很多初学者在自学Java时候都卡在了Java多态,本教程从实际案例出发阐述Java多态现象及Java多态的原理。
通过案例理解多态的现象
需求描述
多态是类在继承关系下的一种形态,下边先通过一个需求展示下多态的现象。
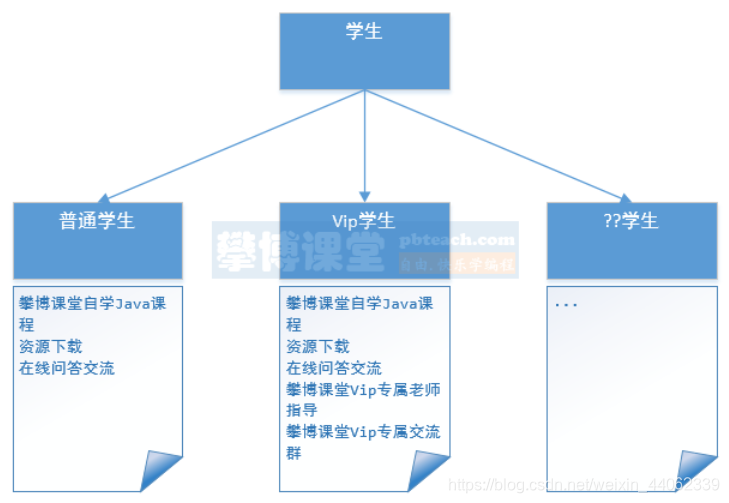
攀博课堂是一个在线教育学习平台,有一个具体的功能需求:当学员登录后系统需要根据学员的类型获取他在攀博课堂的服务权限,比如:对于普通学生他可以自学Java课程、下载资源、在线问答交流,对于Vip学员还可以额外有专属老师指导、专属交流群等 Vip服务,如何使用面向对象的编程思想实现这一功能需求。
每种学生类型的服务内容如下:
解决方案1
根据不同的学生类型获取不同的服务内容,首先想到的就是分支结构,在学生类中设置一个成员变量记录学生类型,在获取服务内容的方法中判断学生类型,然后根据不同的学生类型获取不同的服务内容。

代码如下:
课程类:
package com.pbteach.javase.oop.polymorphism.v1;/*** 课程* @author 攀博课堂(www.pbteach.com)**/
public class PbCourse {//课程标识private long id;//课程名称private String courseName;//课程价格private float price;public PbCourse() {}public PbCourse(long id, String courseName, float price) {this.id = id;this.courseName = courseName;this.price = price;}public long getId() {return id;}public void setId(long id) {this.id = id;}public String getCourseName() {return courseName;}public void setCourseName(String courseName) {this.courseName = courseName;}public float getPrice() {return price;}public void setPrice(float price) {this.price = price;}}
学生类:
package com.pbteach.javase.oop.polymorphism.v1;/*** 攀博课堂学生类* @author 攀博课堂(www.pbteach.com)**/
public class PbStudent{//用户idprivate String id;//昵称private String nickname;//邮箱private String email;//头像private String pic;//密码private String password;//选课列表private PbCourse[] selections;//用户分组private int group;//获取服务public void getService() {if(group == 1) {//普通学生System.out.println("攀博课堂自学Java课程");System.out.println("资源下载");System.out.println("在线问答交流");}else if(group == 2) {//vip学生System.out.println("攀博课堂自学Java课程");System.out.println("资源下载");System.out.println("在线问答交流");System.out.println("攀博课堂Vip专属老师指导");System.out.println("攀博课堂Vip专属交流群");}//..有其它类型的学生向后加}public PbStudent() {System.out.println("PbStudent="+this);}//提供三个基本数据的构造方法public PbStudent(String id,String nickname,String email,int group) {this.id = id;this.nickname = nickname;this.email = email;this.group = group;}public void selectCourse(PbCourse course) {System.out.println("学生选课"+course.getCourseName());}public String getId() {return id;}public void setId(String id) {this.id = id;}public String getNickname() {return nickname;}public void setNickname(String nickname) {this.nickname = nickname;}public String getEmail() {return email;}public void setEmail(String email) {this.email = email;}public String getPassword() {return password;}public void setPassword(String password) {this.password = password;}public PbCourse[] getSelections() {return selections;}public void setSelections(PbCourse[] selections) {this.selections = selections;}public String getPic() {return pic;}public void setPic(String pic) {this.pic = pic;}}
测试类:
package com.pbteach.javase.oop.polymorphism.v1;public class PbMain {public static void main(String[] args) {//普通学生
// PbStudent student = new PbStudent("101", "攀博", "pbteach@126.com",1);//Vip学生PbStudent student = new PbStudent("101", "攀博", "pbteach@126.com",2);student.getService();}}
本实现的核心代码如下,使用分支结构的问题是如果再增加学生类型需要修改代码,程序的可维护性差。
//获取服务public void getService() {if(group == 1) {//普通学生System.out.println("攀博课堂自学Java课程");System.out.println("资源下载");System.out.println("在线问答交流");}else if(group == 2) {//vip学生System.out.println("攀博课堂自学Java课程");System.out.println("资源下载");System.out.println("在线问答交流");System.out.println("攀博课堂Vip专属老师指导");System.out.println("攀博课堂Vip专属交流群");}//..有其它类型的学生向后加}
解决方案2
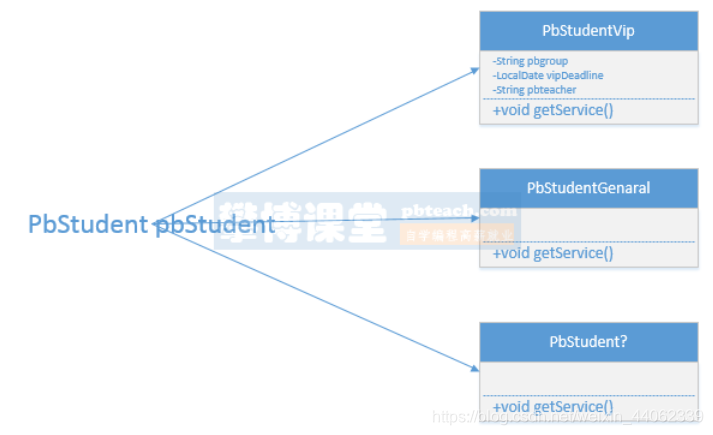
本方案是使用继承关系实现,根据需求描述中的图示,见下图,可以定义一个学生基础类,定义普通学生类和Vip学生类,然后分别在两个子类中增加获取服务内容的方法getService(),如下图:
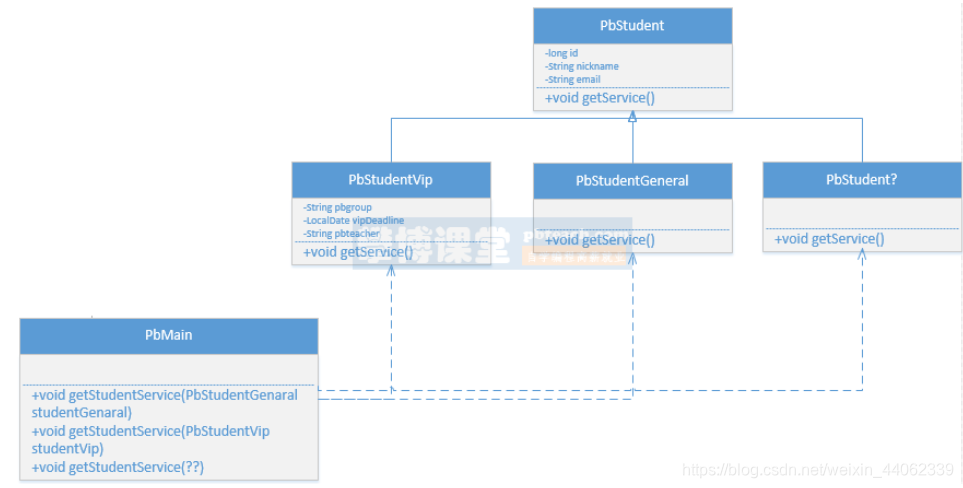
在PbMain类中分别针对不同的学生子类定义重载方法getStudentService()。
代码如下:
课程类:
package com.pbteach.javase.oop.polymorphism.v2;/*** 课程类* @author 攀博课堂(www.pbteach.com)**/
public class PbCourse {//课程标识private long id;//课程名称private String courseName;//课程价格private float price;public PbCourse() {}public PbCourse(long id, String courseName, float price) {this.id = id;this.courseName = courseName;this.price = price;}public long getId() {return id;}public void setId(long id) {this.id = id;}public String getCourseName() {return courseName;}public void setCourseName(String courseName) {this.courseName = courseName;}public float getPrice() {return price;}public void setPrice(float price) {this.price = price;}}
学生基础类:
package com.pbteach.javase.oop.polymorphism.v2;/*** 攀博课堂学生基础类* @author 攀博课堂(www.pbteach.com)**/
public class PbStudent{//用户idprivate String id;//昵称private String nickname;//邮箱private String email;//头像private String pic;//密码private String password;//选课列表private PbCourse[] selections;//获取服务public void getService() {}public PbStudent() {System.out.println("PbStudent="+this);}//提供三个基本数据的构造方法public PbStudent(String id,String nickname,String email) {this.id = id;this.nickname = nickname;this.email = email;}public void selectCourse(PbCourse course) {System.out.println("学生选课"+course.getCourseName());}public String getId() {return id;}public void setId(String id) {this.id = id;}public String getNickname() {return nickname;}public void setNickname(String nickname) {this.nickname = nickname;}public String getEmail() {return email;}public void setEmail(String email) {this.email = email;}public String getPassword() {return password;}public void setPassword(String password) {this.password = password;}public PbCourse[] getSelections() {return selections;}public void setSelections(PbCourse[] selections) {this.selections = selections;}public String getPic() {return pic;}public void setPic(String pic) {this.pic = pic;}}
普通学生类:
package com.pbteach.javase.oop.polymorphism.v2;/*** 攀博课堂普通学生类* @author 攀博课堂(www.pbteach.com)**/
public class PbStudentGeneral extends PbStudent{public PbStudentGenaral(String id,String nickname,String email) {super(id, nickname, email);}//获取服务public void getService() {System.out.println("攀博课堂自学Java课程");System.out.println("资源下载");System.out.println("在线问答交流");}
}
Vip学生类:
package com.pbteach.javase.oop.polymorphism.v2;import java.time.LocalDate;/*** 攀博课堂Vip学生类* @author 攀博课堂(www.pbteach.com)**/
public class PbStudentVip extends PbStudent {// vip服务截止时间private LocalDate vipDeadline;// vip专属指导老师private String pbteacher;// vip专属群private String pbgroup;//获取服务public void getService() {System.out.println("攀博课堂自学Java课程");System.out.println("资源下载");System.out.println("在线问答交流");System.out.println("攀博课堂Vip专属老师指导");System.out.println("攀博课堂Vip专属交流群");}//校验有效性public boolean isValid() {//服务截至时间大于当前时间则账户有效if(vipDeadline.isAfter(LocalDate.now())) {return true;}return false;}//方法重写public void selectCourse(PbCourse course) {//校验vip有效性if(!isValid()) {return ;}//调用父类的选课方法super.selectCourse(course);}//提供四个基本数据类型的构造方法public PbStudentVip(String id,String nickname,String email,LocalDate vipDeadline) {//调用父类的构造方法进行初始化super(id, nickname, email);this.vipDeadline = vipDeadline;}public LocalDate getVipDeadline() {return vipDeadline;}public void setVipDeadline(LocalDate vipDeadline) {this.vipDeadline = vipDeadline;}public String getPbteacher() {return pbteacher;}public void setPbteacher(String pbteacher) {this.pbteacher = pbteacher;}public String getPbgroup() {return pbgroup;}public void setPbgroup(String pbgroup) {this.pbgroup = pbgroup;}}
测试类:
package com.pbteach.javase.oop.polymorphism.v2;import java.time.LocalDate;public class PbMainOld {//获取普通学生服务内容public static void getStudentService(PbStudentGenaral studentGenaral) {studentGenaral.getService();}//获取Vip学生服务内容public static void getStudentService(PbStudentVip studentVip) {studentVip.getService();}public static void main(String[] args) {//创建普通学生类PbStudentGenaral pbStudentGenaral = new PbStudentGenaral("101", "攀博", "pbteach@126.com");//获取学生服务内容PbMain.getStudentService(pbStudentGenaral);//创建vip学生类PbStudentVip pbStudentVip = new PbStudentVip("101", "攀博", "pbteach@126.com", LocalDate.now().plusDays(365));//获取vip学生服务内容PbMain.getStudentService(pbStudentVip);}}
使用继承关系就没有分支结构的繁琐,每种学生类型各自己实现自己的方法,如果增加学生类型只需要增加相应的类即可。
问题依然存在,在PbMain主控类中,针对每个学生类型都需要定义一个getStudentService重载方法,后期如果增加其它学生类型还需要增加相应的getStudentService。
总结多态的现象
解决方案2相比解决方案1更加整洁,没有if分支判断的繁琐,但对代码的可维护性还很差,如果使用多态即可解决,我们更改PbMain中的方法,即可实现我们的目标:
package com.pbteach.javase.oop.polymorphism.v2;import java.time.LocalDate;public class PbMain {//获取学生服务内容public static void getStudentService(PbStudent student) {student.getService();}public static void main(String[] args) {//创建普通学生类PbStudentGenaral pbStudentGenaral = new PbStudentGenaral("101", "攀博", "pbteach@126.com");//获取学生服务内容PbMain.getStudentService(pbStudentGenaral);//创建vip学生类PbStudentVip pbStudentVip = new PbStudentVip("101", "攀博", "pbteach@126.com", LocalDate.now().plusDays(365));//获取vip学生服务内容PbMain.getStudentService(pbStudentVip);}}
上边的代码即使用多态实现了需求,使用统一方法查询学生的服务类型:
//获取学生服务内容
public static void getStudentService(PbStudent student) {student.getService();
}
此方法接收PbStudent的子类型,当传入PbStudentGenaral普通学生对象则查询普通学生对象的服务 内容,当传入PbStudentVip学生对象则查询 Vip学生的服务内容,注意调用的就是同一个student.getService();方法。
多态就是同一方法对不同的子类对象所产生的不同的形态。
多态的原理-向上转型
向上转型
多态是如何实现向一个方法传入不同的类型得到不同的结果?这里是因为出现了叫上转型,即将子类对象地址赋值给父类引用,void getStudentService(PbStudent student)方法接收了不同的子类对象地址。
既然可以可上转型 那么多态的代码可以写成如下的方式:
请尝试找到下边代码的不同点:
原来:
//创建普通学生类
PbStudentGenaral pbStudentGenaral = new PbStudentGenaral("101", "攀博", "pbteach@126.com");
//创建vip学生类
PbStudentVip pbStudentVip = new PbStudentVip("101", "攀博", "pbteach@126.com", LocalDate.now().plusDays(365));更改后:
//创建普通学生类
PbStudent studentGenaral = new PbStudentGenaral("101", "攀博", "pbteach@126.com");
//创建Vip学生类
PbStudent studentVip = new PbStudentVip("101", "攀博", "pbteach@126.com", LocalDate.now().plusDays(365));
更改后的代码验证了向上转型。
向下转型
有向上转型自然有向下转型,如果想调用子类特有的方法必须向下转型,如下:
在PbStudentVip类中isValid()方法是它特有的,如果通过父类调用子类特有的方法是编译不通过的,因为父类没有子类特有的方法。
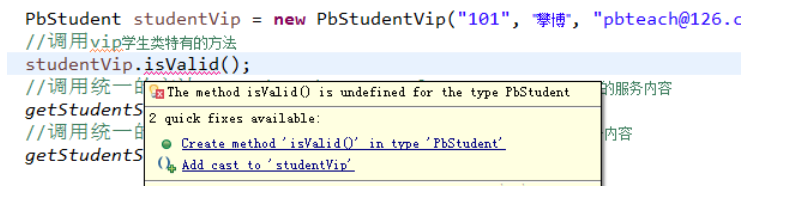
如果要调用子类的方法必须向下转型,即由父类型转为子类型。
PbStudent studentVip = new PbStudentVip("101", "攀博", "pbteach@126.com", LocalDate.now().plusDays(365));//将studentVip转为PbStudentVip类型PbStudentVip pbStudentVip = (PbStudentVip) studentVip;//调用vip学生类特有的方法pbStudentVip.isValid();
(PbStudentVip) studentVip;表示将studentVip的类型转为PbStudentVip类型。
注意:向下转型是非常危险的,要谨慎使用,如果studentVip并不是PbStudentVip类型,但是编译时并不报错,在调用isValid()方法时则报错。所以必须确切知道 studentVip可以转为PbStudentVip类型才可以用向下转型。
instanceof
向下转型可以用instanceof进行判断,如下代码:
PbStudent studentVip = new PbStudentVip("101", "攀博", "pbteach@126.com", LocalDate.now().plusDays(365));if (studentVip instanceof PbStudentVip) {//将studentVip转为PbStudentVip类型PbStudentVip pbStudentVip = (PbStudentVip) studentVip;//调用vip学生类特有的方法pbStudentVip.isValid();}
instanceof 是一个双目运算符,用来判断对象是否为某个类型,studentVip instanceof PbStudentVip表示判断studentVip 指向的对象是否为PbStudentVip, 因为Java允许向上转型,所以父类引用变量可能会指向它的子类对象,所以studentVip instanceof PbStudentVip是编译通过的。
如果instanceof 两端是不兼容的变量和类型则编译不通过,因为PbStudent类型的变量所指向的对象不可能是PbCourse类型的,见下图:
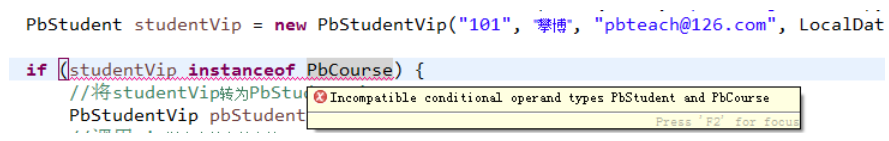
多态的原理-动态绑定
动态绑定
使用向上转型将子类对象地址赋值给父类引用,如下代码:
//创建普通学生类
PbStudent studentGenaral = new PbStudentGenaral("101", "攀博", "pbteach@126.com");
studentGenaral.getService();
//创建Vip学生类
PbStudent studentVip = new PbStudentVip("101", "攀博", "pbteach@126.com", LocalDate.now().plusDays(365));
studentVip.getService();
上边的代码显示不管是构造PbStudentGenaral类型的对象还是PbStudentVip类型的对象,都是调用的父类PbStudent的getService();,却可以产生不同的输出结果。
首先查询父类PbStudent的getService();的方法:
//获取服务
public void getService() {
}
大吃一惊,方法竟然是空的!这是什么原因呢?
其实,在运行时调用的方法并不是父类的这个空方法,而是具体的子类对象的方法,当引用指向的是普通学生类对象则调用普通学生类的方法,当指向的是Vip学生类则调用Vip学生类的方法。
这个过程是在程序运行时根据对象所属类型找到具体的方法进行调用,这叫动态绑定,即程序运行期间根据对象类型进行绑定。
空方法有什么用?
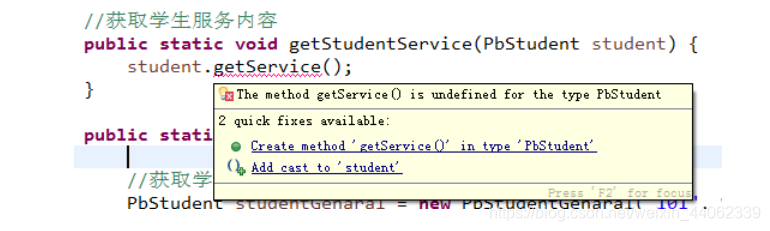
空方法是编译器要求存在的,虽然编译器不知道后期绑定哪个类的方法,但编译器要求必须得有一个父类PbStudent的中方法与代码一致,否则编译不通过。
我们可以尝试屏蔽PbStudent类中的getService() 方法,编译器报错:getService() 在PbStudent中没有定义。
静态绑定
动态 绑定是在运行时才确定的类型,静态绑定则是在编译时就确定类型。
子类无法重写的方法就是静态绑定方法,比如static方法、final方法、private方法。
实现多态过程(总结)
通过向上转型及动态绑定的分析,实现多态的步骤如下:
1、实现继承关系,并在子类实现方法重写。
2、构造子类对象并赋值给父类引用变量。(向上转型)
3、调用父类的的方法,根据父类引用变量指向的对象找到具体子类的方法进行调用。(动态绑定)