paper: Densely Connected Convolutional Networks
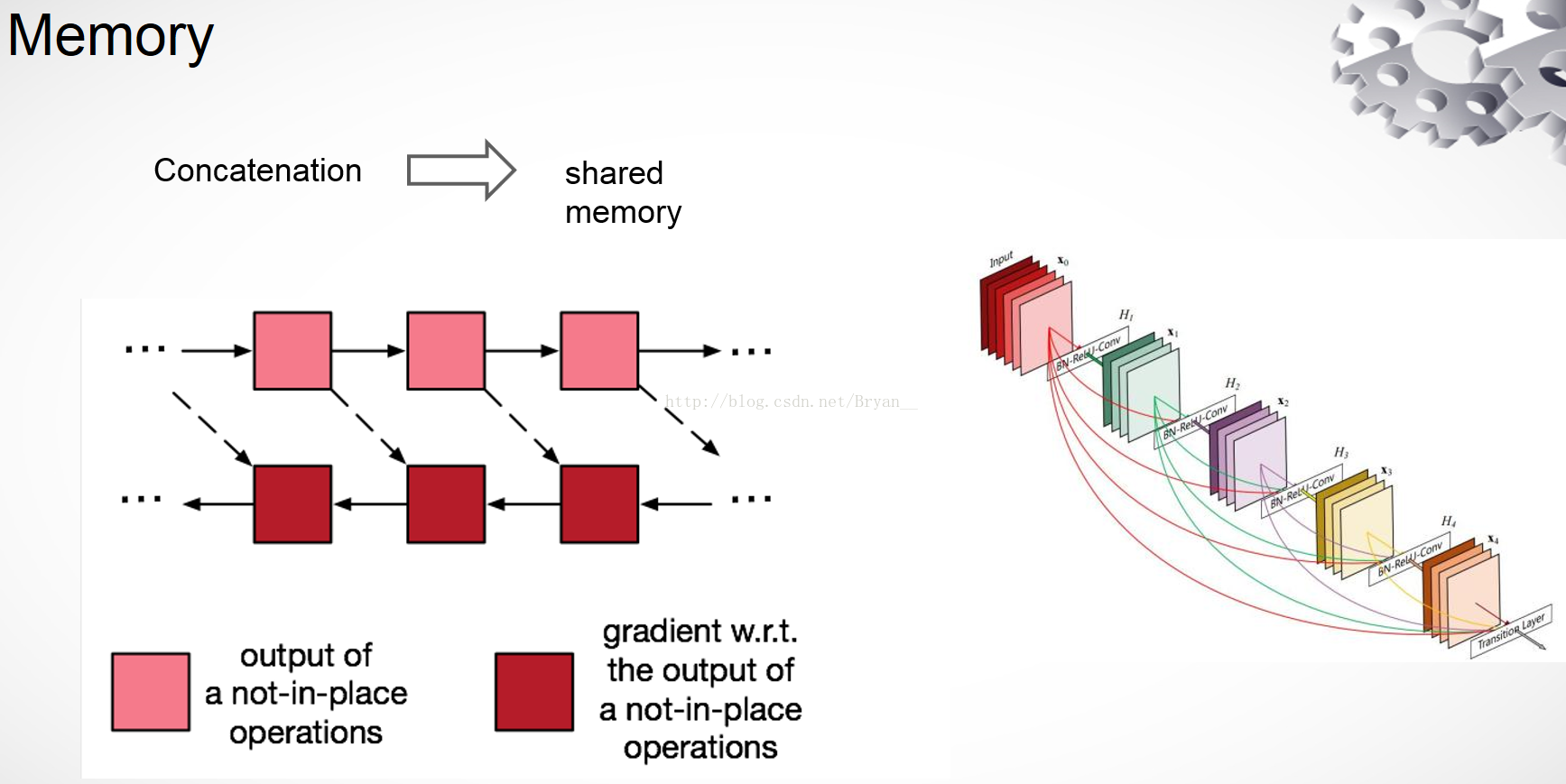
Memory-Efficient Implementation of DenseNets
code: https://github.com/pytorch/vision/blob/main/torchvision/models/densenet.py
在本篇文章中,作者提出了Dense Convolutional Network (DenseNet),下图是一个5层的dense block结构,可以看出每一层都作为后面所有层的输入。
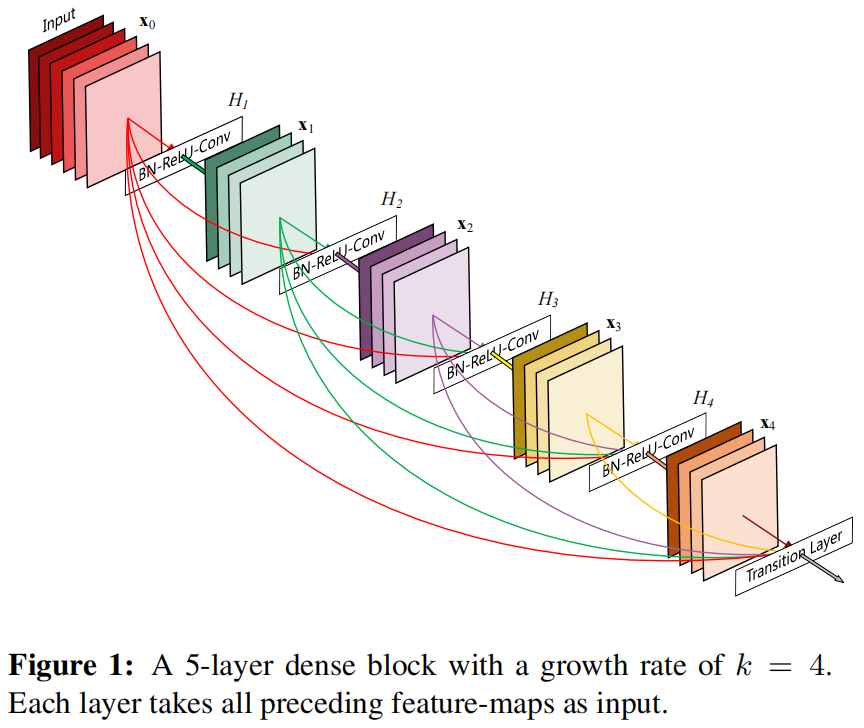
DenseNet有以下几个优点:
- 缓解了梯度消失问题
- 加强了特征的传播
- 增强了特征重用
- 大幅减少了参数数量
作者指出ResNet的一个优势是梯度可以通过identity函数直接从后面的层传播到前面的层,但是identity函数是通过相加(summation)和卷积结果进行融合的,这可能会阻碍网络中的信息流动。因此作者通过拼接(concatenation)的方式在每一层与后面所有的层之间都建立连接,来进一步改善层之间的信息流动。
实现细节:
- 层之间是一个包含三个连续的运算的复合函数:BN - ReLU - Conv(3x3)
- 在DenseNet中复合函数用的是pre-activation即BN-ReLU-Conv,而不是常见的post-activation即Conv-BN-ReLU,作者在文中提到pre-activation对DenseNet的最终效果影响很大,换成post-activation在cifar10和cifar100数据集上都会掉点
- dense block之间的transition层负责下采样,具体包括:BN - Conv(1x1) - 2x2 average pooling
-
假设一个dense block的输入特征图通道数为 \(k_{0}\),其中每一层的输出通道数为 \(k\),则第 \(l\) 层的输入通道数为 \(k_{0}+k\times (l-1)\)。这里的超参 \(k\) 就是网络的 growth rate。比较反直觉的是DenseNet的参数较少,就是因为这里的 \(k\) 可以设置的较小,文章中设置 \(k=32\),而不用像其它网络那样输出通道数达到1024、2048。
-
尽管每一层的输出通道数 \(k\) 比较小,但是因为输入包含了前面所有层因此输入的通道数很大,因此作者又提出了DenseNet-B,在每个3x3卷积层前添加1x1卷积作为bottleneck layer来进行降维,进一步提高计算效率。这样每一层的复合函数就变成了BN - ReLU - Conv(1x1) - BN - ReLU - Conv(3x3),文中1x1卷积的输出通道设置为 \(4k\)。
-
为了进一步减少参数,可以减少transition layer的输出通道数,如果dense block的输出通道为 \(m\),设置transition layer的输出为 \(\theta m\),对 \(\theta < 1\) 的DenseNet称为DenseNet-C。文中设置 \(\theta = 0.5\),对于含有bottleneck layer并且 \(\theta < 1\) 的DenseNet称为DenseNet-BC。
-
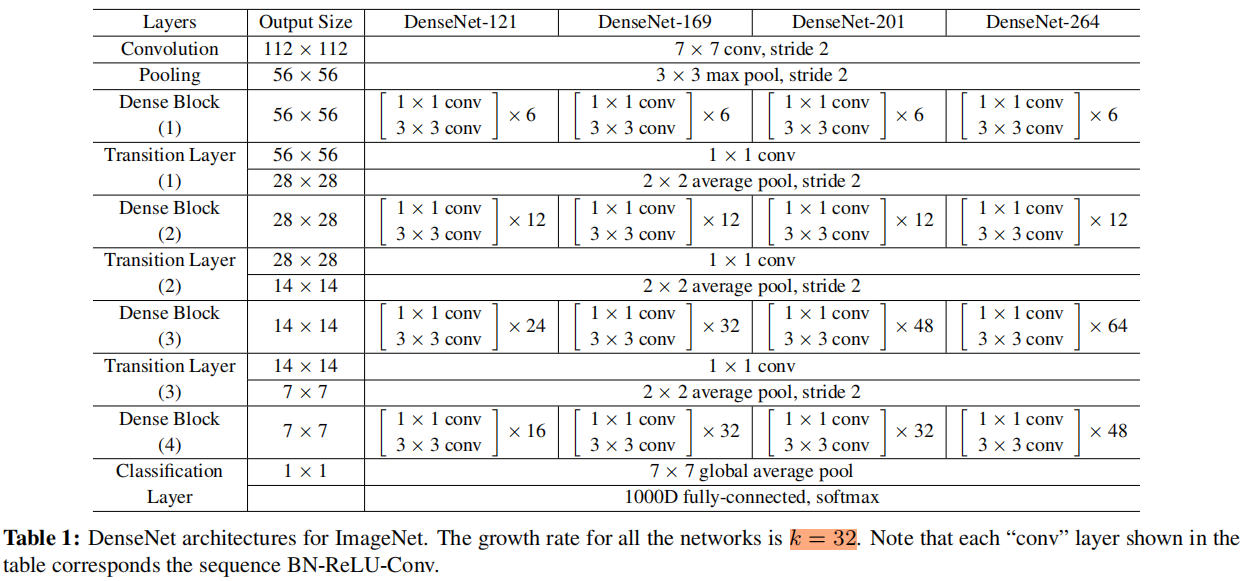
文中对于ImageNet数据集,作者使用含有4个dense block的DenseNet-BC,在第一个dense block前是一个7x7 stride=2 输出通道为 \(2k\) 的卷积层,然后是一个3x3 stride=2的max pooling层。在最后一个dense block后是一个全局平均池化,然后是softmax分类器。
不同层数的DenseNet结构如下表所示
代码
这里的代码是torchvision的官方实现
import re
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.utils.checkpoint as cp
from collections import OrderedDict
from .._internally_replaced_utils import load_state_dict_from_url
from torch import Tensor
from typing import Any, List, Tuple__all__ = ['DenseNet', 'densenet121', 'densenet169', 'densenet201', 'densenet161']model_urls = {'densenet121': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/densenet121-a639ec97.pth','densenet169': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/densenet169-b2777c0a.pth','densenet201': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/densenet201-c1103571.pth','densenet161': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/densenet161-8d451a50.pth',
}class _DenseLayer(nn.Module):def __init__(self,num_input_features: int,growth_rate: int,bn_size: int,drop_rate: float,memory_efficient: bool = False) -> None:super(_DenseLayer, self).__init__()self.norm1: nn.BatchNorm2dself.add_module('norm1', nn.BatchNorm2d(num_input_features))self.relu1: nn.ReLUself.add_module('relu1', nn.ReLU(inplace=True))self.conv1: nn.Conv2dself.add_module('conv1', nn.Conv2d(num_input_features, bn_size *growth_rate, kernel_size=1, stride=1,bias=False))self.norm2: nn.BatchNorm2dself.add_module('norm2', nn.BatchNorm2d(bn_size * growth_rate))self.relu2: nn.ReLUself.add_module('relu2', nn.ReLU(inplace=True))self.conv2: nn.Conv2dself.add_module('conv2', nn.Conv2d(bn_size * growth_rate, growth_rate,kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1,bias=False))self.drop_rate = float(drop_rate)self.memory_efficient = memory_efficientdef bn_function(self, inputs: List[Tensor]) -> Tensor:concated_features = torch.cat(inputs, 1)bottleneck_output = self.conv1(self.relu1(self.norm1(concated_features))) # noqa: T484return bottleneck_output# todo: rewrite when torchscript supports anydef any_requires_grad(self, input: List[Tensor]) -> bool:for tensor in input:if tensor.requires_grad:return Truereturn False@torch.jit.unused # noqa: T484def call_checkpoint_bottleneck(self, input: List[Tensor]) -> Tensor:def closure(*inputs):return self.bn_function(inputs)return cp.checkpoint(closure, *input)@torch.jit._overload_method # noqa: F811def forward(self, input: List[Tensor]) -> Tensor:pass@torch.jit._overload_method # noqa: F811def forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:pass# torchscript does not yet support *args, so we overload method# allowing it to take either a List[Tensor] or single Tensordef forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor: # noqa: F811if isinstance(input, Tensor):prev_features = [input]else:prev_features = inputif self.memory_efficient and self.any_requires_grad(prev_features):if torch.jit.is_scripting():raise Exception("Memory Efficient not supported in JIT")bottleneck_output = self.call_checkpoint_bottleneck(prev_features)else:bottleneck_output = self.bn_function(prev_features)new_features = self.conv2(self.relu2(self.norm2(bottleneck_output)))if self.drop_rate > 0:new_features = F.dropout(new_features, p=self.drop_rate,training=self.training)return new_featuresclass _DenseBlock(nn.ModuleDict):_version = 2def __init__(self,num_layers: int,num_input_features: int,bn_size: int,growth_rate: int,drop_rate: float,memory_efficient: bool = False) -> None:super(_DenseBlock, self).__init__()for i in range(num_layers):layer = _DenseLayer(num_input_features + i * growth_rate,growth_rate=growth_rate,bn_size=bn_size,drop_rate=drop_rate,memory_efficient=memory_efficient,)self.add_module('denselayer%d' % (i + 1), layer)def forward(self, init_features: Tensor) -> Tensor:features = [init_features]for name, layer in self.items():new_features = layer(features)features.append(new_features)return torch.cat(features, 1)class _Transition(nn.Sequential):def __init__(self, num_input_features: int, num_output_features: int) -> None:super(_Transition, self).__init__()self.add_module('norm', nn.BatchNorm2d(num_input_features))self.add_module('relu', nn.ReLU(inplace=True))self.add_module('conv', nn.Conv2d(num_input_features, num_output_features,kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False))self.add_module('pool', nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2))class DenseNet(nn.Module):r"""Densenet-BC model class, based on`"Densely Connected Convolutional Networks" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1608.06993.pdf>`_.Args:growth_rate (int) - how many filters to add each layer (`k` in paper)block_config (list of 4 ints) - how many layers in each pooling blocknum_init_features (int) - the number of filters to learn in the first convolution layerbn_size (int) - multiplicative factor for number of bottle neck layers(i.e. bn_size * k features in the bottleneck layer)drop_rate (float) - dropout rate after each dense layernum_classes (int) - number of classification classesmemory_efficient (bool) - If True, uses checkpointing. Much more memory efficient,but slower. Default: *False*. See `"paper" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1707.06990.pdf>`_."""def __init__(self,growth_rate: int = 32,block_config: Tuple[int, int, int, int] = (6, 12, 24, 16),num_init_features: int = 64,bn_size: int = 4,drop_rate: float = 0,num_classes: int = 1000,memory_efficient: bool = False) -> None:super(DenseNet, self).__init__()# First convolutionself.features = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([('conv0', nn.Conv2d(3, num_init_features, kernel_size=7, stride=2,padding=3, bias=False)),('norm0', nn.BatchNorm2d(num_init_features)),('relu0', nn.ReLU(inplace=True)),('pool0', nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)),]))# Each denseblocknum_features = num_init_featuresfor i, num_layers in enumerate(block_config):block = _DenseBlock(num_layers=num_layers,num_input_features=num_features,bn_size=bn_size,growth_rate=growth_rate,drop_rate=drop_rate,memory_efficient=memory_efficient)self.features.add_module('denseblock%d' % (i + 1), block)num_features = num_features + num_layers * growth_rateif i != len(block_config) - 1:trans = _Transition(num_input_features=num_features,num_output_features=num_features // 2)self.features.add_module('transition%d' % (i + 1), trans)num_features = num_features // 2# Final batch normself.features.add_module('norm5', nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features))# Linear layerself.classifier = nn.Linear(num_features, num_classes)# Official init from torch repo.for m in self.modules():if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight)elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor:features = self.features(x)out = F.relu(features, inplace=True)out = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(out, (1, 1))out = torch.flatten(out, 1)out = self.classifier(out)return outdef _load_state_dict(model: nn.Module, model_url: str, progress: bool) -> None:# '.'s are no longer allowed in module names, but previous _DenseLayer# has keys 'norm.1', 'relu.1', 'conv.1', 'norm.2', 'relu.2', 'conv.2'.# They are also in the checkpoints in model_urls. This pattern is used# to find such keys.pattern = re.compile(r'^(.*denselayer\d+\.(?:norm|relu|conv))\.((?:[12])\.(?:weight|bias|running_mean|running_var))$')state_dict = load_state_dict_from_url(model_url, progress=progress)for key in list(state_dict.keys()):res = pattern.match(key)if res:new_key = res.group(1) + res.group(2)state_dict[new_key] = state_dict[key]del state_dict[key]model.load_state_dict(state_dict)def _densenet(arch: str,growth_rate: int,block_config: Tuple[int, int, int, int],num_init_features: int,pretrained: bool,progress: bool,**kwargs: Any
) -> DenseNet:model = DenseNet(growth_rate, block_config, num_init_features, **kwargs)if pretrained:_load_state_dict(model, model_urls[arch], progress)return modeldef densenet121(pretrained: bool = False, progress: bool = True, **kwargs: Any) -> DenseNet:r"""Densenet-121 model from`"Densely Connected Convolutional Networks" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1608.06993.pdf>`_.The required minimum input size of the model is 29x29.Args:pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNetprogress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderrmemory_efficient (bool) - If True, uses checkpointing. Much more memory efficient,but slower. Default: *False*. See `"paper" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1707.06990.pdf>`_."""return _densenet('densenet121', 32, (6, 12, 24, 16), 64, pretrained, progress,**kwargs)def densenet161(pretrained: bool = False, progress: bool = True, **kwargs: Any) -> DenseNet:r"""Densenet-161 model from`"Densely Connected Convolutional Networks" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1608.06993.pdf>`_.The required minimum input size of the model is 29x29.Args:pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNetprogress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderrmemory_efficient (bool) - If True, uses checkpointing. Much more memory efficient,but slower. Default: *False*. See `"paper" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1707.06990.pdf>`_."""return _densenet('densenet161', 48, (6, 12, 36, 24), 96, pretrained, progress,**kwargs)def densenet169(pretrained: bool = False, progress: bool = True, **kwargs: Any) -> DenseNet:r"""Densenet-169 model from`"Densely Connected Convolutional Networks" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1608.06993.pdf>`_.The required minimum input size of the model is 29x29.Args:pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNetprogress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderrmemory_efficient (bool) - If True, uses checkpointing. Much more memory efficient,but slower. Default: *False*. See `"paper" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1707.06990.pdf>`_."""return _densenet('densenet169', 32, (6, 12, 32, 32), 64, pretrained, progress,**kwargs)def densenet201(pretrained: bool = False, progress: bool = True, **kwargs: Any) -> DenseNet:r"""Densenet-201 model from`"Densely Connected Convolutional Networks" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1608.06993.pdf>`_.The required minimum input size of the model is 29x29.Args:pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNetprogress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderrmemory_efficient (bool) - If True, uses checkpointing. Much more memory efficient,but slower. Default: *False*. See `"paper" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1707.06990.pdf>`_."""return _densenet('densenet201', 32, (6, 12, 48, 32), 64, pretrained, progress,**kwargs)
Memory-Efficient Implementation
DenseNet虽然参数很少,但因为每一层的输入都要对之前所有层的输出进行拼接,在大多数框架如Tensorflow和Pytorch中,每进行一次拼接操作,都会开辟新的内存用于保存拼接后的结果,因此对于一个 \(L\) 层的DenseNet,这就要占用 \(L(L+1)/2\) 层的内存。对于一个普通的卷积网络如vgg、resnet,中间特征图的数量随着网络深度的加深呈线性增长,因此将这些特征图保存在内存中不会带来显著的内存负担。但对于一个有 \(m\) 层的dense block,保存中间特征图会导致 \(O(m^2)\) 的内存使用,这种指数级的增长会导致显存不够的情况。
解决方法:深度学习框架中之所以要保存中间结果,是因为反向传播过程中需要用到这些中间结果来计算梯度。具体解决方法是前向过程中不保存中间结果,而是保存输入和具体的运算函数(比如卷积、BN、池化等),这样在反向过程中需要用到前向的中间结果时,通过保存的输入和函数重新计算,这样就大大减小了显存的占用,但同时也导致了训练时间的增加,算是一种用时间换空间的方法。
在上面torchvision的实现中,通过torch.utils.checkpoint.checkpoint来实现,并且只对复合函数BN - ReLU - Conv(1x1) - BN - ReLU - Conv(3x3)中的前半部分进行该操作,因为当 \(growth\_rate=k\) 时,1x1卷积的输出通道数是 \(4k\),3x3卷积的输出是 \(k\),前半部分的显存占用更多。