1. 基本概念
1.1 Instrumentation是什么?
顾名思义,仪器仪表,用于在应用程序中进行“测量”和“管理”工作。一个应用程序中只有一个Instrumentation实例对象,且每个Activity都有此对象的引用。Instrumentation将在任何应用程序运行前初始化,可以通过它监测系统与应用程序之间的所有交互,即类似于在系统与应用程序之间安装了个“窃听器”。
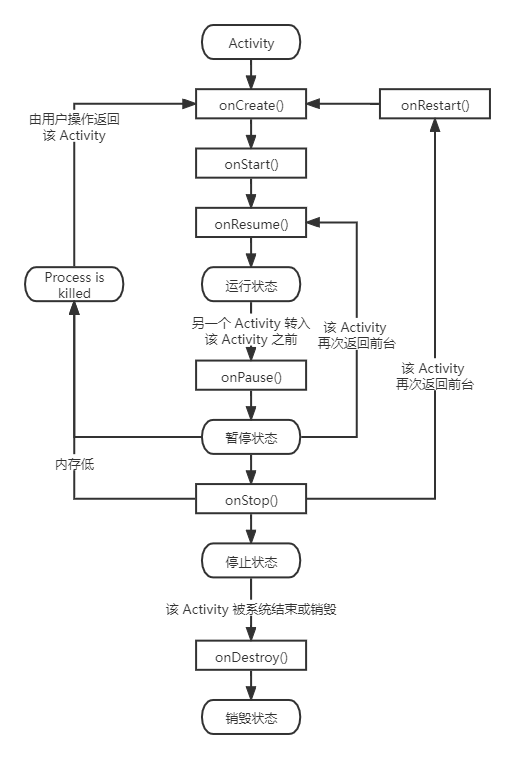
当ActivityThread 创建(callActivityOnCreate)、暂停、恢复某个Activity时,通过调用此对象的方法来实现,如:
1) 创建: callActivityOnCreate
2) 暂停: callActivityOnPause
3) 恢复: callActivityOnResume
Instrumentation和ActivityThread的关系,类似于老板与经理的关系,老板负责对外交流(如与Activity Manager Service<AMS>),Instrumentation负责管理并完成老板交待的任务。
它通过以下两个成员变量来对当前应用进程中的Activity进行管理:
private List<ActivityWaiter> mWaitingActivities;private List<ActivityMonitor> mActivityMonitors;其功能函数下表所示:
| 功能 | 函数 |
| 增加删除Monitor | addMonitor(ActivityMonitor monitor) removeMonitor(ActivityMonitor monitor) |
| Application与Activity生命周期控制 | newApplication(Class<?> clazz, Context context) newActivity(ClassLoader cl, String className,Intent intent) callActivityOnCreate(Activity activity, Bundle icicle) callActivityOnDestroy(Activity activity) callActivityOnStart(Activity activity) callActivityOnRestart(Activity activity) callActivityOnResume(Activity activity) callActivityOnStop(Activity activity) callActivityOnPause(Activity activity) |
| Instrumentation生命周期控制 | onCreate(Bundle arguments) start() onStart() finish(int resultCode, Bundle results) onDestroy() |
| 发送用户操控信息到当前窗口 | sendCharacterSync(int keyCode) sendPointerSync(MotionEvent event) sendTrackballEventSync(MotionEvent event) sendTrackballEventSync(MotionEvent event) |
| 同步操作 | startActivitySync(Intent intent) //它调用Context.startActivity runOnMainSync(Runnable runner) waitForIdle() |
2. Android应用程序启动过程(MainActivity)
即MainActivity的启动过程,在此过程中,将创建一个新的进程来执行此MainActivity。
Android应用程序从Launcher启动流程如下所示:
/****************************************************************** Launcher通过Binder告诉ActivityManagerService,* 它将要启动一个新的Activity;****************************************************************/
Launcher.startActivitySafely->
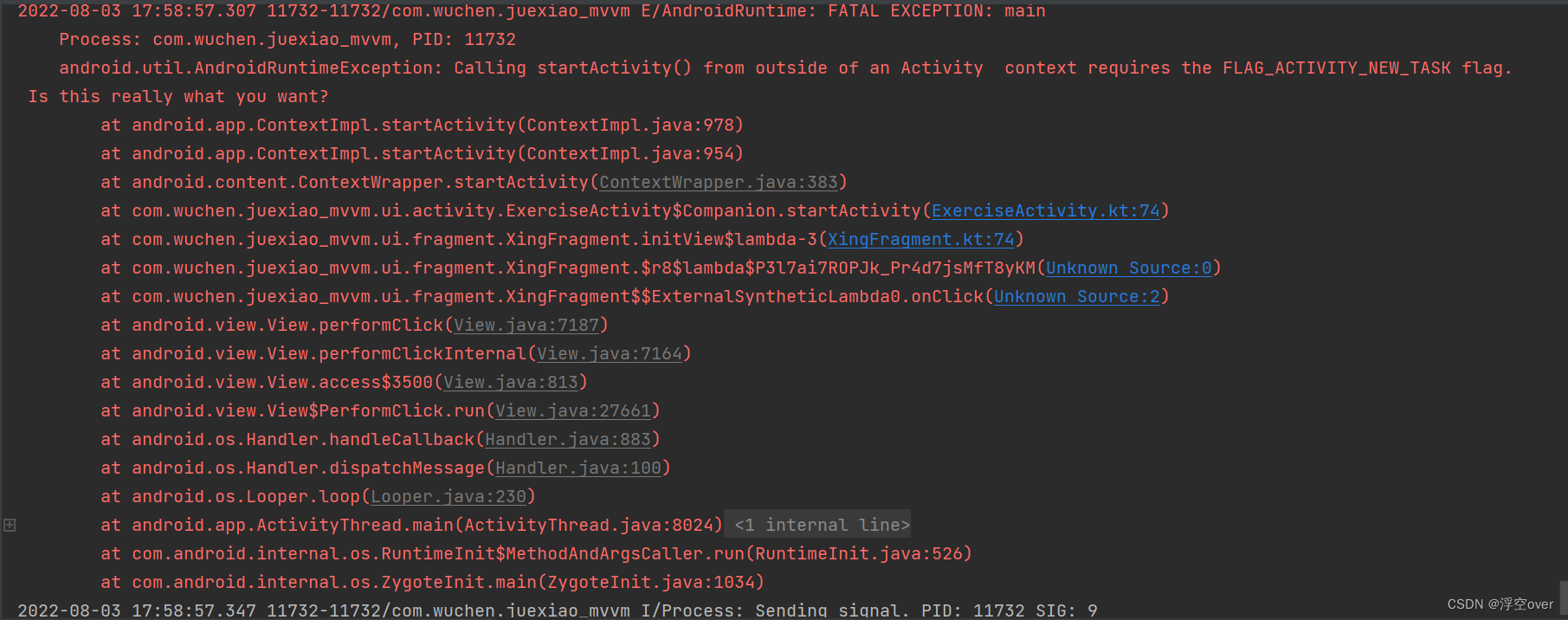
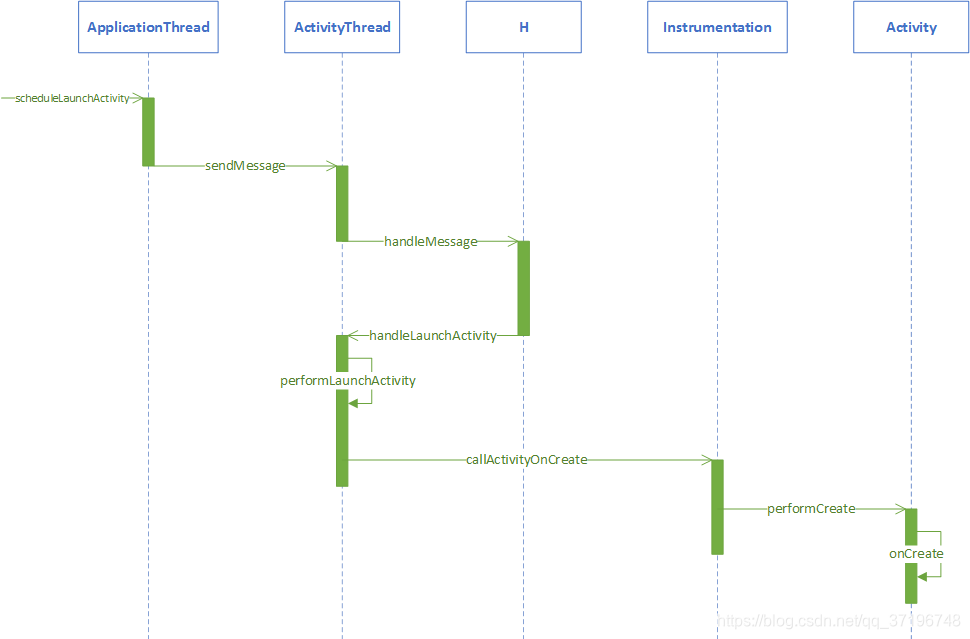
Launcher.startActivity-> //要求在新的Task中启动此Activity //intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK) Activity.startActivity-> Activity.startActivityForResult-> Instrumentation.execStartActivity-> // ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()返回AMS Proxy接口 ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().startActivity-> ActivityManagerProxy.startActivity-> ActivityManagerService.startActivity-> (AMS) ActivityManagerService.startActivityAsUser-> ActivityStack.startActivityMayWait-> ActivityStack.resolveActivity(获取ActivityInfo) //aInfo.name为main Activity,如:com.my.test.MainActivity //aInfo.applicationInfo.packageName为包名,如com.my.test ActivityStack.startActivityLocked-> //ProcessRecord callerApp; 调用者即Launcher信息 //ActivityRecord sourceRecord; Launcher Activity相关信息 //ActivityRecord r=new ActivityRecord(...),将要创建的Activity相关信息 ActivityStack.startActivityUncheckedLocked-> //Activity启动方式:ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_MULTIPLE/LAUNCH_SINGLE_INSTANCE/ // ActivityInfo.LAUNCH_SINGLE_TASK/LAUNCH_SINGLE_TOP) // 创建一个新的task,即TaskRecord,并保存在ActivityRecord.task中 //r.setTask(new TaskRecord(mService.mCurTask, r.info, intent), null, true) // 把新创建的Activity放在栈顶 ActivityStack.startActivityLocked-> ActivityStack.resumeTopActivityLocked-> ActivityStack.startPausingLocked (使Launcher进入Paused状态)-> /****************************************************************** AMS通过Binder通知Launcher进入Paused状态****************************************************************/ApplicationThreadProxy.schedulePauseActivity-> //private class ApplicationThread extends ApplicationThreadNative ApplicationThread.schedulePauseActivity-> ActivityThread.queueOrSendMessage-> // 调用Activity.onUserLeaveHint // 调用Activity.onPause // 通知activity manager我进入了pause状态 ActivityThread.handlePauseActivity-> /****************************************************************** Launcher通过Binder告诉AMS,它已经进入Paused状态****************************************************************/ActivityManagerProxy.activityPaused-> ActivityManagerService.activityPaused-> ActivityStack.activityPaused->(把Activity状态修改为PAUSED) ActivityStack.completePauseLocked-> // 参数为代表Launcher这个Activity的ActivityRecord // 使用栈顶的Activity进入RESUME状态 ActivityStack.resumeTopActivityLokced-> //topRunningActivityLocked将刚创建的放于栈顶的activity取回来 // 即在ActivityStack.startActivityUncheckedLocked中创建的 /****************************************************************** AMS创建一个新的进程,用来启动一个ActivityThread实例,* 即将要启动的Activity就是在这个ActivityThread实例中运行****************************************************************/ActivityStack.startSpecificActivityLocked-> // 创建对应的ProcessRecord ActivityManagerService.startProcessLocked-> // 启动一个新的进程 // 新的进程会导入android.app.ActivityThread类,并且执行它的main函数, // 即实例化ActivityThread, 每个应用有且仅有一个ActivityThread实例 Process.start("android.app.ActivityThread",...)-> // 通过zygote机制创建一个新的进程 Process.startViaZygote-> // 这个函数在进程中创建一个ActivityThread实例,然后调用 // 它的attach函数,接着就进入消息循环 ActivityThread.main-> /****************************************************************** ActivityThread通过Binder将一个ApplicationThread类的Binder对象* 传递给AMS,以便AMS通过此Binder对象来控制Activity整个生命周期****************************************************************/ActivityThread.attach-> IActivityManager.attachApplication(mAppThread)-> ActivityManagerProxy.attachApplication-> ActivityManagerService.attachApplication-> // 把在ActivityManagerService.startProcessLocked中创建的ProcessRecord取出来 ActivityManagerService.attachApplicationLocked-> /****************************************************************** AMS通过Binder通知ActivityThread一切准备OK,它可以真正启动新的Activity了****************************************************************/ // 真正启动Activity ActivityStack.realStartActivityLocked-> ApplicationThreadProxy.scheduleLaunchActivity-> ApplicationThread.scheduleLaunchActivity-> ActivityThread.handleLaunchActivity-> // 加载新的Activity类,并执行它的onCreate ActivityThread.performLaunchActivity /*1) Instrumentation.newActivity: 加载新类,即创建Activity对象; 2) ActivityClientRecord.packageInfo.makeApplication:创建Application对象; <LoadedApk.makeApplication> 3) Activity.attach(Context context, ActivityThread aThread, Instrumentation instr, IBinder token, int ident, Application application, Intent intent, ActivityInfo info, CharSequence title, Activity parent, String id, NonConfigurationInstances lastNonConfigurationInstances, Configuration config):把Application attach到Activity, 即把Activtiy 相关信息设置到新创建的Activity中 4) Instrumentation.callActivityOnCreate:调用onCreate;*/ // 使用Activity进入RESUMED状态,并调用onResume ActivityThread.handleResumeActivity
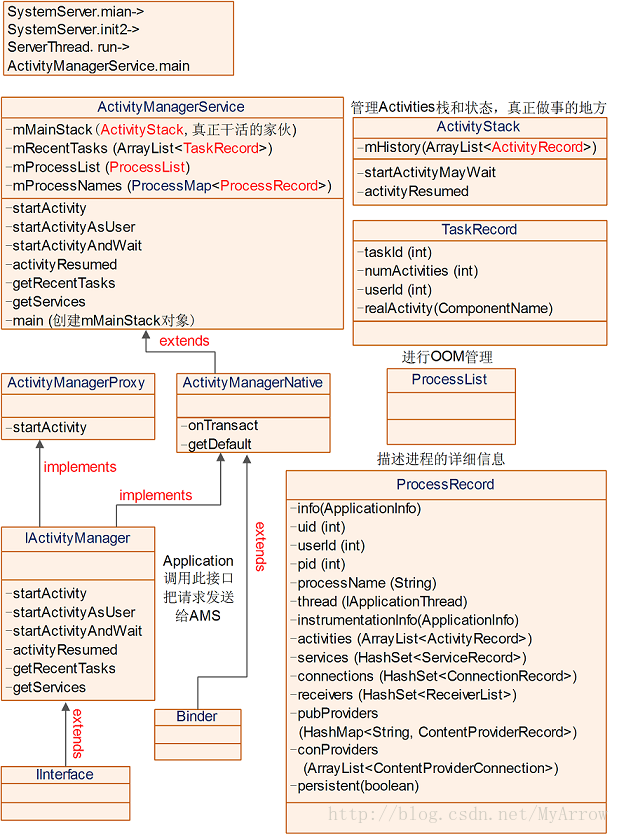
3. ActivityManagerService
3.1 类中关键信息
public final class ActivityManagerService extends ActivityManagerNativeimplements Watchdog.Monitor, BatteryStatsImpl.BatteryCallback {...// Maximum number of recent tasks that we can remember.static final int MAX_RECENT_TASKS = 20;public ActivityStack mMainStack; // 管理Activity堆栈// Whether we should show our dialogs (ANR, crash, etc) or just perform their// default actuion automatically. Important for devices without direct input// devices.private boolean mShowDialogs = true;/*** Description of a request to start a new activity, which has been held* due to app switches being disabled.*/static class PendingActivityLaunch {ActivityRecord r;ActivityRecord sourceRecord;int startFlags;}/*** Activity we have told the window manager to have key focus.*/ActivityRecord mFocusedActivity = null;/*** List of intents that were used to start the most recent tasks.*/final ArrayList<TaskRecord> mRecentTasks = new ArrayList<TaskRecord>();/*** Process management.*/final ProcessList mProcessList = new ProcessList();/*** All of the applications we currently have running organized by name.* The keys are strings of the application package name (as* returned by the package manager), and the keys are ApplicationRecord* objects.*/final ProcessMap<ProcessRecord> mProcessNames = new ProcessMap<ProcessRecord>();/*** The currently running isolated processes.*/final SparseArray<ProcessRecord> mIsolatedProcesses = new SparseArray<ProcessRecord>();...public static final Context main(int factoryTest) { //main入口函数AThread thr = new AThread();thr.start();synchronized (thr) {while (thr.mService == null) {try {thr.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {}}}ActivityManagerService m = thr.mService;mSelf = m;ActivityThread at = ActivityThread.systemMain();mSystemThread = at;Context context = at.getSystemContext();context.setTheme(android.R.style.Theme_Holo);m.mContext = context;m.mFactoryTest = factoryTest;m.mMainStack = new ActivityStack(m, context, true); // 创建ActivityStackm.mBatteryStatsService.publish(context);m.mUsageStatsService.publish(context);synchronized (thr) {thr.mReady = true;thr.notifyAll();}m.startRunning(null, null, null, null);return context;}
}
3.2 家族图谱
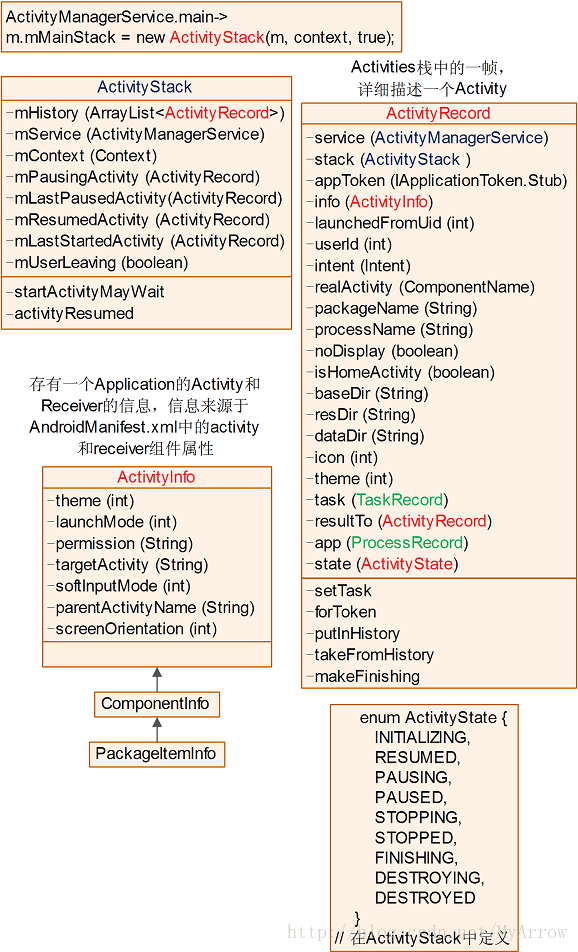
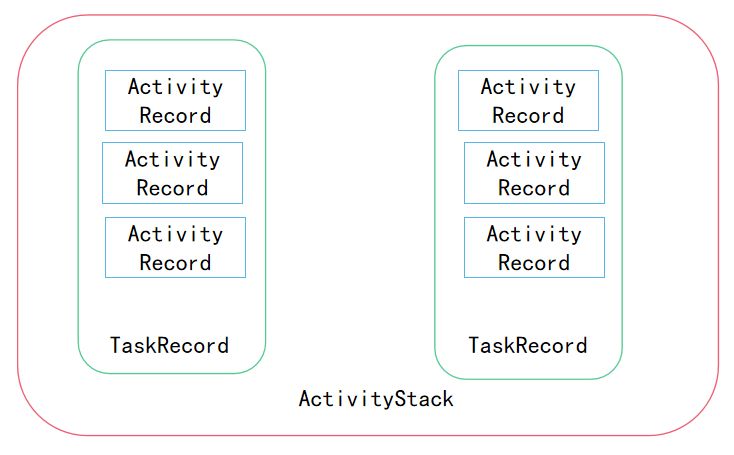
4. ActivityStack-真正做事的家伙
ActivityManagerService使用它来管理系统中所有的Activities的状态,Activities使用stack的方式进行管理。它是真正负责做事的家伙,很勤快的,但外界无人知道!
4.1 类中关键信息
/*** State and management of a single stack of activities.*/
final class ActivityStack {final ActivityManagerService mService;final boolean mMainStack;final Context mContext;enum ActivityState {INITIALIZING,RESUMED,PAUSING,PAUSED,STOPPING,STOPPED,FINISHING,DESTROYING,DESTROYED}/*** The back history of all previous (and possibly still* running) activities. It contains HistoryRecord objects.*/final ArrayList<ActivityRecord> mHistory = new ArrayList<ActivityRecord>();/*** Used for validating app tokens with window manager.*/final ArrayList<IBinder> mValidateAppTokens = new ArrayList<IBinder>();/*** List of running activities, sorted by recent usage.* The first entry in the list is the least recently used.* It contains HistoryRecord objects.*/final ArrayList<ActivityRecord> mLRUActivities = new ArrayList<ActivityRecord>();/*** List of activities that are waiting for a new activity* to become visible before completing whatever operation they are* supposed to do.*/final ArrayList<ActivityRecord> mWaitingVisibleActivities= new ArrayList<ActivityRecord>();/*** List of activities that are ready to be stopped, but waiting* for the next activity to settle down before doing so. It contains* HistoryRecord objects.*/final ArrayList<ActivityRecord> mStoppingActivities= new ArrayList<ActivityRecord>();/*** List of activities that are in the process of going to sleep.*/final ArrayList<ActivityRecord> mGoingToSleepActivities= new ArrayList<ActivityRecord>();/*** When we are in the process of pausing an activity, before starting the* next one, this variable holds the activity that is currently being paused.*/ActivityRecord mPausingActivity = null;/*** This is the last activity that we put into the paused state. This is* used to determine if we need to do an activity transition while sleeping,* when we normally hold the top activity paused.*/ActivityRecord mLastPausedActivity = null;/*** Current activity that is resumed, or null if there is none.*/ActivityRecord mResumedActivity = null;/*** This is the last activity that has been started. It is only used to* identify when multiple activities are started at once so that the user* can be warned they may not be in the activity they think they are.*/ActivityRecord mLastStartedActivity = null;/*** Set to indicate whether to issue an onUserLeaving callback when a* newly launched activity is being brought in front of us.*/boolean mUserLeaving = false;ActivityStack(ActivityManagerService service, Context context, boolean mainStack) {mService = service;mContext = context;mMainStack = mainStack;...}...
}
4.2 家族图谱
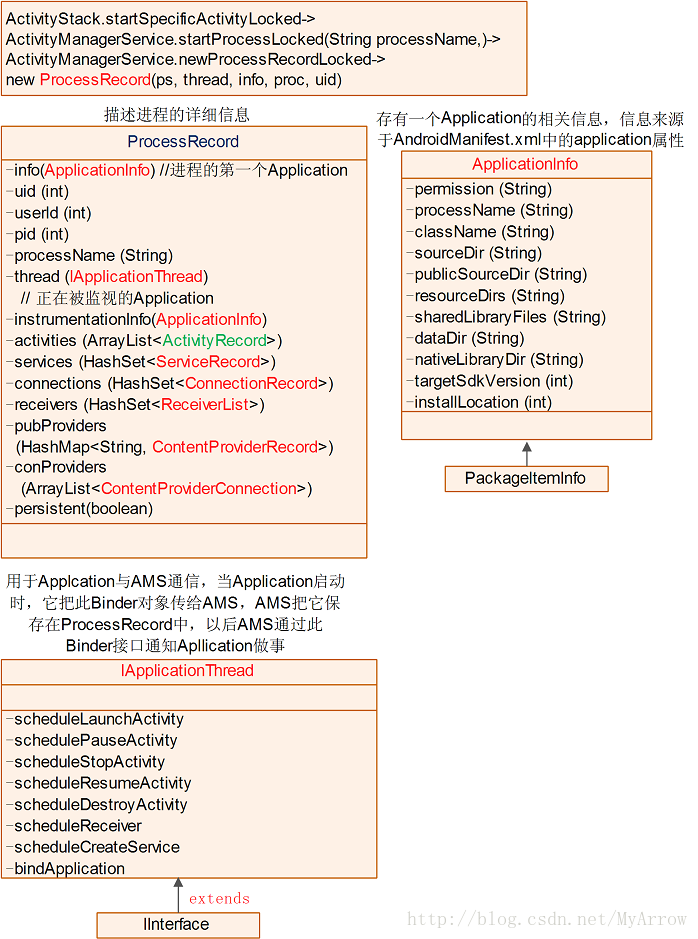
5. ProcessRecord
记录了一个进程的相关信息。
5.1 类中关键信息
/*** Full information about a particular process that* is currently running.*/
class ProcessRecord {final ApplicationInfo info; // all about the first app in the processfinal boolean isolated; // true if this is a special isolated processfinal int uid; // uid of process; may be different from 'info' if isolatedfinal int userId; // user of process.final String processName; // name of the processIApplicationThread thread; // the actual proc... may be null only if// 'persistent' is true (in which case we// are in the process of launching the app)// 是ApplicationThread对象的远程接口,// 通过此接口通知Activity进入对应的状态int pid; // The process of this application; 0 if noneApplicationInfo instrumentationInfo; // the application being instrumentedBroadcastRecord curReceiver;// receiver currently running in the app// contains HistoryRecord objectsfinal ArrayList<ActivityRecord> activities = new ArrayList<ActivityRecord>();// all ServiceRecord running in this processfinal HashSet<ServiceRecord> services = new HashSet<ServiceRecord>();// services that are currently executing code (need to remain foreground).final HashSet<ServiceRecord> executingServices= new HashSet<ServiceRecord>();// All ConnectionRecord this process holdsfinal HashSet<ConnectionRecord> connections= new HashSet<ConnectionRecord>(); // all IIntentReceivers that are registered from this process.final HashSet<ReceiverList> receivers = new HashSet<ReceiverList>();// class (String) -> ContentProviderRecordfinal HashMap<String, ContentProviderRecord> pubProviders= new HashMap<String, ContentProviderRecord>(); // All ContentProviderRecord process is usingfinal ArrayList<ContentProviderConnection> conProviders= new ArrayList<ContentProviderConnection>();boolean persistent; // always keep this application running?boolean crashing; // are we in the process of crashing?Dialog crashDialog; // dialog being displayed due to crash.boolean notResponding; // does the app have a not responding dialog?Dialog anrDialog; // dialog being displayed due to app not resp.boolean removed; // has app package been removed from device?boolean debugging; // was app launched for debugging?boolean waitedForDebugger; // has process show wait for debugger dialog?Dialog waitDialog; // current wait for debugger dialogProcessRecord(BatteryStatsImpl.Uid.Proc _batteryStats, IApplicationThread _thread,ApplicationInfo _info, String _processName, int _uid) {batteryStats = _batteryStats;info = _info;isolated = _info.uid != _uid;uid = _uid;userId = UserHandle.getUserId(_uid);processName = _processName;pkgList.add(_info.packageName);thread = _thread;maxAdj = ProcessList.HIDDEN_APP_MAX_ADJ;hiddenAdj = clientHiddenAdj = emptyAdj = ProcessList.HIDDEN_APP_MIN_ADJ;curRawAdj = setRawAdj = -100;curAdj = setAdj = -100;persistent = false;removed = false;}...
}
5. 2 家族图谱
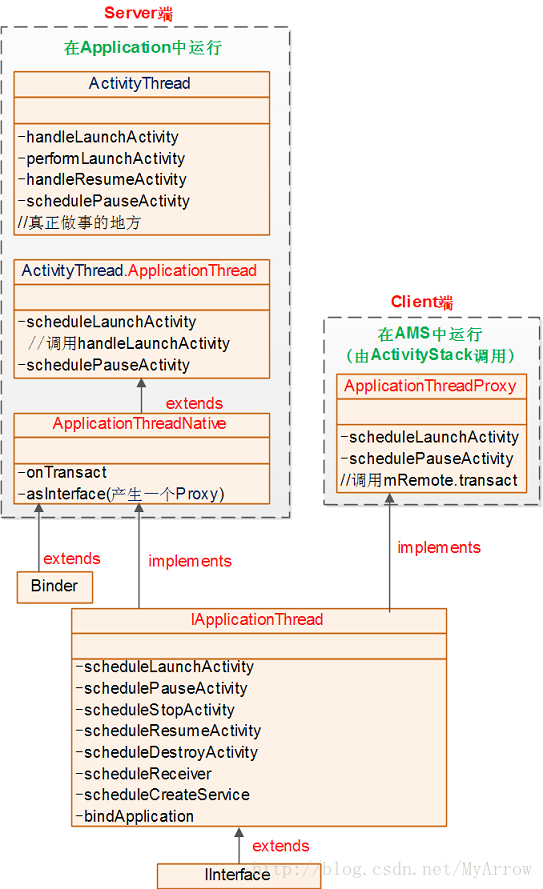
6. IApplicationThread接口AMS->Application
IApplicationThread为AMS作为客户端访问Application服务器端的Binder接口。当创建Application时,将把此Binder对象传递给AMS,然后AMS把它保存在mProcessNames.ProcessRecord.thread中。当需要通知Application工作时,则调用IApplicationThread中对应的接口函数。
其相互关系如下图所示: