文章目录
- 一、实验目的
- 二、实验原理与要求
- 1、原理
- 2、要求
- 三、实验设备
- 四、实验内容
- 五、实验步骤
- 1. 单词内码表
- 2. 定义语言文法
- 3. 语法分析器的实现(编码)
- 4. 测试
- 六、配套资源
一、实验目的
理解自顶向下语法分析的基本模式,熟悉递归下降分析程序的构造。
二、实验原理与要求
1、原理
每个非终结符抽象为一个函数,语法树的上下级关系对应于函数的递归调用。
2、要求
(1)针对一个具体语言子集,设计出相应的文法。
(2)递归过程按规定的模式。
(3)测试用例覆盖每个产生式候选。
三、实验设备
配置有C/C++开发环境的计算机设备。
四、实验内容
采用递归下降分析法对变量定义语句、赋值语句、while语句、if语句进行语法分析。对每个非终结符设计递归子函数。
五、实验步骤
1. 单词内码表
在实验一 词法分析程序的设计的基础上,要求考虑while语句、if语句。以下为一参考实现:

2. 定义语言文法
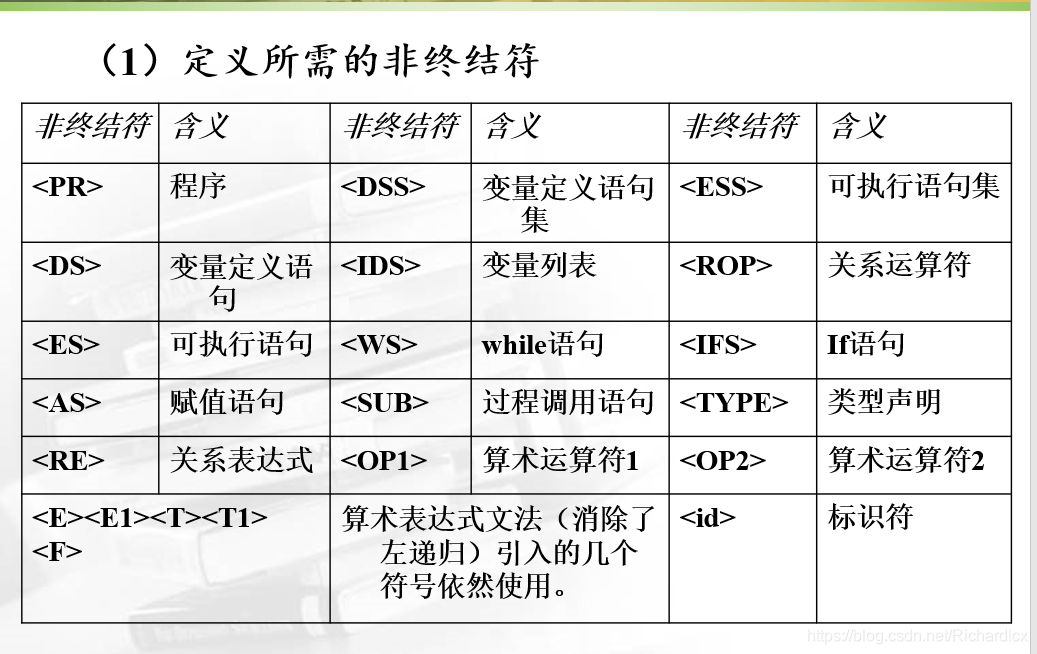
选取高级语言的部分语句,先定义其中所涉及的非终结符:

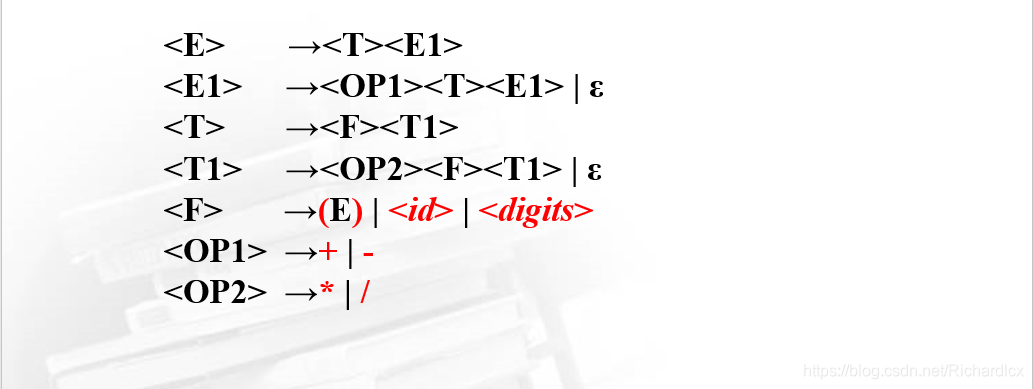
说明:
(1)把识别出来的单词均作为终结符对待。
(2)在本实验中用单词种类编号表示单词,所以和当前输入符号比较的时候比较的是单词种类编号。例如:
if(str[ip]==’(‘) 改成 if(str[ip]==19)
else if(str[ip]==’a’) 改成 else if(str[ip]==100)
3. 语法分析器的实现(编码)
// -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
// @ Date : 2020/5/20 13:14
// @ Author : RichardLau_Cx
// @ file : Richard.cpp
// @ IDE : Dex-C++
// @ Source : 编译原理实验#include <iostream>
#include "实验一 词法分析程序.cpp" // 调用实验一的代码文件 using namespace std;typedef int vtType; // 终结符类型,用实验一识别出的单词作为终结符,并且用单词的种类编号(int)表示单词
vtType lookAhead; // 用来存放当前读出的输入符号(即:存放从Result[]中,当前读出的单词)
char value[100]; // 读出当前单词的内码值
int ip=0; // ip指向从Result[]中,当前读出单词的下标
// lookAhead = Result[ip].typeNumber void error2();
void match();void PR();
void DSS();
void DS();
void TYPE();
void ES();
void ESS();
void IDS();
void WS();
void IFS();
void AS();
void RE();void E();
void ROP();
void T();
void E1();
void OP1();
void OP2();
void F();
void T1();void grammar(); void error2()
{cout << endl << "语法发现错误!位置为:" << ip << endl; exit(0);
}void match()
{// 当前输入符号和推导过程中,待匹配符号相等,则“匹配 ”,输入串指示器ip指向下一个输入符号ip++;lookAhead = Result[ip].typeNumber; // 读出下一个符号种别编码
// value = Result[ip].code; // 读出下一个符号内码值
}void PR()
{ // <PR> -> <DSS><ESS>DSS();ESS();
}void DSS()
{ // <DSS> -> <DS><DSS> | εif (lookAhead == 4 || lookAhead == 5 || lookAhead == 6){ /** lookAhead属于FIRST(<DS><DSS>)* FIRST(<DS><DSS>) = {int, float, char} = {4, 5, 6}* 求出FIRST集经过计算之后,才能用代码表示*/ DS();DSS(); // 相当于递归调用 }
}void ESS()
{ // <ESS> -> <ES><ESS> | εif (lookAhead == 3 || lookAhead == 1 || lookAhead == 100) {/** lookAhead属于FIRST(<ES><ESS>) * FIRST(<ES><ESS>) = {while, if, <id>} = {3, 1, 100} */ES();ESS();}
}void DS()
{ // <DS> -> <TYPE><id><IDS>;TYPE();if (lookAhead == 100){match();IDS();if (lookAhead == 18){ // ";"的种别编码为18 match();} else {error2();}} else {error2();}
}void TYPE()
{ // <TYPE> -> int | float | char cout << "lookAhead: " << lookAhead << endl; if (lookAhead == 4){ // 匹配到int
// printf("\n匹配到int!\n");match(); }else if (lookAhead == 5){ // 匹配到floatmatch();} else if (lookAhead == 6){ // 匹配到charmatch(); }else{error2(); // 语法错误 }
}void IDS()
{ // <IDS> -> ,<id><IDS> | εif (lookAhead == 17){ // ","的种别编码为17 match();if (lookAhead == 100){match();IDS();}}// 因为有ε,所以不用写else error();
}void ES()
{// <ES> -> <WS> | <IFS> | <AS>/*** FIRST(<WS>) = {while} = {3},* FIRST(<IFS>) = {if} = {1},* FIRSR(<AS>) = {<id>} = {100}*/if (lookAhead == 3){
// match();WS();} else if (lookAhead == 1){
// match();IFS();}else if (lookAhead == 100){
// match();AS();} else {error2();} }void WS()
{ // <WS> -> while "(" <RE> ")" {<ESS>} // 因为皆为递进关系,所以需要嵌套着写 if (lookAhead == 3){ // 读出while match(); if (lookAhead == 19){ // 读出"(" match();RE();if (lookAhead == 20){ // 读出")" match();if (lookAhead == 23){ // 读出"{" match();ESS();if (lookAhead == 24){ // 读出"}" match();}else {error2();}}else{error2();} }else {error2();} }else{error2();}}else{error2();} } void IFS()
{ // if "(" <RE> ")" { <ESS> } else { <ESS> }if (lookAhead == 1){ // 读出if match();if (lookAhead == 19){ // 读出"(" match();RE();if (lookAhead == 20){ // 读出")" match();if (lookAhead == 23){ // 读出"{" match();ESS();if (lookAhead == 24){ // 读出"}" match();if (lookAhead == 2){ // 读出else match();if (lookAhead == 23){ // 读出"{" match();ESS();if (lookAhead == 24){ // 读出"}" match();}else{error2();}}else {error2();}}else {error2();}} else{error2();}}else{error2();}} else{error2();}}else{error2();}} else{error2();}
}void AS()
{ // <AS> -> <id>=<E>;if (lookAhead == 100){match();if (lookAhead == 13){ // 读出"=" match();E();if (lookAhead == 18){ // ";"的种别编码为18 match();} else{error2();}}else{error2();} }else{error2();}
}void RE()
{ // <RE> -> <E><ROP><E>E();ROP();E();
}void ROP()
{ // <ROP> -> > | >= | < | <= | == | != if (lookAhead == 10){ // 读出">" match();} else if (lookAhead == 11){ // 读出">=" match();}else if (lookAhead == 25){ // 读出"<" match();}else if (lookAhead == 26){ // 读出"<=" match();}else if (lookAhead == 14){ // 读出"==" match();}else if (lookAhead == 28){ // 读出"!=" match();}else{error2();}} void E()
{ // <E> -> <T><E1> T();E1();
}void E1()
{ // <E1 -> <OP1><T><E1> | ε/** 先计算FIRST(<OP1><T><E1>) = {+, -} = {7, 21}*/if (lookAhead == 7 || lookAhead == 21){OP1();T();E1();}
}void T()
{ // <T> -> <F><T1> F();T1();
}void T1()
{ // <T1> -> <OP2><F><T1> | ε/** 先计算FIRST(<OP2><F><T1>) = {*, /} = {15, 22}*/if (lookAhead == 15 || lookAhead == 22){OP2();F();T1();} } void F()
{ // F -> (E) | <id> | <digis>if (lookAhead == 19){ // 读出"("match(); E();if (lookAhead == 20){ // 读出")" match();}}else if (lookAhead == 100){ // 读出标识符 match(); } // else if (atoi(value))
//else if ("0" <= value || value <= "999")else if (lookAhead == 110){match();}else{error2();}} void OP1()
{ // <OP1> -> + | -if (lookAhead == 7){match();} else if (lookAhead == 21){match();}else{error2();}
}void OP2()
{ // <OP2> -> * | /if (lookAhead == 15){match();} else if (lookAhead == 22){match();}else{error2();}
}void grammar()
{ // 语法分析 cout << "function: grammar(): " << endl;PR();if (ip == number){ // 相当于读取到最后一个单词,相当于从左至右扫描输入串到达尾部 cout << endl << "\n语法检查通过!\n" << endl; }else { // 如3+2; 语法错误,而a=3+2; 语法正确 cout << endl << "\n语法检查未通过!\n" << endl; }} int main() // 注:需要把实验一的main函数注释掉
{words(); // 词法分析lookAhead = Result[ip].typeNumber; // lookAhead存放第一个单词,相当于从输入串中读第一个符号的种别编码// printf("\nlookAhead: %d\n", lookAhead); grammar(); // 语法分析 return 0;}
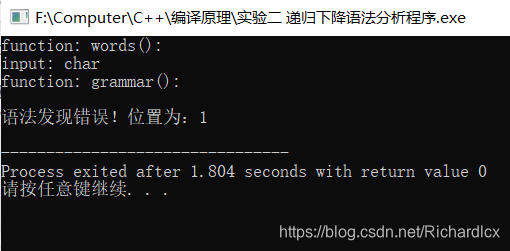
4. 测试
- Notice:其中的位置是针对词为单位的。
- 输入:char
- 构造正反测试用例:
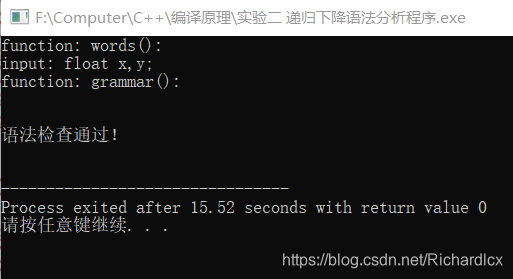
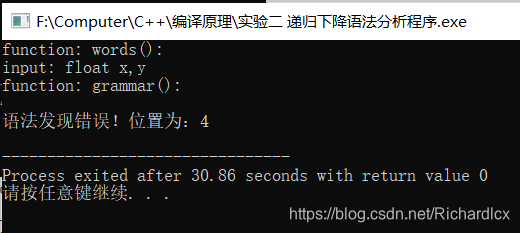
- 正确实例:float x, y; 错误实例:float x, y
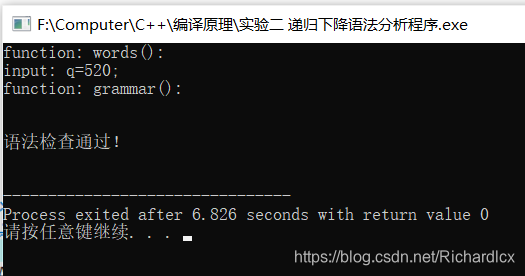
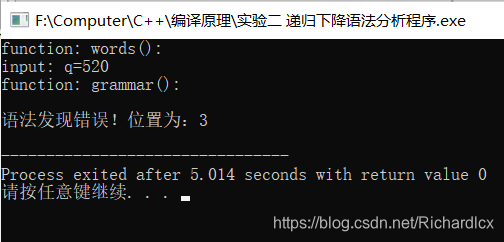
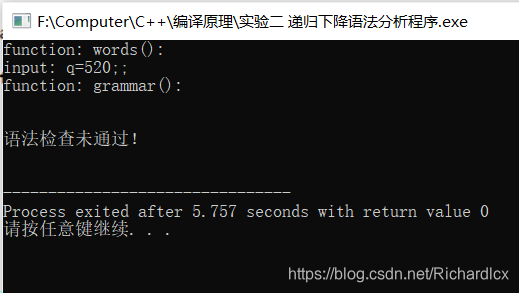
- 正确实例:q=520; 错误实例:q=520 错误实例:q=520;;
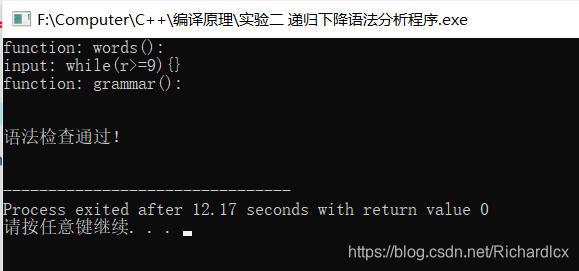
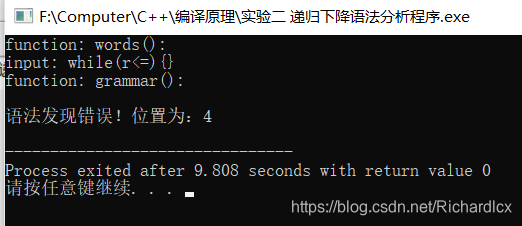
- 正确实例:while(r>=9){} 错误实例:while(r>=){}
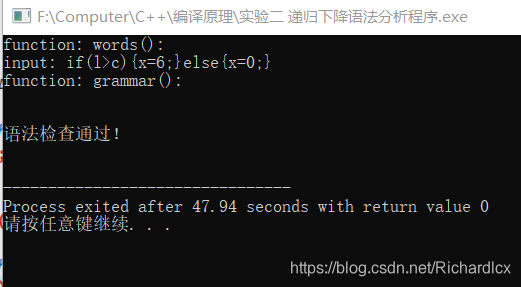
- 正确实例:if(l>c){x=6;} else{x=0;} 错误实例:if(x>y)z=t; else k=t;
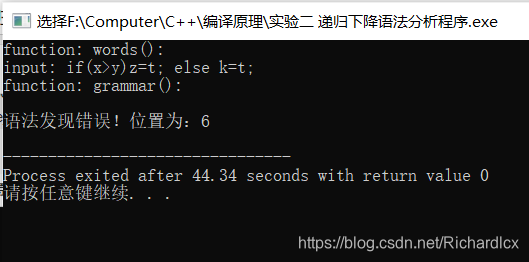
Notice:本程序内部分支多,且实验时间有限。要达到较为全面测试覆盖比较难,因此只要求变量定义语句、赋值语句、while、if四种语句均有正反测试用例。
六、配套资源
- 实验指导书