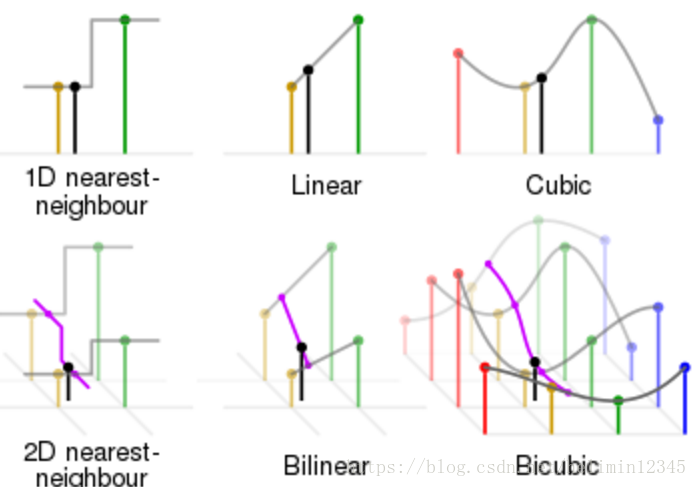
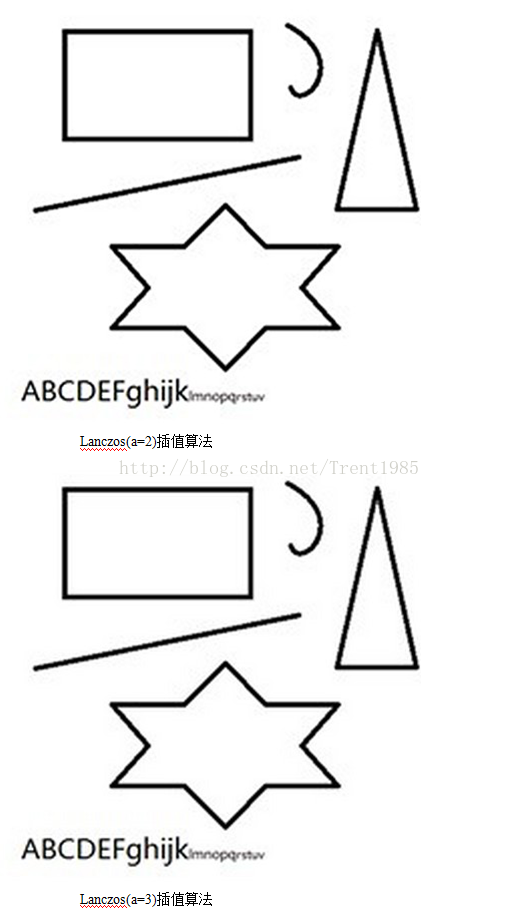
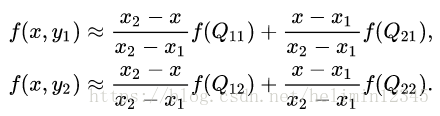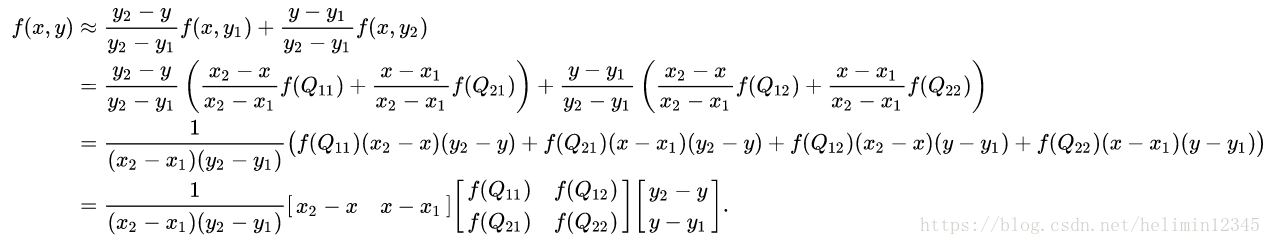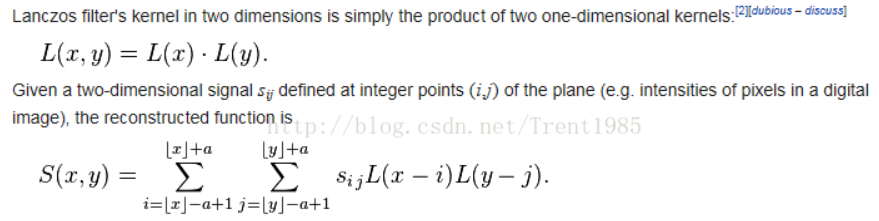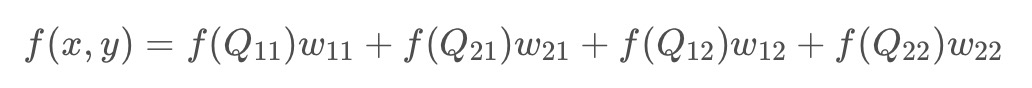sensor、codec、display device都是基于pixel的,高分辨率图像能呈现更多的detail,由于sensor制造和chip的限制,我们需要用到图像插值(scaler/resize)技术,这种方法代价小,使用方便。同时,该技术还可以放大用户希望看到的感兴趣区域。图像缩放算法往往基于插值实现,常见的图像插值算法包括最近邻插值(Nearest-neighbor)、双线性插值(Bilinear)、双立方插值(bicubic)、lanczos插值、方向插值(Edge-directed interpolation)、example-based插值、深度学习等算法。
插值缩放的原理是基于目标分辨率中的点,将其按照缩放关系对应到源图像中,寻找源图像中的点(不一定是整像素点),然后通过源图像中的相关点插值得到目标点。本篇文章,我们介绍Nearest-neighbor和Bilinear插值的原理及C实现。
插值算法原理如下:
1. Nearest-neighbor
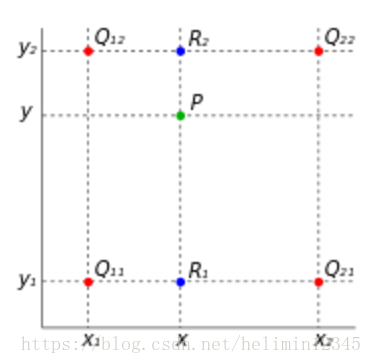
最近邻插值,是指将目标图像中的点,对应到源图像中后,找到最相邻的整数点,作为插值后的输出。如下图所示,P为目标图像对应到源图像中的点,Q11、Q12、Q21、Q22是P点周围4个整数点,Q12与P离的最近,因此P点的值等于Q12的值。
由于图像中像素具有邻域相关性,因此,用这种拷贝的方法会产生明显的锯齿。
2. Bilinear
双线性插值使用周围4个点插值得到输出,双线性插值,是指在xy方法上,都是基于线性距离来插值的。
如图1,目标图像中的一点对应到源图像中点P(x,y),我们先在x方向插值:
然后,进行y方向插值:
可以验证,先进行y方向插值再进行x方向插值,结果也是一样的。值得一提的是,双线性插值在单个方向上是线性的,但对整幅图像来说是非线性的。
3. C实现
使用VS2010,工程包含三个文件,如下:
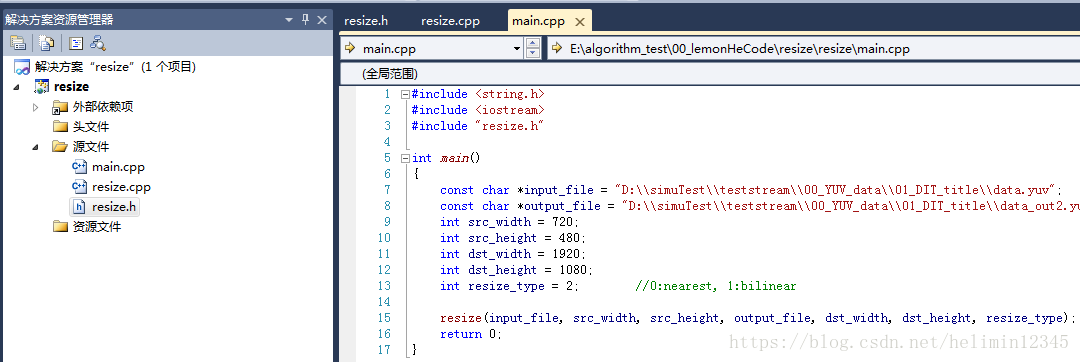
main.cpp
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
#include "resize.h"int main()
{const char *input_file = "D:\\simuTest\\teststream\\00_YUV_data\\01_DIT_title\\data.yuv"; //absolute pathconst char *output_file = "D:\\simuTest\\teststream\\00_YUV_data\\01_DIT_title\\data_out2.yuv"; //absolute path int src_width = 720;int src_height = 480;int dst_width = 1920;int dst_height = 1080;int resize_type = 1; //0:nearest, 1:bilinearresize(input_file, src_width, src_height, output_file, dst_width, dst_height, resize_type);return 0;
}
resize.cpp
#include "resize.h"int clip3(int data, int min, int max)
{return (data > max) ? max : ((data < min) ? min : data);if(data > max)return max;else if(data > min)return data;elsereturn min;
}//bilinear takes 4 pixels (2×2) into account
/*
* 函数名: bilinearHorScaler
* 说明: 水平方向双线性插值
* 参数:
*/
void bilinearHorScaler(int *src_image, int *dst_image, int src_width, int src_height, int dst_width, int dst_height)
{double resizeX = (double)dst_width / src_width;for(int ver = 0; ver < dst_height; ++ver){for(int hor = 0; hor < dst_width; ++hor){double srcCoorX = hor / resizeX;double weight1 = srcCoorX - (double)((int)srcCoorX);double weight2 = (double)((int)(srcCoorX + 1)) - srcCoorX;double dstValue = *(src_image + src_width * ver + clip3((int)srcCoorX, 0, src_width - 1)) * weight2 + *(src_image + src_width * ver + clip3((int)(srcCoorX + 1), 0, src_width - 1)) * weight1;*(dst_image + dst_width * ver + hor) = clip3((uint8)dstValue, 0, 255);}}
}/*
* 函数名: bilinearVerScaler
* 说明: 垂直方向双线性插值
* 参数:
*/
void bilinearVerScaler(int *src_image, int *dst_image, int src_width, int src_height, int dst_width, int dst_height)
{double resizeY = (double)dst_height / src_height;for(int ver = 0; ver < dst_height; ++ver){for(int hor = 0; hor < dst_width; ++hor){double srcCoorY = ver / resizeY;double weight1 = srcCoorY - (double)((int)srcCoorY);double weight2 = (double)((int)(srcCoorY + 1)) - srcCoorY;double dstValue = *(src_image + src_width * clip3((int)srcCoorY, 0, src_height - 1) + hor) * weight2 + *(src_image + src_width * clip3((int)(srcCoorY + 1), 0, src_height - 1) + hor) * weight1;*(dst_image + dst_width * ver + hor) = clip3((uint8)dstValue, 0, 255);}}
}/*
* 函数名: yuv420p_NearestScaler
* 说明: 最近邻插值
* 参数:
*/
void nearestScaler(int *src_image, int *dst_image, int src_width, int src_height, int dst_width, int dst_height)
{double resizeX = (double)dst_width /src_width; //水平缩放系数double resizeY = (double)dst_height / src_height; //垂直缩放系数int srcX = 0;int srcY = 0;for(int ver = 0; ver < dst_height; ++ver) {for(int hor = 0; hor < dst_width; ++hor) {srcX = clip3(int(hor/resizeX + 0.5), 0, src_width - 1);srcY = clip3(int(ver/resizeY + 0.5), 0, src_height - 1);*(dst_image + dst_width * ver + hor) = *(src_image + src_width * srcY + srcX);}}
}void resize(const char *input_file, int src_width, int src_height, const char *output_file, int dst_width, int dst_height, int resize_type)
{//define and init src bufferint *src_y = new int[src_width * src_height];int *src_cb = new int[src_width * src_height / 4];int *src_cr = new int[src_width * src_height / 4];memset(src_y, 0, sizeof(int) * src_width * src_height);memset(src_cb, 0, sizeof(int) * src_width * src_height / 4);memset(src_cr, 0, sizeof(int) * src_width * src_height / 4);//define and init dst bufferint *dst_y = new int[dst_width * dst_height];int *dst_cb = new int[dst_width * dst_height / 4];int *dst_cr = new int[dst_width * dst_height / 4];memset(dst_y, 0, sizeof(int) * dst_width * dst_height);memset(dst_cb, 0, sizeof(int) * dst_width * dst_height / 4);memset(dst_cr, 0, sizeof(int) * dst_width * dst_height / 4);//define and init mid bufferint *mid_y = new int[dst_width * src_height];int *mid_cb = new int[dst_width * src_height / 4];int *mid_cr = new int[dst_width * src_height / 4];memset(mid_y, 0, sizeof(int) * dst_width * src_height);memset(mid_cb, 0, sizeof(int) * dst_width * src_height / 4);memset(mid_cr, 0, sizeof(int) * dst_width * src_height / 4);uint8 *data_in_8bit = new uint8[src_width * src_height * 3 / 2];memset(data_in_8bit, 0, sizeof(uint8) * src_width * src_height * 3 / 2);uint8 *data_out_8bit = new uint8[dst_width * dst_height * 3 / 2];memset(data_out_8bit, 0, sizeof(uint8) * dst_width * dst_height * 3 / 2);FILE *fp_in = fopen(input_file,"rb");if(NULL == fp_in){//exit(0);printf("open file failure");}FILE *fp_out = fopen(output_file, "wb+");//data readfread(data_in_8bit, sizeof(uint8), src_width * src_height * 3 / 2, fp_in);//Y componentfor(int ver = 0; ver < src_height; ver++){for(int hor =0; hor < src_width; hor++){src_y[ver * src_width + hor] = data_in_8bit[ver * src_width + hor];}}//c component YUV420Pfor(int ver = 0; ver < src_height / 2; ver++){for(int hor =0; hor < src_width / 2; hor++){src_cb[ver * (src_width / 2) + hor] = data_in_8bit[src_height * src_width + ver * src_width / 2 + hor];src_cr[ver * (src_width / 2) + hor] = data_in_8bit[src_height * src_width + src_height * src_width / 4 + ver * src_width / 2 + hor];}}//resizeif(0 == resize_type){nearestScaler(src_y, dst_y, src_width, src_height, dst_width, dst_height);nearestScaler(src_cb, dst_cb, src_width / 2, src_height / 2, dst_width / 2, dst_height / 2);nearestScaler(src_cr, dst_cr, src_width / 2, src_height / 2, dst_width / 2, dst_height / 2);}else if(1 == resize_type){bilinearHorScaler(src_y, mid_y, src_width, src_height, dst_width, src_height);bilinearHorScaler(src_cb, mid_cb, src_width / 2, src_height / 2, dst_width / 2, src_height / 2);bilinearHorScaler(src_cr, mid_cr, src_width / 2, src_height / 2, dst_width / 2, src_height / 2);bilinearVerScaler(mid_y, dst_y, dst_width, src_height, dst_width, dst_height);bilinearVerScaler(mid_cb, dst_cb, dst_width / 2, src_height / 2, dst_width / 2, dst_height / 2);bilinearVerScaler(mid_cr, dst_cr, dst_width / 2, src_height / 2, dst_width / 2, dst_height / 2);} else{nearestScaler(src_y, dst_y, src_width, src_height, dst_width, dst_height);nearestScaler(src_cb, dst_cb, src_width / 2, src_height / 2, dst_width / 2, dst_height / 2);nearestScaler(src_cr, dst_cr, src_width / 2, src_height / 2, dst_width / 2, dst_height / 2);}//data writefor(int ver = 0; ver < dst_height; ver++){for(int hor =0; hor < dst_width; hor++){data_out_8bit[ver * dst_width + hor] = clip3(dst_y[ver * dst_width + hor], 0, 255);}}for(int ver = 0; ver < dst_height / 2; ver++){for(int hor = 0; hor < dst_width / 2; hor++){data_out_8bit[dst_height * dst_width + ver * dst_width / 2 + hor] = clip3(dst_cb[ver * (dst_width / 2) + hor], 0, 255);data_out_8bit[dst_height * dst_width + dst_height * dst_width / 4 + ver * dst_width / 2 + hor] = clip3(dst_cr[ver * (dst_width / 2) + hor], 0, 255);}}fwrite(data_out_8bit, sizeof(uint8), dst_width * dst_height * 3 / 2, fp_out);delete [] src_y;delete [] src_cb;delete [] src_cr;delete [] dst_y;delete [] dst_cb;delete [] dst_cr;delete [] mid_y;delete [] mid_cb;delete [] mid_cr;delete [] data_in_8bit;delete [] data_out_8bit;fclose(fp_in);fclose(fp_out);}
resize.h
#ifndef RESIZE_H
#define RESIZE_H#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>typedef unsigned char uint8;
typedef unsigned short uint16;int clip3(int data, int min, int max);
void bilinearHorScaler(int *src_image, int *dst_image, int src_width, int src_height, int dst_width, int dst_height);
void bilinearVerScaler(int *src_image, int *dst_image, int src_width, int src_height, int dst_width, int dst_height);
void nearestScaler(int *src_image, int *dst_image, int src_width, int src_height, int dst_width, int dst_height);
void resize(const char *input_file, int src_width, int src_height, const char *output_file, int dst_width, int dst_height, int resize_type);#endif
效果比较
将720x480分辨率图像放大到1080p,1:1截取局部画面如下,左边是最近邻放大的效果,右边是双线性效果,可以看到,双线性放大的锯齿要明显比最近邻小。
Matlab
常用的matlab缩放方法有两种,如下
- B = imresize(A, scale, method) B = imresize(A, 0.5, ‘bicubic’)使用双立方插值将宽高各缩小1/2
- B = imresize(A, outputSize, method) B = imresize(A, [1080,1920], ‘bilinear’)使用双线性插值缩放到1920x1080分辨率
Opencv
常用的opencv中resize调用方法也有两种
- dsize=0,指定fx和fy,此时目标图像大小会自动计算出,dsize=Size(round(fxsrc.cols),round(fysrc,rows))
resize(src, dst, Size(0, 0), 0.5, 0.5, 2); //缩小为原来的1/2,使用双立方插值(2)
- fx和fy为0,指定dsize
resize(src, dst, Size(1024,1024), 0, 0, 1); //缩放到1024x1024分辨率,使用双线性插值(1)
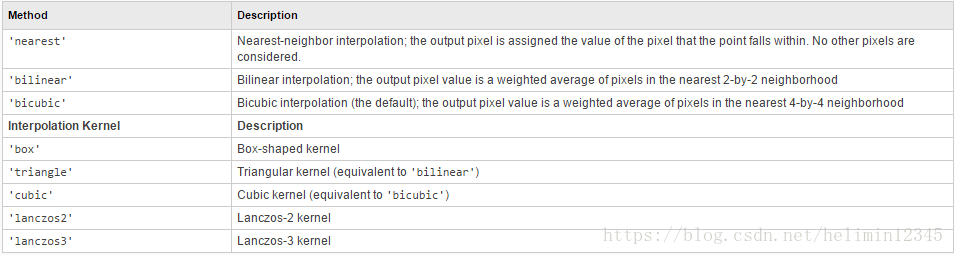
Opencv提供5种插值方法有5种:最近邻、双线性、双立方、面积关联、兰佐斯。
Resize函数声名及插值方式玫举定义:
CV_EXPORTS_W void resize( InputArray src, OutputArray dst,Size dsize, double fx=0, double fy=0,int interpolation=INTER_LINEAR );enum
{INTER_NEAREST=CV_INTER_NN, //!< nearest neighbor interpolationINTER_LINEAR=CV_INTER_LINEAR, //!< bilinear interpolationINTER_CUBIC=CV_INTER_CUBIC, //!< bicubic interpolationINTER_AREA=CV_INTER_AREA, //!< area-based (or super) interpolationINTER_LANCZOS4=CV_INTER_LANCZOS4, //!< Lanczos interpolation over 8x8 neighborhoodINTER_MAX=7,WARP_INVERSE_MAP=CV_WARP_INVERSE_MAP
};enum
{CV_INTER_NN =0,CV_INTER_LINEAR =1,CV_INTER_CUBIC =2,CV_INTER_AREA =3,CV_INTER_LANCZOS4 =4
};
参考
[1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nearest-neighbor_interpolation
[2] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bilinear_interpolation