导语
在日常的开发中通常会遇到截取List的情况,而大多数会选择使用subList方法进行截取,但是好多人对这个方法的理解都只是停留在使用层面上?这篇文章会非常详细达到源码级别的讲解sublList方法,需要的朋友赶紧收藏起来吧。
关于SubList
先通过下面这个例子,看看具体的返回类型:
public class TestSubList {public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {list.add(""+i);}List<String> subList = list.subList(3, 6);System.out.println(subList.getClass()+" "+subList);System.out.println(list.getClass()+" "+list);}
}
输出结果:
class java.util.ArrayList$SubList [3, 4, 5]
class java.util.ArrayList [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
通过例子可以看出,当对list进行subList之后返回的subList对象,其实是一个内部类SubList,严格意思上来说,subList是ArrayList对象的一个视图,对于subList对象的操作都会映射到原来的ArrayList集合中。再通过下面这个例子看下具体的操作影响。
public class TestSubList {public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {list.add(""+i);}List<String> subList = list.subList(3, 6);System.out.println(subList.getClass()+" "+subList);System.out.println(list.getClass()+" "+list);System.out.println("----------------");subList.add("subList添加");System.out.println(subList.getClass()+" "+subList);System.out.println(list.getClass()+" "+list);}
}
输出结果:
class java.util.ArrayList$SubList [3, 4, 5]
class java.util.ArrayList [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
----------------
class java.util.ArrayList$SubList [3, 4, 5, subList添加]
class java.util.ArrayList [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, subList添加, 6, 7, 8, 9]
从上面可以看出,对subList的操作已经影响到ArrayList了,下面咱根据源码进行详细的分析一下原因。
关于集合类,《阿里巴巴Java开发手册》中其实还有另外一个规定:

源码概览
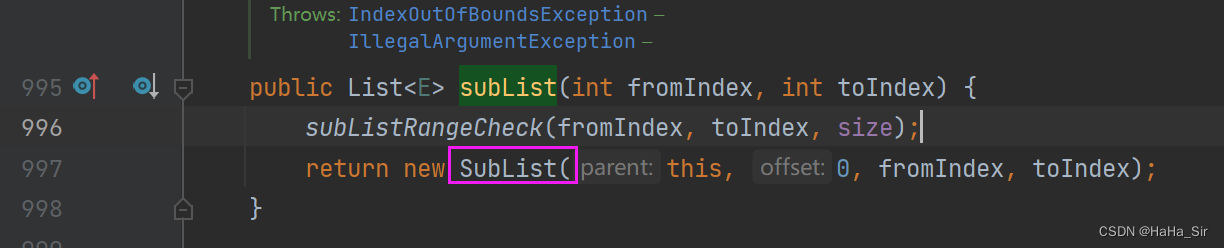
// subList方法
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size);return new SubList(this, 0, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
从源码中可以看出,其实subList方法返回的是ArrayList的内部类SubList,并不是ArrayList,所以,在使用的时候会有许多的注意细节。
private class SubList extends AbstractList<E> implements RandomAccess {private final AbstractList<E> parent;private final int parentOffset;private final int offset;int size;SubList(AbstractList<E> parent,int offset, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {this.parent = parent;this.parentOffset = fromIndex;this.offset = offset + fromIndex;this.size = toIndex - fromIndex;this.modCount = ArrayList.this.modCount;}public E set(int index, E e) {rangeCheck(index);checkForComodification();E oldValue = ArrayList.this.elementData(offset + index);ArrayList.this.elementData[offset + index] = e;return oldValue;}public E get(int index) {rangeCheck(index);checkForComodification();return ArrayList.this.elementData(offset + index);}public int size() {checkForComodification();return this.size;}public void add(int index, E e) {rangeCheckForAdd(index);checkForComodification();parent.add(parentOffset + index, e);this.modCount = parent.modCount;this.size++;}public E remove(int index) {rangeCheck(index);checkForComodification();E result = parent.remove(parentOffset + index);this.modCount = parent.modCount;this.size--;return result;}protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {checkForComodification();parent.removeRange(parentOffset + fromIndex,parentOffset + toIndex);this.modCount = parent.modCount;this.size -= toIndex - fromIndex;}public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {return addAll(this.size, c);}public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {rangeCheckForAdd(index);int cSize = c.size();if (cSize==0)return false;checkForComodification();parent.addAll(parentOffset + index, c);this.modCount = parent.modCount;this.size += cSize;return true;}}
其实从SubList类的源码中可以看出,SubList类中也实现了和ArrayList中的一样的方法,所以在调用subList的一些方法时,运行的是SubList中的实现,而且从上面可以看出,真正操作的还是原ArrayList对象。
源码详解
先看subList方法以及SubList的构造方法:
// subList方法
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size);return new SubList(this, 0, fromIndex, toIndex);
}// SubList构造方法
SubList(AbstractList<E> parent,int offset, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {this.parent = parent;this.parentOffset = fromIndex;this.offset = offset + fromIndex;// 将截取长度作为SubList的长度this.size = toIndex - fromIndex;// 将ArrayList对象的modCount赋值给SubList对象this.modCount = ArrayList.this.modCount;
}
从上面可以看出,当构造SubList对象的时候,会存储原集合在parent变量中,并且把截取的开始下标存为parentOffset。
下面详细看一个SubList的add方法,对上面的现象进行一个详细的分析。
// SubList对象的add方法
public void add(int index, E e) {// 检查下标是否合规rangeCheckForAdd(index);// 检查modCount是否和ArrayList的modCount一致(注:modCount表示的是集合的结构变化次数)checkForComodification();// 在原ArrayList指定位置添加元素parent.add(parentOffset + index, e);// 将ArrayList对象的modCount赋值给SubList对象this.modCount = parent.modCount;// 使SubList对象的长度加一this.size++;
}
通过上面的方法讲解,可以看出,对SubList对象的操作,其实就是对ArrayList对象的操作,其他的方法也都是同理。
总结
本篇文章详细介绍了ArrayList的subLIst方法以及SubList类的用法,由于纯手打,难免会有纰漏,如果发现错误的地方,请第一时间告诉我,这将是我进步的一个很重要的环节。













![[数学建模] 大数据建模五步法](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20025dff73ff4c80b017e2f6a77836be.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L1dTQTE2MzU=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)