1.软件版本
MATLAB2021a
2.本算法理论知识
[1]钱坤. 基于MSER和遗传优化SVM的交通标志识别的研究[D]. 大连理工大学.
[2]王斌, 常发亮, 刘春生. 基于MSER和SVM的快速交通标志检测[J]. 光电子.激光, 2016.
3.部分源码
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% %
% MSER algorithm - Linear Time MSER %clc
clear
close alltic
% Read input image
img = imread('img/smp_6.jpg');
height = size(img,1);
width = size(img,2);
total_pixels_img = width*height;
usage = 'segmented'; % select between segmented or gray scale% image as input: 'segmented' / 'gray'% Parameters to set
min_area_mser = 1000;
max_area_mser = 1000000;
mser_p.delta = 2;
mser_p.min_area = 0.00001*width*height;
mser_p.max_area = 0.25*width*height;
mser_p.max_variation = 0.5;
mser_p.min_diversity = 0.33;
color_of_interest = 'blue'; % Options are: red, green, blue
color_threshold = 100; % range from 0-255
ratio = 1.2; % ration between color interest and% others: 20%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% INIT ALGORITHM% 1) Select input image to process if it's gray or segmented and create a single
% row vector with the image
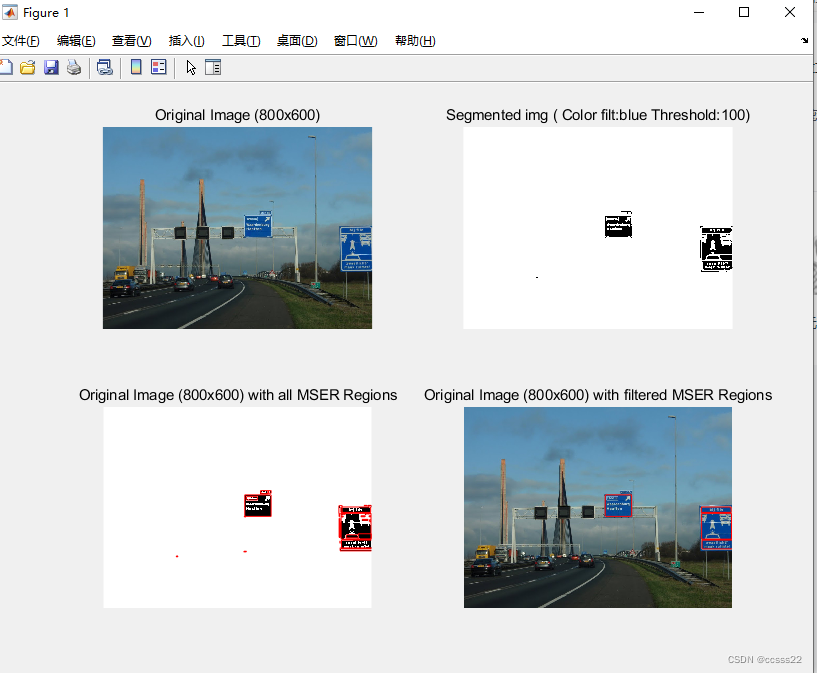
switch usagecase 'segmented'% Simple segmentation by color thresholdimg_seg = f_seg(img, color_threshold, color_of_interest, ratio);subplot(2,2,1);imshow(img);title(['Original Image (' num2str(width) 'x' num2str(height) ')']);subplot(2,2,2);imshow(img_seg);title(['Segmented img ( Color filt:' color_of_interest ' Threshold:' ...num2str(color_threshold) ')']);i = 1;for y=1:heightfor x=1:widthif img_seg(y,x) == 0img_scan(i,1) = 1;elseimg_scan(i,1) = img_seg(y,x);endi=i+1;endendimg_selected = img_seg;case 'gray'% Image converted in gray scaleimg_grey = rgb2gray(img);subplot(2,2,1);imshow(img);title(['Original Image (' num2str(width) 'x' num2str(height) ')']);subplot(2,2,2);imshow(img_grey);title(['Gray Image (' num2str(size(img_grey,2)) 'x' ...num2str(size(img_grey,1)) ')']);i = 1;for y=1:heightfor x=1:widthif img_grey(y,x) == 0img_scan(i,1) = 1;elseimg_scan(i,1) = img_grey(y,x);endi=i+1;endendimg_selected = img_grey;
end% 2) Create the bin mask with accessed pixels
bin_mask_access = zeros(total_pixels_img,1);% 3) Initialize control variables
priority = 256; % Variable that defines the smallest% 'dark' pixel
current_pixel = 1;
current_edge = 0;
current_level = img_scan(current_pixel);
bin_mask_access(current_pixel) = 1;
index_regions = 0;
g_index_stack = 0;% Create the LIFO for the 256 gray leves
for i=1:256boundary_pixels(i) = CStack();
end% Insert into the tree the most 'bright' pixel that equivalent to 256
g_index_stack = g_index_stack + 1;
index_regions = index_regions + 1;
region_stack(index_regions).level = 256;
region_stack(index_regions).area = 0;
region_stack(index_regions).mom(1) = 0;
region_stack(index_regions).mom(2) = 0;
region_stack(index_regions).mom(3) = 0;
region_stack(index_regions).mom(4) = 0;
region_stack(index_regions).mom(5) = 0;
region_stack(index_regions).variation_mser = 999999;
region_stack(index_regions).stable = 0;
region_stack(index_regions).parent = 0;
region_stack(index_regions).child = 0;
region_stack(index_regions).next = 0;
% This is an auxiliary vector (LIFO) to store the regions pushed and not process
% ed by the function 'process_stack' yet, which defines the parent and child nod
% es. In normal behavior this must inflate and deinflate during the image proces
% sing
stack(g_index_stack).node = index_regions;% Each region_stack has a correspondent rect that represents the rectangle assoc
% iated with that region, it facilitates in the later step
rect(index_regions).top = Inf;
rect(index_regions).bottom = 0;
rect(index_regions).left = Inf;
rect(index_regions).right = 0;
rect(index_regions).draw = 1;% Insert into the tree the first region for the first pixel level in the image
g_index_stack = g_index_stack + 1;
index_regions = index_regions + 1;
region_stack(index_regions).level = current_level;
region_stack(index_regions).area = 0;
region_stack(index_regions).mom(1) = 0;
region_stack(index_regions).mom(2) = 0;
region_stack(index_regions).mom(3) = 0;
region_stack(index_regions).mom(4) = 0;
region_stack(index_regions).mom(5) = 0;
region_stack(index_regions).variation_mser = 999999;
region_stack(index_regions).stable = 0;
region_stack(index_regions).parent = 0;
region_stack(index_regions).child = 0;
region_stack(index_regions).next = 0;
stack(g_index_stack).node = index_regions;rect(index_regions).top = Inf;
rect(index_regions).bottom = 0;
rect(index_regions).left = Inf;
rect(index_regions).right = 0;
rect(index_regions).draw = 1;% 4) Run the main algorithm that will scan all pixels inside the image
gCounter = 0;
done = 0;
while (done == 0)gCounter = gCounter+1; % ...it'll always be the total_pixels_img% While loop to scan all edges of the pixel in analisyswhile current_edge < 4% ...get the neighbor pixel according to correspondent edge in the BIG row v% ector that contains all pixelsneighbor_pixel = f_neighbor_pixel(current_pixel,current_edge,width,height);if (bin_mask_access(neighbor_pixel) == 0)neighbor_level = img_scan(neighbor_pixel,1);bin_mask_access(neighbor_pixel) = 1;% If the neighbor pixel has a 'lowest (black)' level than the current one,% let push a new region and define as our new current pixelif (neighbor_level < current_level)% In this step we need to store the old current pixel and its current ed% ge and to execute this, we are joining with OR - logical operation the% two informations with this approach:%% 8 bits 4 bits% Pixel to map after -> current pixel position current edge% (remember that now, this is) (we add +1)% (just a number in a row) (because we want)% (the next edge)%% Example:% CUR_PIXEL (8) 1010 1010 << 4% EDGE (4) + 1111% Later processing (12) 1010 1010 1111boundary_pixels(current_level).push(bitor(bitshift(current_pixel,4), ...(current_edge+1)));% ..always define priority as the 'darkest' pixel founded, because we'll% search for that pixel in the boundary stack after if we do not find an% y pixel lowest (black) in the edgesif (current_level < priority)priority = current_level;endcurrent_pixel = neighbor_pixel;current_edge = 0;current_level = neighbor_level;% Push a new region with the new 'darkest' pixel foundedindex_regions = index_regions + 1;region_stack(index_regions).level = current_level;region_stack(index_regions).area = 0;region_stack(index_regions).mom(1) = 0;region_stack(index_regions).mom(2) = 0;region_stack(index_regions).mom(3) = 0;region_stack(index_regions).mom(4) = 0;region_stack(index_regions).mom(5) = 0;region_stack(index_regions).variation_mser = 999999;region_stack(index_regions).stable = 0;region_stack(index_regions).parent = 0;region_stack(index_regions).child = 0;region_stack(index_regions).next = 0;g_index_stack = g_index_stack + 1;stack(g_index_stack).node = index_regions;% ..and its rectangle combinedrect(index_regions).top = Inf;rect(index_regions).bottom = 0;rect(index_regions).left = Inf;rect(index_regions).right = 0;rect(index_regions).draw = 1;continue;end% If the current pixel is the 'lowest (black)', store the neighboor for la% ter search iterationboundary_pixels(neighbor_level).push(bitor(bitshift(neighbor_pixel,4),0));if (neighbor_level < priority)priority = neighbor_level;endendcurrent_edge = current_edge + 1;end% We need to discover in the MxN representation, the value of the pixel for im% age math processing, for later computingx = mod(current_pixel, width); % Give us the offset in the line of the imageif x == 0x = width;endy = floor(current_pixel/width);% As the MSER alg. we need to accumulate the latest pixel in the latest region[region_stack rect] = f_accumulate(region_stack, rect, stack, ...g_index_stack, x, y);% If our priority is 256 we don't have a lowest pixel anymore, then we finish!% ..and we need to process all stack creating the tree with the regions to be% this way:% Example:% ________________256_______________% | | | |% _243_ _ 251_ _202_ _215_% | | | | | | | |% 145 20 200 10 198 52 20 112% ...................................................%% PARENT% |% NODE% / \% NEXT CHILD%if (priority == 256)% PROCESS STACKnew_pixel_grey_level = 256; % Passing 256 as the new pixel grey level matche% s to create the root tree node[region_stack ...rect ...index_regions ...g_index_stack ...stack] = f_process_stack(new_pixel_grey_level, ...region_stack, ...stack, ...g_index_stack, ...index_regions, ...rect);done = 1;break;end% Remove the pixel with lowest (black) value stored in the stack to process...% we remove top because it's a LIFOpixel_component = boundary_pixels(priority).top();% Undo the concatenation made previous beforecurrent_pixel = bitshift(pixel_component,-4);current_edge = bitand(pixel_component,15);boundary_pixels(priority).pop();% If we empty the stack in that black level, we need to increase the prioritywhile (boundary_pixels(priority).isempty() && (priority < 256))priority = double(priority + 1);end% Get the black level for our new current pixelnew_pixel_grey_level = img_scan(current_pixel);if (new_pixel_grey_level ~= current_level)% PROCESS STACK[region_stack ...rect ...index_regions ...g_index_stack ...stack] = f_process_stack(new_pixel_grey_level, ...region_stack, ...stack, ...g_index_stack, ...index_regions, ...rect);current_level = new_pixel_grey_level;end
end% END OF MAIN ALGORITHM
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% Post-processing step
% 5) Stable analisys of each region to determine the MSER regions
stable_counter = 0;
for i=1:size(region_stack,2)reg = region_stack(i);parent = region_stack(i);while (parent.parent && region_stack(parent.parent).level <= reg.level + ...mser_p.delta)parent = region_stack(parent.parent);endreg.variation_mser = (parent.area - reg.area)/reg.area;reg.stable = (reg.area >= mser_p.min_area) && ...(reg.area <= mser_p.max_area) && (reg.variation_mser <= ...mser_p.max_variation);id = reg.parent;if id ~= 0parent = region_stack(id);while (parent.parent && reg.area > mser_p.min_diversity*parent.area)if(parent.variation_mser <= reg.variation_mser)reg.stable = false;endif(reg.variation_mser < parent.variation_mser)parent.stable = false;endrect(id).stable = parent.stable;region_stack(id) = parent;id = parent.parent;parent = region_stack(id);endendif (reg.stable == 1)stable_counter = stable_counter + 1;endrect(i).stable = reg.stable;region_stack(i) = reg;
end% Saving just the stable regions
t = 0;
for p=1:size(rect,2)if(rect(p).stable == 1)t = t+1;tmp(t) = rect(p);end
endrect = tmp;subplot(2,2,3);
imshow(img_selected);
title(['Original Image (' num2str(width) 'x' num2str(height) ...') with all MSER Regions']);
k=0;
for i=1:size(rect,2)if (rect(i).draw == 1)k=k+1;width_n = rect(i).right-rect(i).left;height_n = rect(i).bottom-rect(i).top;rectangle('Position',[rect(i).left rect(i).top width_n height_n], ...'EdgeColor','r');end
end% 6) Filtering just the rectangles with some specific area range
for i=1:size(rect,2)rect(i).height = rect(i).bottom - rect(i).top;rect(i).width = rect(i).right - rect(i).left;rect(i).size = rect(i).height*rect(i).width;if (rect(i).size > min_area_mser && rect(i).size < max_area_mser)rect(i).draw = 1;elserect(i).draw = 0;end
endsubplot(2,2,4);
imshow(img);
title(['Original Image (' num2str(width) 'x' num2str(height) ...') with filtered MSER Regions']);% 7) Draw the rectangles in the original image
k=0;
for i=1:size(rect,2)if (rect(i).draw == 1)k=k+1;width_n = rect(i).right-rect(i).left;height_n = rect(i).bottom-rect(i).top;rectangle('Position',[rect(i).left rect(i).top width_n height_n], ...'EdgeColor','r');end
endtime_p = toc;% 8) Reports
fprintf('\tConclusion Reports');
fprintf('\nImage size: Width=%d x Height=%d',width,height);
fprintf('\nTotal number of pixels: %d',total_pixels_img);
fprintf('\nFounded regions: %d',index_regions);
fprintf('\nStable regions: %d',stable_counter);
fprintf('\nRectangles drawed: %d', k);
fprintf('\nTime to process the image: %d seconds', time_p);
fprintf('\nMSER Parameters: ');
mser_p4.仿真
D238














![python从小白到大牛百度云盘_Java从小白到大牛 (关东升著) 中文pdf+mobi版[36MB]](https://img.jbzj.com/do/uploads/litimg/190528/1H5032I915.jpg)
