原文:https://blog.csdn.net/davion_zhang/article/details/52233043
一、版本说明
嵌入式Linux 下面的reboot命令看似简单,但出问题时定位起来发现别有洞天。
下面就按在shell下执行reboot命令之后程序的执行过程进行解析。
Busybox:1.23.2 ——制作跟文件系统,/sbin/reboot程序的由来
Libc:2.6.1 ——标准C库
Linux kernel:2.6.35 ——内核版本
二、流程简介
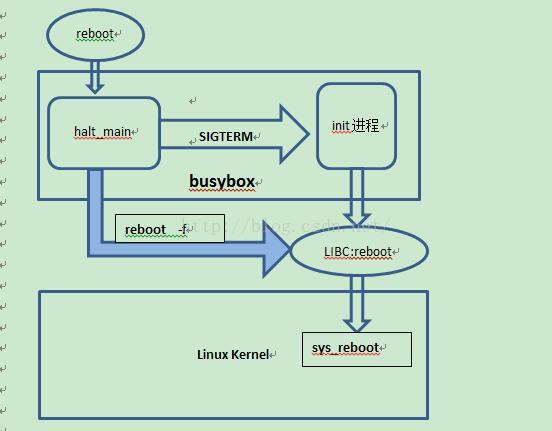
如图所示是reboot的简要流程图。
普通的reboot是通过busybox为入口,进入halt_main函数,然后给init进程发送SIGTERM信号,init进程接收到信号后给其他进程发送终止信号,最后调用C库函数reboot,reboot通过系统调用sys_reboot进入内核,内核将整个系统重启。其中在shell中执行reboot –f则通过halt_main直接调用C函数reboot,不经过init进程。
三、代码详解
1.reboot命令端
执行reboot命令,busybox检查当前命令为reboot,进入函数halt_main,
reboot,halt和poweroff都会进入这个函数,不同的命令发送的信号和执行的操作不同。
现只分析reboot的情况。
代码如下
int halt_main(int argc, char **argv) MAIN_EXTERNALLY_VISIBLE;
int halt_main(int argc UNUSED_PARAM, char **argv)
{static const int magic[] = {RB_HALT_SYSTEM,RB_POWER_OFF,RB_AUTOBOOT};static const smallint signals[] = { SIGUSR1, SIGUSR2, SIGTERM };int delay = 0;int which, flags, rc;/* Figure out which applet we're running */for (which = 0; "hpr"[which] != applet_name[0]; which++)continue;/* Parse and handle arguments */opt_complementary = "d+"; /* -d N *//* We support -w even if !ENABLE_FEATURE_WTMP,* in order to not break scripts.* -i (shut down network interfaces) is ignored.*/flags = getopt32(argv, "d:nfwi", &delay);sleep(delay);write_wtmp();if (flags & 8) /* -w */return EXIT_SUCCESS;if (!(flags & 2)) /* no -n */sync();/* Perform action. */rc = 1;if (!(flags & 4)) { /* no -f */
//TODO: I tend to think that signalling linuxrc is wrong
// pity original author didn't comment on it...if (ENABLE_FEATURE_INITRD) {/* talk to linuxrc *//* bbox init/linuxrc assumed */pid_t *pidlist = find_pid_by_name("linuxrc");if (pidlist[0] > 0)rc = kill(pidlist[0], signals[which]);if (ENABLE_FEATURE_CLEAN_UP)free(pidlist);}if (rc) {/* talk to init */if (!ENABLE_FEATURE_CALL_TELINIT) {/* bbox init assumed */rc = kill(1, signals[which]);} else {/* SysV style init assumed *//* runlevels:* 0 == shutdown* 6 == reboot */execlp(CONFIG_TELINIT_PATH,CONFIG_TELINIT_PATH,which == 2 ? "6" : "0",(char *)NULL);bb_perror_msg_and_die("can't execute '%s'",CONFIG_TELINIT_PATH);}}} else {rc = reboot(magic[which]);}if (rc)bb_perror_nomsg_and_die();return rc;
}
该函数判断reboot是否带了 -f 参数,如果带了,直接调用reboot调用C函数库
如果没带,则通过
kill(1, signals[which]);
给init进程发送SIGTERM信号。
2.init进程端
init进程初始化函数init_main将部分信号进行重定义
bb_signals_recursive_norestart(0+ (1 << SIGINT) /* Ctrl-Alt-Del */+ (1 << SIGQUIT) /* re-exec another init */
#ifdef SIGPWR+ (1 << SIGPWR) /* halt */
#endif+ (1 << SIGUSR1) /* halt */+ (1 << SIGTERM) /* reboot */+ (1 << SIGUSR2) /* poweroff */
#if ENABLE_FEATURE_USE_INITTAB+ (1 << SIGHUP) /* reread /etc/inittab */
#endif, record_signo);
void record_signo(int signo)
{bb_got_signal = signo;
}
将SIGUSR1(halt) SIGUSR2(poweroff) SIGTERM(reboot)信号存入全局变量bb_got_signal中。
在init_main的最后进入一个while(1)循环,不断检查信号和等待子进程的退出
其中check_delayed_sigs就是用来检查这个全局变量的,如下:
while (1) {int maybe_WNOHANG;maybe_WNOHANG = check_delayed_sigs();/* (Re)run the respawn/askfirst stuff */run_actions(RESPAWN | ASKFIRST);maybe_WNOHANG |= check_delayed_sigs();/* Don't consume all CPU time - sleep a bit */sleep(1);maybe_WNOHANG |= check_delayed_sigs();/* Wait for any child process(es) to exit.** If check_delayed_sigs above reported that a signal* was caught, wait will be nonblocking. This ensures* that if SIGHUP has reloaded inittab, respawn and askfirst* actions will not be delayed until next child death.*/if (maybe_WNOHANG)maybe_WNOHANG = WNOHANG;while (1) {pid_t wpid;struct init_action *a;/* If signals happen _in_ the wait, they interrupt it,* bb_signals_recursive_norestart set them up that way*/wpid = waitpid(-1, NULL, maybe_WNOHANG);if (wpid <= 0)break;a = mark_terminated(wpid);if (a) {message(L_LOG, "process '%s' (pid %d) exited. ""Scheduling for restart.",a->command, wpid);}/* See if anyone else is waiting to be reaped */maybe_WNOHANG = WNOHANG;}} /* while (1) */
而里面的while(1)一般会阻塞在waitpid中,那么信号检查是不是会有问题?
WNOHANG 如果没有可用的子进程退出状态,立即返回而不是阻塞
但maybe_WNOHANG的值应该是0,不是WNOHANG(=1)感觉还是会阻塞。我这样理解的,因为所有的用户进程都是init进程的子进程,我判断前面执行reboot时也是一个子进程,halt_main发送完信号后就会退出,init接收到信号而且waitpid成功,然后跳出循环检查信号。
下面看一下信号的处理部分
static int check_delayed_sigs(void)
{int sigs_seen = 0;while (1) {smallint sig = bb_got_signal;if (!sig)return sigs_seen;bb_got_signal = 0;sigs_seen = 1;
#if ENABLE_FEATURE_USE_INITTABif (sig == SIGHUP)reload_inittab();
#endifif (sig == SIGINT)run_actions(CTRLALTDEL);if (sig == SIGQUIT) {exec_restart_action();/* returns only if no restart action defined */}if ((1 << sig) & (0
#ifdef SIGPWR+ (1 << SIGPWR)
#endif+ (1 << SIGUSR1)+ (1 << SIGUSR2)+ (1 << SIGTERM))) {halt_reboot_pwoff(sig);}}
}
判断为SIGTERM进入halt_reboot_pwoff函数
static void halt_reboot_pwoff(int sig)
{const char *m;unsigned rb;/* We may call run() and it unmasks signals,* including the one masked inside this signal handler.* Testcase which would start multiple reboot scripts:* while true; do reboot; done* Preventing it:*/reset_sighandlers_and_unblock_sigs();run_shutdown_and_kill_processes();m = "halt";rb = RB_HALT_SYSTEM;if (sig == SIGTERM) {m = "reboot";rb = RB_AUTOBOOT;} else if (sig == SIGUSR2) {m = "poweroff";rb = RB_POWER_OFF;}message(L_CONSOLE, "Requesting system %s", m);pause_and_low_level_reboot(rb);/* not reached */
}reset_sighandlers_and_unblock_sigs函数将信号重置回默认处理。
static void reset_sighandlers_and_unblock_sigs(void)
{bb_signals(0+ (1 << SIGUSR1)+ (1 << SIGUSR2)+ (1 << SIGTERM)+ (1 << SIGQUIT)+ (1 << SIGINT)+ (1 << SIGHUP)+ (1 << SIGTSTP)+ (1 << SIGSTOP), SIG_DFL);sigprocmask_allsigs(SIG_UNBLOCK);
}run_shutdown_and_kill_processes函数给所有进程发送SIGTERM信号并执行sync(保存数据)
延时后再次发送SIGKILL信号,这里说明一下为什么要发送SIGKILL信号,一般的SIGINT和SIGTERM信号都可以屏蔽或转作他用,SIGKILL信号是不可被屏蔽的,
这样告诉其他进程必须终止。
static void run_shutdown_and_kill_processes(void)
{/* Run everything to be run at "shutdown". This is done _prior_* to killing everything, in case people wish to use scripts to* shut things down gracefully... */run_actions(SHUTDOWN);message(L_CONSOLE | L_LOG, "The system is going down NOW!");/* Send signals to every process _except_ pid 1 */kill(-1, SIGTERM);message(L_CONSOLE | L_LOG, "Sent SIG%s to all processes", "TERM");sync();sleep(1);kill(-1, SIGKILL);message(L_CONSOLE, "Sent SIG%s to all processes", "KILL");sync();/*sleep(1); - callers take care about making a pause */
}
最终进入函数pause_and_low_level_reboot,起一个轻量级进程执行reboot标准C函数
static void pause_and_low_level_reboot(unsigned magic)
{pid_t pid;/* Allow time for last message to reach serial console, etc */sleep(1);/* We have to fork here, since the kernel calls do_exit(EXIT_SUCCESS)* in linux/kernel/sys.c, which can cause the machine to panic when* the init process exits... */pid = vfork();if (pid == 0) { /* child */reboot(magic);_exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);}while (1)sleep(1);
}
到这里busybox里面的内容全部处理完。
3.标准C函数reboot
前面执行reboot -f 就是直接执行的这个函数
reboot函数比较简单,直接进行系统调用进入内核。(0xffe1dead feeldead这个魔术还是比较有意思的)
其中参数howto为RB_AUTOBOOT=0x01234567
sysdeps/unix/sysv/linux/reboot.c
int
reboot (int howto)
{return INLINE_SYSCALL (reboot, 3, (int) 0xfee1dead, 672274793, howto);
}4.内核系统调用
kernel/sys.c
SYSCALL_DEFINE4(reboot, int, magic1, int, magic2, unsigned int, cmd,void __user *, arg)
{
。。。mutex_lock(&reboot_mutex);switch (cmd) {case LINUX_REBOOT_CMD_RESTART:kernel_restart(NULL);break;case LINUX_REBOOT_CMD_CAD_ON:C_A_D = 1;break;case LINUX_REBOOT_CMD_CAD_OFF:C_A_D = 0;break;case LINUX_REBOOT_CMD_HALT:kernel_halt();do_exit(0);panic("cannot halt");case LINUX_REBOOT_CMD_POWER_OFF:kernel_power_off();do_exit(0);break;。。。default:ret = -EINVAL;break;}mutex_unlock(&reboot_mutex);return ret;
}进入
case LINUX_REBOOT_CMD_RESTART:
kernel_restart(NULL);
break;
调用kernel_restart函数
——>machine_restart
void machine_restart(char *cmd)
{machine_shutdown();if (ppc_md.restart)ppc_md.restart(cmd);
#ifdef CONFIG_SMPsmp_send_stop();
#endifprintk(KERN_EMERG "System Halted, OK to turn off power\n");local_irq_disable();while (1) ;
}这个函数之后就与具体的架构有关系了。
下面是powerpc P1020芯片的复位
ppc_md.restart(cmd);的函数原型在/arch/powerpc/platforms/85xx中定义
define_machine(p2020_rdb_pc) {.name = "P2020RDB-PC",.probe = p2020_rdb_pc_probe,.setup_arch = mpc85xx_rdb_setup_arch,.init_IRQ = mpc85xx_rdb_pic_init,
#ifdef CONFIG_PCI.pcibios_fixup_bus = fsl_pcibios_fixup_bus,
#endif.get_irq = mpic_get_irq,.restart = fsl_rstcr_restart,.calibrate_decr = generic_calibrate_decr,.progress = udbg_progress,
};void fsl_rstcr_restart(char *cmd)
{local_irq_disable();if (rstcr)/* set reset control register */out_be32(rstcr, 0x2); /* HRESET_REQ */while (1) ;
}最终cpu往寄存器Reset control register(0x000E_00B0)中写2
也就是往管脚HRESET_REQ发出了一个信号,该信号应该与HRESET硬复位管脚相连
这样就实现了CPU的复位
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
下面是 TI am5728的reboot内核调用的调用过程
SyS_rebootkernel_restartmachine_restartarm_pm_restartomap44xx_restartomap_prm_reset_systemprm_ll_data->reset_system();omap4_prminst_global_warm_sw_reset最终往PRM_RSTCTRL[0]写1,触发一个全局软件热复位。