文章目录
- 前言
- 什么是回调函数
- 第0个版本
- 第1个版本
- 第2个版本
- 第3个版本
- 第4个版本
- 第5个版本
- 第6个版本
- 回头解析前言描述的问题
- 1. MethodIntrospector.selectMethods()
- 2. 抽象类MethodIntrospector
- 3. 方法selectMethods()
- 4. 成员变量USER_DECLARED_METHODS
- 5. 方法doWithMethods()
- 6. doWithMethods()方法里调用的getMappingForMethod()方法
- 7. getMappingForMethod()方法里调用的createRequestMappingInfo()
前言
在看Handler时看到了这么语段代码顿时就蒙了
Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> {try {return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);}catch (Throwable ex) {throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" +userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex);}});
经过指点知道这是回调函数,马上来补充一下~
什么是回调函数
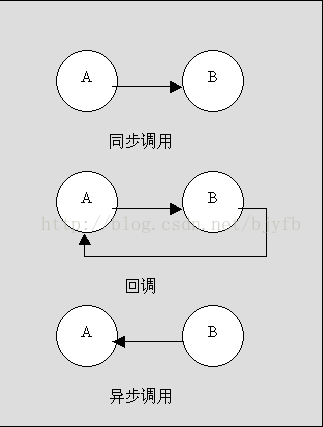
回调函数,是一个通过函数指针调用的函数。如果你把函数的指针(地址)作为参数传递给另一个函数,当这个指针被用来调用其所指向的函数时,我们就说这是回调函数。
在Java中,指针即所谓的引用。回调函数不是由该函数的实现方直接调用,而是在特定的事件或条件发生时由另外的一方调用的,用于对该事件或条件进行响应。
第一次看这知识点,是真的懵。下面看我拆解后逐步理解它的思路。
第0个版本
初代版本
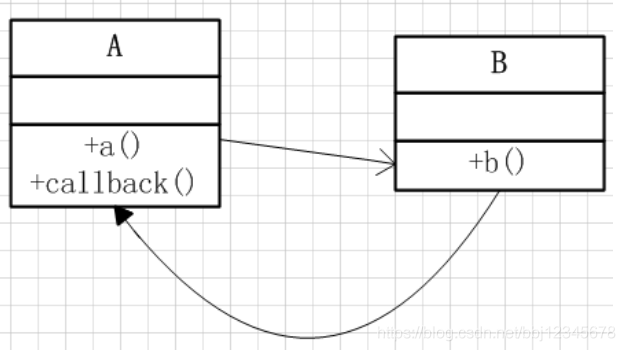
我调用了你,在我调用你的方法里你又调用了我(回调)
public class ClassA {public void a() {System.out.println("执行了a方法");ClassB b = new ClassB();b.b();}public void backs(){System.out.println("A:我就是A的回调函数!");}
}
public class ClassB {public void b() {System.out.println("我执行了b");System.out.println("B:我开始调用A的回调-->");ClassA a = new ClassA();a.backs();System.out.println("B: <--我完成调用A的回调");}
}
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {ClassA a = new ClassA();a.a();}
}
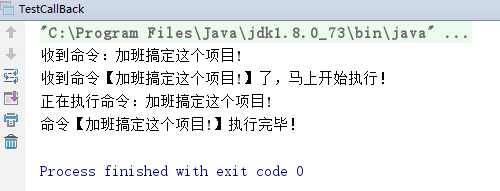
执行结果
执行了a方法
我执行了b
B:我开始调用A的回调-->
A:我就是A的回调函数!
B: <--我完成调用A的回调
第1个版本
演变一下把在B里创建的A,用对象的形式在A里调用时就带过去。
写一个回调用的接口
public class ClassA {public void a() {System.out.println("执行了a方法");ClassB b = new ClassB();b.b(this);}public void backs(){System.out.println("A:我就是A的回调函数!");}
}
public class ClassB {public void b(ClassA a) {System.out.println("我执行了b");System.out.println("B:我开始调用A的回调-->");a.backs();System.out.println("B: <--我完成调用A的回调");}
}
Main方法不用变
执行结果,执行结果不变
执行了a方法
我执行了b
B:我开始调用A的回调-->
A:我就是A的回调函数!
B: <--我完成调用A的回调
第2个版本
把第1个版本中的这个类换成接口Interface
创建一个接口
public interface Interface {public void backs();
}
public class ClassA {public void a() {System.out.println("执行了a方法");ClassB b = new ClassB();b.b(new Interface() {@Overridepublic void backs() {System.out.println("A:我就是A的回调函数!");}});}
}
public class ClassB {public void b(Interface in) {System.out.println("我执行了b");System.out.println("B:我开始调用A的回调-->");in.backs();System.out.println("B: <--我完成调用A的回调");}
}
Main依然不变
执行结果也不变
执行了a方法
我执行了b
B:我开始调用A的回调-->
A:我就是A的回调函数!
B: <--我完成调用A的回调
第3个版本
给接口加一个入参,让回调方法可以传参
public interface Interface {public void backs(String n);
}
public class ClassA {public void a() {System.out.println("执行了a方法");ClassB b = new ClassB();b.b(new Interface() {@Overridepublic void backs(String n) {System.out.println("A:我就是A的回调函数!我打印:" + n);}});}
}
public class ClassB {public void b(Interface in) {System.out.println("我执行了b");System.out.println("B:我开始调用A的回调-->");in.backs("《我是B传的参数》");System.out.println("B: <--我完成调用A的回调");}
}
执行结果
执行了a方法
我执行了b
B:我开始调用A的回调-->
A:我就是A的回调函数!我打印:《我是B传的参数》
B: <--我完成调用A的回调
第4个版本
给接口加个返回的参数
public interface Interface {public String backs(String n);
}
public class ClassA {public void a() {System.out.println("执行了a方法");ClassB b = new ClassB();b.b(new Interface() {@Overridepublic String backs(String n) {System.out.println("A:我就是A的回调函数!我打印:" + n);return "A:我就是A的回调函数!我打印:" + n + "的返回。";}});}
}
public class ClassB {public void b(Interface in) {System.out.println("我执行了b");System.out.println("B:我开始调用A的回调-->");String backs = in.backs("《我是B传的参数》");System.out.println("B:我收到了回调的结果:"+backs);System.out.println("B: <--我完成调用A的回调");}
}
执行结果
执行了a方法
我执行了b
B:我开始调用A的回调-->
A:我就是A的回调函数!我打印:《我是B传的参数》
B:我收到了回调的结果:A:我就是A的回调函数!我打印:《我是B传的参数》的返回。
B: <--我完成调用A的回调
第5个版本
public interface Interface {public String backs(String n);
}
public class ClassA {public void a() {System.out.println("执行了a方法");ClassB b = new ClassB();String b1 = b.b(new Interface() {@Overridepublic String backs(String n) {System.out.println("A:我就是A的回调函数!我打印:" + n);return "A:我就是A的回调函数!我打印:" + n + "的返回。";}});System.out.println("A:执行完得到的结果:" + b1);}
}
public class ClassB {public String b(Interface in) {System.out.println("我执行了b");System.out.println("B:我开始调用A的回调-->");String backs = in.backs("《我是B传的参数》");System.out.println("B:我收到了回调的结果:"+backs + "<--我完成调用A的回调");return "《我是B的返回》";}
}
执行结果:
执行了a方法
我执行了b
B:我开始调用A的回调-->
A:我就是A的回调函数!我打印:《我是B传的参数》
B:我收到了回调的结果:A:我就是A的回调函数!我打印:《我是B传的参数》的返回。<--我完成调用A的回调
A:执行完得到的结果:《我是B的返回》
第6个版本
先声明回调函数,再使用
public class ClassA {public void a() {System.out.println("执行了a方法");Interface in = (n -> {System.out.println("A:我是直接使用回调接口,我接收的参数是:" + n);return "我是回调的返回数据";});String backs = in.backs("我A,我是《in》的使用者");System.out.println("backes:" + backs);}
}
调用
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {ClassA a = new ClassA();a.a();}
}
执行结果
执行了a方法
A:我是直接使用回调接口,我接收的参数是:我A,我是《in》的使用者
backes:我是回调的返回数据
回头解析前言描述的问题
1. MethodIntrospector.selectMethods()
Map<Method, Set<Scheduled>> annotatedMethods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(targetClass,// 接口需要MetadataLookup类型,做一个类型转换。// T:Set<Scheduled>,这个参数是被调用类传过来的。// 看调用代码,点方法selectMethods进去// 里面这句代码为回调 metadataLookup.inspect(specificMethod);// (MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<Set<Scheduled>>) method -> {// 使用方法和类型级别的RequestMapping注解来创建RequestMappingInfo。Set<Scheduled> scheduledMethods = AnnotatedElementUtils.getMergedRepeatableAnnotations(method, Scheduled.class, Schedules.class);return (!scheduledMethods.isEmpty() ? scheduledMethods : null);});
2. 抽象类MethodIntrospector
在这之前先看下这个回调的接口,这是MethodIntrospector类里的内部类
public abstract class MethodIntrospector {public interface MetadataLookup<T> {T inspect(Method method);}
}
3. 方法selectMethods()
public static <T> Map<Method, T> selectMethods(Class<?> targetType, final MetadataLookup<T> metadataLookup) {final Map<Method, T> methodMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();Set<Class<?>> handlerTypes = new LinkedHashSet<>();Class<?> specificHandlerType = null;// 是否是代理类if (!Proxy.isProxyClass(targetType)) {// 通过这个类取到这个类,检测是否是CGLIB 生成的子类,是则返回原始类。specificHandlerType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(targetType);// 添加到set哈希表中handlerTypes.add(specificHandlerType);}// 把这个类的所有接口类添加到set哈希表中handlerTypes.addAll(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetType));for (Class<?> currentHandlerType : handlerTypes) {// 这个不知道为啥,不使用循环里的类。也就是不使用接口,要使用实际的实现类,是这个意思?final Class<?> targetClass = (specificHandlerType != null ? specificHandlerType : currentHandlerType);// 霍,刚那个回调函数还没完成,又来一个。// 3个参数,1-接口或实现类 2-被调函数传过来的 // 3-预构建的 MethodFilter 匹配所有未在java.lang.Object声明的非桥非合成方法。ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(currentHandlerType, method -> {// 从这个类中找到这个方法Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, targetClass);// 再向上回调到调用此方法的类中执行对应的方法,带着这个类。返回的是RequestMappingInfo的对象 /admin/testT result = metadataLookup.inspect(specificMethod);if (result != null) {// 找到提供的bridge Method的原始方法。Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod);if (bridgedMethod == specificMethod || metadataLookup.inspect(bridgedMethod) == null) {methodMap.put(specificMethod, result);}}}, ReflectionUtils.USER_DECLARED_METHODS);}// <Method,RequestMappingInfo>的Mapreturn methodMap;}
4. 成员变量USER_DECLARED_METHODS
// 这里又是一个回调函数的使用,在ReflectionUtils里的成员变量
public static final MethodFilter USER_DECLARED_METHODS =(method -> !method.isBridge() && !method.isSynthetic());// 看下回调接口,这也是个内部类
public abstract class ReflectionUtils {public interface MethodFilter {boolean matches(Method method);}
}
// 理解:这个就是上面没写调用直接使用里面的回调了生成了一个里面只有一个接口的对象,接口里面已经有实现
// 调用这个就是相当于调用了这个方法。
5. 方法doWithMethods()
接selectMethods调用doWithMethods。对给定类和超类(或给定接口和超接口)的所有匹配方法执行给定的回调操作。
public static void doWithMethods(Class<?> clazz, MethodCallback mc, @Nullable MethodFilter mf) {// Keep backing up the inheritance hierarchy.// 缓存下,并该类中的所有方法Method[] methods = getDeclaredMethods(clazz, false);for (Method method : methods) {// 使用回调函数得到的接口对象。判断是否不是桥且不是可执行文件是合成结构 不是跳过if (mf != null && !mf.matches(method)) {// 是桥或是可执行文件跳过continue;}try {// 这个就是调用doWithMethods的回调在调用它的类里执行,传过去的是这个类中的方法mc.doWith(method);}catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {throw new IllegalStateException("Not allowed to access method '" + method.getName() + "': " + ex);}}if (clazz.getSuperclass() != null && (mf != USER_DECLARED_METHODS || clazz.getSuperclass() != Object.class)) {doWithMethods(clazz.getSuperclass(), mc, mf);}else if (clazz.isInterface()) {for (Class<?> superIfc : clazz.getInterfaces()) {doWithMethods(superIfc, mc, mf);}}
}
6. doWithMethods()方法里调用的getMappingForMethod()方法
protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType) {// 根据提供的annotatedElement是类还是方法提供适当的自定义RequestCondition 。// 接收的是一个 AnnotatedElement 类型,// Method 继承 Executable,Executable 实现 GenericDeclaration// GenericDeclaration 继承 AnnotatedElement,可以看下// 创建方法上的 RequestMappingInfoRequestMappingInfo info = createRequestMappingInfo(method);if (info != null) {// 创建方法的类上的 RequestMappingInfoRequestMappingInfo typeInfo = createRequestMappingInfo(handlerType);if (typeInfo != null) {// 把两个 RequestMappingInfo 组合在一起info = typeInfo.combine(info);}String prefix = getPathPrefix(handlerType);if (prefix != null) {info = RequestMappingInfo.paths(prefix).options(this.config).build().combine(info);}}return info;
}
看下效果更深刻
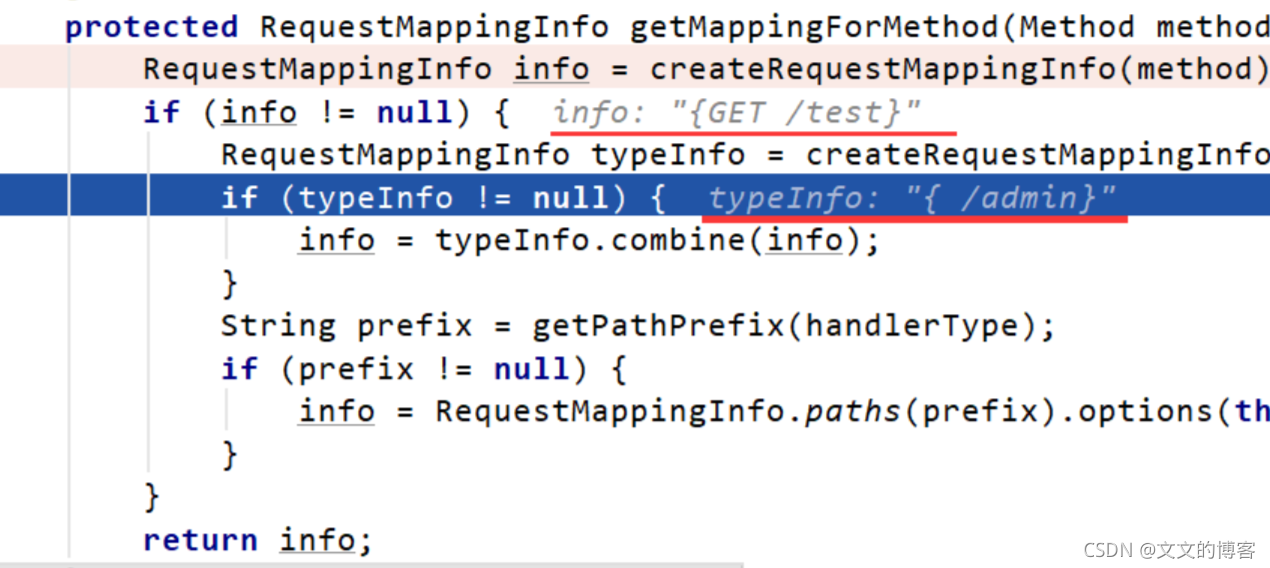
组合
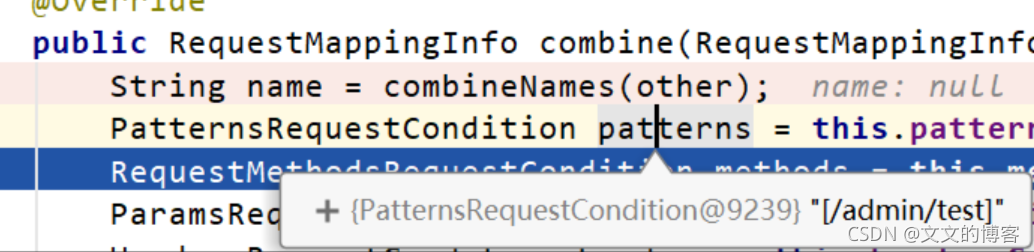
组合完后的RequestMappingInfo
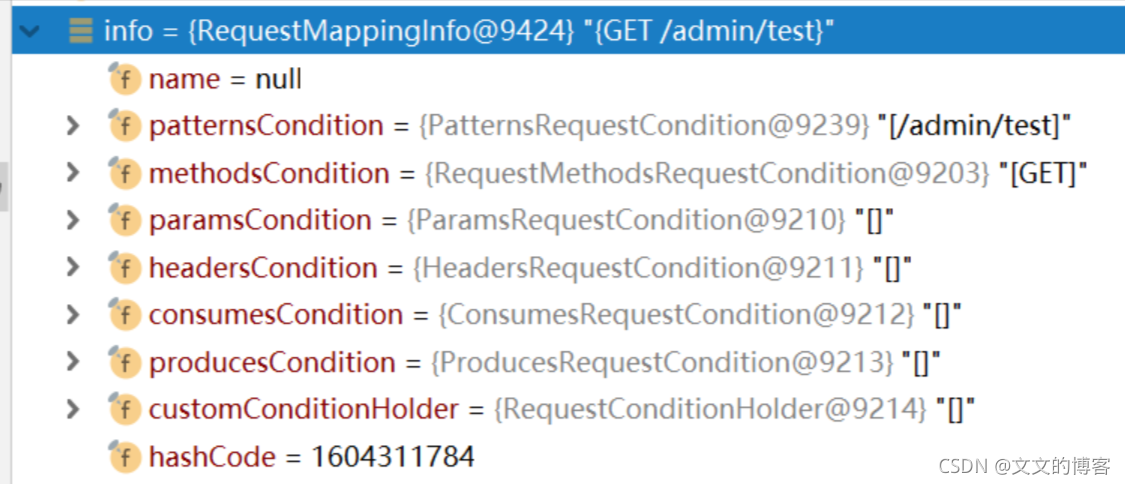
7. getMappingForMethod()方法里调用的createRequestMappingInfo()
private RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(AnnotatedElement element) {// 找到这个方法第一个@RequestMappingRequestMapping requestMapping = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(element, RequestMapping.class);// 两个方法都是返回的null,看上去能被覆盖。不过这个启动没有直接返回的null,所以condition是nullRequestCondition<?> condition = (element instanceof Class ?getCustomTypeCondition((Class<?>) element) : getCustomMethodCondition((Method) element));// 生成RequestMappingInfo对象return (requestMapping != null ? createRequestMappingInfo(requestMapping, condition) : null);
}
好奇,find什么样
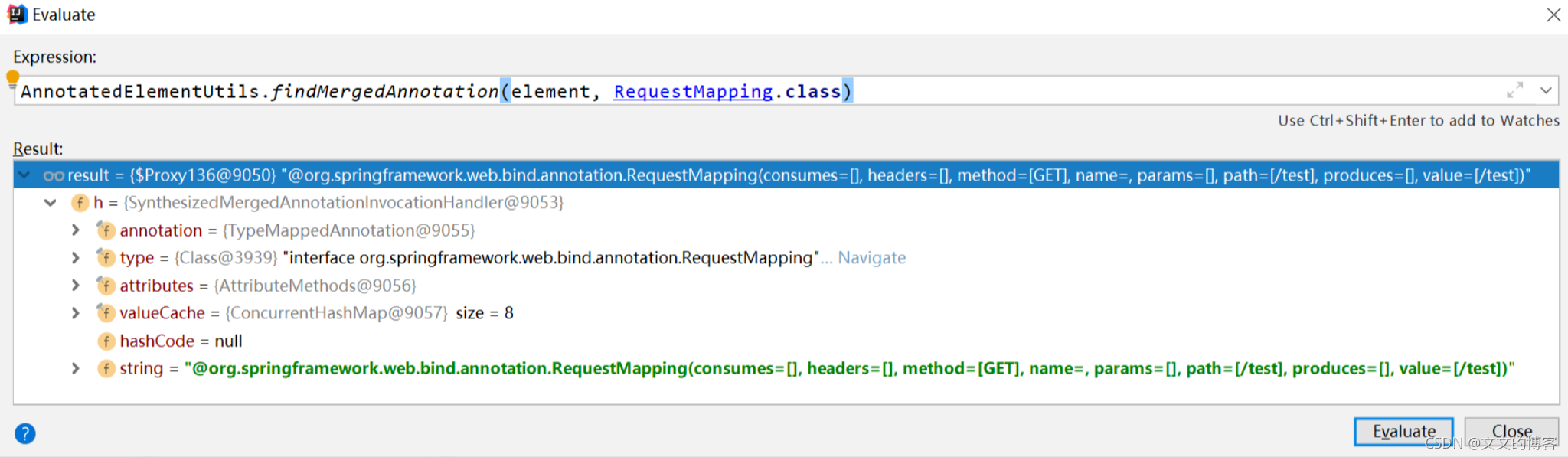
实际我这个方法我怎么标记的?
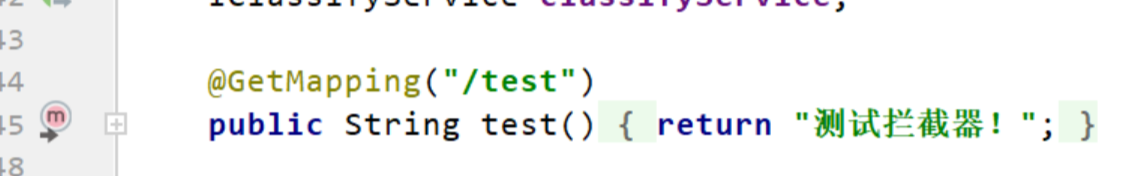
调用创建RequestMappingInfo的构造
protected RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(RequestMapping requestMapping, @Nullable RequestCondition<?> customCondition) {RequestMappingInfo.Builder builder = RequestMappingInfo.paths(resolveEmbeddedValuesInPatterns(requestMapping.path())).methods(requestMapping.method()).params(requestMapping.params()).headers(requestMapping.headers()).consumes(requestMapping.consumes()).produces(requestMapping.produces()).mappingName(requestMapping.name());if (customCondition != null) {builder.customCondition(customCondition);}return builder.options(this.config).build();
}
创建完长这样
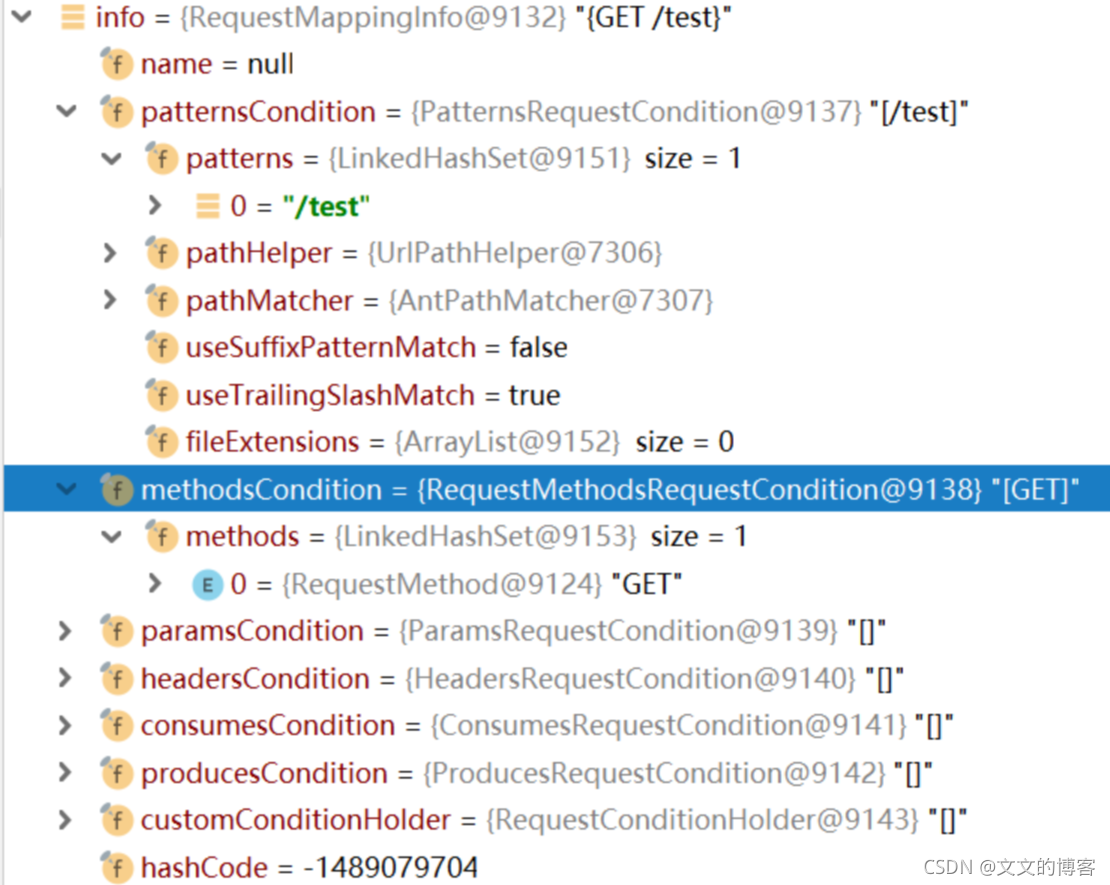
结言
所以最后的结果就是把这个类下所有方法标RequestMapping注解的方法以<Method,RequestMappingInfo>放入Map
全文完~
文文的博客,博学躬行。欢迎指正~