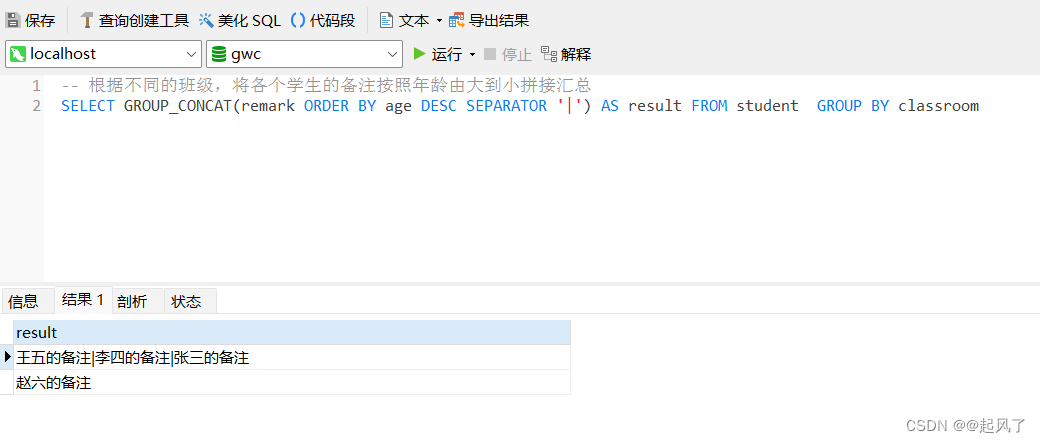
1. 最长公共子序列

(1)DFS暴搜(超时)
class Solution{public static int longestCommonSubsequence(String text1, String text2) {char[] t1Chars = text1.toCharArray();char[] t2Chars = text2.toCharArray();return process(t1Chars, t2Chars, t1Chars.length, t2Chars.length);}//返回text1长度x,text2长度为y情况下的最长公共子序列长度private static int process(char[] t1Chars, char[] t2Chars, int x, int y) {if (x == 0 || y == 0) return 0;return t1Chars[x-1] == t2Chars[y-1] ? (process(t1Chars, t2Chars, x-1, y-1) + 1): Math.max(process(t1Chars, t2Chars, x-1, y), process(t1Chars, t2Chars, x, y-1));}
}
(2)记忆化DFS
暴力递归慢就慢在对于一个位置值的重复求解,比如说process(3,3),在(4,4)的时候可能求一次,在(3,4)可能又求一次…等等,反正会被求到很多次
- 记忆化:针对性的优化:使用缓存,将求过的值进行保存,下次直接使用
class Solution{public int longestCommonSubsequence(String text1, String text2) {char[] t1Chars = text1.toCharArray();char[] t2Chars = text2.toCharArray();HashMap<String,Integer> cache = new HashMap<>();return process2(t1Chars, t2Chars, t1Chars.length, t2Chars.length, cache);}private int process2(char[] t1Chars, char[] t2Chars, int x, int y, HashMap<String, Integer> cache) {//存储当前text1长度x,text2长度为y情况下的最长公共子序列长度,下次重复递归时可以直接使用String key = x + "_" + y;if (cache.containsKey(key)) return cache.get(key);if (x == 0 || y == 0) {cache.put(key,0);return 0;}int result = t1Chars[x - 1] == t2Chars[y - 1] ? (process2(t1Chars, t2Chars, x - 1, y - 1,cache) + 1): Math.max(process2(t1Chars, t2Chars, x - 1, y,cache), process2(t1Chars, t2Chars, x, y - 1,cache));//存储当前计算的text1长度x,text2长度为y情况下的最长公共子序列长度cache.put(key,result);return result;}
}
(3)DP
- 单个数组或者字符串要用动态规划时,可以把动态规划 dp[i] 定义为 nums[0:i] 中想要求的结果
- 当两个数组或者字符串要用动态规划时,可以把动态规划定义成两维的 dp[i][j] ,其含义是在 A[0:i] 与 B[0:j] 之间匹配得到的想要的结果
- 本题可以定义 dp[i][j] 表示 text1[0:i-1] 和 text2[0:j-1] 的最长公共子序列。
- 注:text1[0:i-1] 表示的是 text1 的 第 0 个元素到第 i - 1 个元素,两端都包含)
之所以 dp[i][j] 的定义不是 text1[0:i] 和 text2[0:j] ,是为了方便当 i = 0 或者 j = 0 的时候,dp[i][j]表示的为空字符串和另外一个字符串的匹配,这样 dp[i][j] 可以初始化为 0。
class Solution {public int longestCommonSubsequence(String text1, String text2) {int len1 = text1.length();int len2 = text2.length();if (text1 == null || text2 == null || len1 < 1 || len2 < 1) return 0;//定义 dp[i][j] 表示 text1[0:i-1] 和 text2[0:j-1] 的最长公共子序列。 所以需要 + 1//之所以 dp[i][j] 的定义不是 text1[0:i] 和 text2[0:j] ,是为了方便当 i = 0 或者 j = 0 的时候,//dp[i][j]表示的为空字符串和另外一个字符串的匹配,这样 dp[i][j] 可以初始化为 0。int[][] dp = new int[len1 + 1][len2 + 1];for (int i = 1; i <= len1; ++i) {for (int j = 1; j <= len2; ++j) {//由于当 i 和 j 取值为 0 的时候,dp[i][j] = 0,而 dp 数组本身初始化就是为 0,所以,直接让 i 和 j 从 1 开始遍历//遍历的结束应该是字符串的长度为 len(text1) 和 len(text2)。if (text1.charAt(i - 1) == text2.charAt(j - 1)) {//两个子字符串的最后一位相等,所以最长公共子序列又增加了 1dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;} else {//两个子字符串的最后一位不相等,那么此时的状态 dp[i][j] 应该是 dp[i - 1][j] 和 dp[i][j - 1] 的最大值dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);}}}return dp[len1][len2];}
}2. 最长公共子串(最长重复数组)
假如有两个字符串,s1=“people"和s2=“eplm”,我们要求他俩最长的公共子串。我们一眼就能看出他们的最长公共子串是"pl”,长度是2。但如果字符串特别长的话就不容易那么观察了。
(1)暴力
public int getLCS(String s, String s2) {if (s == null || t == null) {return 0;}int l1 = s1.length();int l2 = s2.length();int res = 0;for (int i = 0; i < l1; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < l2; j++) {int m = i;int n = j;int len = 0;while (m < l1 && n < l2 && s1.charAt(m) == s2.charAt(n)) {len++;m++;n++;}res = Math.max(res, len);}}return res;}
(2)DP
-
用一个二维数组dp[i][j]表示 第一个字符串前 i 个字符 和 第二个字符串前 j 个字符 组成的最长公共字符串的长度。
-
那么我们在计算dp[i][j]的时候,我们首先要判断s1.charAt(i)是否等于s2.charAt(j):
- 如果不相等,说明当前字符无法构成公共子串,所以dp[i][j]=0。
- 如果相等,说明可以构成公共子串,我们还要加上他们前一个字符构成的最长公共子串长度,也就是dp[i-1][j-1]。所以我们很容易找到递推公式
-
递推公式为:
if(s1.charAt(i) == s2.charAr(j))dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1;
elsedp[i][j] = 0;
具体代码:
public static int maxLong(String str1, String str2) {if (str1 == null || str2 == null || str1.length() == 0 || str2.length() == 0)return 0;int max = 0;// +1是为了防止边界条件判断 和 减少初始化当 i 或 j 等于 0 时,初始化子串就是为0,初始化数组也是为0int[][] dp = new int[str1.length() + 1][str2.length() + 1];for (int i = 1; i <= str1.length(); i++) {for (int j = 1; j <= str2.length(); j++) {if (str1.charAt(i - 1) == str2.charAt(j - 1))dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;elsedp[i][j] = 0;//最大值不一定出现在数组的最后一个位置,所以要用一个临时变量记录下来。max = Math.max(max, dp[i][j]); }}return max;
}
(3)DP优化
public static int maxLong(String str1, String str2) {if (str1 == null || str2 == null || str1.length() == 0 || str2.length() == 0)return 0;int max = 0;int[] dp = new int[str2.length() + 1];for (int i = 1; i <= str1.length(); i++) {//使用的倒序的方式,这是因为dp数组后面的值会依赖前面的值,而前面的值不依赖后面的值,所以后面的值先修改对前面的没影响,但前面的值修改会对后面的值有影响,所以这里要使用倒序的方式。for (int j = str2.length(); j >= 1; j--) {if (str1.charAt(i - 1) == str2.charAt(j - 1))dp[j] = dp[j - 1] + 1;elsedp[j] = 0;max = Math.max(max, dp[j]);}}return max;
}