什么是事务
事务即英文Transaction,在软件开发过程中,难免需要考虑处理事务。从微观层面看亦或者从成员最早了解到这个词汇看,事务通常指多条写入数据库的语句需要并发成功执行,从宏观层面看得话则是客户端发出的并发请求需要一致性并发成功完成,即要么都成功要么都失败。这样以来常见的事务分为了单库事务、分布式事务,当然事务数也演进为了一个衡量服务性能的度量单位,比如在推进性能测试验证时用到的tps指标。
事务的特点
根据事务的定义,可总结出四个特点ACID,即:
原子性(Atomicity): 事务是数据库的逻辑工作单位,事务中包括的诸操作要么全成功,要么全失败。
一致性(Consistency): 事务执行的结果必须是使数据库从一个一致性状态变到另一个一致性状态。一致性与原子性是密切相关的。当然这个看上去更多是从微观层面提炼的特点描述。
隔离性(Isolation): 一个事务的执行不能被其他事务干扰。
持续性/永久性(Durability): 一个事务一旦提交,它对数据库中数据的改变就应该是永久性的。
事务的控制
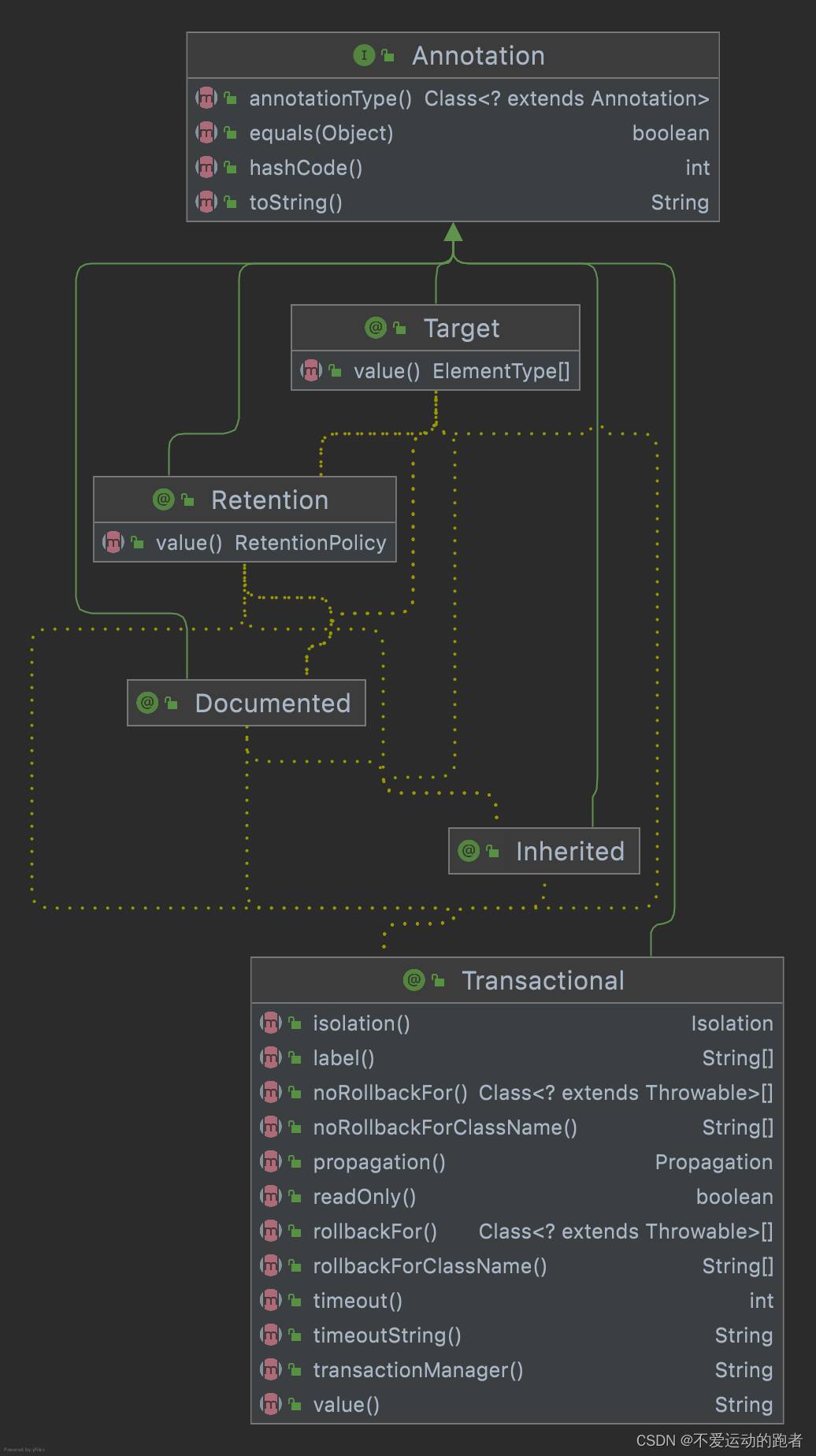
事务的控制无非就是对事务的特点进行严格控制以对活动操作的完整准备性提供保障。微观层面的事务控制也是我们最常见的事务控制,无非还是基于数据库层面得。作为Java语言出身的编码人士,此刻第一想到的便是Spring框架中的@Transactional注解,在大多数人看来使用了@Transactional注解即可控制事务以达成特点的要求。然而真的是那样吗,我们还是看看这个注解的描述。
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface Transactional {/*** Alias for {@link #transactionManager}.* @see #transactionManager*/@AliasFor("transactionManager")String value() default "";/*** A <em>qualifier</em> value for the specified transaction.* <p>May be used to determine the target transaction manager, matching the* qualifier value (or the bean name) of a specific* {@link org.springframework.transaction.TransactionManager TransactionManager}* bean definition.* @since 4.2* @see #value* @see org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager* @see org.springframework.transaction.ReactiveTransactionManager*/@AliasFor("value")String transactionManager() default "";/*** Defines zero (0) or more transaction labels.* <p>Labels may be used to describe a transaction, and they can be evaluated* by individual transaction managers. Labels may serve a solely descriptive* purpose or map to pre-defined transaction manager-specific options.* <p>See the documentation of the actual transaction manager implementation* for details on how it evaluates transaction labels.* @since 5.3* @see org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.DefaultTransactionAttribute#getLabels()*/String[] label() default {};/*** The transaction propagation type.* <p>Defaults to {@link Propagation#REQUIRED}.* @see org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAttribute#getPropagationBehavior()*/Propagation propagation() default Propagation.REQUIRED;/*** The transaction isolation level.* <p>Defaults to {@link Isolation#DEFAULT}.* <p>Exclusively designed for use with {@link Propagation#REQUIRED} or* {@link Propagation#REQUIRES_NEW} since it only applies to newly started* transactions. Consider switching the "validateExistingTransactions" flag to* "true" on your transaction manager if you'd like isolation level declarations* to get rejected when participating in an existing transaction with a different* isolation level.* @see org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAttribute#getIsolationLevel()* @see org.springframework.transaction.support.AbstractPlatformTransactionManager#setValidateExistingTransaction*/Isolation isolation() default Isolation.DEFAULT;/*** The timeout for this transaction (in seconds).* <p>Defaults to the default timeout of the underlying transaction system.* <p>Exclusively designed for use with {@link Propagation#REQUIRED} or* {@link Propagation#REQUIRES_NEW} since it only applies to newly started* transactions.* @return the timeout in seconds* @see org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAttribute#getTimeout()*/int timeout() default TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT;/*** The timeout for this transaction (in seconds).* <p>Defaults to the default timeout of the underlying transaction system.* <p>Exclusively designed for use with {@link Propagation#REQUIRED} or* {@link Propagation#REQUIRES_NEW} since it only applies to newly started* transactions.* @return the timeout in seconds as a String value, e.g. a placeholder* @since 5.3* @see org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAttribute#getTimeout()*/String timeoutString() default "";/*** A boolean flag that can be set to {@code true} if the transaction is* effectively read-only, allowing for corresponding optimizations at runtime.* <p>Defaults to {@code false}.* <p>This just serves as a hint for the actual transaction subsystem;* it will <i>not necessarily</i> cause failure of write access attempts.* A transaction manager which cannot interpret the read-only hint will* <i>not</i> throw an exception when asked for a read-only transaction* but rather silently ignore the hint.* @see org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAttribute#isReadOnly()* @see org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionSynchronizationManager#isCurrentTransactionReadOnly()*/boolean readOnly() default false;/*** Defines zero (0) or more exception {@linkplain Class classes}, which must be* subclasses of {@link Throwable}, indicating which exception types must cause* a transaction rollback.* <p>By default, a transaction will be rolled back on {@link RuntimeException}* and {@link Error} but not on checked exceptions (business exceptions). See* {@link org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.DefaultTransactionAttribute#rollbackOn(Throwable)}* for a detailed explanation.* <p>This is the preferred way to construct a rollback rule (in contrast to* {@link #rollbackForClassName}), matching the exception type, its subclasses,* and its nested classes. See the {@linkplain Transactional class-level javadocs}* for further details on rollback rule semantics and warnings regarding possible* unintentional matches.* @see #rollbackForClassName* @see org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.RollbackRuleAttribute#RollbackRuleAttribute(Class)* @see org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.DefaultTransactionAttribute#rollbackOn(Throwable)*/Class<? extends Throwable>[] rollbackFor() default {};/*** Defines zero (0) or more exception name patterns (for exceptions which must be a* subclass of {@link Throwable}), indicating which exception types must cause* a transaction rollback.* <p>See the {@linkplain Transactional class-level javadocs} for further details* on rollback rule semantics, patterns, and warnings regarding possible* unintentional matches.* @see #rollbackFor* @see org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.RollbackRuleAttribute#RollbackRuleAttribute(String)* @see org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.DefaultTransactionAttribute#rollbackOn(Throwable)*/String[] rollbackForClassName() default {};/*** Defines zero (0) or more exception {@link Class Classes}, which must be* subclasses of {@link Throwable}, indicating which exception types must* <b>not</b> cause a transaction rollback.* <p>This is the preferred way to construct a rollback rule (in contrast to* {@link #noRollbackForClassName}), matching the exception type, its subclasses,* and its nested classes. See the {@linkplain Transactional class-level javadocs}* for further details on rollback rule semantics and warnings regarding possible* unintentional matches.* @see #noRollbackForClassName* @see org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.NoRollbackRuleAttribute#NoRollbackRuleAttribute(Class)* @see org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.DefaultTransactionAttribute#rollbackOn(Throwable)*/Class<? extends Throwable>[] noRollbackFor() default {};/*** Defines zero (0) or more exception name patterns (for exceptions which must be a* subclass of {@link Throwable}) indicating which exception types must <b>not</b>* cause a transaction rollback.* <p>See the {@linkplain Transactional class-level javadocs} for further details* on rollback rule semantics, patterns, and warnings regarding possible* unintentional matches.* @see #noRollbackFor* @see org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.NoRollbackRuleAttribute#NoRollbackRuleAttribute(String)* @see org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.DefaultTransactionAttribute#rollbackOn(Throwable)*/String[] noRollbackForClassName() default {};}
从定义来看这个注解的属性主要体现在从这么几个方面控制:
1. 作用范围,不仅仅可以添加在方法上面,还可以添加到类级别上。
当注解放在类级别时,表示所有该类的公共方法都配置相同的事务属性信息。如果类级别配置了 @transactional,方法级别也配置了 @transactional,应用程序会以方法级别的事务属性信息来管理事务。
2.作用场景,即在什么情况下提交事务或者回滚事务,将有@Transactional相关的配置参数来决定。
| 参数名 | 释义 | 举例 |
| value | 事务管理器 | 设置 Spring 容器中的 Bean 名称,这个 Bean 需要实现接口 PlatformTransactionManager。 |
isolation | 事务隔离级别 |
|
| propagation | 事务传播行为 | |
| timeout | 事务超时时间 | 单位为秒,默认值为-1,当事务超时时会抛出异常,进行回滚操作。 |
| readOnly | 是否开启只读事务 | 是否开启只读事务,默认 false |
| rollbackFor | 回滚事务异常类定义 | 当方法中出异常,且异常类和该参数指定的类相同时,进行回滚操作,否则提交事务。 |
| noRollbackFor | 非回滚事务异常类定义 | 指定发生哪些异常不回滚事务,当方法中出异常,且异常类和该参数指定的类相同时,不回滚而是将继续提交事务。 |
当然@Transactional并非直接加到方法头或者类头上就万事大吉了,还需要了解这么几个潜规则:
1.由于自调用方法不走Spring的代理类,所以无法确保private方法无法受到Spring AOP的代理,默认为私有private方法设置@Transactional注解无法生效事务。除非使用AspectJ做静态织入,否则需要确保只有public方法才设置@Transactional注解
2.只有异常传播出了标记了@Transactional注解的方法,事务才能遇到异常的情况下回滚,同时需要避免 catch住异常,或者通过TransactionAspectSupport.currentTransactionStatus().setRollbackOnly()手动回滚事务。默认情况下,出现 RuntimeException(非受检异常)或Error的时候,Spring 才会回滚事务,因此我们需要人为的去设置@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class),来突破默认不回滚受检异常的限制
3.默认事务传播策略是REQUIRED,即子方法会复用当前事务,当子方法出异常后会回滚当前事务,导致父方法也无法提交事务。如果不需要这样的效果,则需要人为的修改设置传播方式即propagation参数为REQUIRES_NEW方式的事务传播策略,让子方法运行在独立事务中。
当然还有分布式事务的控制,则显得稍有复杂,待笔者抽时间整理好后再呈现。