一.火墙介绍
从RHEL7以后,iptables服务的启动脚本已被忽略。请使用firewalld来取代iptables服务。
防火墙是一组规则。当数据包进出受保护的网络区域时,进出内容(特别是关于其来源、目标和使用的协议等信息)会根据防火墙规则进行检测,以确定是否允许其通过。
在RHEL7里有几种防火墙共存:firewalld、iptables、ebtables,默认是使用firewalld来管理netfilter子系统,不过底层调用的命令仍然是iptables等。
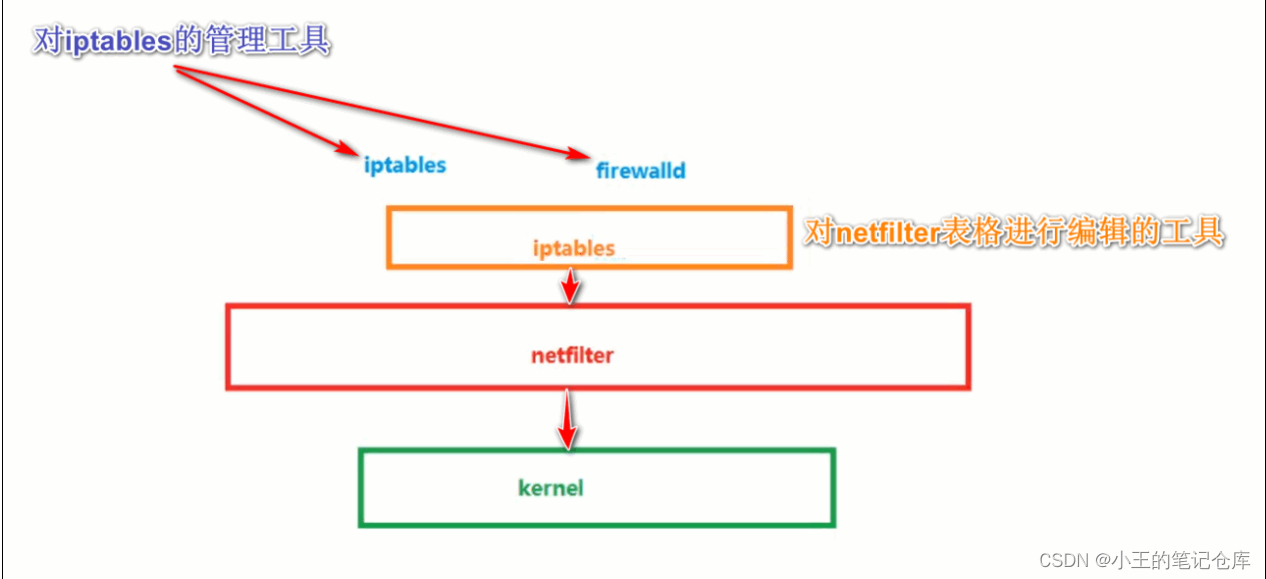
其实Iptables服务与Firewalld服务都不是真正的防火墙,它们都只是用来定义防火墙策略功能的“防火墙管理工具”。
二.iptables(太难了 闲了继续写)
netfilter/iptables可简称为iptables,为Linux平台下的包过滤防火墙,是开源的,内核自带的,可以代替成本较高的企业级硬件防火墙,能够实现如下功能:
- 数据包过滤,即防火墙
- 数据包重定向,即转发
- 网络地址转换,即可NAT
因为CensOS7之后默认使用firewalld服务,所以我们首先要切换到iptables。
1.切换到iptables
yum install iptables-services systemctl stop firewalld
systemctl disable firewalld
systemctl mask firewalld
# 如果之前锁定过iptables需要先解锁
# systemctl unmask iptablessystemctl enable --now iptables
2.iptables五表五链
| 默认策略中的5条链 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| input | 处理入站数据包 |
| output | 处理出站数据包 |
| forward | 处理转发数据包(主要是将数据包转发至本机其它网卡) |
| postrouting | 在进行路由选择前处理数据包,修改到达防火墙数据包的目的IP地址,用于判断目标主机 |
| prerouting | 在进行路由选择后处理数据包,修改要离开防火墙数据包的源IP地址,判断经由哪一接口送往下一跳 |
iptables中表的概念
每个“规则链”上都设置了一串规则,这样的话,我们就可以把不同的“规则链”组合成能够完成某一特定功能集合分类,而这个集合分类我们就称为表,iptables中共有5张表,学习iptables需要搞明白每种表的作用。
- filter: 过滤功能,确定是否放行该数据包,属于真正防火墙,内核模块:iptables_filter
- nat: 网络地址转换功能,修改数据包中的源、目标IP地址或端口;内核模块:iptable_nat
- mangle: 对数据包进行重新封装功能,为数据包设置标记;内核模块:iptable_mangle
- raw: 确定是否对数据包进行跟踪;内核模块:iptables_raw
- security:是否定义强制访问控制规则;后加上的
三.firewalld
FireWalld属于动态防火墙,是CentOS7系统中用于对netfilter内核模块用户空间管理工具。
FireWalld仅仅替代了iptables service部分,其底层还是使用iptables做为防火墙规则管理入口。
1.切换到firewalld
dnf install firewalld systemctl stop iptables.service
systemctl disable iptables
systemctl mask iptables
systemctl unmask firewalld systemctl enable --now firewalld
2.firewalld中“区域”的概念
firewalld增加了区域(zone)的概念,所谓区域是指,firewalld 预先准备了几套防火墙策略的集合,类似于策略的模板,用户可以根据需求选择区域。
| 九个默认区域 | 默认策略 |
|---|---|
| trusted | 允许所有数据包 |
| home | 拒绝流入的流量,除非与流出的流量相关,允许ssh,mdns,ippclient,samba-client,dhcpv6-client服务通过 |
| internal | 等同于home |
| work | 拒绝流入的流量,除非与流出的流量相关,允许ssh,ipp-client,dhcpv6-client服务通过 |
| public | 拒绝流入的流量,除非与流出的流量相关,允许ssh,dhcpv6-client服务通过 |
| external | 拒绝流入的流量,除非与流出的流量相关,允许ssh服务通过 |
| dmz | 拒绝流入的流量,除非与流出的流量相关,允许ssh服务通过 |
| block | 拒绝流入的流量,除非与流出的流量相关,非法流量采取拒绝操作 |
| drop | 拒绝流入的流量,除非与流出的流量相关,非法流量采取丢弃操作 |
3.域的管理
/etc/firewalld 火墙配置目录
/lib/firewalld 火墙模块目录
firewall-cmd --state #查看火墙状态
firewall-cmd --get-zones #查看所有支持的区域
firewall-cmd --get-default-zone #查看默认域
firewall-cmd --set-default-zone=trusted #设定默认域后面加域名
firewall-cmd --list-all #查看当前区域的火墙策略
firewall-cmd --list-all --zone=public #查看指定域的火墙策略
firewall-cmd --get-active-zones #查看当前火墙中生效的域
4.添加允许通过的服务或端口(重点)
☆ 通过服务的名称添加规则
案例:把http服务添加到防火墙的规则中,允许通过防火墙
#查看所有可以设定的服务
firewall-cmd --get-services#在public域中,允许http服务通过防火墙
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=http
#查看当前域火墙策略,可以看到http服务已经被添加
firewall-cmd --list-all
firewall-cmd --list-services#移除服务
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --remove-service=http
#使用--permanent参数一定要重载火墙
firewall-cmd --reload
firewall-cmd --list-all
☆ 通过服务的端口号添加规则
案例:把80/tcp添加到防火墙规则中,允许通过防火墙
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=80/tcp
firewall-cmd --list-all #查看是否添加成功#从firewalld防火墙中把80端口的规则移除掉
firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-port=80/tcp
☆ 永久模式permanent
在Linux的新版防火墙firewalld中,其模式一共分为两大类:运行模式(临时模式)+ 永久模式。
运行模式:不会把规则保存到防火墙的配置文件中,设置完成后立即生效
永久模式:会把规则写入到防火墙的配置文件中,但是其需要reload重载(firewall-cmd --reload)后才会立即生效
5.指定数据来源访问指定域
#指定数据来源访问指定域
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-source=172.25.254.0/24 --zone=block
firewall-cmd --reload#删除指定域中的数据来源
firewall-cmd --permanent --remove-source=172.25.254.0/24 --zone=block
firewall-cmd --reload
6.添加指定域的网络接口
如果为双网卡主机,可以单独指定某块网卡接口使用的域
#删除指定域的网络接口
firewall-cmd --remove-interface=ens160 --zone=public#添加指定域的网络接口
firewall-cmd --add-interface=ens160 --zone=public#更改网络接口到指定域
firewall-cmd --change-interface=ens160 --zone=public
7.firewalld的高级规则
问题:若使用firewall-cmd --permanent --remove-service=ssh将ssh服务从火墙策略中移除,对于双网卡主机来说,通过ens160和ens224的ssh来连接的所有数据会被拒绝。
#现在要求只允许172.25.254网段的主机可以ssh连接#查看高级规则
firewall-cmd --direct --get-all-rules#添加高级规则,使许172.25.254网段主机使用22端口访问双网卡主机
firewall-cmd --direct --add-rule ipv4 filter INPUT 1
-p tcp --dport 22 -s 172.25.254.0/24 -j ACCEPT#删除此高级规则
firewall-cmd --direct --remove-rule ipv4 filter INPUT 1
-p tcp --dport 22 -s 172.25.254.0/24 -j ACCEPT
8.端口转发
#SNAT
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-masquerade
firewall-cmd --query-masquerade #查询SNAT的状态
firewall-cmd --reload #DNAT
firewall-cmd --permanent
--add-forward-port=port=22:proto=tcp:toaddr=172.25.254.10
firewall-cmd --reload
Rich规则
四.iptables和firewalld区别
-
firewalld可以动态修改单条规则,动态管理规则集,允许更新规则而不破坏现有会话和连接。而iptables,在修改了规则后必须得全部刷新才可以生效。
-
firewalld使用区域和服务而不是链式规则。
-
firewalld默认是拒绝的,需要设置以后才能放行。而iptables默认是允许的,需要拒绝的才去限制。
-
firewalld自身并不具备防火墙的功能,而是和iptables一样需要通过内核的netfilter来实现。也就是说,firewalld和iptables一样,它们的作用都用于维护规则,而真正使用规则干活的是内核的netfilter。