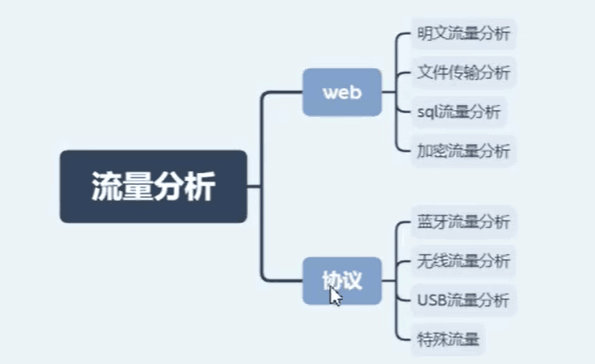
流量分析基础知识学习
wireshark基础语法



常见套路
查看关键字
http contains "flag" //直接出
追踪流
右键-》追踪流-》TCP
分组字节流
文件-》导出选择分组字节流
查看隐藏
binwalk查看
然后再用搜索
然后导出分组字节流
做题方法
flag明文
直接搜索flag,flag{
flag编码
flag经过16进制编码,或者其他编码
flag-->666C6167unicode转ascii
f-->f
直接上脚本 python2 的脚本
# encoding:utf-8
import os
import os.path
import sys
import subprocess#打印可打印字符串
def str_re(str1):str2=""for i in str1.decode('utf8','ignore'):try:#print(ord(i))if ord(i) <= 126 and ord(i) >= 33:str2 += iexcept:str2 += ""#print(str2)return str2#写入文本函数
def txt_wt(name,txt1):with open("output.txt","a") as f:f.write('filename:'+name)f.write("\n")f.write('flag:'+txt1)f.write("\n")#第一次运行,清空output文件
def clear_txt():with open("output.txt","w") as f:print "clear output.txt!!!"# 递归遍历的所有文件
def file_bianli():# 路径设置为当前目录path = os.getcwd()# 返回文件下的所有文件列表file_list = []for i, j, k in os.walk(path):for dd in k:if ".py" not in dd and "output.txt" not in dd:file_list.append(os.path.join(i, dd))return file_list#查找文件中可能为flag的字符串def flag(file_list,flag):for i in file_list:try:with open(i,"rb") as f:for j in f.readlines():j1=str_re(j)#可打印字符串#print j1for k in flag:if k in j1:txt_wt(i, j1)print 'filename:',iprint 'flag:',j1except:print 'err'flag_txt = ['flag{', '666c6167','flag','Zmxh','f', '666C6167']#清空输出的文本文件
clear_txt()
#遍历文件名
file_lt=file_bianli()
#查找flag关键字
flag(file_lt,flag_txt)压缩包流量
flag放在压缩包中。zip、7z、rar、tar.gz里
解法:
1.直接找到流量数据:右键->显示分组字节->去掉标志位(菜刀是前三位)->左下角有个解码为->解码为压缩包
2.导出压缩包:右键->显示分组字节->左下角有个显示为->改为原始数据->save as->1.zip
3.直接导出压缩包:右键->导出分子字节流->1.zip
4.在追踪流中导出压缩包:右键追踪流->左下角选择返回包->显示原始数据->save as->1.zip
telnet
不可打印字符
显示为Hex转储,然后再在ascii表中找到该编码对应的字符,如08对应退格。需要减掉这个字符。蓝牙协议
1.直接查找flag
2.统计->协议分级->找到OBEX协议(蓝牙中的传输文件协议)->直接搜索obex->找到传输的文件->导出分组字节流
PIN码在分组详情中搜索。
USB协议
键盘流量
这里直接使用脚本。把
# -*- coding: cp936 -*-
import os
os.system("tshark -r test.pcapng -T fields -e usb.capdata > usbdata.txt")
normalKeys = {"04":"a", "05":"b", "06":"c", "07":"d", "08":"e", "09":"f", "0a":"g", "0b":"h", "0c":"i", "0d":"j", "0e":"k", "0f":"l", "10":"m", "11":"n", "12":"o", "13":"p", "14":"q", "15":"r", "16":"s", "17":"t", "18":"u", "19":"v", "1a":"w", "1b":"x", "1c":"y", "1d":"z","1e":"1", "1f":"2", "20":"3", "21":"4", "22":"5", "23":"6","24":"7","25":"8","26":"9","27":"0","28":"<RET>","29":"<ESC>","2a":"<DEL>", "2b":"\t","2c":"<SPACE>","2d":"-","2e":"=","2f":"[","30":"]","31":"\\","32":"<NON>","33":";","34":"'","35":"<GA>","36":",","37":".","38":"/","39":"<CAP>","3a":"<F1>","3b":"<F2>", "3c":"<F3>","3d":"<F4>","3e":"<F5>","3f":"<F6>","40":"<F7>","41":"<F8>","42":"<F9>","43":"<F10>","44":"<F11>","45":"<F12>"}shiftKeys = {"04":"A", "05":"B", "06":"C", "07":"D", "08":"E", "09":"F", "0a":"G", "0b":"H", "0c":"I", "0d":"J", "0e":"K", "0f":"L", "10":"M", "11":"N", "12":"O", "13":"P", "14":"Q", "15":"R", "16":"S", "17":"T", "18":"U", "19":"V", "1a":"W", "1b":"X", "1c":"Y", "1d":"Z","1e":"!", "1f":"@", "20":"#", "21":"$", "22":"%", "23":"^","24":"&","25":"*","26":"(","27":")","28":"<RET>","29":"<ESC>","2a":"<DEL>", "2b":"\t","2c":"<SPACE>","2d":"_","2e":"+","2f":"{","30":"}","31":"|","32":"<NON>","33":"\"","34":":","35":"<GA>","36":"<","37":">","38":"?","39":"<CAP>","3a":"<F1>","3b":"<F2>", "3c":"<F3>","3d":"<F4>","3e":"<F5>","3f":"<F6>","40":"<F7>","41":"<F8>","42":"<F9>","43":"<F10>","44":"<F11>","45":"<F12>"}nums = []
keys = open('usbdata.txt')
for line in keys:#print(line)if len(line)!=17: #首先过滤掉鼠标等其他设备的USB流量continuenums.append(line[0:2]+line[4:6]) #取一、三字节#print(nums)
keys.close()
output = ""
for n in nums:if n[2:4] == "00" :continueif n[2:4] in normalKeys:if n[0:2]=="02": #表示按下了shiftoutput += shiftKeys [n[2:4]]else :output += normalKeys [n[2:4]]else:output += '[unknown]'
print('output :' + output)
鼠标流量
高版本wireshark默认支持USB-HID协议,需要在分析-启用的协议 禁用USB-HID协议
#sniffer.py
import os
os.system("tshark -r test2.pcapng -T fields -e usb.capdata > usbdata.txt")
#sniffer.py
nums = []
keys = open('usbdata.txt','r')
result=open('result.txt','w')
posx = 0
posy = 0
for line in keys:if len(line) != 13 :#????continuex = int(line[4:6],16)y = int(line[6:8],16)if x > 127 :x -= 256if y >120 :#??????????????????????????????y -=264#??????????????????????????????????posx += xposy += ybtn_flag = int(line[2:4],16) # 1 for left , 2 for right , 0 for nothingif btn_flag == 1 :result.write(str(posx)+' '+str(-posy)+'\n')
print(result)
keys.close()
result.close()#os.system("gnuplot.exe -e \"plot \'result.txt\'\" -p") #画图
无线流量
802.11:无线局域网流量协议
爆破无线密码
aircrack-ng ctf.pcap -w password.txt带入无线密码到pcap中,输出1.pcap
airdecap-ng ctf.pcap -e 'target network SSID' -p 密码 -o 1.pcap也可以直接把密码添加到原pacp中:
编辑->首选项->Protocols->IEEE 802.11->Edit->添加一个wpa-pwd,值是刚才爆破的密码。然后视图->重新加载
SSL流量
TLS协议:经过加密的流量
导入密钥
编辑->首选项->Protocols->TLS->导入log文件
查找http流量
导出分组字节
分段传输的压缩包
TCP分段传输的压缩包
TCP分段传输的压缩包,我们可以直接跟踪HTTP流,HTTP会把压缩包流量整合,然后导出分组字节流出来。
5.0以上压缩包爆破,用脚本。5.0以下用软件就可以
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import subprocessrar_name="11.rar"
#载入字典
with open('10000.txt',"r") as f:for p in f.readlines():# rar.exe在winrarcmd = "rar.exe e {0} -y -p{1}".format(rar_name,p.strip())r = subprocess.getstatusoutput(cmd)# print(r)# print(r[0])if r[0] == 0:print("pass = %s" % p)break
#纯数字爆破
for p in range(0,999999):cmd = "rar.exe e {0} -y -p{1}".format(rar_name,str(p))r = subprocess.getstatusoutput(cmd)if r[0] == 0:print("pass = %s" % p)#breakrar5.0爆破