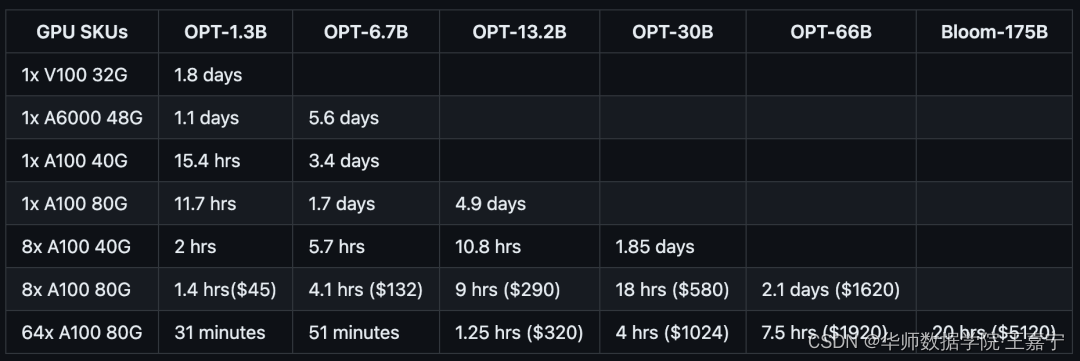
基于DeepSpeed训练可以实现在普通的GPU上训练超大规模语言模型,对照表如下所示: