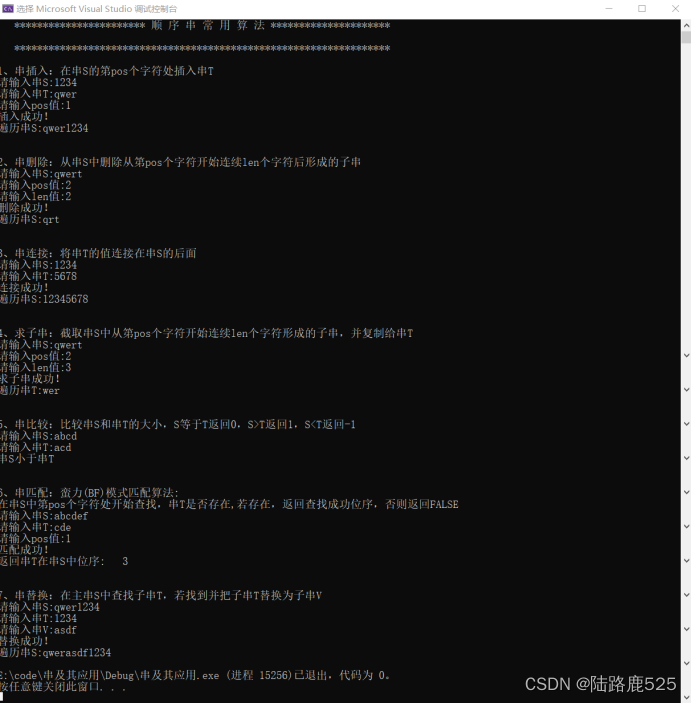
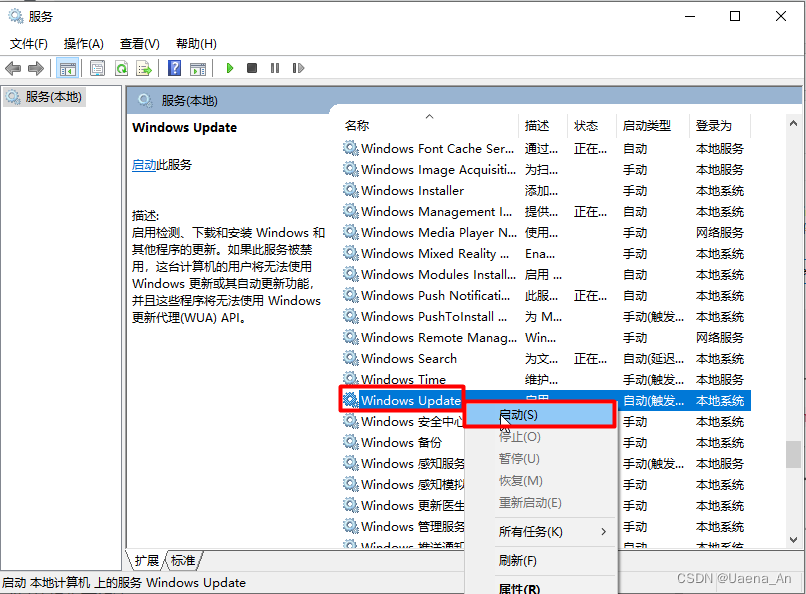
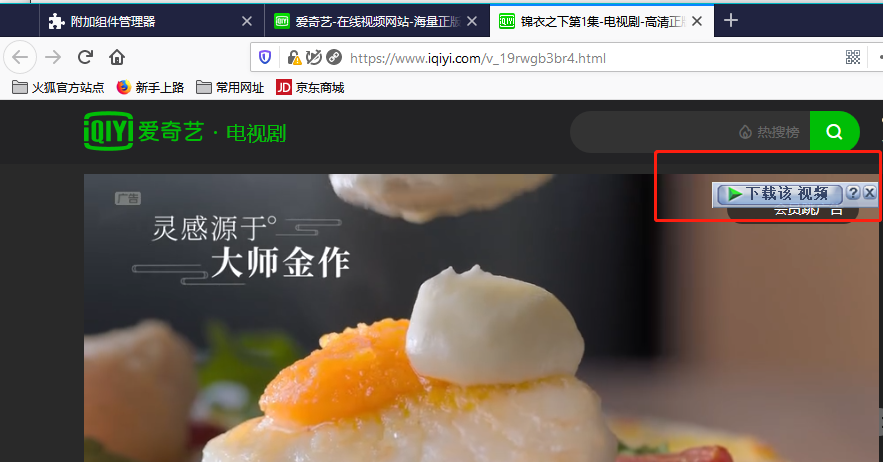
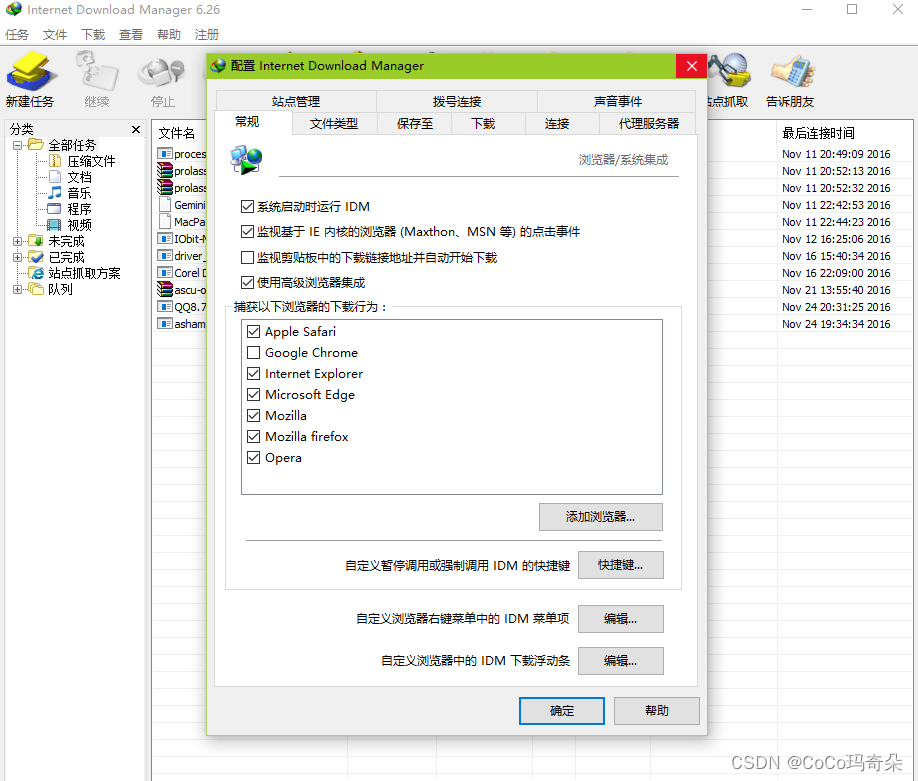
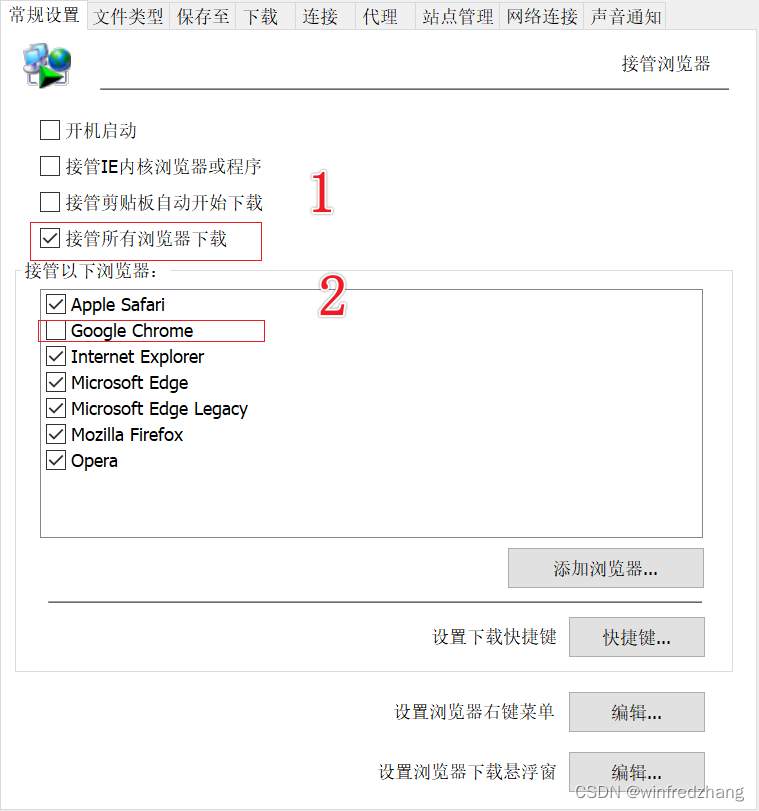
1.并转串
module b2c(clk,ain,rst,bout,load,ready);//并转串input clk,rst,load;input [7:0] ain;output reg bout;output reg ready;reg [7:0] temp;always @(posedge clk or posedge rst)beginif(rst)begintemp<=8'dx;bout<=1'bx;ready=1'b1;//复位时可以接收输入数据endelsebeginif(load && ready)//置数begintemp<=ain;endif(temp[7]||!temp[7])//temp[7]有数beginbout<=temp[7];//输出由temp[7]决定,每次左移1位,并且在最低位补xtemp<={temp[6:0],1'bx};ready<=1'b0;end elsebeginready<=1'b1;bout<=1'bx;end end end
endmodule
另一种计数器方法:
module b2c(clk,din,rst,ordy,bout);input clk,rst;input [3:0] din;output bout;output reg ordy;reg [1:0] count;reg [3:0] temp;reg ready;always @(posedge clk)beginif(rst)begincount <= 0;temp <= 0;// bout <= 0;ordy <= 0;ready <= 1;//开始置数endelse beginif(ready)begintemp <= din;//置数,同时计数归零ready <= 0;count <= 0;endelsebegintemp <= {temp[2:0],1'bx};//左移count <= count + 1'b1;if(count < 3)beginordy <= 1;endelsebeginordy <= 0;ready <= 1;endendendendassign bout = temp[3];
endmodule
2.串转并
module b2c(clk,ain,rst,bout,load,ready);//并转串input clk,rst,load;input [7:0] ain;output reg bout;output reg ready;reg [7:0] temp;always @(posedge clk or posedge rst)beginif(rst)begintemp<=8'dx;bout<=1'bx;ready=1'b1;//复位时可以接收输入数据endelsebeginif(load && ready)//置数begintemp<=ain;endif(temp[7]||!temp[7])//temp[7]有数beginbout<=temp[7];//输出由temp[7]决定,每次左移1位,并且在最低位补xtemp<={temp[6:0],1'bx};ready<=1'b0;end elsebeginready<=1'b1;bout<=1'bx;end end end
endmodule
另一种计数器方法:
module c2b(clk,ain,rst,bout,ready);//串转并input clk,rst;input ain;output [3:0] bout;output reg ready;reg [3:0] temp;reg [1:0] count;always @(posedge clk)beginif(rst)begintemp <= 4'dx;count <= 0;ready <= 0;endelse begintemp <= {temp[2:0],ain};//左移count <= count + 1'd1;if(count == 3)beginready <= 1;endelsebeginready <= 0;endendendassign bout = temp;
endmodule