webaudio
Previously on "Deep Note via WebAudio":
以前在“通过WebAudio进行深度注释”中:
intro
介绍
play a sound
播放声音
2.1. boots and cats
2.1。 靴子和猫
play a sound
播放声音
loop and change pitch
循环并改变音高
multiple sounds
多种声音
nodes
节点
In part 4 we figured out how to play all 30 sounds of the Deep Note at the same time. The problem is that's way too loud. Depending on the browser and speakers you use you may: go deaf (usually with headphones), get distortion (Chrome), your OS turns it down (Mac, built-in speakers) or experience any other undesired effect. We need to "TURN IT DOWN!". This is where the Gain node comes in. Think of it as simply volume.
在第4部分中,我们弄清楚了如何同时播放Deep Note的所有30种声音。 问题是那太响了。 取决于您使用的浏览器和扬声器,您可能会:充耳不闻(通常使用耳机),失真(Chrome),操作系统将其调低(Mac,内置扬声器)或体验任何其他不良效果。 我们需要“拒绝它!”。 这就是“增益”节点的所在。将其简单地视为音量。
插入增益节点 (Plug in the Gain node)
So we have this sort of node graph:
因此,我们有这种节点图:
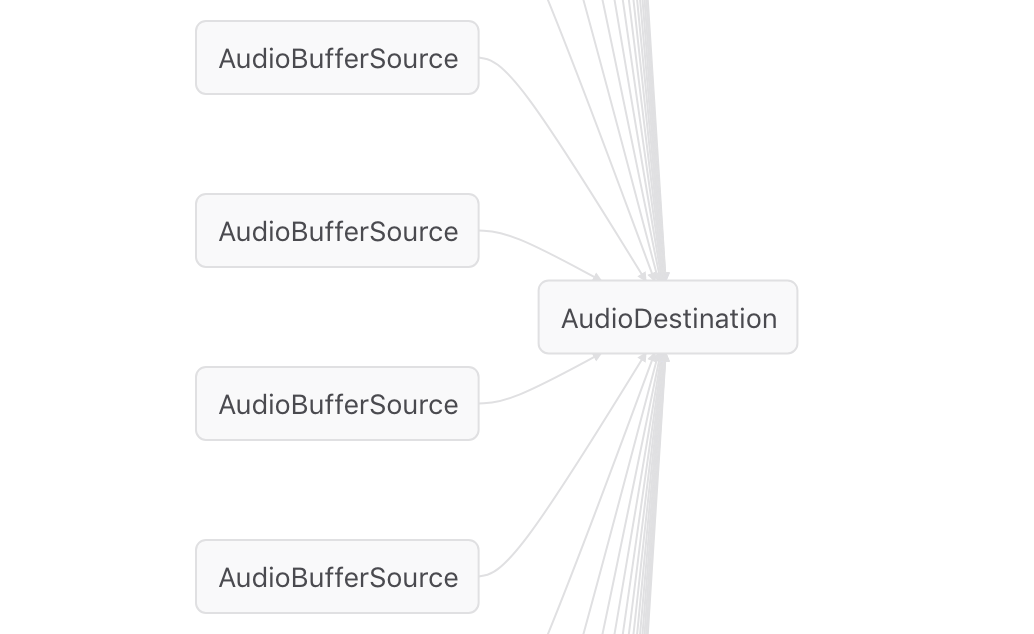
And we want to make it like so:
我们想要这样:
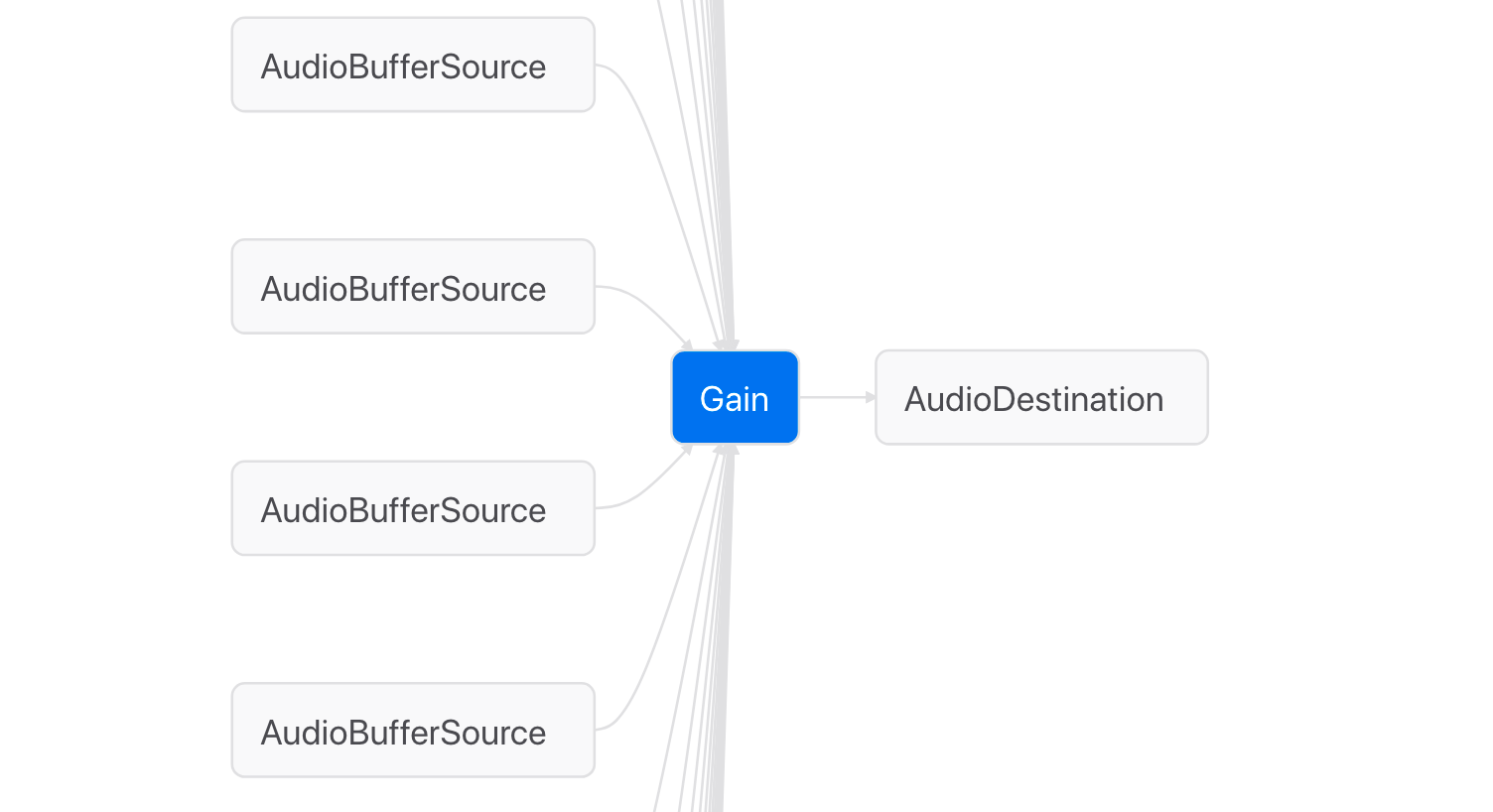
Having this will allow us to turn down the volume of all the sounds at the same time.
有了这个,我们可以同时调低所有声音的音量。
The implementation is fairly straightforward. First, create (construct) the node:
实现非常简单。 首先,创建(构造)节点:
const volume = audioContext.createGain();
Its initial value is 1. So turn it way down:
它的初始值为1。因此将其调低:
volume.gain.value = 0.1;
Connect (plug in) to the destination:
连接(插入)到目的地:
volume.connect(audioContext.destination);
Finally, for every sound, instead of connecting to the destination as before, connect to the gain node:
最后,对于每种声音,不要像以前那样连接到目标,而要连接到增益节点:
// BEFORE:
// source.connect(audioContext.destination);
// AFTER:
source.connect(volume);
Ahhh, that's much easier on the ears.
啊,这在耳朵上要容易得多。
AudioParam (AudioParam)
As you see, the Gain node we called volume has a gain property. This property is itself an object of the AudioParam type. One way to manipulate the audio parameter is via its value property. But that's not the only way. There are a number of methods too that allow you to manipulate the value in time, allowing you to schedule its changes. We'll do just that in a second.
如您所见,我们称为volume的增益节点具有gain属性。 此属性本身是AudioParam类型的对象。 操纵音频参数的一种方法是通过其value属性。 但这不是唯一的方法。 也有许多方法可以让您及时操纵该值,从而可以安排其更改时间。 我们将在一秒钟内完成。
个人喜好 (Personal preference)
I like to call my gain nodes "volume" instead of "gain". Otherwise it feels a little parrot-y to type gain.gain.value = 1. Often I find myself skipping one of the gains (because it feels awkward) and then wondering why the volume isn't working.
我喜欢将增益节点称为“体积”,而不是“增益”。 否则,键入gain.gain.value = 1会感到有些gain.gain.value = 1 。 我经常发现自己跳过了其中一项收益(因为感觉很尴尬),然后想知道为什么音量不起作用。
增益值 (Gain values)
0 is silence, 1 is the default. Usually you think of 1 as maximum volume, but in fact you can go over 1, all the way to infinity. Negative values are accepted too, they work just like the positive ones: -1 is as loud as 1.
0为静音,默认为1。 通常您将1视为最大音量,但实际上您可以超过1,一直到无穷大。 负值也被接受,它们的作用与正值一样:-1等于1。
安排变更 (Scheduling changes)
Now we come to the beginning of the enchanting journey through the world of scheduling noises. Let's start simple. Deep Note starts out of nothing (a.k.a. silence, a.k.a. gain 0) and progresses gradually to full volume. Let's say it reaches full volume in 1 second.
现在,我们进入了安排噪音的世界的迷人旅程的开始。 让我们开始简单。 Deep Note从一无所有开始(也称为静音,也称为增益0),然后逐渐发展到最大音量。 假设它在1秒钟内达到了最大音量。
Thanks to a couple of methods that every AudioParam has, called setValueAtTime() and setTargetAtTime(), we can do this:
由于每个AudioParam都有一些名为setValueAtTime()和setTargetAtTime() ,我们可以执行以下操作:
volume.gain.setValueAtTime(0, audioContext.currentTime);
volume.gain.setTargetAtTime(0.1, audioContext.currentTime, 1);
And we do this whenever we decide to hit the Play button. The first line says: right now, set the volume (the gain value) to 0. The second line schedules the volume to be 0.1. audioContext.currentTime is the time passed since the audio context was initialized, in seconds. The number 1 (third argument in the second line) means that it will take 1 second to start from 0, move exponentially and reach the 0.1 value. So in essence we set the gain to 0 immediately and also immediately we begin an exponential transition to the value 0.1 and get there after a second.
每当我们决定点击“播放”按钮时,我们都会这样做。 第一行说:现在,将音量(增益值)设置为0。第二行将音量安排为0.1。 audioContext.currentTime是自音频上下文初始化以来经过的时间,以秒为单位。 数字1(第二行的第三个参数)表示从0开始,以指数方式移动并达到0.1值需要1秒。 因此,从本质上讲,我们立即将增益设置为0,并且还立即开始了指数跃迁到值0.1的操作,并在一秒钟后到达该值。
All in all there are 5 methods that allow you to schedule AudioParam changes:
总而言之,共有5种方法可让您安排AudioParam的更改:
setValueAtTime(value, time)- no transitions, at a giventime, set the value tovaluesetValueAtTime(value, time)-没有过渡,在给定的time,将值设置为valuesetTargetAtTime(value, start, duration)- atstarttime start moving exponentially tovalueand arrive there atstart + durationo'clocksetTargetAtTime(value, start, duration)-在start时间开始以指数方式移动到value并在start + duration到达此处exponentialRampToValueAtTime(value, end)- start moving exponentially tovalueright now and get there at theendtimeexponentialRampToValueAtTime(value, end)-立即开始以指数方式移动到value并在end时间到达linearRampToValueAtTime()- same as above, but move lineary, not exponentiallylinearRampToValueAtTime()-与上面相同,但是线性移动,而不是指数移动setValueCurveAtTime(values, start, duration)- move through predefined list of valuessetValueCurveAtTime(values, start, duration)-在预定义的值列表中移动
Above we used two of these functions, let's try another one.
上面我们使用了其中两个功能,让我们尝试另一个功能。
更温和的stop() (A gentler stop())
Sometimes in audio you hear "clicks and pops" (see the "A note on looping a source" in a previous post) when you suddenly cut off the waveform. It happens when you stop a sound for example. But we can fix this, armed with the scheduling APIs we now know of.
有时候在音频听到“咔嗒声”(请参阅在“关于循环来源的说明”以前的帖子)当你突然切断波形。 例如,当您停止声音时,就会发生这种情况。 但是我们可以使用现在知道的调度API来解决此问题。
Instead of stopping abruptly, we can quickly lower the volume, so it's imperceptible and sounds like a stop. Then we stop for real. Here's how:
除了Swift停止播放,我们还可以快速降低音量,因此它是察觉不到的,听起来像是停止。 然后我们停止真实。 这是如何做:
const releaseTime = 0.1;
function stop() {
volume.gain.linearRampToValueAtTime(
0,
audioContext.currentTime + releaseTime
);
for (let i = 0; i < sources.length; i++) {
sources[i] && sources[i].stop(audioContext.currentTime + 1);
delete sources[i];
}
}
Here we use linearRampToValueAtTime() and start turning down the volume immediately and reach 0 volume after 0.1 seconds. And when we loop through the sources, we stop them after a whole second. At this time they are all silent so that time value doesn't matter much. So long as we don't stop immediately.
在这里,我们使用linearRampToValueAtTime()并立即开始调低音量,并在0.1秒后达到0音量。 当我们遍历信号源时,我们会在一秒钟后停止它们。 此时,他们都保持沉默,因此时间值并不重要。 只要我们不立即停止。
That's a neat trick. Every time you suffer pops and clicks, try to quickly lower the volume and see if that helps.
真是个绝招。 每次遇到s啪声和咔嗒声时,请尝试快速降低音量,看看是否有帮助。
And what's the deal with all the exponential stuff as opposed to linear? I think we perceive exponential changes in sound as more natural. In the case above it didn't matter since the change is so quick it's perceived as an immediate stop anyway.
那么,所有与线性相反的指数函数又如何处理呢? 我认为我们认为声音的指数变化更为自然。 在上述情况下,这并不重要,因为更改是如此之快,无论如何它都被视为立即停止。
再见! (Bye-o!)
A demo of all we talked about in this post is here, just view source for the complete code listing.
我们在本文中讨论的所有内容的演示都在这里,仅查看完整代码清单的源代码。
Thanks for reading and talk soon!
感谢您的阅读和讨论!
Tell your friends about this post on Facebook and Twitter
在Facebook和Twitter上告诉您的朋友有关此帖子的信息
翻译自: https://www.phpied.com/webaudio-deep-note-part-5-gain-node/
webaudio