Java 递归 跳出死循环
学习了知道树形数据,如何遍历子集,生成List数据,如果数据里面是带各种循环的呢? 要如何处理? 如何跳出死循环?
要求:
根据当前环节id,比如18,找到前置路径: 17到11; 或是14的前置路径: 13,12,11
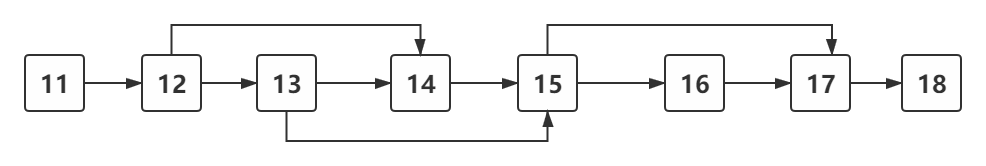
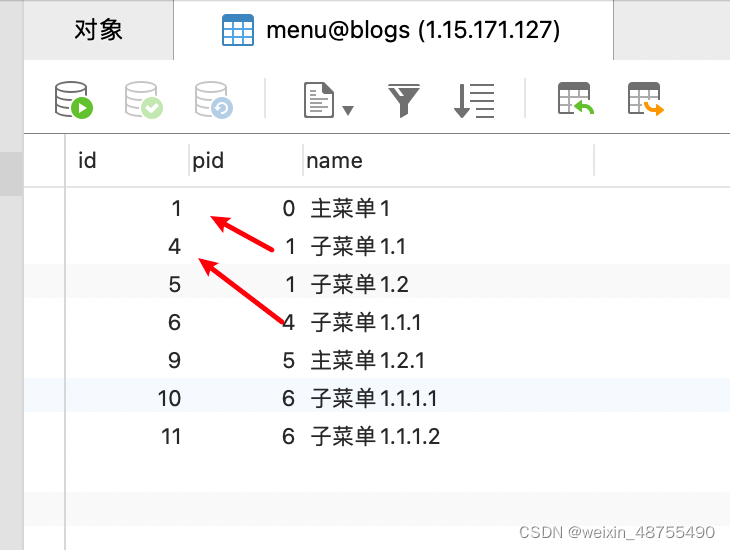
数据是树形变成后的List数据:
[{"TCH_MOD": 11,"NEXT_TCH_MOD": 12
}, {"TCH_MOD": 12,"NEXT_TCH_MOD": 13
}, {"TCH_MOD": 13,"NEXT_TCH_MOD": 14
}, {"TCH_MOD": 14,"NEXT_TCH_MOD": 15
}, {"TCH_MOD": 15,"NEXT_TCH_MOD": 16
}, {"TCH_MOD": 16,"NEXT_TCH_MOD": 17
}, {"TCH_MOD": 17,"NEXT_TCH_MOD": 18
}, {"TCH_MOD": 12,"NEXT_TCH_MOD": 14
}, {"TCH_MOD": 13,"NEXT_TCH_MOD": 15
}, {"TCH_MOD": 15,"NEXT_TCH_MOD": 17
}]
思路:
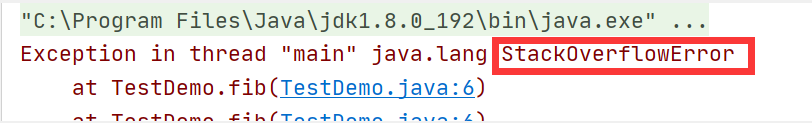
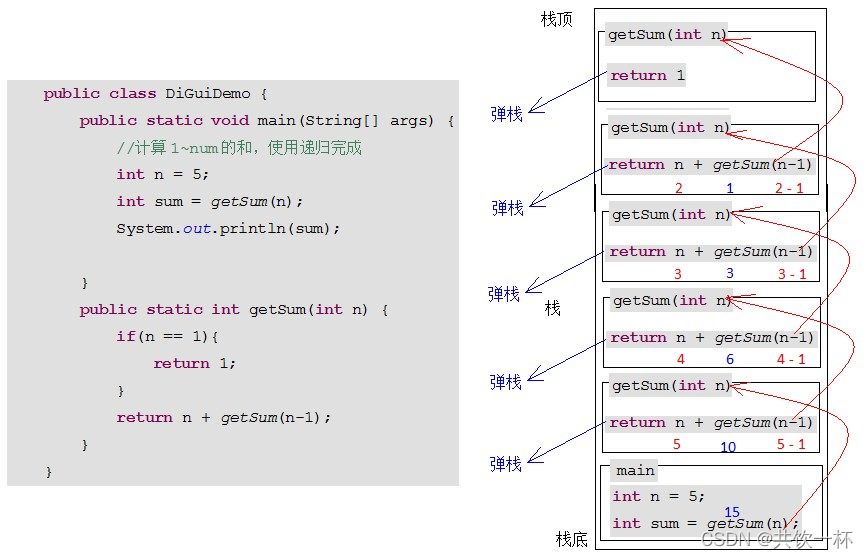
在递归的时候,对数据进行标记,出现了多次的,就不进行处理。这样就不会进行死循环中。 (PS:递归的使用,除了找到规律,判断递归终止条件也是很重要的。有时候找不到终止条件,主要是对整个过程不理解,或是一知半解)
处理:
代码:
import org.apache.commons.collections4.ListUtils;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.MapUtils;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;public class RemarkRecurTreeList {private List<Map<String, Object>> treeNodeList;private String rootValue;// 添加一个list作为标记用于判断是否循环private List<String> preValues = new ArrayList<>();public RemarkRecurTreeList(List<Map<String, Object>> treeNodeList, String rootValue) {this.treeNodeList = treeNodeList;this.rootValue = rootValue;}//建立树形结构public List<Map<String, Object>> builTree(String parentTag, String childTag) {List<Map<String, Object>> rootNodeList = getRootNode(parentTag);LinkedList<Map<String, Object>> flatTreeList = new LinkedList<>();preValues.add(rootValue);for (Map<String, Object> e : ListUtils.emptyIfNull(rootNodeList)) {buildChilTree(e, parentTag, childTag, flatTreeList);flatTreeList.add(e);}return ListUtils.emptyIfNull(flatTreeList).stream().filter(Objects::nonNull).collect(Collectors.toList());}//递归,建立子树形结构 返回private Map<String, Object> buildChilTree(Map<String, Object> pNode, String parentTag, String childTag, List<Map<String, Object>> flatTreeList) {String nextValue1 = MapUtils.getString(pNode, childTag);if(!preValues.contains(nextValue1)){preValues.add(nextValue1); // 添加标记for (Map<String, Object> e : ListUtils.emptyIfNull(treeNodeList)) {// 跟上一个进行匹配String curValue = MapUtils.getString(e, parentTag);String nextValue = MapUtils.getString(pNode, childTag);if (StringUtils.equals(curValue, nextValue) ) { // && !curValue.equals(rootValue)flatTreeList.add(buildChilTree(e, parentTag, childTag, flatTreeList));}}return pNode;}return null;}//获取根节点private List<Map<String, Object>> getRootNode(String parentTag) {List<Map<String, Object>> rootNodeLists = new ArrayList<>();for (Map<String, Object> e : ListUtils.emptyIfNull(treeNodeList)) {if (StringUtils.equals(MapUtils.getString(e, parentTag), rootValue)) {rootNodeLists.add(e);}}return rootNodeLists;}}测试:
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONArray;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.ListUtils;import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;public class RemarkRecurTreeListTest {public static void main(String[] args){List<Map<String,Object>> areaList = changeFormat(initData());System.out.println("init data "+ areaList.toString());// 构建树形RemarkRecurTreeList commonTree = new RemarkRecurTreeList(areaList, "18");List<Map<String, Object>> result = commonTree.builTree("NEXT_TCH_MOD", "TCH_MOD");System.out.println();result.forEach(e -> {System.out.println(e.get("TCH_MOD")+ " <-- "+ e.get("NEXT_TCH_MOD"));});}private static List<Map<String,Object>> changeFormat(String areaInfo){JSONArray areaArr = JSONArray.parseArray(areaInfo);return ListUtils.emptyIfNull(areaArr).stream().map(e -> (JSONObject) e).map(e -> (Map<String, Object>)JSONObject.parseObject( e.toJSONString())).collect(Collectors.toList());}private static String initData(){// 初始循环的return "[{\"TCH_MOD\":11,\"NEXT_TCH_MOD\":12},{\"TCH_MOD\":12,\"NEXT_TCH_MOD\":13},{\"TCH_MOD\":13,\"NEXT_TCH_MOD\":14},{\"TCH_MOD\":14,\"NEXT_TCH_MOD\":15},{\"TCH_MOD\":15,\"NEXT_TCH_MOD\":16},{\"TCH_MOD\":16,\"NEXT_TCH_MOD\":17},{\"TCH_MOD\":17,\"NEXT_TCH_MOD\":18},{\"TCH_MOD\":12,\"NEXT_TCH_MOD\":14},{\"TCH_MOD\":13,\"NEXT_TCH_MOD\":15},{\"TCH_MOD\":15,\"NEXT_TCH_MOD\":17}]";}}结果:
init data [{"NEXT_TCH_MOD":12,"TCH_MOD":11}, {"NEXT_TCH_MOD":13,"TCH_MOD":12}, {"NEXT_TCH_MOD":14,"TCH_MOD":13}, {"NEXT_TCH_MOD":15,"TCH_MOD":14}, {"NEXT_TCH_MOD":16,"TCH_MOD":15}, {"NEXT_TCH_MOD":17,"TCH_MOD":16}, {"NEXT_TCH_MOD":18,"TCH_MOD":17}, {"NEXT_TCH_MOD":14,"TCH_MOD":12}, {"NEXT_TCH_MOD":15,"TCH_MOD":13}, {"NEXT_TCH_MOD":17,"TCH_MOD":15}]11 <-- 12
12 <-- 13
13 <-- 14
14 <-- 15
15 <-- 16
16 <-- 17
17 <-- 18
总结:
在递归有循环指向的数据的时候,要进行标记处理,找到跳出循环的条件,不然会出现递归死循环的情况。