一 音频架构
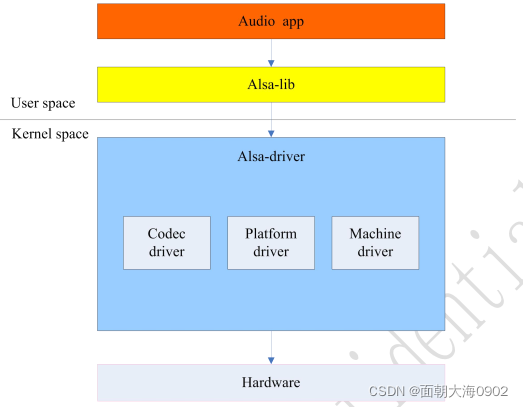
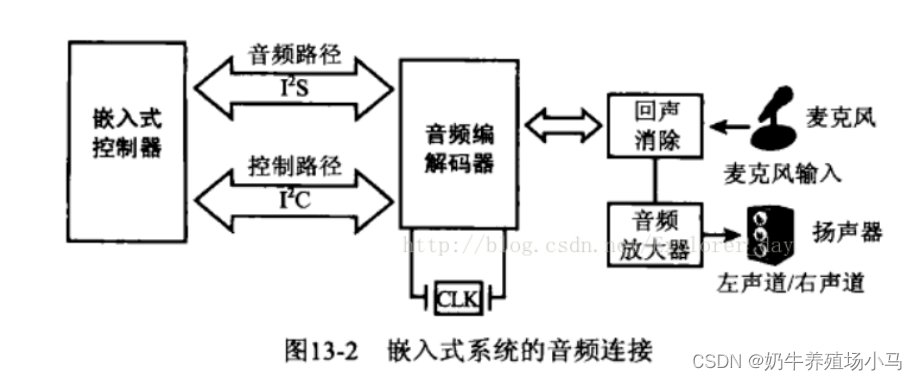
如图所示 是 嵌入式系统的音频连接
音频编解码器将数字音频信号 转换成 扬声器播放所需要的模拟声音信号。而通过麦克风时,则执行相反的过程。
数字音频信号通过 PCM技术对模拟信号以某个比特率采样得到的,编解码器的任务就是以支持的PCM比特率 采样和记录音频,并能以不同的 PCM比特率播放采样的音频。
编解码器的任务:
1 即对PCM音频信号进行D/A转换,把数字的音频信号转换为模拟信号,输送给耳机或音响,即播放声音;
2 对麦克风或者其他输入源的模拟信号进行A/D转换,把模拟的声音信号转变CPU能够处理的数字信号,即录音;
3 对音频信号做出相应的处理,例如音量控制,功率放大,EQ控制等等
AC97 和 I2S总线是连接音频控制器和编解码器的工业标准接口的一个例子。
下图的嵌入式设备 使用I2S 将音频数据发送给编解码器。对编解码器的I/O寄存器的编程通过I2C总线进行。
二 ALSA概述
ALSA(Advanced Linux Sound Architecture)是linux上主流的音频结构,在没有出现ALSA架构之前,一直使用的是OSS(Open Sound System)音频架构主要的区别就是在OSS架构下,App访问底层是直接通过Sound设备节点访问的。而在ALSA音频架构下,App是通过ALSA提供的alsa-lib库访问底层硬件的操作,不再访问Sound设备节点了。这样做的好处可以简化App实现的难度。
**Linux ALSA子系统 : **
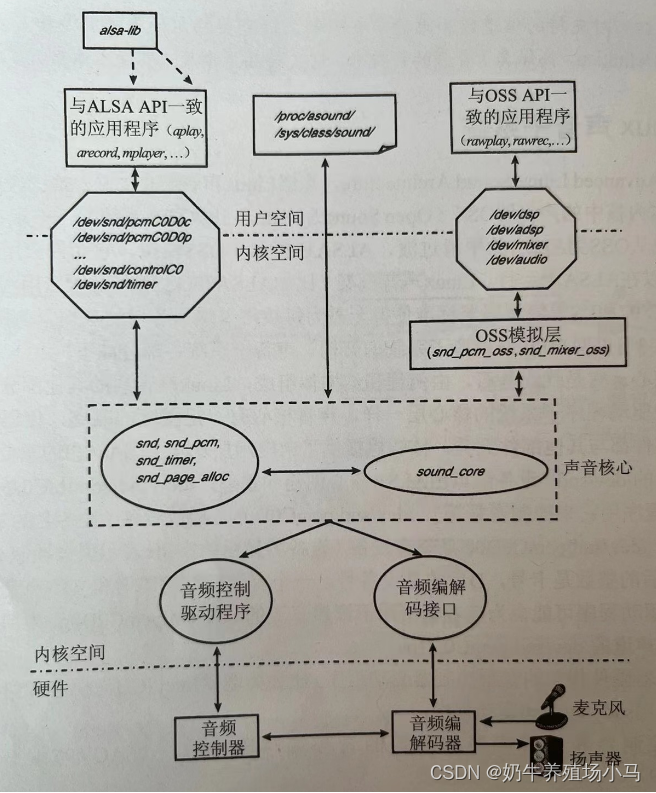
1 声音核心部分: 核心层有一定程度的隔离,是的声音子系统的每个部件都与其他部件无关,并且提供了向应用层输出 ALSA API 的重要功能。上图中显示的 /dev/snd/* 设备节点是由 ALSA核心层创建和管理的:
/dev/snd/controlC0 是一个控制节点,应用程序用它来控制音量等
/dev/snd/pcmC0D0p 是播放设备,设备名最后一个字符p表示播放
/dev/snd/pcmC0D0c 是录音设备,设备名最后一个字符c表示捕获
这些设备名中,C后的整数是卡号,D后的是设备号。
2 音频控制驱动程序:与控制器硬件相关的音频控制器驱动程序
3 音频编解码接口 : 协助控制器和编解码器之间通信的音频编解码接口
4 OSS模拟层 :在OSS应用程序和由ALSA启用的内核之间充当通道 的OSS模拟层。该层输出 /dev 节点,这些节点(如 /dev/dsp /dev/adsp /dev/mixer )允许OSS应用程序不用修改就在ALSA上运行。OSS节点 /dev/dsp 映射成 ALSA 节点 /dev/snd/pcmC0D0* , /dev/adsp 对应 /dev/snd/pcmC0D1* , /dev/mixer 对应 /dev/snd/controlC0
5 procfs 和 sysfs 接口实现,用于通过 /proc/asound 和 /sys/class/sound 获取信息
cd /proc/asound
lscard0 //声卡0
cards //系统可用的声卡
devices //alsa下所有注册的声卡子设备,包括 control pcm timer seq等等
version //ALSA版本信息
...等等
6 用户空间 ALSA 库 alsa-lib。他提供了 libasound.so 对象。这个库通过提供一些访问 ALSA驱动程序的封装例程,使ALSA应用程序编写更加方便。
7 alsa-utils工具包,包括 alsamixer,amixer, alsactl, aplay等工具。alsamixer,amixer 用于改变音频信号(如 音频线输入,音频线输出,麦克风信号等)的音量。alsactl用于控制ALSA驱动程序的设置, aplay用于在ALSA上播放音频。
三 ALSA驱动
1 关于声卡设备抽象 和 声卡中的功能逻辑设备抽象
内核中用 snd_card来描述一个声卡设备。
struct snd_card {int number; //声卡编号,因为系统中可能有多张声卡,需要对每一个声卡编号char id[16]; //声卡ID标识符char driver[16]; //声卡驱动名
...//链表,声卡的所有逻辑设备都会挂入该链表struct list_head devices; //声卡的控制逻辑设备对应的devicestruct device ctl_dev; /* control device */void *private_data; //声卡的私有数据,可以在创建声卡时通过参数指定数据的大小
...struct list_head ctl_files; //若干个进程打开"/dev/snd/controlCx"时生成ctl_file的链 表头。一般用于pcm有多个substream时配置选用哪个substream.struct list_head controls; //通过设备节点"/dev/snd/controlCx"提供给用户空间的controls. 常用于控制音量,音频流的通路等struct device *dev; //此声卡的父设备,通过何种方式挂载声卡。如usb/pci/platform…struct device *card_dev; //声卡对应的device,用于注册到设备模型
};
某款Codec内部结构图如下:
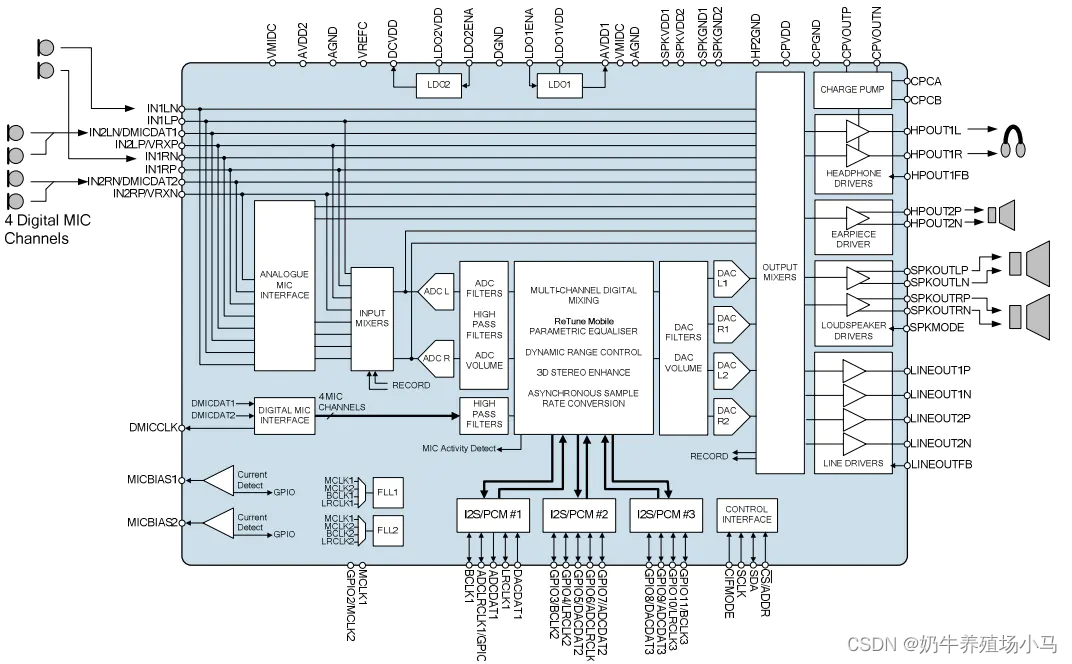
从接口上看,有:
INL-连接音响设备,输入模拟声音信号
MIC-连接麦克风,输入模拟语音信号
DMIC-连接数字麦克风,输入数字音频信号
I2S/PCM-连接CPU,输入数字音频信号
CONTROL INTERFACE-输入控制信号
HP-连接耳机,输出模拟声音信号
SPKOUT-连接喇叭,输出模拟声音信号
LINEOUT-连接功放设备,输出模拟声音信号
从内部看,有:
MIXER-混音器,多路模拟声音混合输出
PGA-放大器,调节音量
ADC-模拟信号转数字信号
DAC-数字信号转模拟信号
Filter-滤波器,把数字信号转换到不同的频率,控制播放快慢
ALSA Core把这些内部功能部件抽象成一个个的逻辑设备,用 struct snd_device结构体描述一个声卡的逻辑设备,结构体定义如下:
struct snd_device {struct list_head list; /* 用于挂入snd_card的devices链表 */struct snd_card *card; /* 指向所属的snd_card */enum snd_device_state state; /* state of the device */enum snd_device_type type; /* 逻辑设备的类型 */void *device_data; /* device structure */struct snd_device_ops *ops; /* 操作集 */
};struct snd_device_ops {//释放逻辑设备时,会调用dev_free回调int (*dev_free)(struct snd_device *dev);//注册逻辑设备时,会调用dev_register回调int (*dev_register)(struct snd_device *dev);//注销逻辑设备时,会调用dev_disconnect回调int (*dev_disconnect)(struct snd_device *dev);
};
逻辑设备的类型如下种类:
enum snd_device_type {SNDRV_DEV_LOWLEVEL,SNDRV_DEV_CONTROL, //控制逻辑设备,对应与Codec里面的控制部件,控制音量大小、快慢等SNDRV_DEV_INFO,SNDRV_DEV_BUS,SNDRV_DEV_CODEC,SNDRV_DEV_PCM, //pcm逻辑设备,对应与Codec里面的ADC或DAC,实现录音或播放声音的功能SNDRV_DEV_COMPRESS,SNDRV_DEV_RAWMIDI,SNDRV_DEV_TIMER,SNDRV_DEV_SEQUENCER,SNDRV_DEV_HWDEP,SNDRV_DEV_JACK,
};
这里说明一下 pcm逻辑设备 与 控制逻辑设备。
pcm逻辑设备,所代表的逻辑功能就是 录音和播放
playback,把用户空间的应用程序发过来的PCM数据进行D/A转换,转化为人耳可以辨别的模拟音频。
capture,把麦克风或者其他输入源的模拟信号进行A/D转换,把模拟的声音信号转变CPU能够处理的数字信号。
控制逻辑设备,所代表的逻辑功能就是如音量调节等控制功能,主要让用户空间的应用程序可以访问和控制音频codec芯片中的多路开关,滑动控件等,进行音量控制、静音等。
所以综上所述。snd_card有一devices链表,声卡所有的逻辑设备会挂入该链表。
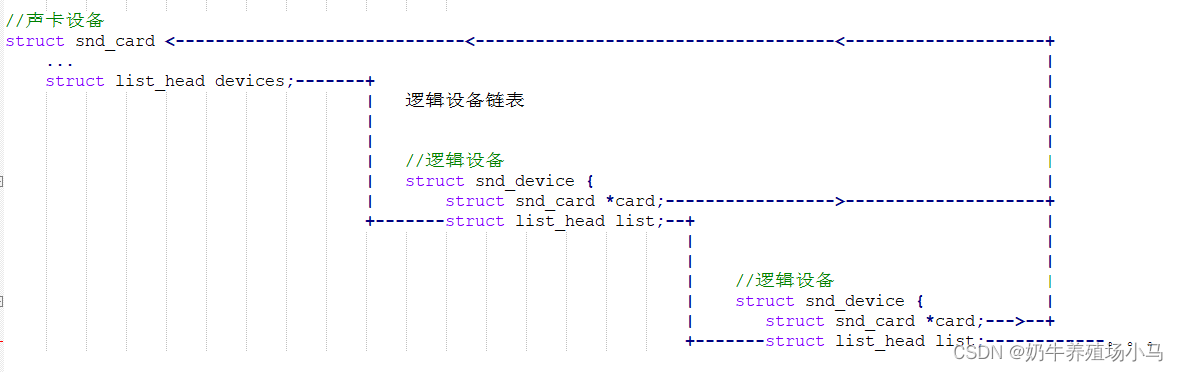
2 ALSA驱动
主要工作:
1 创建声卡snd_card的一个实例;
2 创建声卡snd_card的功能部件(逻辑设备)snd_device ,例如PCM、Control等;;
3 设置 逻辑设备 的操作方法
4 注册声卡设备snd_card;
1 创建声卡实例
/* 参数说明:* parent,声卡的父设备* idx,声卡的编号,如何传入-1,则让系统分配一个没占用的编号* xid,字符串,声卡标识符,alsa-lib通过标识符找到对应的snd_card* extra_size,私有数据大小,保存在返回的 snd_card结构体的 private_data字段,额外分配的内存由snd_card->private_data指向* card_ret,保存创建的snd_card实例的指针*/int snd_card_new(struct device *parent, int idx, const char *xid,struct module *module, int extra_size,struct snd_card **card_ret)
与之相对的是 snd_card_free() 将snd_card 从ALSA 架构中释放。
2 创建 pcm 逻辑功能设备 实例
/* card,声卡实例* id,pcm设备的标识符* device,表示目前创建的是该声卡下的第几个pcm,第一个pcm设备从0开始* playback_count,表示该pcm将会有几个playback substream 即 支持的播放流数目* capture_count,表示该pcm将会有几个capture substream 即 支持的录音流数目*/int snd_pcm_new(struct snd_card *card, const char *id, int device,int playback_count, int capture_count, struct snd_pcm **rpcm)
{return _snd_pcm_new(card, id, device, playback_count, capture_count,false, rpcm);
}static int _snd_pcm_new(struct snd_card *card, const char *id, int device,int playback_count, int capture_count, bool internal,struct snd_pcm **rpcm)
{struct snd_pcm *pcm;int err;//不同的逻辑设备 操作集不同static struct snd_device_ops ops = {.dev_free = snd_pcm_dev_free,.dev_register = snd_pcm_dev_register,.dev_disconnect = snd_pcm_dev_disconnect,};
...//创建一个snd_pcm pcm = kzalloc(sizeof(*pcm), GFP_KERNEL);if (!pcm)return -ENOMEM;pcm->card = card;//所属声卡pcm->device = device;//设备索引
...//创建playback的substreamserr = snd_pcm_new_stream(pcm, SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_PLAYBACK, playback_count);//创建capture的substreamserr = snd_pcm_new_stream(pcm, SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_CAPTURE, capture_count);//创建snd_device,并挂入snd_card的devices链表err = snd_device_new(card, SNDRV_DEV_PCM, pcm,internal ? &internal_ops : &ops);
...}int snd_pcm_new_stream(struct snd_pcm *pcm, int stream, int substream_count)
{int idx, err;struct snd_pcm_str *pstr = &pcm->streams[stream];struct snd_pcm_substream *substream, *prev;...pstr->stream = stream;pstr->pcm = pcm;pstr->substream_count = substream_count;...dev_set_name(&pstr->dev, "pcmC%iD%i%c", pcm->card->number, pcm->device,stream == SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_PLAYBACK ? 'p' : 'c');...prev = NULL;for (idx = 0, prev = NULL; idx < substream_count; idx++) {substream = kzalloc(sizeof(*substream), GFP_KERNEL);if (!substream)return -ENOMEM;substream->pcm = pcm;substream->pstr = pstr;substream->number = idx;substream->stream = stream;sprintf(substream->name, "subdevice #%i", idx);...}return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(snd_pcm_new_stream);int snd_device_new(struct snd_card *card, enum snd_device_type type,void *device_data, struct snd_device_ops *ops)
{struct snd_device *dev;struct list_head *p;...dev->card = card;dev->type = type;dev->state = SNDRV_DEV_BUILD;dev->device_data = device_data;dev->ops = ops;/* insert the entry in an incrementally sorted list */list_for_each_prev(p, &card->devices) {struct snd_device *pdev = list_entry(p, struct snd_device, list);if ((unsigned int)pdev->type <= (unsigned int)type)break;}list_add(&dev->list, p);return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(snd_device_new);
至此 可以得到如下关系图:
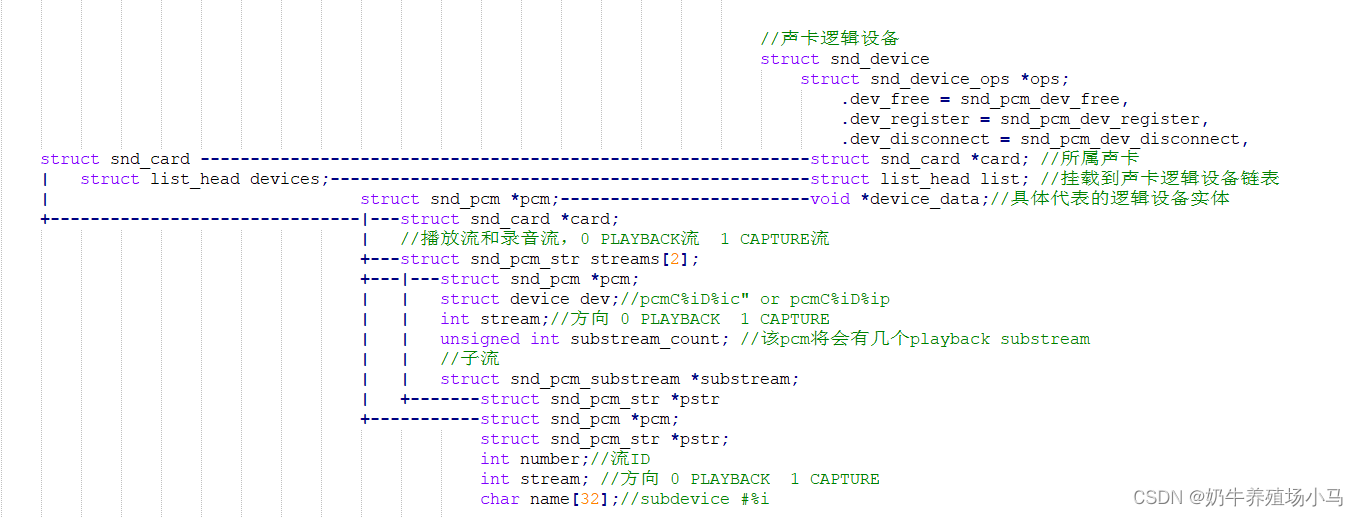
3 设置 pcm逻辑设备(播放或者录音)的子流的具体操作功能
/*** snd_pcm_set_ops - set the PCM operators* @pcm: the pcm instance* @direction: stream direction, SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_XXX* @ops: the operator table** Sets the given PCM operators to the pcm instance.*/
void snd_pcm_set_ops(struct snd_pcm *pcm, int direction,const struct snd_pcm_ops *ops)
{struct snd_pcm_str *stream = &pcm->streams[direction];struct snd_pcm_substream *substream;for (substream = stream->substream; substream != NULL; substream = substream->next)substream->ops = ops;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(snd_pcm_set_ops);
如:
static const struct snd_pcm_ops snd_ad1889_playback_ops = {.open = snd_ad1889_playback_open,.close = snd_ad1889_playback_close,.ioctl = snd_pcm_lib_ioctl,.hw_params = snd_ad1889_hw_params,.hw_free = snd_ad1889_hw_free,//如 准备传输音频流,设置音频格式,采样速率,配置时钟源,使能中断等操作.prepare = snd_ad1889_playback_prepare,//如 将ALSA框架生成的音频缓冲区映射等操作.trigger = snd_ad1889_playback_trigger,.pointer = snd_ad1889_playback_pointer,
};static const struct snd_pcm_ops snd_ad1889_capture_ops = {.open = snd_ad1889_capture_open,.close = snd_ad1889_capture_close,.ioctl = snd_pcm_lib_ioctl,.hw_params = snd_ad1889_hw_params,.hw_free = snd_ad1889_hw_free,.prepare = snd_ad1889_capture_prepare,.trigger = snd_ad1889_capture_trigger,.pointer = snd_ad1889_capture_pointer,
};snd_pcm_set_ops(pcm, SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_PLAYBACK, &snd_ad1889_playback_ops);
snd_pcm_set_ops(pcm, SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_CAPTURE, &snd_ad1889_capture_ops);
4 注册声卡设备,将声卡注册进ALSA框架
int snd_card_register(struct snd_card *card)int snd_card_register(struct snd_card *card)
{int err;if (!card->registered) {err = device_add(&card->card_dev);if (err < 0)return err;card->registered = true;}if ((err = snd_device_register_all(card)) < 0)return err;
...}
...return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(snd_card_register);/** register all the devices on the card.* called from init.c*/
int snd_device_register_all(struct snd_card *card)
{struct snd_device *dev;int err;
...list_for_each_entry(dev, &card->devices, list) {err = __snd_device_register(dev);if (err < 0)return err;}return 0;
}static int __snd_device_register(struct snd_device *dev)
{if (dev->state == SNDRV_DEV_BUILD) {if (dev->ops->dev_register) {//.dev_register = snd_pcm_dev_register,int err = dev->ops->dev_register(dev);if (err < 0)return err;}dev->state = SNDRV_DEV_REGISTERED;}return 0;
}//pcm逻辑设备实体 所包含的两个流各自的 操作集函数
const struct file_operations snd_pcm_f_ops[2] = {{.owner = THIS_MODULE,.write = snd_pcm_write,.write_iter = snd_pcm_writev,.open = snd_pcm_playback_open,.release = snd_pcm_release,.llseek = no_llseek,.poll = snd_pcm_poll,.unlocked_ioctl = snd_pcm_ioctl,.compat_ioctl = snd_pcm_ioctl_compat,.mmap = snd_pcm_mmap,.fasync = snd_pcm_fasync,.get_unmapped_area = snd_pcm_get_unmapped_area,},{.owner = THIS_MODULE,.read = snd_pcm_read,.read_iter = snd_pcm_readv,.open = snd_pcm_capture_open,.release = snd_pcm_release,.llseek = no_llseek,.poll = snd_pcm_poll,.unlocked_ioctl = snd_pcm_ioctl,.compat_ioctl = snd_pcm_ioctl_compat,.mmap = snd_pcm_mmap,.fasync = snd_pcm_fasync,.get_unmapped_area = snd_pcm_get_unmapped_area,}
};static int snd_pcm_dev_register(struct snd_device *device)
{int cidx, err;struct snd_pcm_substream *substream;struct snd_pcm *pcm;...//对于一个pcm设备,有两个流,一个是playback,一个是capture,for (cidx = 0; cidx < 2; cidx++) {int devtype = -1;if (pcm->streams[cidx].substream == NULL || pcm->internal)continue;switch (cidx) {case SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_PLAYBACK://pcm功能部件(逻辑设备)命名规则sprintf(str, "pcmC%iD%ip", pcm->card->number, pcm->device);devtype = SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_PCM_PLAYBACK;break;case SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_CAPTURE://pcm功能部件(逻辑设备)命名规则sprintf(str, "pcmC%iD%ic", pcm->card->number, pcm->device);devtype = SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_PCM_CAPTURE;break;}/* register pcm *//*1 流类型(播放/录音)2 pcm 所属的声卡 snd_card 3 pcm逻辑设备实体 所包含的两个流各 其中一个的 操作集函数 file_operations 4 pcm 逻辑设备实体5 逻辑设备对应的struct device struct snd_pcm *pcm;struct snd_pcm_str streams[2];struct device dev;*/err = snd_register_device(devtype, pcm->card, pcm->device,&snd_pcm_f_ops[cidx], pcm,&pcm->streams[cidx].dev);
...
}/* 1 流类型(播放/录音)2 pcm 所属的声卡 snd_card 3 pcm逻辑设备实体 所包含的两个流各 其中一个的 操作集函数 file_operations 4 pcm 逻辑设备实体5 逻辑设备对应的struct device struct snd_pcm *pcm;struct snd_pcm_str streams[2];struct device dev;*/int snd_register_device(int type, struct snd_card *card, int dev,const struct file_operations *f_ops,void *private_data, struct device *device)
{int minor;int err = 0;//声卡逻辑设备信息集合struct snd_minor *preg;if (snd_BUG_ON(!device))return -EINVAL;preg = kmalloc(sizeof *preg, GFP_KERNEL);if (preg == NULL)return -ENOMEM;/*流类型 播放/录音声卡卡号设备号pcm逻辑设备实体 所包含的两个流各 其中一个的 操作集函数 file_operations const struct file_operations snd_pcm_f_ops[2] = {所属代表的声卡逻辑设备实体 pcm所属的声卡设备 snd_card*/preg->type = type;preg->card = card ? card->number : -1;preg->device = dev;preg->f_ops = f_ops;preg->private_data = private_data;preg->card_ptr = card;mutex_lock(&sound_mutex);minor = snd_find_free_minor(type, card, dev);if (minor < 0) {err = minor;goto error;}preg->dev = device;device->devt = MKDEV(major, minor);err = device_add(device);if (err < 0)goto error;snd_minors[minor] = preg;error:mutex_unlock(&sound_mutex);if (err < 0)kfree(preg);return err;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(snd_register_device);
至此注册结束 有如下关系

三 应用层读写流
在sound/core/sound.c文件中会注册字符设备://字符设备,只有一个open 说明此处的open只是一个转接口,只起到中转换作用,后面一定会调用目标流自己的open()
static const struct file_operations snd_fops =
{.owner = THIS_MODULE,.open = snd_open,.llseek = noop_llseek,
};//注册声卡设备
static int __init alsa_sound_init(void)
{snd_major = major;snd_ecards_limit = cards_limit;//注册 声卡设备 为字符设备if (register_chrdev(major, "alsa", &snd_fops)) {snd_printk(KERN_ERR "unable to register native major device number %d\n", major);return -EIO;}//在proc下创建 asound 目录,并且创建version、devices、module、cards等信息if (snd_info_init() < 0) {unregister_chrdev(major, "alsa");return -ENOMEM;}snd_info_minor_register();return 0;
}
open
static int snd_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{//首先从设备节点中取出设备号unsigned int minor = iminor(inode);struct snd_minor *mptr = NULL;const struct file_operations *old_fops;int err = 0;//从 snd_minors[minor]全局数组中取出目标 逻辑设备信息集合 snd_minor,mptr = snd_minors[minor];...//并且把file->f_op替换为 逻辑设备实体的 某个流(播放/录音)的操作集f_ops//const struct file_operations snd_pcm_f_ops[2] = {file->f_op = fops_get(mptr->f_ops);if (file->f_op == NULL) {file->f_op = old_fops;err = -ENODEV;}//直接调用 播放/录音流的 file_operations --> open()// snd_pcm_playback_open()/snd_pcm_capture_open()if (file->f_op->open) {err = file->f_op->open(inode, file);if (err) {fops_put(file->f_op);file->f_op = fops_get(old_fops);}}...return err;
}
open(“/dev/snd/pcmC0D0p”,…) 后面则会逐级调用 最终会是 子流的snd_pcm_substream 的 open()