本文是这篇文章的(翻译)简化版。
本文代码地址
已经不止一次有人说代码地址打不开,但是每次我都打得开。。这里放个阿里云的地址吧Active_Learning_Tutorial.ipynb。需要的去阿里云下载文件就行了。
建议直接看代码地址(代码地址包含了本文全部内容)
文章目录
- 主动学习教程(与代码框架)
- 主动学习简介
- 主动学习分类
- 主动学习代码框架
- 导入使用的库
- 数据集
- 模型
- 训练
- 样本挑选
- 正则化
- 用于第一次训练的K个随机样本
- 整个流程
- 运行代码
- 不同模型结果对比
- 不同样本挑选方式结果对比
主动学习教程(与代码框架)
主动学习简介
众所周知这是个大数据时代,我们可以从许多来源(如学术和贸易机构)获取到大量的未标记数据。未标记数据相对来说是可以廉价获取的,然而标记数据却是昂贵的,许多公司雇佣相关专家或志愿者来为数据打标签[1](如医学图像)。对于众多的小型AI机构而言,标记数据的代价往往是难以忍受的,此时主动学习就能派上用场了。
需要注意下面几点:
- AL实际上是一种策略而非算法(是逐渐增加数据量来训练模型的过程)
- AL建立的基础在于“数据量和信息量不成正比”这一基本现象
- 可以认为AL的优势在于得到更好的学习曲线(learning curves"
- 数据标签难以获取(且难度不同),打标签代价较大且消耗时间
主动学习分类
按照标签查询方式的不同,可将AL分为三类
- Membership query synthesis
- Stream-Based selective sampling
- Pool-Based sampling[2]
许多主动学习工作都是基于池的(Pool-Based sampling),下面简单介绍基于池的主动学习流程
- Divide the data to a ‘pool’ and a test-set
- Select ‘k’ samples from the pool for the initial train-set and label them, the remaining data will be the validation-set
- Normalize all the sets
- Train the Model using the train-set, with balanced weights.
- Use the trained model with the validation-set, get probabilities per sample.
- Use the trained model with the test-set, get performance measures.
- Select ‘k’ most-informative samples based on per-sample-probabilities, i.e., those that the model was most uncertain about regarding their labelling.
- Move these ‘k’ samples from the validation set to the train-set and query their labels.
- Inverse normalization for all the data-sets
- Stop according to the stop criterion, otherwise go to 3.
主动学习代码框架
导入使用的库
import os
import time
import json
import pickle
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.mlab as mlab
from scipy import stats
from pylab import rcParams
from sklearn.utils import check_random_state
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_openml
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
from sklearn.preprocessing import scale
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
from sklearn.mixture import GaussianMixture
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC, SVC
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn import metrics
from sklearn.metrics import pairwise_distances_argmin_min
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
from sklearn.metrics import precision_recall_curve
from sklearn.metrics import average_precision_score
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier, \GradientBoostingClassifiermax_queried = 500
数据集
使用著名的基本数据集MNIST,采取60k/10k的划分方法。
trainset_size = 60000 # ie., testset_size = 10000def download():mnist = fetch_openml('mnist_784')X = mnist.data.astype('float64')y = mnist.targetprint ('MNIST:', X.shape, y.shape)return (X, y)def split(train_size):X_train_full = X[:train_size]y_train_full = y[:train_size]X_test = X[train_size:]y_test = y[train_size:]return (X_train_full, y_train_full, X_test, y_test)
模型
先构造一个基本类,所用模型包括SVM, logistic regression, random forest and gradient boosting.
class BaseModel(object):def __init__(self):passdef fit_predict(self):passclass SvmModel(BaseModel):model_type = 'Support Vector Machine with linear Kernel'def fit_predict(self, X_train, y_train, X_val, X_test, c_weight):print ('training svm...')self.classifier = SVC(C=1, kernel='linear', probability=True,class_weight=c_weight)self.classifier.fit(X_train, y_train)self.test_y_predicted = self.classifier.predict(X_test)self.val_y_predicted = self.classifier.predict(X_val)return (X_train, X_val, X_test, self.val_y_predicted,self.test_y_predicted)class LogModel(BaseModel):model_type = 'Multinominal Logistic Regression' def fit_predict(self, X_train, y_train, X_val, X_test, c_weight):print ('training multinomial logistic regression')train_samples = X_train.shape[0]self.classifier = LogisticRegression(C=50. / train_samples,multi_class='multinomial',penalty='l1',solver='saga',tol=0.1,class_weight=c_weight,)self.classifier.fit(X_train, y_train)self.test_y_predicted = self.classifier.predict(X_test)self.val_y_predicted = self.classifier.predict(X_val)return (X_train, X_val, X_test, self.val_y_predicted,self.test_y_predicted)class RfModel(BaseModel):model_type = 'Random Forest'def fit_predict(self, X_train, y_train, X_val, X_test, c_weight):print ('training random forest...')self.classifier = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=500, class_weight=c_weight)self.classifier.fit(X_train, y_train)self.test_y_predicted = self.classifier.predict(X_test)self.val_y_predicted = self.classifier.predict(X_val)return (X_train, X_val, X_test, self.val_y_predicted, self.test_y_predicted)
训练
class TrainModel:def __init__(self, model_object): self.accuracies = []self.model_object = model_object() def print_model_type(self):print (self.model_object.model_type)# we train normally and get probabilities for the validation set. i.e., we use the probabilities to select the most uncertain samplesdef train(self, X_train, y_train, X_val, X_test, c_weight):print ('Train set:', X_train.shape, 'y:', y_train.shape)print ('Val set:', X_val.shape)print ('Test set:', X_test.shape)t0 = time.time()(X_train, X_val, X_test, self.val_y_predicted,self.test_y_predicted) = \self.model_object.fit_predict(X_train, y_train, X_val, X_test, c_weight)self.run_time = time.time() - t0return (X_train, X_val, X_test) # we return them in case we use PCA, with all the other algorithms, this is not needed.# we want accuracy only for the test setdef get_test_accuracy(self, i, y_test):classif_rate = np.mean(self.test_y_predicted.ravel() == y_test.ravel()) * 100self.accuracies.append(classif_rate) print('--------------------------------')print('Iteration:',i)print('--------------------------------')print('y-test set:',y_test.shape)print('Example run in %.3f s' % self.run_time,'\n')print("Accuracy rate for %f " % (classif_rate)) print("Classification report for classifier %s:\n%s\n" % (self.model_object.classifier, metrics.classification_report(y_test, self.test_y_predicted)))print("Confusion matrix:\n%s" % metrics.confusion_matrix(y_test, self.test_y_predicted))print('--------------------------------')
样本挑选
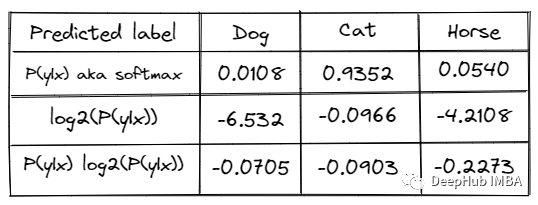
class BaseSelectionFunction(object):def __init__(self):passdef select(self):passclass RandomSelection(BaseSelectionFunction):@staticmethoddef select(probas_val, initial_labeled_samples):random_state = check_random_state(0)selection = np.random.choice(probas_val.shape[0], initial_labeled_samples, replace=False)# print('uniques chosen:',np.unique(selection).shape[0],'<= should be equal to:',initial_labeled_samples)return selectionclass EntropySelection(BaseSelectionFunction):@staticmethoddef select(probas_val, initial_labeled_samples):e = (-probas_val * np.log2(probas_val)).sum(axis=1)selection = (np.argsort(e)[::-1])[:initial_labeled_samples]return selectionclass MarginSamplingSelection(BaseSelectionFunction):@staticmethoddef select(probas_val, initial_labeled_samples):rev = np.sort(probas_val, axis=1)[:, ::-1]values = rev[:, 0] - rev[:, 1]selection = np.argsort(values)[:initial_labeled_samples]return selection
正则化
class Normalize(object):def normalize(self, X_train, X_val, X_test):self.scaler = MinMaxScaler()X_train = self.scaler.fit_transform(X_train)X_val = self.scaler.transform(X_val)X_test = self.scaler.transform(X_test)return (X_train, X_val, X_test) def inverse(self, X_train, X_val, X_test):X_train = self.scaler.inverse_transform(X_train)X_val = self.scaler.inverse_transform(X_val)X_test = self.scaler.inverse_transform(X_test)return (X_train, X_val, X_test)
用于第一次训练的K个随机样本
def get_k_random_samples(initial_labeled_samples, X_train_full,y_train_full):random_state = check_random_state(0)permutation = np.random.choice(trainset_size,initial_labeled_samples,replace=False)print ()print ('initial random chosen samples', permutation.shape),
# permutation)X_train = X_train_full[permutation]y_train = y_train_full[permutation]X_train = X_train.reshape((X_train.shape[0], -1))bin_count = np.bincount(y_train.astype('int64'))unique = np.unique(y_train.astype('int64'))print ('initial train set:',X_train.shape,y_train.shape,'unique(labels):',bin_count,unique,)return (permutation, X_train, y_train)
整个流程
实现主动学习流程
class TheAlgorithm(object):accuracies = []def __init__(self, initial_labeled_samples, model_object, selection_function):self.initial_labeled_samples = initial_labeled_samplesself.model_object = model_objectself.sample_selection_function = selection_functiondef run(self, X_train_full, y_train_full, X_test, y_test):# initialize process by applying base learner to labeled training data set to obtain Classifier(permutation, X_train, y_train) = \get_k_random_samples(self.initial_labeled_samples,X_train_full, y_train_full)self.queried = self.initial_labeled_samplesself.samplecount = [self.initial_labeled_samples]# permutation, X_train, y_train = get_equally_k_random_samples(self.initial_labeled_samples,classes)# assign the val set the rest of the 'unlabelled' training dataX_val = np.array([])y_val = np.array([])X_val = np.copy(X_train_full)X_val = np.delete(X_val, permutation, axis=0)y_val = np.copy(y_train_full)y_val = np.delete(y_val, permutation, axis=0)print ('val set:', X_val.shape, y_val.shape, permutation.shape)print ()# normalize datanormalizer = Normalize()X_train, X_val, X_test = normalizer.normalize(X_train, X_val, X_test) self.clf_model = TrainModel(self.model_object)(X_train, X_val, X_test) = self.clf_model.train(X_train, y_train, X_val, X_test, 'balanced')active_iteration = 1self.clf_model.get_test_accuracy(1, y_test)# fpfn = self.clf_model.test_y_predicted.ravel() != y_val.ravel()# print(fpfn)# self.fpfncount = []# self.fpfncount.append(fpfn.sum() / y_test.shape[0] * 100)while self.queried < max_queried:active_iteration += 1# get validation probabilitiesprobas_val = \self.clf_model.model_object.classifier.predict_proba(X_val)print ('val predicted:',self.clf_model.val_y_predicted.shape,self.clf_model.val_y_predicted)print ('probabilities:', probas_val.shape, '\n',np.argmax(probas_val, axis=1))# select samples using a selection functionuncertain_samples = \self.sample_selection_function.select(probas_val, self.initial_labeled_samples)# normalization needs to be inversed and recalculated based on the new train and test set.X_train, X_val, X_test = normalizer.inverse(X_train, X_val, X_test) # get the uncertain samples from the validation setprint ('trainset before', X_train.shape, y_train.shape)X_train = np.concatenate((X_train, X_val[uncertain_samples]))y_train = np.concatenate((y_train, y_val[uncertain_samples]))print ('trainset after', X_train.shape, y_train.shape)self.samplecount.append(X_train.shape[0])bin_count = np.bincount(y_train.astype('int64'))unique = np.unique(y_train.astype('int64'))print ('updated train set:',X_train.shape,y_train.shape,'unique(labels):',bin_count,unique,)X_val = np.delete(X_val, uncertain_samples, axis=0)y_val = np.delete(y_val, uncertain_samples, axis=0)print ('val set:', X_val.shape, y_val.shape)print ()# normalize again after creating the 'new' train/test setsnormalizer = Normalize()X_train, X_val, X_test = normalizer.normalize(X_train, X_val, X_test) self.queried += self.initial_labeled_samples(X_train, X_val, X_test) = self.clf_model.train(X_train, y_train, X_val, X_test, 'balanced')self.clf_model.get_test_accuracy(active_iteration, y_test)print ('final active learning accuracies',self.clf_model.accuracies)
运行代码
(X, y) = download()
(X_train_full, y_train_full, X_test, y_test) = split(trainset_size)
print ('train:', X_train_full.shape, y_train_full.shape)
print ('test :', X_test.shape, y_test.shape)
classes = len(np.unique(y))
print ('unique classes', classes)def pickle_save(fname, data):filehandler = open(fname,"wb")pickle.dump(data,filehandler)filehandler.close() print('saved', fname, os.getcwd(), os.listdir())def pickle_load(fname):print(os.getcwd(), os.listdir())file = open(fname,'rb')data = pickle.load(file)file.close()print(data)return datadef experiment(d, models, selection_functions, Ks, repeats, contfrom):algos_temp = []print ('stopping at:', max_queried)count = 0for model_object in models:if model_object.__name__ not in d:d[model_object.__name__] = {}for selection_function in selection_functions:if selection_function.__name__ not in d[model_object.__name__]:d[model_object.__name__][selection_function.__name__] = {}for k in Ks:d[model_object.__name__][selection_function.__name__][str(k)] = [] for i in range(0, repeats):count+=1if count >= contfrom:print ('Count = %s, using model = %s, selection_function = %s, k = %s, iteration = %s.' % (count, model_object.__name__, selection_function.__name__, k, i))alg = TheAlgorithm(k, model_object, selection_function)alg.run(X_train_full, y_train_full, X_test, y_test)d[model_object.__name__][selection_function.__name__][str(k)].append(alg.clf_model.accuracies)fname = 'Active-learning-experiment-' + str(count) + '.pkl'pickle_save(fname, d)if count % 5 == 0:print(json.dumps(d, indent=2, sort_keys=True))print ()print ('---------------------------- FINISHED ---------------------------')print ()return dmax_queried = 500 repeats = 1models = [SvmModel, RfModel, LogModel] selection_functions = [RandomSelection, MarginSamplingSelection, EntropySelection] Ks = [250,125,50,25,10] d = {}
stopped_at = -1 # print('directory dump including pickle files:', os.getcwd(), np.sort(os.listdir()))
# d = pickle_load('Active-learning-experiment-' + str(stopped_at) + '.pkl')
# print(json.dumps(d, indent=2, sort_keys=True))d = experiment(d, models, selection_functions, Ks, repeats, stopped_at+1)
print (d)
results = json.loads(json.dumps(d, indent=2, sort_keys=True))
print(results)
不同模型结果对比
通过对比发现随机森林是几种模型中最好的
def performance_plot(fully_supervised_accuracy, dic, models, selection_functions, Ks, repeats): fig, ax = plt.subplots()ax.plot([0,500],[fully_supervised_accuracy, fully_supervised_accuracy],label = 'algorithm-upper-bound')for model_object in models:for selection_function in selection_functions:for idx, k in enumerate(Ks):x = np.arange(float(Ks[idx]), 500 + float(Ks[idx]), float(Ks[idx])) Sum = np.array(dic[model_object][selection_function][k][0])for i in range(1, repeats):Sum = Sum + np.array(dic[model_object][selection_function][k][i])mean = Sum / repeatsax.plot(x, mean ,label = model_object + '-' + selection_function + '-' + str(k))ax.legend()ax.set_xlim([50,500])ax.set_ylim([40,100])ax.grid(True)plt.show()models_str = ['SvmModel', 'RfModel', 'LogModel']
selection_functions_str = ['RandomSelection', 'MarginSamplingSelection', 'EntropySelection']
Ks_str = ['250','125','50','25','10']
repeats = 1
random_forest_upper_bound = 97.
svm_upper_bound = 94.
log_upper_bound = 92.47
total_experiments = len(models_str) * len(selection_functions_str) * len(Ks_str) * repeatsprint('So which is the better model? under the stopping condition and hyper parameters - random forest is the winner!')
performance_plot(random_forest_upper_bound, d, ['RfModel'] , selection_functions_str , Ks_str, 1)
performance_plot(svm_upper_bound, d, ['SvmModel'] , selection_functions_str , Ks_str, 1)
performance_plot(log_upper_bound, d, ['LogModel'] , selection_functions_str , Ks_str, 1)

不同样本挑选方式结果对比
通过对比,margin sampling是最好的样本挑选方式
print('So which is the best sample selection function? margin sampling is the winner!')
performance_plot(random_forest_upper_bound, d, ['RfModel'], selection_functions_str , Ks_str, 1)
print()
print('So which is the best k? k=10 is the winner')
performance_plot(random_forest_upper_bound, d, ['RfModel'] , ['MarginSamplingSelection'], Ks_str, 1)
[1] Shay Yehezkel, High Dimensional Statistical Pr
ocess Control and Application, M.Sc Thesis.
[2] Stefan Hosein Active Learning: Curious AI Algorithms