vuex工作原理与流程
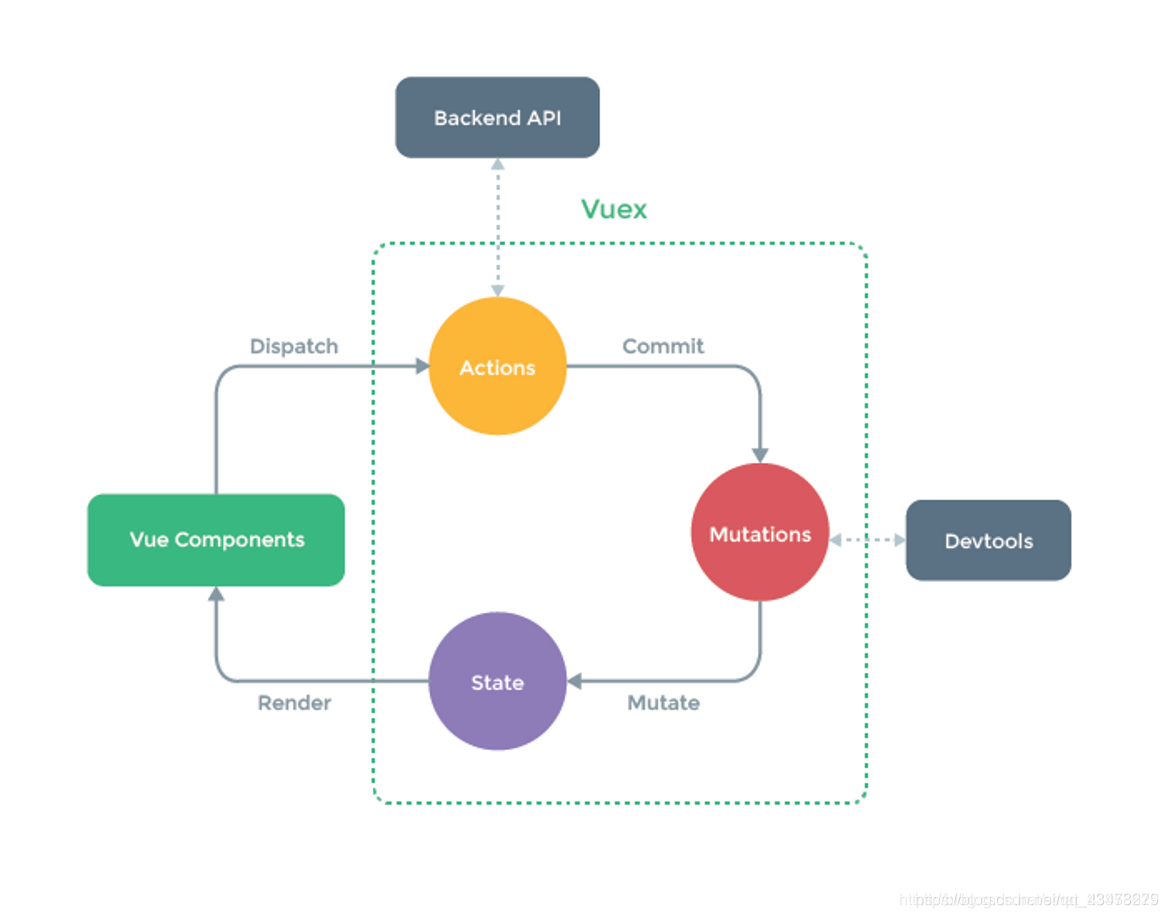
Vue组件(action里面的dispatch )--> actions(commit方法) -->mutations(Mutate)--> state(getter) -->store更新所有调用vuex的组件(Vue Component组件)
1、state
存储应用状态数据的对象,与vue组件中data类似
state的值可以是对象,也可以是返回对象的函数
通过store.state访问状态数据
示例如下:
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex);
//必须在使用vuex之后去创建store
let store = new Vuex.Store({state: {},getters: {},mutations: {},actions: {}
})
//创建state
let state = _=>({a:1})
const store = new Vuex.Store({state
})const store2 = new Vuex.Store({state
})
console.log(store.state == store2.state);
store.state.a = 100;
console.log(store.state.a, store2.state.a);// store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import state from './state'
Vue.use(Vuex);
const store = new Vuex.Store({state
})export default store;
// 在组件中使用state
// stores/state.js
export default () => ({title: '骄阳似火',content: '来杯冷饮吧'
})
<!--Home.vue-->
<template><div class="home"><h2>{{title}}</h2><div>{{content}}</div></div>
</template>
<script>
import store from '@/store'
export default {name: 'home',data() {return {title: store.state.title,content: store.state.content}}
}
</script>
注意:
- 使用函数的方式返回对象,每次返回的都是新的实例对象,而它们的引用地址不同,就避免了修改data数据时,组件相互影响的问题。
- state更新了视图却没有更新,钩子函数未触发导致。使用computed来解决,如下:
<template><div class="home"><h2>{{title}}</h2><div>{{content}}</div></div>
</template>
<script>
import store from '@/store'
export default {name: 'Home',computed: {title() {return store.state.title},content() {return store.state.content}}
}
</script>
2、getters
从state中派生的状态数据
接收state作为第一个参数,第二个为可选参数
类似组件中的 computed,派生数据,在数据出门后进行的加工(对原数据再加工,计算后的结果),这些处理都在getters中
3、mutations
提交mutation来修改store中的状态,同步操作
每个mutation都有一个字符串事件类型(type)与一个回调函数(handler),在回调函数中修改状态
注意:
- 不能直接去调用mutation的回调函数,需要当mutation类型为increment时,才能调用此函数
- mutation必须是同步的
- 在store中初始化时设置好所有的属性
4、actions
与mutations类似,提交修改state的行为,处理异步任务
注意:
- 提交的是mutation,不是直接修改状态
- 可以包含任意异步操作
5、modules
将store分割成模块
每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getters,
模块还可以嵌套子模块——从上至下进行类似的分割
注意:
- 将当前业务所需内容 封装到独立的js文件中,以对象的形式导出
- 在index.js(主控), 的modules中 注册模块
- 组件中使用具体方法时,需要注意语法规范

综合示例
Home.vue
<template><div class="home"><h2>this is an home page</h2><hr><div class="addBox"><!-- 给input框添加一个ref标识newUser --><input type="text" ref="newUser" id="inputName"><button @click="addUsers">添加新用户</button><div v-show="msg">{{msg}}</div></div><ul><li v-for="(user,index) of users" :key="index">{{user.id}}-{{user.username}}-{{user.gender}}</li></ul><hr><ul class="ulist"><li v-for="(user) of sortUsers"><span>ID:{{user.id}}, 姓名:{{user.username}}</span></li></ul><hr><button @click="sortData=!sortData">排序</button></div>
</template><script>export default {name: 'Home',data() {return {sortData: true,msg: ""}},computed: {users() {// console.log(this.$store.state.showUsers);// vuex中,要对数据加工(计算)都在getters中,通过getters获取showUsersreturn this.$store.getters.showUsers;},sortUsers() {//index.js文件中的getters里面,showSortUsers()函数内返回值封装成一个函数,这里可以调用showSortUsers方法,还可以给它传参数 return this.$store.getters.showSortUsers(this.sortData);}},methods: {/* commit:同步操作,写法:this.$store.commit('mutations方法名',值)dispatch:含有异步操作,比如向后台提交数据,写法: this.$store.dispatch('action方法名',值)*/// addUsers() {/* 通过commit提交操作到mutations对应的方法中commit方法有两个参数 参数1:方法名 参数2:需要的参数 */// 通过$refs获取我们标识过的input框输入的值// console.log(this.$refs.newUser.value);// 通过commit方法提交的addUsers()这个方法与index.js中mutations中的方法名对应// this.$store.commit("addUsers",this.$refs.newUser.value);// 以对象的方式提交// 这里payload传的是个对象,添加后,页面会出现像这样的效果{6,"柯南","男"}// 所以在index.js的mutations中的方法这样写addUsers(state, {payload}) { //将payload解构成对象 }/* this.$store.commit({type:"addUsers",payload:this.$refs.newUser.value}); */// 异步操作:dispatch提交到actionsasync addUsers() {this.msg = ""; //输入框提示信息try {let rs = await this.$store.dispatch({type: "addUsers",//传入实参payload: this.$refs.newUser.value});this.msg = rs;} catch (error) {this.msg = error;}// 每次添加完后将input框内容清空this.$refs.newUser.value = "";}}}
</script>
<style scoped>ul {padding: 0;margin-left: 45%;}ul li {width: 120px;list-style: none;text-align: left;}.addBox input {line-height: 19px;margin-top: 2px;margin-right: 5px;}
</style>
index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'Vue.use(Vuex);let nextID = 5;//写在外面也可以获取到
export default new Vuex.Store({state: {title: "骄阳如火",content: "春天已经远去,夏日款款走来",userGender: "",// nextID:5,//不要在组件中直接去修改数据源(数据私密,不能随意修改)users: [{ id: 1, username: "jack", gender: "男", checked: false },{ id: 2, username: "tom", gender: "男", checked: false },{ id: 3, username: "lucy", gender: "女", checked: false },{ id: 4, username: "mary", gender: "女", checked: false },{ id: 5, username: "john", gender: "男", checked: false }],},// 类似组件中的 computed,派生数据,在数据出门后进行的加工(对原数据再加工,计算后的结果),这些处理都在getters中getters: {// 筛选数据 // showUsers:function(){}showUsers({ users, userGender }) {// 返回筛选后的数据return '' === userGender ? users : users.filter(users => users.id);},// 排序showSortUsers({ users }) {// 返回排序后的数据// 对新数组操作,原数组不变,深拷贝//这里返回的是计算结果,在组件中是获取,而不能直接调用// return [...users].sort((a,b)=>{// // 排序的方式(顺序或者倒序)// return a.id - b.id// });//返回 一个带参数sort的函数,在组件中可以直接调用showSortUsers函数return (sort = true) => {//返回排序后(按照id大小)的结果return [...users].sort((a, b) => {// a.id - b.id 从低到高排序// b.id - a.id 从高到低排序// 如何排序后的结果return sort ? a.id - b.id : b.id - a.id;});}}},// 直接操作数据源:// (1)会把异步操作当成同步处理 // (2)无法拿到异步处理的结果(源码中没有异步的机制)// 注意:对state中数据的操作:添加、删除、修改按照js方式操作即可/* mutations中的方法,接收两个参数 参数1:state 当前的store仓库参数2:通过commit方法传过来的数据*/mutations: {//因为组件方法中payload是存在对象中的,这里要以对象的形式结构出来addUsers(state, payload) {// 将新数据以对象的形式添加进来state.users.push({id: ++nextID,username: payload,gender: '男',checked: false});}},// 异步处理在actions中,然后通过commit提交给mutation// actions中的方法,第一个参数默认是store// 将store解构成一个对象{state},下面调用方法时直接可以用stateactions: {//paylod是input输入框的值,使用addUsers({state,commit}, {payload} ) {// Promise帮助处理异步操作return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {setTimeout(() => {// 不允许用户重名(两次输入相同的用户名或者输入users数据中已有的用户名,不能添加,并给出用户名已存在的提示)if (state.users.find(user => user.username === payload)) {reject("该用户已存在");} else {//这里payload直接作为属性值传过去的,所以actions中方法addUsers()中的参数payload不需要解构了commit("addUsers", payload);// 添加成功resolve("新用户添加成功");}}, 1000);});// 模拟异步// setTimeout(() => {// if (state.users.find(user => user.username===payload)) {// return;// } else {// // 将新数据以对象的形式添加进来// state.users.push({// id: ++nextID,// username: payload,// gender: '男',// checked: false// });// }// }, 1000);}},// 模块化()modules: {}
});