1.概念
LRU是Least Recently Used的缩写,意思是最近最少使用,它是一种Cache替换算法。
Cache的容量有限,因此当Cache的容量用完后,而又有新的内容需要添加进来时, 就需要挑选并舍弃原有的部分内容,从而腾出空间来放新内容。LRU Cache 的替换原则就是将最近最少使用的内容替换掉。其实,LRU译成最久未使用会更形象, 因为该算法每次替换掉的就是一段时间内最久没有使用过的内容。
2.LRUCache的实现原理
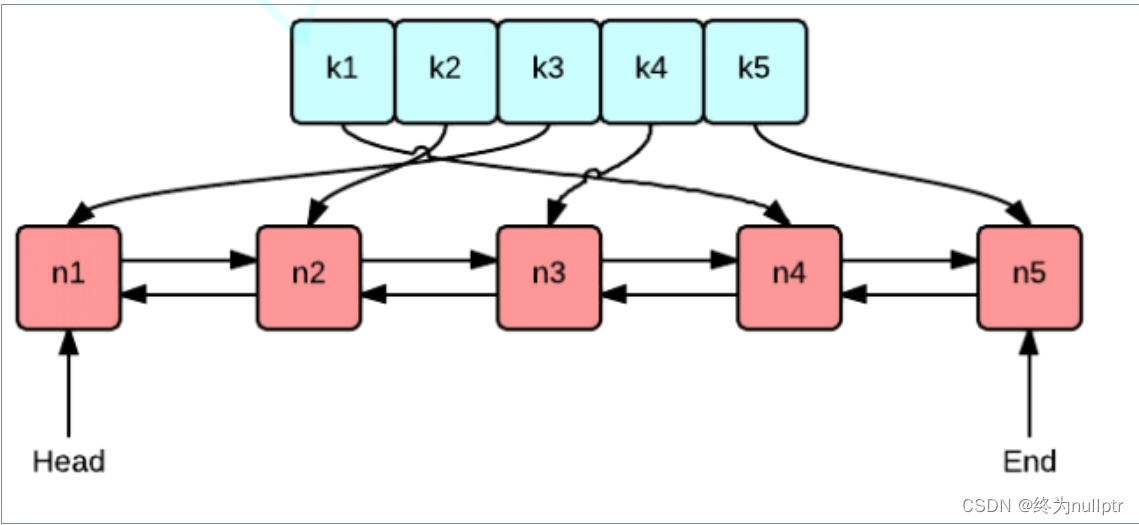
实现LRU Cache的方法和思路很多,但是要保持高效实现O(1)的put和get,那么使用双向链表和哈希表的搭配是最高效和经典的。
使用双向链表是因为双向链表可以实现任意位置O(1)的插入和删除,
使用哈希表是因为哈希表的增删查改也是O(1)。
package test;import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;class Node {public int key;public int val;public Node prev;public Node next;public Node() {}public Node(int key, int val) {this.key = key;this.val = val;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Node{" +"key=" + key +", val=" + val +'}';}
}public class MyLRUCache {public Node head;public Node tail;public int usedsize;public Map<Integer, Node> cache;public int capacity;public MyLRUCache(int capacity) {this.head = new Node();this.tail = new Node();head.next = tail;tail.prev = head;cache = new HashMap<>();this.capacity = capacity;}//插入元素public void put(int key, int val) {Node node = cache.get(key);if (node == null) {Node newnode = new Node(key, val);cache.put(key, newnode);addToTail(newnode);usedsize++;//检查当前双向链表的有效数据个数 是不是超过了capacityif (usedsize > capacity) {Node removeNode = removeHead();cache.remove(removeNode.key);usedsize--;}printNodes("put");} else {//更新val的值,其实没必要node.val = val;moveTotail(node);}}//删除指定节点public void removeNode(Node node) {node.prev.next = node.next;node.next.prev = node.prev;}//移动当前节点到尾巴节点public void moveTotail(Node node) {removeNode(node);addToTail(node);}//添加到尾巴节点public void addToTail(Node node) {tail.prev.next = node;node.prev = tail.prev;node.next = tail;tail.prev = node;}//删除最近没使用的头结点public Node removeHead() {Node del = head.next;head.next = del.next;del.next.prev = head;return del;}//访问当前的key 把你访问的节点放到尾巴public int get(int key) {Node node = cache.get(key);if (node == null) {return -1;}//把最近使用的放到了尾巴moveTotail(node);printNodes("get");return node.val;}public void printNodes(String str) {System.out.println(str + " ");Node cur = head.next;while (cur != tail) {System.out.print(cur + " ");cur = cur.next;}System.out.println();}public static void main(String[] args) {MyLRUCache myLRUCache = new MyLRUCache(3);myLRUCache.put(100, 1);myLRUCache.put(200, 2);myLRUCache.put(300, 3);System.out.println("获取元素");myLRUCache.get(200);myLRUCache.get(100);System.out.println("存放元素,会删除头结点,因为头节点是最近最少使用的");myLRUCache.put(999, 9);}
}
3.jdk当中LRUCache被封装到了LinkedHashMap
package test;import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;public class LRUCache extends LinkedHashMap<String, Integer> {public int capacity;public LRUCache(int capacity) {super(capacity, 0.75f, true);this.capacity = capacity;}@Overridepublic Integer get(Object key) {return super.getOrDefault(key, -1);}@Overridepublic Integer put(String key, Integer value) {return super.put(key, value);}@Overrideprotected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<String, Integer> eldest) {return size() > capacity;}public static void main(String[] args) {LRUCache lruCache = new LRUCache(3);lruCache.put("a", 1);lruCache.put("b", 2);lruCache.put("c", 3);System.out.println(lruCache);System.out.println("获取元素");System.out.println(lruCache.get("b"));System.out.println(lruCache);System.out.println(lruCache.get("a"));System.out.println(lruCache);System.out.println("存放元素,会删除头结点,因为头结点是最近最少使用的");lruCache.put("d", 4);System.out.println(lruCache);}public static void main2(String[] args) {LinkedHashMap<String, Integer> linkedHashMap =new LinkedHashMap<String, Integer>(16, 0.7f, true);linkedHashMap.put("a", 1);linkedHashMap.put("b", 2);linkedHashMap.put("c", 3);System.out.println(linkedHashMap);System.out.println("获取元素");System.out.println(linkedHashMap.get("a"));System.out.println(linkedHashMap);System.out.println(linkedHashMap.get("b"));System.out.println(linkedHashMap);System.out.println(linkedHashMap.get("c"));System.out.println(linkedHashMap);//把常用的数据放到了尾巴 不常用的放在头部便于删除}public static void main1(String[] args) {LinkedHashMap<String, Integer> linkedHashMap =new LinkedHashMap<String, Integer>(16, 0.7f, false);linkedHashMap.put("a", 1);linkedHashMap.put("b", 2);linkedHashMap.put("c", 3);System.out.println(linkedHashMap);System.out.println("获取元素");System.out.println(linkedHashMap.get("a"));System.out.println(linkedHashMap);}
}
4.LRU缓存

class Node {public int key;public int val;public Node prev;public Node next;public Node() {}public Node(int key, int val) {this.key = key;this.val = val;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Node{" +"key=" + key +", val=" + val +'}';}
}public class LRUCache {public Node head;public Node tail;public int usedsize;public Map<Integer, Node> cache;public int capacity;public LRUCache(int capacity) {this.head = new Node();this.tail = new Node();head.next = tail;tail.prev = head;cache = new HashMap<>();this.capacity = capacity;}//插入元素public void put(int key, int val) {Node node = cache.get(key);if (node == null) {Node newnode = new Node(key, val);cache.put(key, newnode);addToTail(newnode);usedsize++;//检查当前双向链表的有效数据个数 是不是超过了capacityif (usedsize > capacity) {Node removeNode = removeHead();cache.remove(removeNode.key);usedsize--;}} else {//更新val的值,其实没必要node.val = val;moveTotail(node);}}//删除指定节点public void removeNode(Node node) {node.prev.next = node.next;node.next.prev = node.prev;}//移动当前节点到尾巴节点public void moveTotail(Node node) {removeNode(node);addToTail(node);}//添加到尾巴节点public void addToTail(Node node) {tail.prev.next = node;node.prev = tail.prev;node.next = tail;tail.prev = node;}//删除最近没使用的头结点public Node removeHead() {Node del = head.next;head.next = del.next;del.next.prev = head;return del;}//访问当前的key 把你访问的节点放到尾巴public int get(int key) {Node node = cache.get(key);if (node == null) {return -1;}//把最近使用的放到了尾巴moveTotail(node);return node.val;}public void printNodes(String str) {System.out.println(str + " ");Node cur = head.next;while (cur != tail) {System.out.print(cur + " ");cur = cur.next;}System.out.println();}
}