目录
版本对应的坑
关键技术点
源码解析
将jar包引入到spring boot中
@EnableAutoConfiguration原理
JasyptSpringBootAutoConfiguration
一是其@Import的StringEncryptorConfiguration.class
二是其对spring环境中包含的PropertySource对象的处理
一是AbstractApplicationContext的refresh方法
二是BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的作用
EnableEncryptablePropertySourcesPostProcessor
具体的解密过程
补充1:查看JDK提供的Cipher算法
补充2:PBE的基础算法demo,
参考:
首先介绍一下jasypt的使用方法
可以参考下面这篇文章:
Get史上最优雅的加密方式!没有之一!
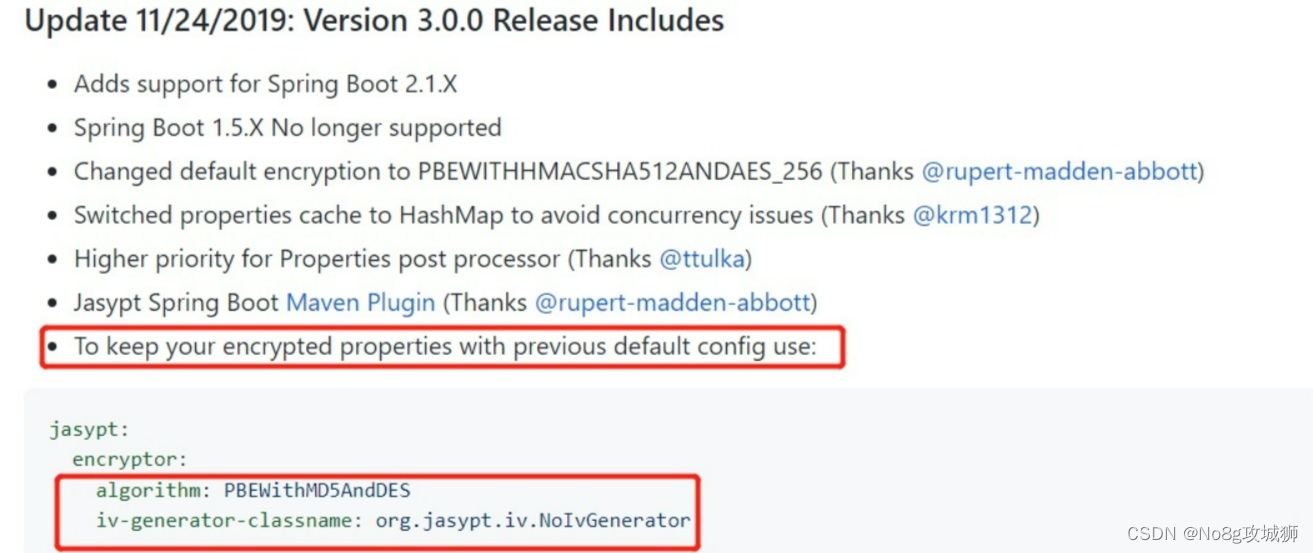
版本对应的坑
使用的时候还是遇到一个坑,就是jasypt的版本与spring boot版本存在对应情况。可以看到jasypt是区分java7和java8的,也存在依赖spring版本的情况。
自己尝试了一下
在使用jasypt-spring-boot-starter的前提下
| jasypt版本 | springboot版本 |
| 2.1.0 | 2.1.0 |
| 1.5 | 1.4.2 |
| 1.5 | 1.5.3 |
| 1.8 | 1.4.2 |
所以如果引入maven之后启动系统报错,那么可以根据版本对应情况这个角度进行排查。
关键技术点
下面说一下jasypt的两个关键的技术实现点
一是如何实现对spring环境中包含的PropertySource对象实现加密感知的
二是其默认的PBEWITHMD5ANDDES算法是如何工作的,并澄清一下在使用jasypt的时候最常遇到的一个疑问:既然你的password也配置在properties文件中,那么我拿到了加密的密文和password,不是可以直接解密吗?
源码解析
总结来说:其通过BeanFactoryPostProcessor#postProcessBeanFactory方法,获取所有的propertySource对象,将所有propertySource都会重新包装成新的EncryptablePropertySourceWrapper
解密的时候,也是使用EncryptablePropertySourceWrapper#getProperty方法,如果通过 prefixes/suffixes 包裹的属性,那么返回解密后的值;如果没有被包裹,那么返回原生的值。从源头开始走起:
将jar包引入到spring boot中
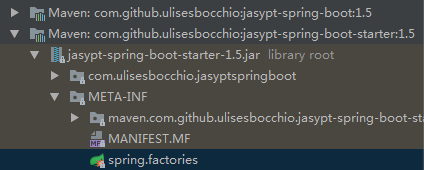
spring.factories
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=com.ulisesbocchio.jasyptspringboot.JasyptSpringBootAutoConfiguration这里补充一下spring boot @EnableAutoConfiguration的原理。
@EnableAutoConfiguration原理
@EnableAutoConfiguration注解@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
这个配置类实现了ImportSelector接口,重写其selectImports方法
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata,attributes);
getCandidateConfigurations方法,会从classpath中搜索所有META-INF/spring.factories配置文件,然后,将其中org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration key对应的配置项加载到spring容器中。这样就实现了在spring boot中加载外部项目的bean或者第三方jar中的bean。
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata,AnnotationAttributes attributes) {List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), getBeanClassLoader());Assert.notEmpty(configurations,"No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you "+ "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");return configurations;
}
其内部实现的关键点有:
1. ImportSelector 该接口的方法的返回值都会被纳入到spring容器的管理中
2. SpringFactoriesLoader 该类可以从classpath中搜索所有META-INF/spring.factories配置文件,读取配置
@EnableAutoConfiguration注解中有spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration=true就开启,默认为true,可以在application.properties中设置此开关项
exclude()方法是根据类排除,excludeName是根据类名排除
在spring-boot-autoconfigure jar中,META-INF中有一个spring.factories文件,其中配置了spring-boot所有的自动配置参数,如GsonAutoConfiguration,配合@ConditionalOnClass(Gson.class),可以实现如果Gson bean存在,就启动自动注入,否则就不启用此注入的灵活配置
好了,有了上面的基础知识,我们就关心JasyptSpringBootAutoConfiguration
JasyptSpringBootAutoConfiguration
其@Import EnableEncryptablePropertySourcesConfiguration
关注两个地方
一是其@Import的StringEncryptorConfiguration.class
如果没有自定义的EncryptorBean,即jasyptStringEncryptor bean,那么就注册默认的jasyptStringEncryptor bean
@Conditional(OnMissingEncryptorBean.class)
@Bean(name = ENCRYPTOR_BEAN_PLACEHOLDER)
public StringEncryptor stringEncryptor(Environment environment) {String encryptorBeanName = environment.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(ENCRYPTOR_BEAN_PLACEHOLDER);LOG.info("String Encryptor custom Bean not found with name '{}'. Initializing String Encryptor based on properties with name '{}'",encryptorBeanName, encryptorBeanName);return new LazyStringEncryptor(() -> {PooledPBEStringEncryptor encryptor = new PooledPBEStringEncryptor();SimpleStringPBEConfig config = new SimpleStringPBEConfig();config.setPassword(getRequiredProperty(environment, "jasypt.encryptor.password"));config.setAlgorithm(getProperty(environment, "jasypt.encryptor.algorithm", "PBEWithMD5AndDES"));config.setKeyObtentionIterations(getProperty(environment, "jasypt.encryptor.keyObtentionIterations", "1000"));config.setPoolSize(getProperty(environment, "jasypt.encryptor.poolSize", "1"));config.setProviderName(getProperty(environment, "jasypt.encryptor.providerName", "SunJCE"));config.setSaltGeneratorClassName(getProperty(environment, "jasypt.encryptor.saltGeneratorClassname", "org.jasypt.salt.RandomSaltGenerator"));config.setStringOutputType(getProperty(environment, "jasypt.encryptor.stringOutputType", "base64"));encryptor.setConfig(config);return encryptor;});
}
StringEncryptor接口提供了加密和解密的方法
我们可以自定义StringEncryptor,如
@Configuration
public class JasyptConfig {@Bean(name = "jasypt.encryptor.bean:jasyptStringEncryptor")public StringEncryptor stringEncryptor() {PooledPBEStringEncryptor encryptor = new PooledPBEStringEncryptor();SimpleStringPBEConfig config = new SimpleStringPBEConfig();config.setPassword("password");config.setAlgorithm("PBEWithMD5AndDES");config.setKeyObtentionIterations("1000");config.setPoolSize("1");config.setProviderName("SunJCE");config.setSaltGeneratorClassName("org.jasypt.salt.RandomSaltGenerator");config.setStringOutputType("base64");encryptor.setConfig(config);return encryptor;}
}
二是其对spring环境中包含的PropertySource对象的处理
@Configuration
@Import(StringEncryptorConfiguration.class)
public class EnableEncryptablePropertySourcesConfiguration implements EnvironmentAware {private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(EnableEncryptablePropertySourcesConfiguration.class);private ConfigurableEnvironment environment;@Beanpublic EnableEncryptablePropertySourcesPostProcessor enableEncryptablePropertySourcesPostProcessor() {boolean proxyPropertySources = environment.getProperty("jasypt.encryptor.proxyPropertySources", Boolean.TYPE, false);InterceptionMode interceptionMode = proxyPropertySources ? InterceptionMode.PROXY : InterceptionMode.WRAPPER;return new EnableEncryptablePropertySourcesPostProcessor(environment, interceptionMode);}@Overridepublic void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {this.environment = (ConfigurableEnvironment) environment;}
}
其提供了两种模式来创建 分别为proxy和wrapper 默认情况下interceptionMode为wrapper
下面就是关键了,new了一个EnableEncryptablePropertySourcesPostProcessor
其implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor
这里又需要两个背景知识
一是AbstractApplicationContext的refresh方法
是启动spring容器的关键方法
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
来注册我们下面的postProcessors
二是BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的作用
BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口提供了postProcessBeanFactory方法,在容器初始化之后执行一次
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors,获取的手动注册的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
/*** Invoke the given BeanFactoryPostProcessor beans.*/
private static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(Collection<? extends BeanFactoryPostProcessor> postProcessors, ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {postProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);}
}
可以看到postProcessors有4个
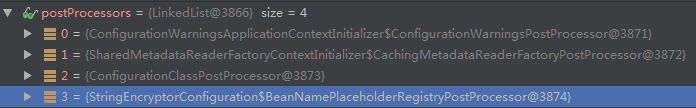
接下来看关键的EnableEncryptablePropertySourcesPostProcessor
EnableEncryptablePropertySourcesPostProcessor
public class EnableEncryptablePropertySourcesPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor, ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent>, Ordered {其实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor以及Ordered接口
其中getOrder方法 让这个jasypt定义的BeanFactoryPostProcessor的初始化顺序最低,即最后初始化
我们知道spring中排序分为两种PriorityOrdered 和Ordered接口,一般来说就是PriorityOrdered 优于Ordered 其次都是按照order大小来的排序
我们就知道了接下来就执行EnableEncryptablePropertySourcesPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory方法,
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {LOG.info("Post-processing PropertySource instances");MutablePropertySources propSources = environment.getPropertySources();StreamSupport.stream(propSources.spliterator(), false).filter(ps -> !(ps instanceof EncryptablePropertySource)).map(s -> makeEncryptable(s, beanFactory)).collect(toList()).forEach(ps -> propSources.replace(ps.getName(), ps));
}
接下来,获取所有的propertySource对象

然后用stream方式遍历,如果是通过jasypt加密的,那么来执行方法makeEncryptable,使得propertySource对象具备加密解密的能力
private <T> PropertySource<T> makeEncryptable(PropertySource<T> propertySource, ConfigurableListableBeanFactory registry) {StringEncryptor encryptor = registry.getBean(environment.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(ENCRYPTOR_BEAN_PLACEHOLDER), StringEncryptor.class);PropertySource<T> encryptablePropertySource = interceptionMode == InterceptionMode.PROXY? proxyPropertySource(propertySource, encryptor) : instantiatePropertySource(propertySource, encryptor);LOG.info("Converting PropertySource {} [{}] to {}", propertySource.getName(), propertySource.getClass().getName(),AopUtils.isAopProxy(encryptablePropertySource) ? "AOP Proxy" : encryptablePropertySource.getClass().getSimpleName());return encryptablePropertySource;
}
首先获取StringEncrypt Bean,然后执行instantiatePropertySource方法。
private <T> PropertySource<T> instantiatePropertySource(PropertySource<T> propertySource, StringEncryptor encryptor) {PropertySource<T> encryptablePropertySource;if (propertySource instanceof MapPropertySource) {encryptablePropertySource = (PropertySource<T>) new EncryptableMapPropertySourceWrapper((MapPropertySource) propertySource, encryptor);} else if (propertySource.getClass().getName().equals("org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigFileApplicationListener$ConfigurationPropertySources")) {//Some Spring Boot code actually casts property sources to this specific type so must be proxied.encryptablePropertySource = proxyPropertySource(propertySource, encryptor);} else if (propertySource instanceof EnumerablePropertySource) {encryptablePropertySource = new EncryptableEnumerablePropertySourceWrapper<>((EnumerablePropertySource) propertySource, encryptor);} else {encryptablePropertySource = new EncryptablePropertySourceWrapper<>(propertySource, encryptor);}return encryptablePropertySource;
}
可以看到将所有propertySource都会重新包装成新的EncryptablePropertySourceWrapper
log日志:将上面的6个对象包装一下

最后的application.properties中的配置项结果

完整的转换完成后的EncryptablePropertySourceWrapper

到这里就注册postProcessor完成了,而且每个PropertySource warpped,具备了加密解密的能力,然后继续回到AbstractApplicationContext的流程
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
具体的解密过程
当spring boot项目启动的时候,需要用到属性值的时候,就是将原本spring中的propertySource的getProperty()方法委托给其自定义的实现EncryptablePropertySourceWrapper,调用其getProperty()方法,在这个方法的自定义实现中。判断是否是已经加密的value,如果是,则进行解密。如果不是,那就返回原值。
调用EncryptablePropertySourceWrapper的getProperty方法,其extends PropertySource,override了getProperty方法
public class EncryptablePropertySourceWrapper<T> extends PropertySource<T> implements EncryptablePropertySource<T> {private final PropertySource<T> delegate;private final StringEncryptor encryptor;public EncryptablePropertySourceWrapper(PropertySource<T> delegate, StringEncryptor encryptor) {super(delegate.getName(), delegate.getSource());Assert.notNull(delegate, "PropertySource delegate cannot be null");Assert.notNull(encryptor, "StringEncryptor cannot be null");this.delegate = delegate;this.encryptor = encryptor;}@Overridepublic Object getProperty(String name) {return getProperty(encryptor, delegate, name);}
}
其getProperty就去调用其implements的EncryptablePropertySource的getProperty方法,于是执行下面
public interface EncryptablePropertySource<T> {public default Object getProperty(StringEncryptor encryptor, PropertySource<T> source, String name) {Object value = source.getProperty(name);if(value instanceof String) {String stringValue = String.valueOf(value);if(PropertyValueEncryptionUtils.isEncryptedValue(stringValue)) {value = PropertyValueEncryptionUtils.decrypt(stringValue, encryptor);}}return value;}
}
isEncryptedValue方法
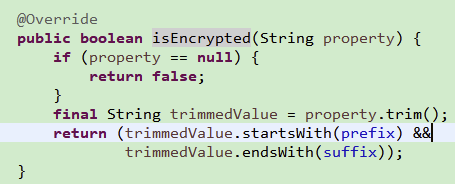
private static final String ENCRYPTED_VALUE_PREFIX = "ENC(";
private static final String ENCRYPTED_VALUE_SUFFIX = ")";public static boolean isEncryptedValue(final String value) {if (value == null) {return false;}final String trimmedValue = value.trim();return (trimmedValue.startsWith(ENCRYPTED_VALUE_PREFIX) && trimmedValue.endsWith(ENCRYPTED_VALUE_SUFFIX));
}
如果通过 prefixes/suffixes 包裹的属性,那么返回解密后的值;
如果没有被包裹,那么返回原生的值;
如果是加密的值,那么就去解密
StandardPBEByteEncryptor
public byte[] decrypt(final byte[] encryptedMessage) throws EncryptionOperationNotPossibleException {if (encryptedMessage == null) {return null;}// Check initializationif (!isInitialized()) {initialize();}if (this.saltGenerator.includePlainSaltInEncryptionResults()) {// Check that the received message is bigger than the saltif (encryptedMessage.length <= this.saltSizeBytes) {throw new EncryptionOperationNotPossibleException();}}try {// If we are using a salt generator which specifies the salt// to be included into the encrypted message itself, get it from // there. If not, the salt is supposed to be fixed and thus the// salt generator can be safely asked for it again.byte[] salt = null; byte[] encryptedMessageKernel = null; if (this.saltGenerator.includePlainSaltInEncryptionResults()) {final int saltStart = 0;final int saltSize = (this.saltSizeBytes < encryptedMessage.length? this.saltSizeBytes : encryptedMessage.length);final int encMesKernelStart =(this.saltSizeBytes < encryptedMessage.length? this.saltSizeBytes : encryptedMessage.length);final int encMesKernelSize = (this.saltSizeBytes < encryptedMessage.length? (encryptedMessage.length - this.saltSizeBytes) : 0);salt = new byte[saltSize];encryptedMessageKernel = new byte[encMesKernelSize];System.arraycopy(encryptedMessage, saltStart, salt, 0, saltSize);System.arraycopy(encryptedMessage, encMesKernelStart, encryptedMessageKernel, 0, encMesKernelSize);} else if (!this.usingFixedSalt){salt = this.saltGenerator.generateSalt(this.saltSizeBytes);encryptedMessageKernel = encryptedMessage;} else {// this.usingFixedSalt == truesalt = this.fixedSaltInUse;encryptedMessageKernel = encryptedMessage;}final byte[] decryptedMessage;if (this.usingFixedSalt) {/** Fixed salt is being used, therefore no initialization supposedly needed*/synchronized (this.decryptCipher) {decryptedMessage = this.decryptCipher.doFinal(encryptedMessageKernel);}} else {/** Perform decryption using the Cipher*/final PBEParameterSpec parameterSpec = new PBEParameterSpec(salt, this.keyObtentionIterations);synchronized (this.decryptCipher) {this.decryptCipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, this.key, parameterSpec);decryptedMessage = this.decryptCipher.doFinal(encryptedMessageKernel);}}// Return the resultsreturn decryptedMessage;} catch (final InvalidKeyException e) {// The problem could be not having the unlimited strength policies// installed, so better give a usefull error message.handleInvalidKeyException(e);throw new EncryptionOperationNotPossibleException();} catch (final Exception e) {// If decryption fails, it is more secure not to return any // information about the cause in nested exceptions. Simply fail.throw new EncryptionOperationNotPossibleException();}}
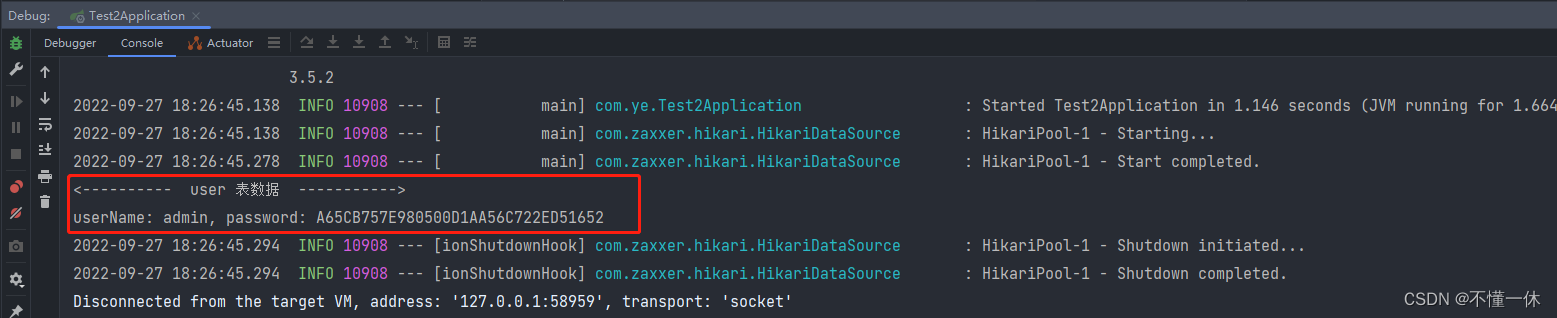
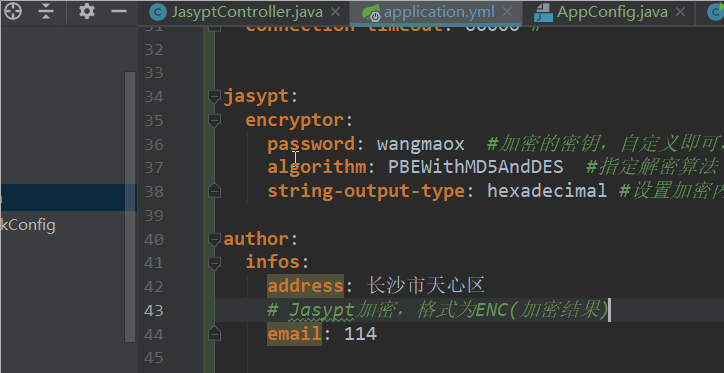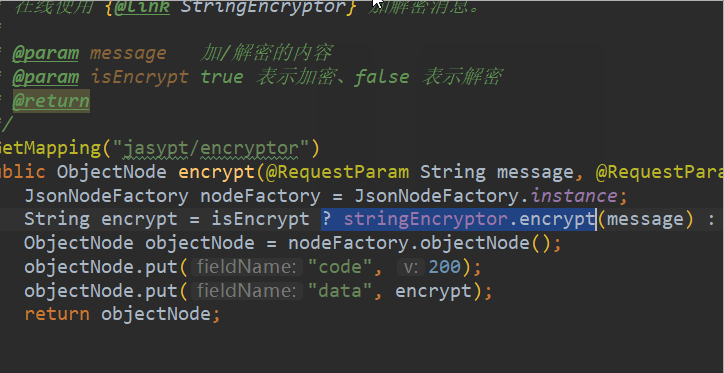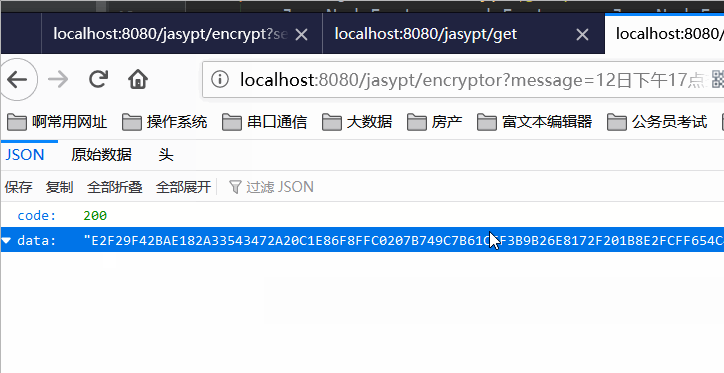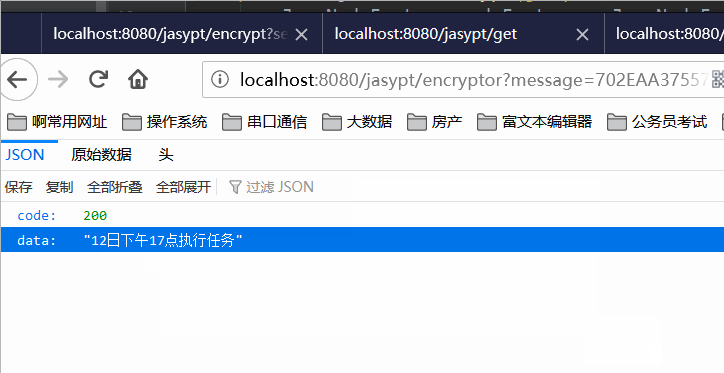
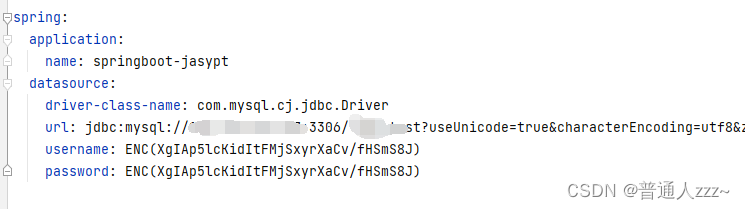
以spring.datasource.username为例:
明文是root
密文是ENC(X4OZ4csEAWqPCEvWf+aRPA==)
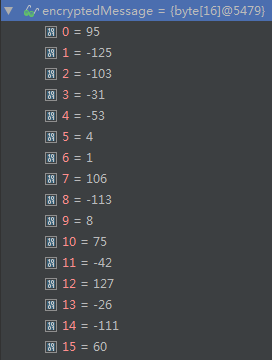
可以看到其salt是encryptedMessage的
System.arraycopy(encryptedMessage, saltStart, salt, 0, saltSize);
System.arraycopy(encryptedMessage, encMesKernelStart, encryptedMessageKernel, 0, encMesKernelSize);
0-7byte解析为salt,8-15byte解析为密文
然后就通过基本的PBE解析方式,来解析出来
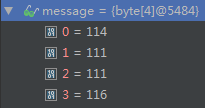
ASCII码对应的结果就是root
PBE解析原理图:
加密过程:每一次随机产生新的salt,所以每一次加密后生成的密文是不同的

解密过程:

所以我们就可以知道,如果我获得了jasypt的password,那么由于其salt是放在encryptedMessage中的,那么我是没什么压力就可以解密的。
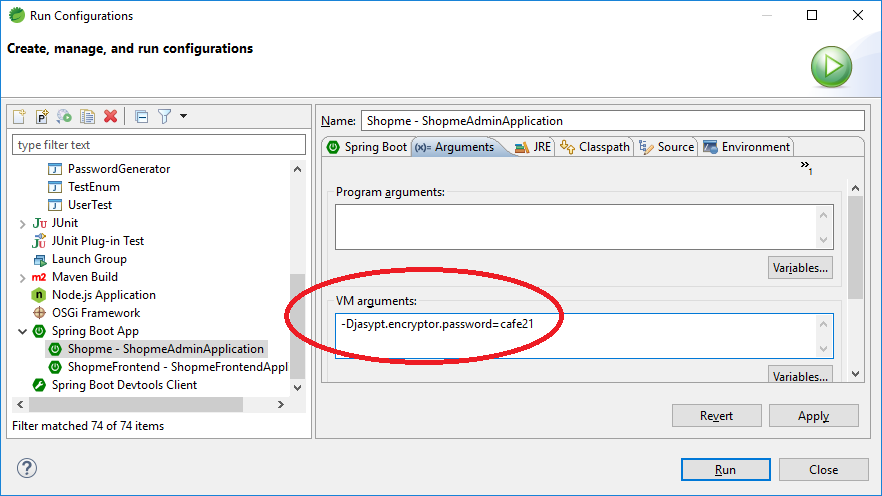
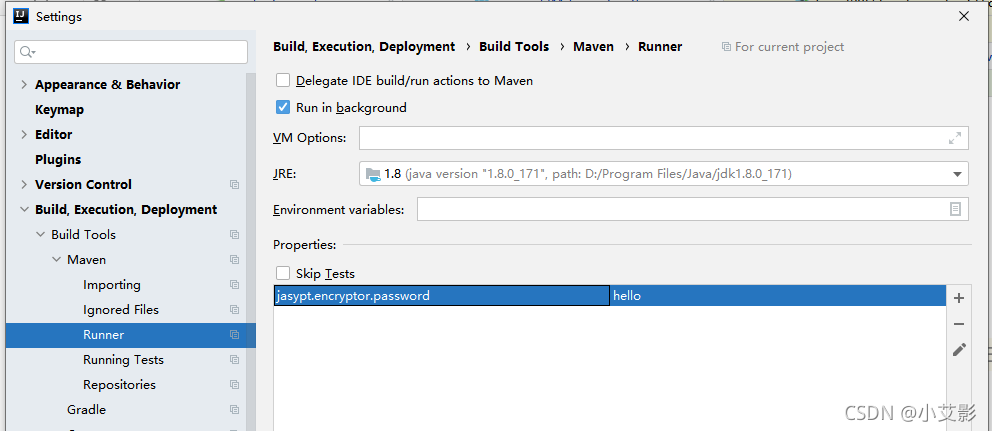
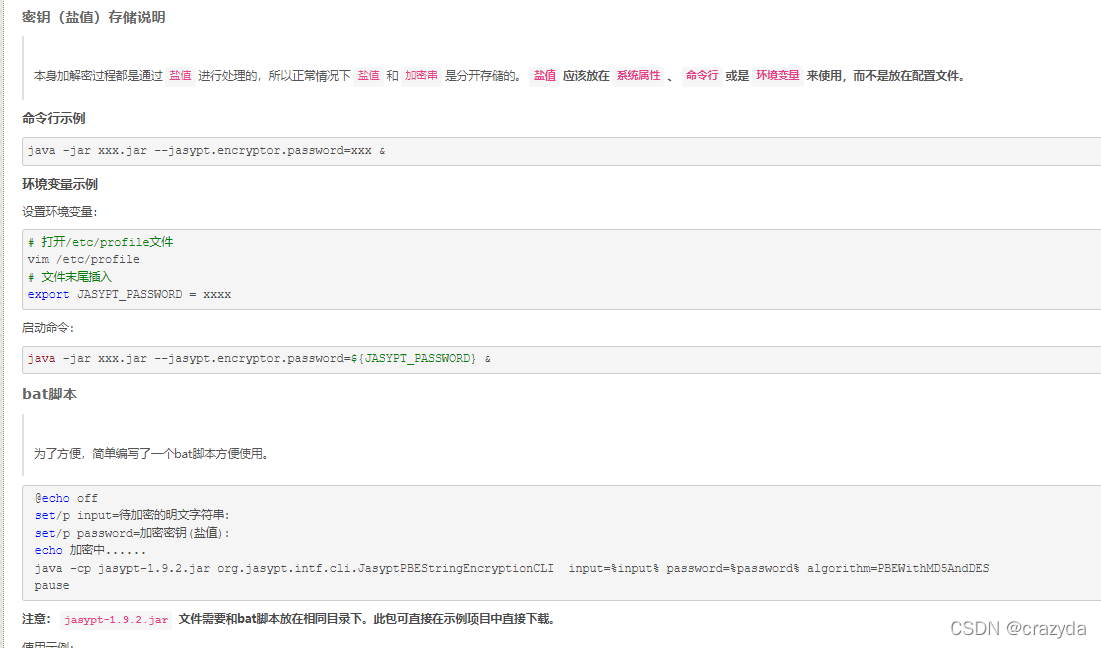
所以应该java -jar –Djasypt.encryptor.password=xxx abc.jar方式来启动服务。这样只要在运维端不泄露password,那么只拿到配置文件的密文,还是安全的。
补充1:查看JDK提供的Cipher算法
jasypt默认使用的是PBEWITHMD5ANDDES,其实JDK中由SunJCE所提供的。
可以通过下面的代码来查看JDK中提供了哪些Cipher算法
@Testpublic void listJdkAlgorithm() {
/* Provider[] providers = Security.getProviders();for (Provider provider :providers) {LOGGER.info("security provider: {} , version: {}", provider.getName(), provider.getVersion());LOGGER.info("security provider info: {}", provider.getInfo());}*/Set<String> messageDigest = Security.getAlgorithms("Cipher");for (String s :messageDigest) {LOGGER.info("MessageDigest: {}",s);}}
更全面的安全方面的算法,如摘要算法、签名算法等,参考:
Standard Algorithm Name Documentation
补充2:PBE的基础算法demo,
而且可以看出来,jasypt中使用了几乎相同的代码来进行加解密的
public class PBECipher {static final String CIPHER_NAME = "PBEwithMD5AndDES";public static byte[] encrypt(String password, byte[] salt, byte[] input) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, InvalidKeySpecException, NoSuchPaddingException, InvalidAlgorithmParameterException, InvalidKeyException, BadPaddingException, IllegalBlockSizeException {PBEKeySpec keySpec = new PBEKeySpec(password.toCharArray());SecretKeyFactory secretKeyFactory = SecretKeyFactory.getInstance(CIPHER_NAME);// 这个secretKey 就是我们将来要使用的加密的密钥SecretKey secretKey = secretKeyFactory.generateSecret(keySpec);// 传入1000,表示用户输入的口令,会与这个salt进行1000次的循环PBEParameterSpec pbeParameterSpec = new PBEParameterSpec(salt, 1000);Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(CIPHER_NAME);cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secretKey, pbeParameterSpec);return cipher.doFinal(input);}public static byte[] decrypt(String password, byte[] salt, byte[] input) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException,InvalidKeySpecException, NoSuchPaddingException, InvalidAlgorithmParameterException, InvalidKeyException, BadPaddingException, IllegalBlockSizeException {PBEKeySpec keySpec = new PBEKeySpec(password.toCharArray());SecretKeyFactory secretKeyFactory = SecretKeyFactory.getInstance(CIPHER_NAME);SecretKey secretKey = secretKeyFactory.generateSecret(keySpec);PBEParameterSpec pbeParameterSpec = new PBEParameterSpec(salt, 1000);Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(CIPHER_NAME);cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secretKey, pbeParameterSpec);return cipher.doFinal(input);}
}
测试
@Test
public void testPBE() throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, UnsupportedEncodingException, NoSuchPaddingException,InvalidKeyException, IllegalBlockSizeException, BadPaddingException, InvalidAlgorithmParameterException, InvalidKeySpecException {String message = "constfafa";String password = "ydbs";byte[] salt = SecureRandom.getInstanceStrong().generateSeed(8);System.out.printf("salt: %032x\n", new BigInteger(1, salt));//加密和解密的salt是一样的byte[] data = message.getBytes("UTF-8");byte[] encrypt = PBECipher.encrypt(password, salt, data);LOGGER.info("encrypted data: {}", Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(encrypt));byte[] decrypt = PBECipher.decrypt(password, salt, encrypt);LOGGER.info("decrypted data: {}", new String(decrypt,"UTF-8"));
}
参考:
Jasypt之源码解析
官方github
8.Java 加解密技术系列之 PBE - crazyYong - 博客园







![Java byte[] 转 String的简单转换](https://upload-images.jianshu.io/upload_images/7208373-b6b96e0acc5cf05f.png)

