/*上机内容:
上机目的:
* Copyright (c) 2012, 烟台大学计算机学院
* All rights reserved.
* 作 者: 徐本锡
* 完成日期:2013 年 6 月 3日
* 版 本 号:v1.0
*
* 输入描述:
* 问题描述:
【项目1】根据给出的基类Animal和main()函数。
1、根据给出的main()函数和运行结果的提示,设计出相关的各个类,注意观察运行结果,提取出每个类中需要的数据成员,
并匹配上需要的成员函数。
2、显然,Animal设计为抽象类更合适,Animal不需要能够实例化,是专门作基类使用的。改造程序,使Animal设计为抽象类,
这时main()函数中p = new Animal();将出错,将此行删除。
3、每一个Animal的派生类都有一个“名字”数据成员,这一共有的成员完全可以由基类提供改造上面的程序,
将这一数据成员作为抽象类Animal数据成员被各派生类使用。
下面是给出的基类Animal和main()函数:
* 程序输出:
* 算法设计:
程序代码:*/
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Animal
{
public:
virtual void AnimalName(){cout<<"Animal ";}
virtual void cry()
{
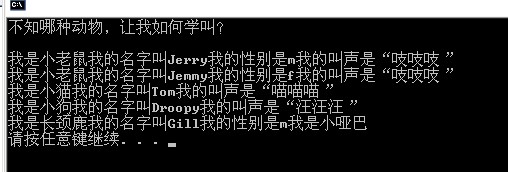
cout<<"不知哪种动物,让我如何学叫?"<<endl;
}
};
class Mouse :public Animal
{
public :
Mouse (string n, char s):name (n),sex(s){}
void AnimalName(){cout<<"Mouse ";}
void cry(){cout<<"我是小老鼠我的名字叫"<<name<<"我的性别是" <<sex<<"我的叫声是“吱吱吱”";}
protected:
string name; char sex;
};
class Cat :public Animal
{
public :
Cat (string n):name (n){}
void AnimalName(){cout<<"Cat ";}
void cry(){cout<<"我是小猫我的名字叫"<<name<<"我的叫声是“喵喵喵”";}
protected:
string name;
};
class Dog:public Animal
{
public :
Dog (string n):name (n){}
void AnimalName(){cout<<"Dog ";}
void cry(){cout<<"我是小狗我的名字叫"<<name<<"我的叫声是“汪汪汪”";}
protected:
string name;
};
class Giraffe :public Animal
{
public :
Giraffe(string n, char s):name (n),sex(s){}
void AnimalName(){cout<<"Mouse ";}
void cry(){cout<<"我是长颈鹿我的名字叫"<<name<<"我的性别是" <<sex<<"我是小哑巴";}
protected:
string name; char sex;
};
int main( )
{
Animal *p;
p = new Animal();
p->cry();
cout<<endl;
Mouse m1("Jerry",'m');
p=&m1;
p->cry();
cout<<endl;
Mouse m2("Jemmy",'f');
p=&m2;
p->cry();
cout<<endl;
Cat c1("Tom");
p=&c1;
p->cry();
cout<<endl;
Dog d1("Droopy");
p=&d1;
p->cry();
cout<<endl;
Giraffe g1("Gill",'m');
p=&g1;
p->cry();
cout<<endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
问题一:
问题二:
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Animal
{
public:
virtual void cry()const =0;
};
class Mouse :public Animal
{
public :
Mouse (string n, char s):name (n),sex(s){}
void cry()const{cout<<"我是小老鼠我的名字叫"<<name<<"我的性别是" <<sex<<"我的叫声是“吱吱吱”";}
protected:
string name; char sex;
};
class Cat :public Animal
{
public :
Cat (string n):name (n){}
void cry()const{cout<<"我是小猫我的名字叫"<<name<<"我的叫声是“喵喵喵”";}
protected:
string name;
};
class Dog:public Animal
{
public :
Dog (string n):name (n){}
void cry()const{cout<<"我是小狗我的名字叫"<<name<<"我的叫声是“汪汪汪”";} //..................................................此处需加const
protected:
string name;
};
class Giraffe :public Animal
{
public :
Giraffe(string n, char s):name (n),sex(s){}
void cry()const{cout<<"我是长颈鹿我的名字叫"<<name<<"我的性别是" <<sex<<"我是小哑巴";}
protected:
string name; char sex;
};
int main( )
{
Animal *p;
// p = new Animal();
// p->cry();
//cout<<endl;
Mouse m1("Jerry",'m');
p=&m1;
p->cry();
cout<<endl;
Mouse m2("Jemmy",'f');
p=&m2;
p->cry();
cout<<endl;
Cat c1("Tom");
p=&c1;
p->cry();
cout<<endl;
Dog d1("Droopy");
p=&d1;
p->cry();
cout<<endl;
Giraffe g1("Gill",'m');
p=&g1;
p->cry();
cout<<endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
抽象类是没有对象的,但是有抽象类这个类型,可以定义只想抽象类类型的指针