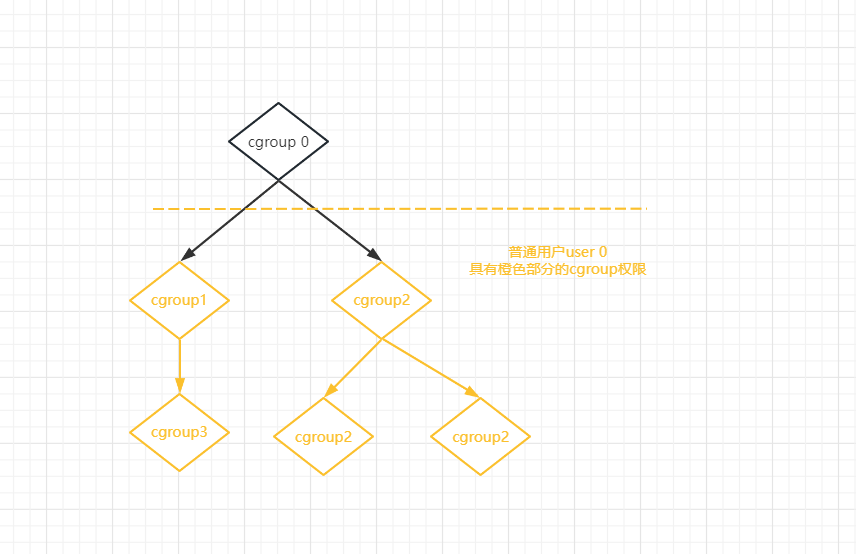
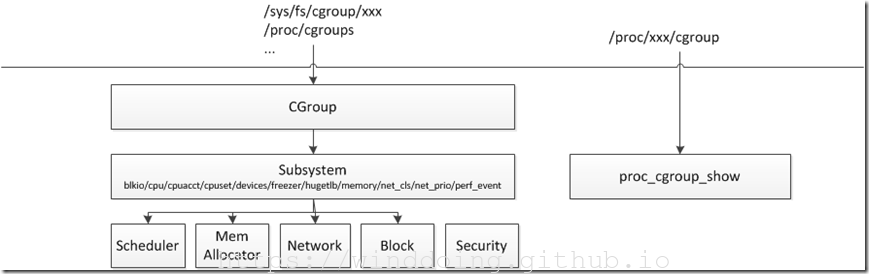
CGoup核心主要创建一系列sysfs文件,用户空间可以通过这些节点控制CGroup各子系统行为,以及各子系统模块根据参数。在执行过程中或调度进程到不同CPU上,或控制CPU占用时间,或控制IO带宽等等。另外,在每个系统的proc文件系统中都有一个cgroup,显示该进程对应的CGroup各子系统信息。
内核配置1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12Symbol: CGROUPS [=y]
Type : boolean
Prompt: Control Group support
Location:
-> General setup
Symbol: CGROUP_SCHED [=y]
Type : boolean
Prompt: Group CPU scheduler
Location:
-> General setup
-> Control Group support (CGROUPS [=y])
通过CONFIG_CGROUPS配置cgroup框架的实现,CONFIG_CGROUP_SCHED控制CPU子系统。
基本应用1
2
3#mount -t cgroup -o cpu cgroup /mnt/
#mkdir tst_cgroup
#rmdir tst_cgroup
在文件系统中cgroup的挂载目录,也就是cgroup虚拟文件系统的根目录用数据结构struct cgroupfs_root表示.而cgroup用struct cgroup表示.
数据结构
主要用于对进程不同资源的管理和配置,以及进程和cgroup之间的关系。
task_struct1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10struct task_struct {
...
#ifdef CONFIG_CGROUPS
/* Control Group info protected by css_set_lock */
struct css_set __rcu *cgroups;
/* cg_list protected by css_set_lock and tsk->alloc_lock */
struct list_head cg_list;
#endif
...
};
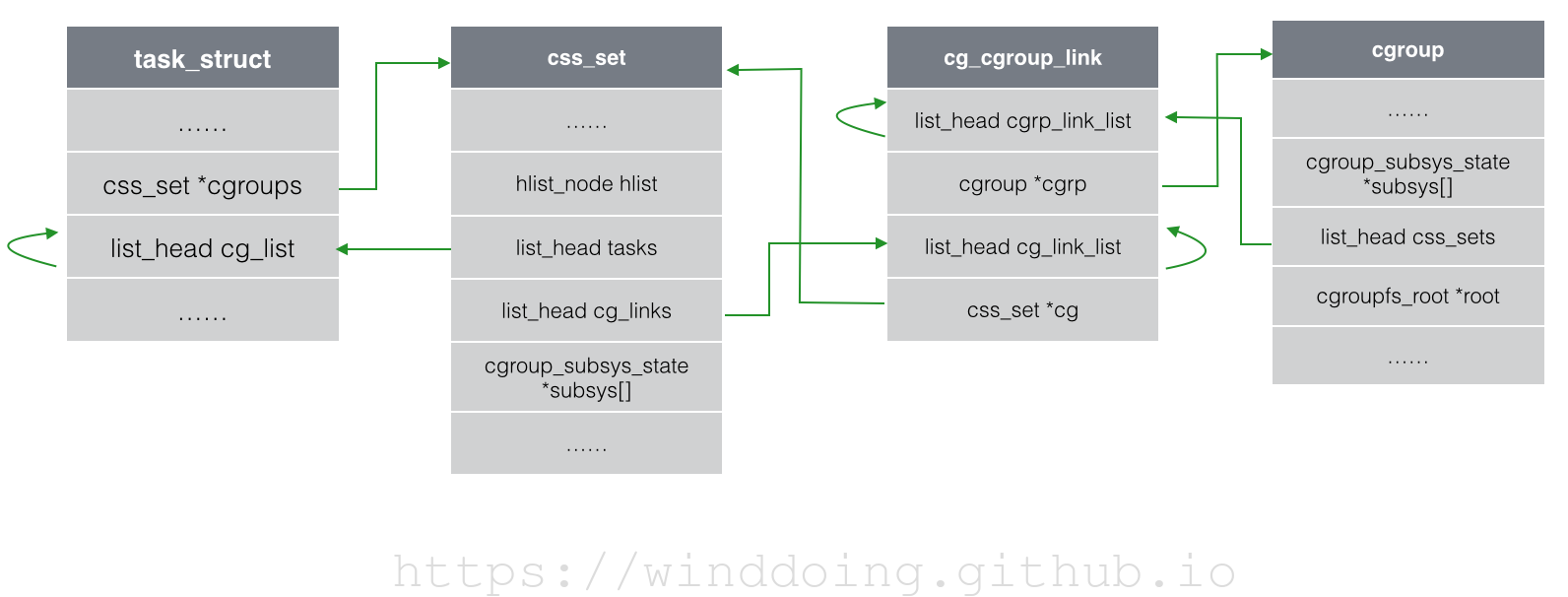
struct task_struct中并没有一个直接的成员指向cgroup,而是指向了struct css_set的结构, css_set存储路与进程相关的cgroup信息。
cg_list: 是一个链表结构,用于将连到同一个css_set的进程组织成一个链表。
css_set1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48/*
* A css_set is a structure holding pointers to a set of
* cgroup_subsys_state objects. This saves space in the task struct
* object and speeds up fork()/exit(), since a single inc/dec and a
* list_add()/del() can bump the reference count on the entire cgroup
* set for a task.
*/
struct css_set {
/* Reference count */
atomic_t refcount; //引用计数,因为一个css_set可以被多个进程共用,这些进程的cgroup信息相同
/*
* List running through all cgroup groups in the same hash
* slot. Protected by css_set_lock
*/
struct hlist_node hlist;
/*
* List running through all tasks using this cgroup
* group. Protected by css_set_lock
*/
struct list_head tasks;
/*
* List of cg_cgroup_link objects on link chains from
* cgroups referenced from this css_set. Protected by
* css_set_lock
*/
//由cg_cgroup_link组成的链表,链表上每一项cg_cgroup_link都指向和css_set关联的cgroup.
struct list_head cg_links;
/*
* Set of subsystem states, one for each subsystem. This array
* is immutable after creation apart from the init_css_set
* during subsystem registration (at boot time) and modular subsystem
* loading/unloading.
*/
/*
*css_set关联的css.每一个subsystem对应数组中相应id的项。
*subsys应当包括所有子系统的css.如果此css_set没有制定某个subsystem的css或者subsystem没有mount,则默认初始化为根css.
*/
struct cgroup_subsys_state *subsys[CGROUP_SUBSYS_COUNT]; //是进程与一个特定子系统相关的信息
/* For RCU-protected deletion */
struct rcu_head rcu_head;
};file: include/linux/cgroup.h
主要用来描述一个个子系统,通过cgroup_subsys_state定义不同子系统的相关控制信息,hlist将同一个子系统下的所有css_set组织成一个hash表,方便内核查找特定的css_set.
tasks指向所有连到此css_set的进程连成的链表。
那从struct css_set怎么转换到cgroup呢? 再来看一个辅助的数据结构struct cg_cgroup_link
cgroup_subsys_state1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24/* Per-subsystem/per-cgroup state maintained by the system. */
struct cgroup_subsys_state {
/*
* The cgroup that this subsystem is attached to. Useful
* for subsystems that want to know about the cgroup
* hierarchy structure
*/
struct cgroup *cgroup;
/*
* State maintained by the cgroup system to allow subsystems
* to be "busy". Should be accessed via css_get(),
* css_tryget() and css_put().
*/
atomic_t refcnt;
unsigned long flags;
/* ID for this css, if possible */
struct css_id __rcu *id;
/* Used to put @cgroup->dentry on the last css_put() */
struct work_struct dput_work;
};file: include/linux/cgroup.h
cgroup指针指向了一个cgroup结构,也就是进程属于的cgroup.
进程受到子系统的控制,实际上是通过加入到特定的cgroup实现的,因为cgroup在特定的层级上,而子系统又是附加到曾经上的 。通过以上三个结构,进程就可以和cgroup关联起来了 :task_struct->css_set->cgroup_subsys_state->cgroup。
cgroup1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75struct cgroup {
unsigned long flags;/* "unsigned long" so bitops work */
/*
* count users of this cgroup. >0 means busy, but doesn't
* necessarily indicate the number of tasks in the cgroup
*/
atomic_t count;
int id;/* ida allocated in-hierarchy ID */
/*
* We link our 'sibling' struct into our parent's 'children'.
* Our children link their 'sibling' into our 'children'.
*/
struct list_head sibling;/* my parent's children */
struct list_head children;/* my children */
struct list_head files;/* my files */
struct cgroup *parent;/* my parent */
struct dentry *dentry;/* cgroup fs entry, RCU protected */
/*
* This is a copy of dentry->d_name, and it's needed because
* we can't use dentry->d_name in cgroup_path().
*
* You must acquire rcu_read_lock() to access cgrp->name, and
* the only place that can change it is rename(), which is
* protected by parent dir's i_mutex.
*
* Normally you should use cgroup_name() wrapper rather than
* access it directly.
*/
struct cgroup_name __rcu *name;
/* Private pointers for each registered subsystem */
//此cgroup关联subsystem的css结构,每个subsystem的css在数组中对应subsys[subsystem->subsys_id].
struct cgroup_subsys_state *subsys[CGROUP_SUBSYS_COUNT];
struct cgroupfs_root *root;
/*
* List of cg_cgroup_links pointing at css_sets with
* tasks in this cgroup. Protected by css_set_lock
*/
struct list_head css_sets; //通过cs_cgroup_link指向此cgroup关联的css_set
struct list_head allcg_node;/* cgroupfs_root->allcg_list */
struct list_head cft_q_node;/* used during cftype add/rm */
/*
* Linked list running through all cgroups that can
* potentially be reaped by the release agent. Protected by
* release_list_lock
*/
struct list_head release_list;
/*
* list of pidlists, up to two for each namespace (one for procs, one
* for tasks); created on demand.
*/
struct list_head pidlists;
struct mutex pidlist_mutex;
/* For RCU-protected deletion */
struct rcu_head rcu_head;
struct work_struct free_work;
/* List of events which userspace want to receive */
struct list_head event_list;
spinlock_t event_list_lock;
/* directory xattrs */
struct simple_xattrs xattrs;
};sibling,children和parent三个list_head负责将同一层级的cgroup连接成一颗cgroup树。
subsys是一个指针数组,存储一组指向cgroup_subsys_state的指针。这组指针指向了此cgroup跟各个子系统相关的信息
root指向了一个cgroupfs_root的结构,就是cgroup所在的层级对应的结构体
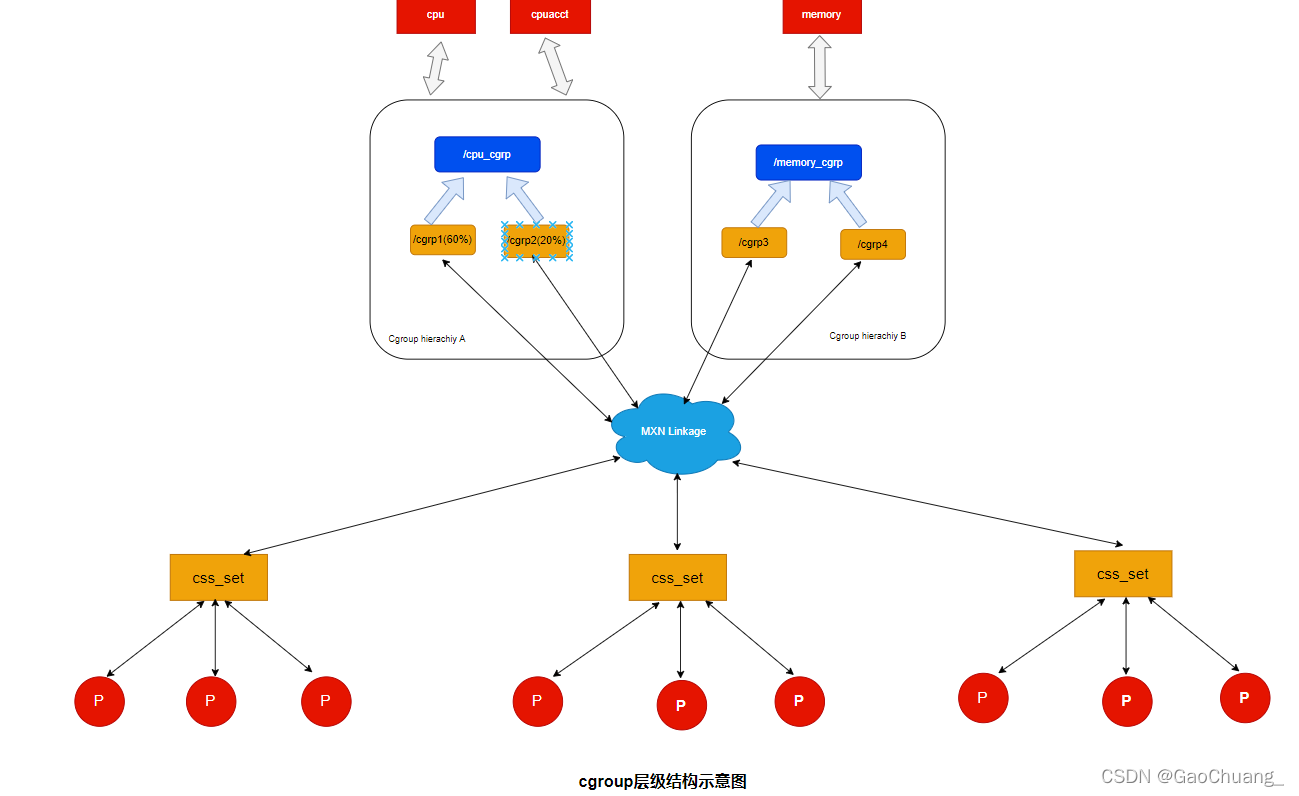
cgroup和css_set是多对多的关系,既:一个css_set可以对应多个cgroup,同时一个cgroup也可以被多个css_set所包含。
这种多对多的映射关系,是通过cg_cgroup_link这个中间结构来关联的。
cg_cgroup_link1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15/* Link structure for associating css_set objects with cgroups */
struct cg_cgroup_link {
/*
* List running through cg_cgroup_links associated with a
* cgroup, anchored on cgroup->css_sets
*/
struct list_head cgrp_link_list;
struct cgroup *cgrp;
/*
* List running through cg_cgroup_links pointing at a
* single css_set object, anchored on css_set->cg_links
*/
struct list_head cg_link_list;
struct css_set *cg;
};
一个cg_cgroup_link需要包含两类信息,即关联的cgroup和css_set信息,一个cg_cgroup_link可以让一个cgroup和一个css_set相关联。但是正如我们前面所说,css_set和cgroup是多对多的对应关系,所以,一个css_set需要保存多个cg_cgroup_link,一个cgroup也需要保存多个cg_cgroup_link信息。具体来说,css_set中的cg_links维护了一个链表,链表中的元素为cg_cgroup_link中的cg_link_list.cgroup中的css_set也维护了一个cg_cgroup_link链表,链表中元素为cgrp_link_list.
cgrp_link_list连入到cgroup->css_set指向的链表,cgrp则指向此cg_cgroup_link相关的cgroup。
cg_link_list则连入到css_set->cg_links指向的链表,cg则指向此cg_cgroup_link相关的css_set。
cgroupfs_root1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47/*
* A cgroupfs_root represents the root of a cgroup hierarchy, and may be
* associated with a superblock to form an active hierarchy. This is
* internal to cgroup core. Don't access directly from controllers.
*/
struct cgroupfs_root {
struct super_block *sb; //cgroup文件系统的超级块
/*
* The bitmask of subsystems intended to be attached to this
* hierarchy
*/
unsigned long subsys_mask; //hierarchy相关联的subsys 位图
/* Unique id for this hierarchy. */
int hierarchy_id;
/* The bitmask of subsystems currently attached to this hierarchy */
unsigned long actual_subsys_mask;
/* A list running through the attached subsystems */
struct list_head subsys_list; //hierarchy中的subsys链表
/* The root cgroup for this hierarchy */
struct cgroup top_cgroup;
/* Tracks how many cgroups are currently defined in hierarchy.*/
int number_of_cgroups;
/* A list running through the active hierarchies */
struct list_head root_list;
/* All cgroups on this root, cgroup_mutex protected */
struct list_head allcg_list;
/* Hierarchy-specific flags */
unsigned long flags;
/* IDs for cgroups in this hierarchy */
struct ida cgroup_ida;
/* The path to use for release notifications. */
char release_agent_path[PATH_MAX];
/* The name for this hierarchy - may be empty */
char name[MAX_CGROUP_ROOT_NAMELEN];
};
top_cgroup指向了所在层级的根cgroup,也就是创建层级时自动创建的那个cgroup。
cgroup_subsys1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68/*
* Control Group subsystem type.
* See Documentation/cgroups/cgroups.txt for details
*/
struct cgroup_subsys {
struct cgroup_subsys_state *(*css_alloc)(struct cgroup *cgrp);
int (*css_online)(struct cgroup *cgrp);
void (*css_offline)(struct cgroup *cgrp);
void (*css_free)(struct cgroup *cgrp);
int (*allow_attach)(struct cgroup *cgrp, struct cgroup_taskset *tset);
int (*can_attach)(struct cgroup *cgrp, struct cgroup_taskset *tset);
void (*cancel_attach)(struct cgroup *cgrp, struct cgroup_taskset *tset);
void (*attach)(struct cgroup *cgrp, struct cgroup_taskset *tset);
void (*fork)(struct task_struct *task);
void (*exit)(struct cgroup *cgrp, struct cgroup *old_cgrp,
struct task_struct *task);
void (*bind)(struct cgroup *root);
int subsys_id;
int disabled;
int early_init;
/*
* True if this subsys uses ID. ID is not available before cgroup_init()
* (not available in early_init time.)
*/
bool use_id;
/*
* If %false, this subsystem is properly hierarchical -
* configuration, resource accounting and restriction on a parent
* cgroup cover those of its children. If %true, hierarchy support
* is broken in some ways - some subsystems ignore hierarchy
* completely while others are only implemented half-way.
*
* It's now disallowed to create nested cgroups if the subsystem is
* broken and cgroup core will emit a warning message on such
* cases. Eventually, all subsystems will be made properly
* hierarchical and this will go away.
*/
bool broken_hierarchy;
bool warned_broken_hierarchy;
#define MAX_CGROUP_TYPE_NAMELEN 32
const char *name;
/*
* Link to parent, and list entry in parent's children.
* Protected by cgroup_lock()
*/
struct cgroupfs_root *root;
struct list_head sibling;
/* used when use_id == true */
struct idr idr;
spinlock_t id_lock;
/* list of cftype_sets */
struct list_head cftsets;
/* base cftypes, automatically [de]registered with subsys itself */
struct cftype *base_cftypes;
struct cftype_set base_cftset;
/* should be defined only by modular subsystems */
struct module *module;
};
Cgroup_subsys定义了一组操作,让各个子系统根据各自的需要去实现。这个相当于C++中抽象基类,然后各个特定的子系统对应cgroup_subsys则是实现了相应操作的子类。类似的思想还被用在了cgroup_subsys_state中,cgroup_subsys_state并未定义控制信息,而只是定义了各个子系统都需要的共同信息,比如该cgroup_subsys_state从属的cgroup。然后各个子系统再根据各自的需要去定义自己的进程控制信息结构体,最后在各自的结构体中将cgroup_subsys_state包含进去,这样通过Linux内核的container_of等宏就可以通过cgroup_subsys_state来获取相应的结构体。
联系
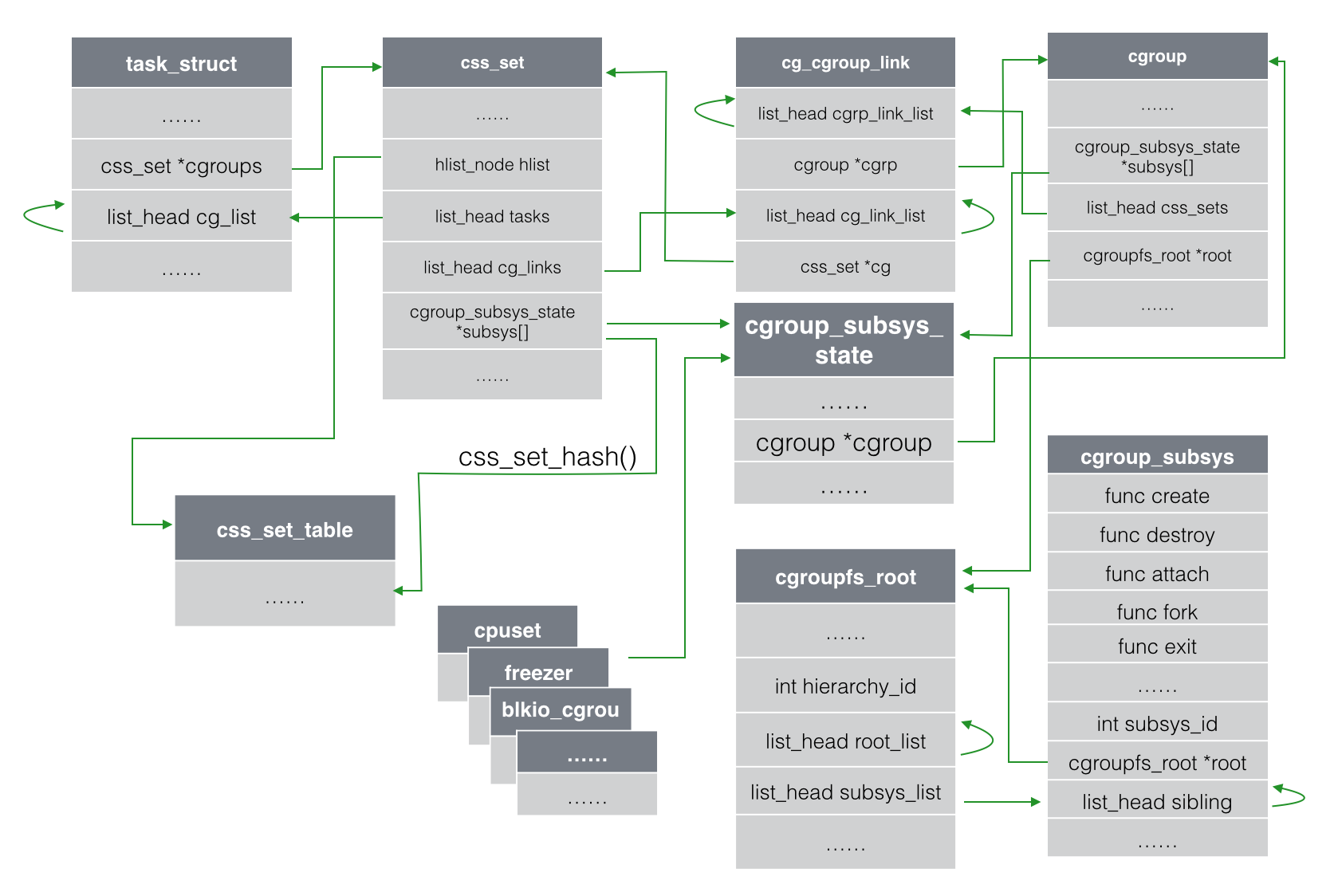 数据结构划分cgroupfs_root层级(hierarchy)
数据结构划分cgroupfs_root层级(hierarchy)
css_set子系统(subsystem)
cgroup进程控制组
cgroup初始化1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8start_kernel
\->cgroup_init_early();
\->init_cgroup_root
\->cgroup_init_subsys
\->cgroup_init();
\->cgroup_init_subsys
\->kobject_create_and_add
\->register_filesystem
cgroup_init_early
第一阶段:主要进行数据结构的初始化和链表之间关系的绑定1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30int __init cgroup_init_early(void)
{
atomic_set(&init_css_set.refcount, 1);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&init_css_set.cg_links); //初始化全局结构体struct css_set init
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&init_css_set.tasks);
INIT_HLIST_NODE(&init_css_set.hlist);
css_set_count = 1; //系统中struct css_set计数
init_cgroup_root(&rootnode); //初始化全局结构体struct cgroupfs_root
root_count = 1;//系统中的层级计数
init_task.cgroups = &init_css_set; //使系统的初始化进程cgroup指向init_css_set
init_css_set_link.cg = &init_css_set;
/* dummytop is a shorthand for the dummy hierarchy's top cgroup */
init_css_set_link.cgrp = dummytop;
list_add(&init_css_set_link.cgrp_link_list,
&rootnode.top_cgroup.css_sets);
list_add(&init_css_set_link.cg_link_list,
&init_css_set.cg_links);
//对一些需要在系统启动时初始化的subsys进行初始化
for (i = 0; i < CGROUP_SUBSYS_COUNT; i++) {
struct cgroup_subsys *ss = subsys[i];
...
if (ss->early_init)
cgroup_init_subsys(ss);
}
return 0;
}
cgroup_init
第二阶段: 主要生成cgroup虚拟文件系统1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37/**
* cgroup_init - cgroup initialization
*
* Register cgroup filesystem and /proc file, and initialize
* any subsystems that didn't request early init.
*/
int __init cgroup_init(void)
{
...
err = bdi_init(&cgroup_backing_dev_info);
for (i = 0; i < CGROUP_SUBSYS_COUNT; i++) {
struct cgroup_subsys *ss = subsys[i];
/* at bootup time, we don't worry about modular subsystems */
if (!ss || ss->module)
continue;
if (!ss->early_init)
cgroup_init_subsys(ss);
if (ss->use_id)
cgroup_init_idr(ss, init_css_set.subsys[ss->subsys_id]);
}
/* Add init_css_set to the hash table */
key = css_set_hash(init_css_set.subsys);
hash_add(css_set_table, &init_css_set.hlist, key);
BUG_ON(!init_root_id(&rootnode));
...
cgroup_kobj = kobject_create_and_add("cgroup", fs_kobj);
err = register_filesystem(&cgroup_fs_type);
proc_create("cgroups", 0, NULL, &proc_cgroupstats_operations);
...
return err;
}
1.bdi_init用于初始化后备存储器的一些字段,这些字段包括回写链表、回写锁等,关系到读写策略,和挂载关系并不大
subsys1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8#define SUBSYS(_x) [_x ## _subsys_id] = &_x ## _subsys,
#define IS_SUBSYS_ENABLED(option) IS_BUILTIN(option)
static struct cgroup_subsys *subsys[CGROUP_SUBSYS_COUNT] = {
#include
#if IS_SUBSYS_ENABLED(CONFIG_CGROUP_DEBUG)
SUBSYS(debug)
#endif
};file: kernel/cgroup.c
cgroup文件系统的挂载mount -t cgroup -o cpu cgroup /mnt/
注册:1
2
3
4
5static struct file_system_type cgroup_fs_type = {
.name = "cgroup",
.mount = cgroup_mount,
.kill_sb = cgroup_kill_sb,
};
调用关系:1
2
3
4
5
6SyS_mount
\->do_mount
\->vfs_kern_mount
\->mount_fs
\->cgroup_mount
\->cgroup_populate_dir //生成基础的文件属性
cgoup基础的文件:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47/*for hysterical raisins, we can't put this on the older files*/
#define CGROUP_FILE_GENERIC_PREFIX "cgroup."
static struct cftype files[] = {
{
.name = "tasks",
.open = cgroup_tasks_open,
.write_u64 = cgroup_tasks_write,
.release = cgroup_pidlist_release,
.mode = S_IRUGO | S_IWUSR,
},
{
.name = CGROUP_FILE_GENERIC_PREFIX "procs",
.open = cgroup_procs_open,
.write_u64 = cgroup_procs_write,
.release = cgroup_pidlist_release,
.mode = S_IRUGO | S_IWUSR,
},
{
.name = "notify_on_release",
.read_u64 = cgroup_read_notify_on_release,
.write_u64 = cgroup_write_notify_on_release,
},
{
.name = CGROUP_FILE_GENERIC_PREFIX "event_control",
.write_string = cgroup_write_event_control,
.mode = S_IWUGO,
},
{
.name = "cgroup.clone_children",
.flags = CFTYPE_INSANE,
.read_u64 = cgroup_clone_children_read,
.write_u64 = cgroup_clone_children_write,
},
{
.name = "cgroup.sane_behavior",
.flags = CFTYPE_ONLY_ON_ROOT,
.read_seq_string = cgroup_sane_behavior_show,
},
{
.name = "release_agent",
.flags = CFTYPE_ONLY_ON_ROOT,
.read_seq_string = cgroup_release_agent_show,
.write_string = cgroup_release_agent_write,
.max_write_len = PATH_MAX,
},
{ } /* terminate */
};
创建子cgroup1
2
3SyS_mkdirat
\->cgroup_mkdir
\->cgroup_create
taskecho $$ > task
将当前进程迁移到一个cgroup中:
Open:1
2
3
4
5
6
7do_sys_open
|->do_filp_open
|-> path_openat.isra.13
|->do_last.isra.12
|->finish_open
|->do_dentry_open.isra.2
|->cgroup_pidlist_open
Write:1
2
3
4
5SyS_write
|->vfs_write
|->cgroup_file_write
|->cgroup_tasks_write
|->attach_task_by_pid
DEBUG子系统实现1
2
3
4
5
6
7struct cgroup_subsys debug_subsys = {
.name = "debug",
.css_alloc = debug_css_alloc,
.css_free = debug_css_free,
.subsys_id = debug_subsys_id,
.base_cftypes = debug_files,
}; SS
参考