9.3 pgrep:查找匹配条件的进程
9.3.1 命令详解
【命令星级】 ★★★★☆
【功能说明】
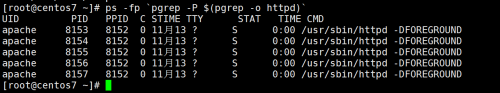
pgrep命令可以查找匹配条件的进程号。
【语法格式】
pgrep [option] [pattern]
pgrep [选项] [匹配添加]
**说明:**在pgrep命令及后面的选项和匹配条件里,每个元素之间都至少要有一个空格。
【选项说明】
表9-3针对该命令的参数选项进行了说明。
表9-3 pgrep命令的参数选项及说明

9.3.2 使用范例
**范例9-11:**显示直接进程的pid命令。
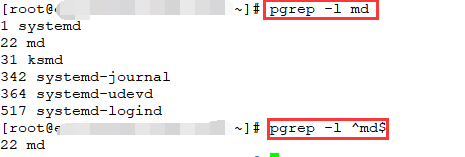
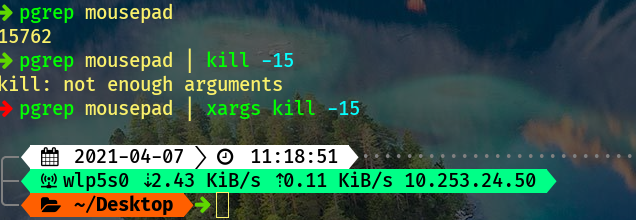
[root@centos7 ~]# pgrep crond#pgrep命令可以看作ps命令和grep命令的结合,pgrep命令指定过滤crond字段,获取到crond进程的进程号。
858
**范例9-12:**显示指定用户的所有进程号。
[root@centos7 ~]# pgrep -u root#使用-u选项显示指定root用户的所有进程号。
1
2
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
30
31
32
33
41
43
44
45
47
60
97
103
223
235
236
237
238
243
244
246
247
248
249
254
255
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
369
399
529
530
531
532
533
534
535
536
743
825
829
830
832
833
854
858
877
982
1311
1313
1314
1475
2029
2089
2140
2146
2189
9.4 kill:终止进程
9.4.1 命令详解
【命令星级】 ★★★★★
【功能说明】
kill命令能够终止你希望停止的进程。
【语法格式】
kill [option] [pid]
kill [选项] [进程号]
**说明:**在kill命令及后面的选项和进程号里,每个元素之间都至少要有一个空格。
【选项说明】
表9-4针对该命令的参数选项进行了说明。
表9-4 kill命令的参数选项及说明

9.4.2 使用范例
**范例9-13:**列出所有信号的名称。
[root@centos7 ~]# kill -l #参数-l显示系统的所有信号。1) SIGHUP 2) SIGINT 3) SIGQUIT 4) SIGILL 5) SIGTRAP6) SIGABRT 7) SIGBUS 8) SIGFPE 9) SIGKILL 10) SIGUSR1
11) SIGSEGV 12) SIGUSR2 13) SIGPIPE 14) SIGALRM 15) SIGTERM
16) SIGSTKFLT 17) SIGCHLD 18) SIGCONT 19) SIGSTOP 20) SIGTSTP
21) SIGTTIN 22) SIGTTOU 23) SIGURG 24) SIGXCPU 25) SIGXFSZ
26) SIGVTALRM 27) SIGPROF 28) SIGWINCH 29) SIGIO 30) SIGPWR
31) SIGSYS 34) SIGRTMIN 35) SIGRTMIN+1 36) SIGRTMIN+2 37) SIGRTMIN+3
38) SIGRTMIN+4 39) SIGRTMIN+5 40) SIGRTMIN+6 41) SIGRTMIN+7 42) SIGRTMIN+8
43) SIGRTMIN+9 44) SIGRTMIN+10 45) SIGRTMIN+11 46) SIGRTMIN+12 47) SIGRTMIN+13
48) SIGRTMIN+14 49) SIGRTMIN+15 50) SIGRTMAX-14 51) SIGRTMAX-13 52) SIGRTMAX-12
53) SIGRTMAX-11 54) SIGRTMAX-10 55) SIGRTMAX-9 56) SIGRTMAX-8 57) SIGRTMAX-7
58) SIGRTMAX-6 59) SIGRTMAX-5 60) SIGRTMAX-4 61) SIGRTMAX-3 62) SIGRTMAX-2
63) SIGRTMAX-1 64) SIGRTMAX [root@centos6 ~]# kill -l SIGKILL #可以使用-l参数对信号名和数字信号互换。
9
[root@centos6 ~]# kill -l 9
KILL
表9-5对常用信号进行了说明。
表9-5 常用信号

更多细节请参考signal在线手册的第七部分(man 7 signal)。
**范例9-14:**终止进程。
kill指令默认使用的信号为15,用于结束进程。如果进程忽略此信号,则可以使用信号9强制终止进程。
一般是先通过ps等命令获取到要终止的进程号,然后直接使用“kill 进程号”就可以了。
kill 2203 #kill命令默认使用的信号为15,这种格式也是最常用的。
kill -s 15 2203 #这种格式使用-s参数明确指定发送值为15的信号,效果和kill 2203一样。
kill -15 2203 #上面的-s 15可以简写为-15。
如果用上面的方法还是无法终止进程,那么我们就可以用KILL(9)信号强制终止进程。
kill -9 2203 #信号9会强行终止进程,这会带来一些副作用,如数据丢失,或者终端无法恢复到正常状态等,因此应尽量避免使用,除非进场使用其他信号无法终止。
9.4.3 扩展:特殊信号0的应用案例
在kill的所有信号中,有一个十分特殊的信号值0,使用格式为kill -0 p i d 。其中的 − 0 表示不发送任何信号给 pid。其中的-0表示不发送任何信号给 pid。其中的−0表示不发送任何信号给pid对应的进程,但是仍然会对 p i d 是否存在对应的进程进行检查,如果 pid是否存在对应的进程进行检查,如果 pid是否存在对应的进程进行检查,如果pid对应的进程已存在,则返回0,若不存在则返回1.下面是系统参考脚本/etc/init.d/mysqld。
[root@centos6 ~]# cat /etc/init.d/mysqld
#!/bin/sh
#
# mysqld This shell script takes care of starting and stopping
# the MySQL subsystem (mysqld).
#
# chkconfig: - 64 36
# description: MySQL database server.
# processname: mysqld
# config: /etc/my.cnf
# pidfile: /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: mysqld
# Required-Start: $local_fs $remote_fs $network $named $syslog $time
# Required-Stop: $local_fs $remote_fs $network $named $syslog $time
# Short-Description: start and stop MySQL server
# Description: MySQL database server
### END INIT INFO# Source function library.
. /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions# Source networking configuration.
. /etc/sysconfig/networkexec="/usr/bin/mysqld_safe"
prog="mysqld"# Set timeouts here so they can be overridden from /etc/sysconfig/mysqld
STARTTIMEOUT=120
STOPTIMEOUT=60[ -e /etc/sysconfig/$prog ] && . /etc/sysconfig/$proglockfile=/var/lock/subsys/$prog# extract value of a MySQL option from config files
# Usage: get_mysql_option SECTION VARNAME DEFAULT
# result is returned in $result
# We use my_print_defaults which prints all options from multiple files,
# with the more specific ones later; hence take the last match.
get_mysql_option(){result=`/usr/bin/my_print_defaults "$1" | sed -n "s/^--$2=//p" | tail -n 1`if [ -z "$result" ]; then# not found, use defaultresult="$3"fi
}get_mysql_option mysqld datadir "/var/lib/mysql"
datadir="$result"
get_mysql_option mysqld socket "$datadir/mysql.sock"
socketfile="$result"
get_mysql_option mysqld_safe log-error "/var/log/mysqld.log"
errlogfile="$result"
get_mysql_option mysqld_safe pid-file "/var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid"
mypidfile="$result"start(){[ -x $exec ] || exit 5# check to see if it's already runningMYSQLDRUNNING=0if [ -f "$mypidfile" ]; thenMYSQLPID=`cat "$mypidfile" 2>/dev/null`if [ -n "$MYSQLPID" ] && [ -d "/proc/$MYSQLPID" ] ; thenMYSQLDRUNNING=1fifiRESPONSE=`/usr/bin/mysqladmin --socket="$socketfile" --user=UNKNOWN_MYSQL_USER ping 2>&1`if [ $MYSQLDRUNNING = 1 ] && [ $? = 0 ]; then# already running, do nothingaction $"Starting $prog: " /bin/trueret=0elif [ $MYSQLDRUNNING = 1 ] && echo "$RESPONSE" | grep -q "Access denied for user"then# already running, do nothingaction $"Starting $prog: " /bin/trueret=0else# prepare for starttouch "$errlogfile" 2>/dev/nullif [ $? -ne 0 ]; then# failed to touch log file, probably insufficient permissionsaction $"Starting $prog: " /bin/falsereturn 4fichown mysql:mysql "$errlogfile" chmod 0640 "$errlogfile"[ -x /sbin/restorecon ] && /sbin/restorecon "$errlogfile"if [ ! -d "$datadir/mysql" ] ; then# First, make sure $datadir is there with correct permissionsif [ ! -e "$datadir" -a ! -h "$datadir" ]thenmkdir -p "$datadir" || exit 1fichown mysql:mysql "$datadir"chmod 0755 "$datadir"[ -x /sbin/restorecon ] && /sbin/restorecon "$datadir"# Now create the databaseaction $"Initializing MySQL database: " /usr/bin/mysql_install_db --datadir="$datadir" --user=mysqlret=$?chown -R mysql:mysql "$datadir"if [ $ret -ne 0 ] ; thenreturn $retfifichown mysql:mysql "$datadir"chmod 0755 "$datadir"# We check if there is already a process using the socket file,# since otherwise this init script could report false positive# result and mysqld_safe would remove the socket file, which# actually uses a different daemon.if fuser "$socketfile" &>/dev/null ; thenecho "Socket file $socketfile exists. Is another MySQL daemon already running with the same unix socket?"action $"Starting $prog: " /bin/falsereturn 1fi# Pass all the options determined above, to ensure consistent behavior.# In many cases mysqld_safe would arrive at the same conclusions anyway# but we need to be sure. (An exception is that we don't force the# log-error setting, since this script doesn't really depend on that,# and some users might prefer to configure logging to syslog.)# Note: set --basedir to prevent probes that might trigger SELinux# alarms, per bug #547485$exec --datadir="$datadir" --socket="$socketfile" \--pid-file="$mypidfile" \--basedir=/usr --user=mysql >/dev/null 2>&1 &safe_pid=$!# Spin for a maximum of N seconds waiting for the server to come up;# exit the loop immediately if mysqld_safe process disappears.# Rather than assuming we know a valid username, accept an "access# denied" response as meaning the server is functioning.ret=0TIMEOUT="$STARTTIMEOUT"while [ $TIMEOUT -gt 0 ]; doRESPONSE=`/usr/bin/mysqladmin --socket="$socketfile" --user=UNKNOWN_MYSQL_USER ping 2>&1`mret=$?if [ $mret -eq 0 ]; thenbreakfi# exit codes 1, 11 (EXIT_CANNOT_CONNECT_TO_SERVICE) are expected,# anything else suggests a configuration errorif [ $mret -ne 1 -a $mret -ne 11 ]; thenecho "$RESPONSE"echo "Cannot check for MySQL Daemon startup because of mysqladmin failure."ret=1breakfiecho "$RESPONSE" | grep -q "Access denied for user" && breakif ! /bin/kill -0 $safe_pid 2>/dev/null;
#验证$safe_pid值对应的进程是否存在。
thenecho "MySQL Daemon failed to start."ret=1breakfisleep 1let TIMEOUT=${TIMEOUT}-1doneif [ $TIMEOUT -eq 0 ]; thenecho "Timeout error occurred trying to start MySQL Daemon."ret=1fiif [ $ret -eq 0 ]; thenaction $"Starting $prog: " /bin/truechmod o+r $mypidfile >/dev/null 2>&1touch $lockfileelseaction $"Starting $prog: " /bin/falsefifireturn $ret
}stop(){if [ ! -f "$mypidfile" ]; then# not running; per LSB standards this is "ok"action $"Stopping $prog: " /bin/truereturn 0fiMYSQLPID=`cat "$mypidfile" 2>/dev/null`if [ -n "$MYSQLPID" ]; then/bin/kill "$MYSQLPID" >/dev/null 2>&1ret=$?if [ $ret -eq 0 ]; thenTIMEOUT="$STOPTIMEOUT"while [ $TIMEOUT -gt 0 ]; do/bin/kill -0 "$MYSQLPID" >/dev/null 2>&1 || breaksleep 1let TIMEOUT=${TIMEOUT}-1doneif [ $TIMEOUT -eq 0 ]; thenecho "Timeout error occurred trying to stop MySQL Daemon."ret=1action $"Stopping $prog: " /bin/falseelserm -f $lockfilerm -f "$socketfile"action $"Stopping $prog: " /bin/truefielseaction $"Stopping $prog: " /bin/falsefielse# failed to read pidfile, probably insufficient permissionsaction $"Stopping $prog: " /bin/falseret=4fireturn $ret
}restart(){stopstart
}condrestart(){[ -e $lockfile ] && restart || :
}# See how we were called.
case "$1" instart)start;;stop)stop;;status)status -p "$mypidfile" $prog;;restart)restart;;condrestart|try-restart)condrestart;;reload)exit 3;;force-reload)restart;;*)echo $"Usage: $0 {start|stop|status|restart|condrestart|try-restart|reload|force-reload}"exit 2
esacexit $?
应用:大家如果想要写一个管理系统服务的脚本,则可以使用这个技巧。