文章目录
- 一、Join多种应用
- 1.1 Reduce Join
- 1.2 Map Join
- 二、计数器应用
- 三、数据清洗(ETL)
- 四、MapReduce开发总结
一、Join多种应用
1.1 Reduce Join
Reduce Join工作原理:
Map端的主要工作:为来自不同表(文件)的key/value对打标签以区别不同来源的记录。然后连接字段作为key,其余部分和新加的标志作为value,最后进行输出。
Reduce端的主要工作:在Reduce端以连接字段作为key的分组已经完成,我们只需要在每一个分组当中将那些来源于不同文件的记录(在Map阶段打标志)分开,最后进行合并即可。
案例:
需求: 将商品信息表中数据根据商品pid合并到订单数据表中
order.txt:
| id | pid | amount |
|---|---|---|
| 1001 | 01 | 1 |
| 1002 | 02 | 2 |
| 1003 | 03 | 3 |
| 1004 | 01 | 4 |
pd.txt:
| pid | pname |
|---|---|
| 01 | 小米 |
| 02 | 华为 |
| 03 | 联想 |
期望获得数据:
| id | pname | amount |
|---|---|---|
| 1001 | 小米 | 1 |
| 1004 | 小米 | 4 |
| 1002 | 华为 | 2 |
| 1003 | 格力 | 3 |
代码实现:
OrderBean实体:
public class OrderBean implements WritableComparable<OrderBean> {private String id;private String pid;private int amount;private String pname;public OrderBean() {}@Overridepublic int compareTo(OrderBean o) {int compare = this.pid.compareTo(o.pid);if (compare == 0) {return o.pname.compareTo(this.pname);} else {return compare;}}@Overridepublic void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {out.writeUTF(id);out.writeUTF(pid);out.writeInt(amount);out.writeUTF(pname);}@Overridepublic void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {this.id = in.readUTF();this.pid = in.readUTF();this.amount = in.readInt();this.pname = in.readUTF();}//省略getter、setter、toString方法...
}
Mapper类:
public class OrderMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, OrderBean, NullWritable> {private OrderBean orderBean = new OrderBean();private String fileName;@Overrideprotected void setup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {FileSplit fs = (FileSplit) context.getInputSplit();fileName = fs.getPath().getName();}@Overrideprotected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {String[] fields = value.toString().split("\t");//根据文件名来创建OrderBean对象if ("order.txt".equals(fileName)){orderBean.setId(fields[0]);orderBean.setPid(fields[1]);orderBean.setAmount(Integer.parseInt(fields[2]));orderBean.setPname("");}else {orderBean.setPid(fields[0]);orderBean.setPname(fields[1]);orderBean.setId("");orderBean.setAmount(0);}context.write(orderBean,NullWritable.get());}
}
Reducer类:
public class OrderReducer extends Reducer<OrderBean, NullWritable, OrderBean, NullWritable> {@Overrideprotected void reduce(OrderBean key, Iterable<NullWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {Iterator<NullWritable> vars = values.iterator();//指针下移获取第一个OrderBeanvars.next();String pname = key.getPname();while (vars.hasNext()) {//指针下移,其对应的key也变化了vars.next();key.setPname(pname);context.write(key, NullWritable.get());}}
}
分组Comparator类:
public class OrderComparator extends WritableComparator {public OrderComparator() {super(OrderBean.class, true);}@Overridepublic int compare(WritableComparable a, WritableComparable b) {OrderBean oa = (OrderBean) a;OrderBean ob = (OrderBean) b;return oa.getPid().compareTo(ob.getPid());}
}
驱动Driver类
public class OrderDriver {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {Configuration conf = new Configuration();Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);job.setJarByClass(OrderDriver.class);job.setMapperClass(OrderMapper.class);job.setReducerClass(OrderReducer.class);job.setMapOutputKeyClass(OrderBean.class);job.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);job.setOutputKeyClass(OrderBean.class);job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);//设置分组Comparatorjob.setGroupingComparatorClass(OrderComparator.class);FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("D:\\MyFile\\test"));//指定_SUCCESS文件的位置FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("d:\\output"));boolean result = job.waitForCompletion(true);System.exit(result ? 0 : 1);}
}
缺点:
Reduce Join合并的操作是在Reduce阶段完成的,Reduce端的处理压力太大,Map节点的运算负载则很低,资源利用率不高,且在Reduce阶段极易产生数据倾斜。
解决方案: 使用Map Join
1.2 Map Join
使用场景:
Map Join适用于一张表非常小、另一表非常大的场景。
在Map端缓存多张表,提前处理业务逻辑,这样增加Map端业务,减少Reduce端数据压力,尽可能的减少数据倾斜。
实现方式:
DistributedCacheDriver缓存小文件- 在
Map的setUp()方法中读取缓存文件
代码:
Mapper类:
public class OrderMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, OrderBean, NullWritable> {private OrderBean orderBean = new OrderBean();private Map<String, String> pMap = new HashMap<>();@Overrideprotected void setup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {URI[] cacheFiles = context.getCacheFiles();String path = cacheFiles[0].getPath();/*** 使用FSDataInputStream会中文乱码*/
// FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(context.getConfiguration());
// FSDataInputStream fis = fs.open(new Path(path));BufferedReader fis = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(path), "UTF-8"));String line;while (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(line = fis.readLine())) {String[] fields = line.split("\t");pMap.put(fields[0], fields[1]);}IOUtils.closeStream(fis);}@Overrideprotected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {String[] fields = value.toString().split("\t");String pname = pMap.get(fields[1]);pname = pname == null ? "" : pname;orderBean.setId(fields[0]);orderBean.setPid(fields[1]);orderBean.setAmount(Integer.parseInt(fields[2]));orderBean.setPname(pname);context.write(orderBean, NullWritable.get());}
}
驱动Driver:
public class OrderDriver {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException, URISyntaxException {Configuration conf = new Configuration();Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);job.setJarByClass(OrderDriver.class);job.setMapperClass(OrderMapper.class);FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("D:\\MyFile\\test"));//指定_SUCCESS文件的位置FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("d:\\output"));//加载缓存数据job.addCacheFile(new URI("file:///d:/MyFile/cache/pd.txt"));//Map端Join的逻辑不需要Reduce阶段,设置ReduceTask数量为0job.setNumReduceTasks(0);boolean result = job.waitForCompletion(true);System.exit(result ? 0 : 1);}
}
二、计数器应用
Hadoop为每个作业维护若干内置计数器,以描述多项指标。例如,某些计数器记录已处理的字节数和记录数,使用户监控已处理的输入数据量和已产生的输出数据量。
- 采用枚举的方式统计计数
enum MyCounter{MALFORORMED,NORMAL}
//对枚举定义的自定义计数器加1
context.getCounter(MyCounter.MALFORORMED).increment(1);
- 采用计数组、计数器名称的方式统计
context.getCounter("counterGroup","counter").increment(1);
- 计数结果在程序运行后的控制台上查看
三、数据清洗(ETL)
在运行核心业务MapReduce程序之前,往往要先对数据进行清洗,清理掉不符合用户要求的数据。清理的过程往往只需要运行Mapper程序,不需要运行Reduce程序。
需求: 去除日志中字段长度小于等于11的日志
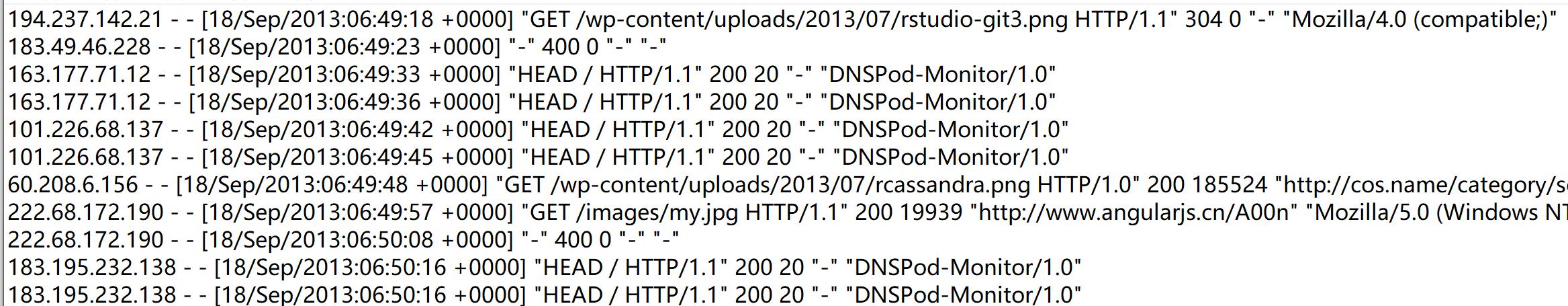
Mappper类:
public class LogMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, NullWritable>{Text k = new Text();@Overrideprotected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {// 1 获取1行数据String line = value.toString();// 2 解析日志boolean result = parseLog(line,context);// 3 日志不合法退出if (!result) {return;}// 4 设置keyk.set(line);// 5 写出数据context.write(k, NullWritable.get());}// 2 解析日志private boolean parseLog(String line, Context context) {// 1 截取String[] fields = line.split(" ");// 2 日志长度大于11的为合法if (fields.length > 11) {// 系统计数器context.getCounter("map", "true").increment(1);return true;}else {context.getCounter("map", "false").increment(1);return false;}}
}
驱动Driver:
public class LogDriver {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {// 1 获取job信息Configuration conf = new Configuration();Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);// 2 加载jar包job.setJarByClass(LogDriver.class);// 3 关联mapjob.setMapperClass(LogMapper.class);// 4 设置最终输出类型job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);// 设置reducetask个数为0job.setNumReduceTasks(0);// 5 设置输入和输出路径FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0]));FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));// 6 提交job.waitForCompletion(true);}
}
计数效果:
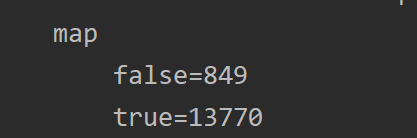
四、MapReduce开发总结
在编写MapReduce程序时,需要考虑的几个方面:
①输入数据接口:InputFormat
- 默认使用的实现类是:
TextInputFormat TextInputFormat的功能逻辑是:一次读一行文本,然后将该行的起始偏移量作为key,行内容作为value返回KeyValueTextInputFormat每一行均为一条记录,被分隔符分割为key,value。默认分隔符是tab (\t)。NlineInputFormat按照指定的行数N来划分切片。CombineTextInputFormat可以把多个小文件合并成一个切片处理,提高处理效率- 用户还可以自定义
InputFormat
②逻辑处理接口:Mapper
用户根据业务需求实现其中三个方法:map()、 setup()、 cleanup ()
③Partitioner分区
有默认实现HashPartitioner,逻辑是根据key的哈希值和numReduces来返回一个分区号;key.hashCode()&Integer.MAXVALUE % numReduces
如果业务上有特别的需求,可以自定义分区。
④Comparable排序
当我们用自定义的对象作为key来输出时,就必须要实现WritableComparable接口,重写其中的compareTo()方法
部分排序:对最终输出的没一个文件进行内部排序
全排序:对所有数据进行排序,通常只有一个Reduce
二次排序:排序的条件有两个
辅助排序:可以让不同的key进入到同一个ReduceTask
⑤Combiner合并
Combiner合并可以提高程序执行效率,减少IO传输。但是使用时必须不能影响原有的业务处理结果。
⑥Reduce端分组:Groupingcomparator
在Reduce端对key进行分组。应用于:在接收的Key为Bean对象时,想让一个或几个字段相同(全部字段比较不相同)的Key进入到同一个Reduce方法时,可以采用分组排序。
⑦逻辑处理接口:Reducer
用户根据业务需求实现其中三个方法: reduce()、 setup()、 cleanup()
⑧输出数据接口:OutputFormat
默认实现类是TextOutputFormat,功能逻辑是:将每一个KV对向目标文本文件中输出为一行。
用户还可以自定义OutputFormat。


![大数据利器:Hadoop的十大应用场景[转]](http://image20.it168.com/201207_500x375/1132/6d0b82a1c25be404.jpg)