前言
spring boot 中有个很诱人的组件–actuator,可以对spring boot应用做监控,只需在pom文件中加入如下配置即可:
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId></dependency>此时我们便可以访问/env,获得spring boot 应用的环境变量.关于如何使用,可以参考如下链接:
Spring Boot Actuator监控端点小结
actuator项目如图:
actuator中的端点类型有3种:
- 应用配置类:获取应用程序中加载的应用配置、环境变量、自动化配置报告等与Spring Boot应用密切相关的配置类信息。实现一般在org.springframework.boot.actuate.endpoint中.
- 度量指标类:获取应用程序运行过程中用于监控的度量指标,比如:内存信息、线程池信息、HTTP请求统计等。
- 操作控制类:提供了对应用的关闭等操作类功能。
我们这里详细说明org.springframework.boot.actuate.endpoint中的实现.通过如下几点来进行分析:
- xxxEndpoint的作用
- xxxEndpoint的字段,构造器
- xxxEndpoint核心方法invoke 实现分析
- xxxEndpoint如何进行配置
- xxxEndpoint如何自动化装配
解析
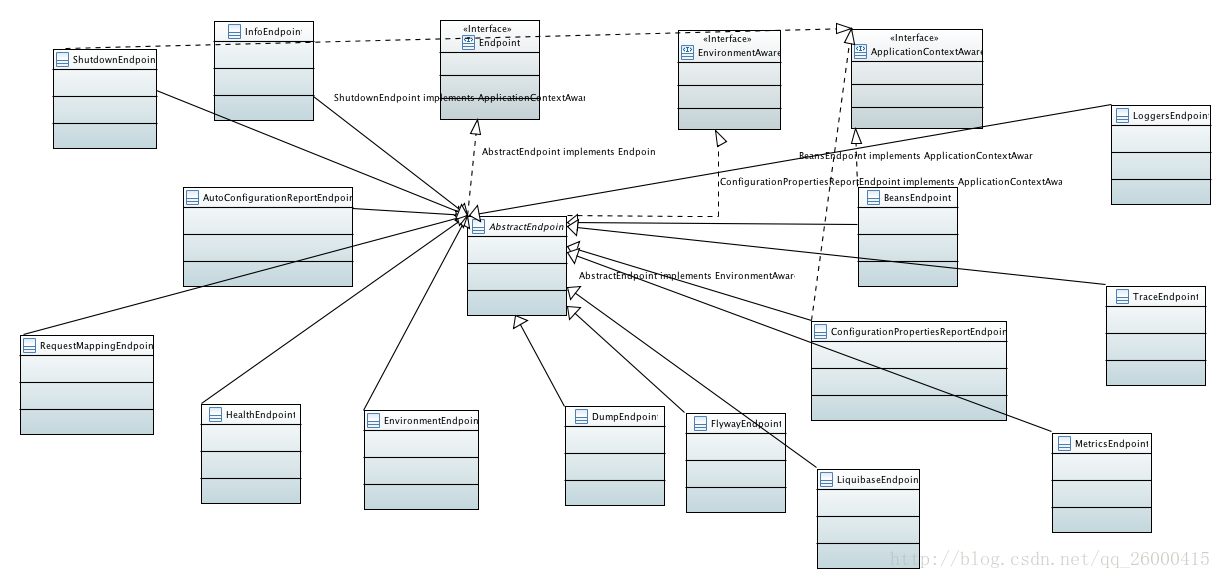
在org.springframework.boot.actuate.endpoint 中还有2个子包-jmx(可通过jmx协议访问),mvc(通过spring mvc 暴露,可通过接口进行访问,在下篇文章进行分析).这里我们不关注这些,这看org.springframework.boot.actuate.endpoint 包下的类,类比较多,先看个类图吧,如下:
Endpoint
Endpoint接口–>一个端点可以用于暴露操作的实用信息.通常暴露信息是通过spring mvc 但是其他一些技术也能实现,可以通过继承AbstractEndpoint的方式实现自己的endpoint.代码如下:
public interface Endpoint<T> {// 端点的逻辑标识(字母、数字和下划线('_') 组成)String getId();// 端点是否启用boolean isEnabled();// 端点是否输出敏感数据boolean isSensitive();// 调用端点,并返回调用结果T invoke();
}其中泛型参数T为暴露的数据类型.方法的作用已经注释,就不再赘述了.
AbstractEndpoint
Endpoint有一个子类–> AbstractEndpoint(Endpoint接口实现的抽象基类),该类实现了EnvironmentAware,因此, AbstractEndpoint也就持有了Environment.
AbstractEndpoint 有如下属性:
// 匹配包括下划线的任何单词字符。类似但不等价于“[A-Za-z0-9_]” private static final Pattern ID_PATTERN = Pattern.compile("\\w+"); // 通过EnvironmentAware接口注入 private Environment environment; // 端点标识符 private String id; // 是否默认敏感 private final boolean sensitiveDefault; // 标识该端点是否暴露敏感信息 private Boolean sensitive; // 是否端点可用 private Boolean enabled;AbstractEndpoint方法实现了Endpoint接口中的getId, isEnabled, isSensitive,其中, getId只需返回AbstractEndpoint中的id属性即可,我们分别来看下其他方法的实现:
isEnabled,代码如下:
public boolean isEnabled() {return EndpointProperties.isEnabled(this.environment, this.enabled); }调用
public static boolean isEnabled(Environment environment, Boolean enabled) {if (enabled != null) {return enabled;}if (environment != null&& environment.containsProperty(ENDPOINTS_ENABLED_PROPERTY)) {return environment.getProperty(ENDPOINTS_ENABLED_PROPERTY, Boolean.class);}return true; }3件事:
- 如果AbstractEndpoint#enabled属性有值,则使用AbstractEndpoint的配置
- 如果Environment 不等于null 并且Environment 配置有endpoints.enabled的属性,则返回其配置的值
- 默认为true
isSensitive和isEnabled实现差不多,如下:
public boolean isSensitive() {return EndpointProperties.isSensitive(this.environment, this.sensitive,this.sensitiveDefault); }调用:
public static boolean isSensitive(Environment environment, Boolean sensitive,boolean sensitiveDefault) {if (sensitive != null) {return sensitive;}if (environment != null&& environment.containsProperty(ENDPOINTS_SENSITIVE_PROPERTY)) {return environment.getProperty(ENDPOINTS_SENSITIVE_PROPERTY, Boolean.class);}return sensitiveDefault; }- 如果AbstractEndpoint#enabled属性有值,则使用sensitive的配置
- 如果environment 不等于null 并且 environment中配置有endpoints.sensitive的属性,则返回其配置值
- 返回指定的默认值(默认为false)
EnvironmentEndpoint
EnvironmentEndpoint–>暴露ConfigurableEnvironment 中的信息,继承了AbstractEndpoint.其默认构造器如下:
public EnvironmentEndpoint() {// 设置 id 为 envsuper("env"); }调用
public AbstractEndpoint(String id) {this(id, true); }最终,设置id为env,标识为敏感数据
其实现了invoke方法,代码如下:
public Map<String, Object> invoke() {// 1. 返回值Map<String, Object> result = new LinkedHashMap<String, Object>();// 2. 将spring boot 中激活的profile 放入result中,key --> profileresult.put("profiles", getEnvironment().getActiveProfiles());// 3. 获得PlaceholderSanitizingPropertyResolver --> 处理占位符,处理敏感数据PropertyResolver resolver = getResolver();// 4. 遍历environment 配置的PropertySource,依次处理之for (Entry<String, PropertySource<?>> entry : getPropertySourcesAsMap().entrySet()) {PropertySource<?> source = entry.getValue();String sourceName = entry.getKey();if (source instanceof EnumerablePropertySource) {// 4.1 只针对EnumerablePropertySource 类型的PropertySource 进行处理--> 依次将属性添加到properties中,// 如果属性值为string,则在添加前进行占位符,数据脱敏的处理EnumerablePropertySource<?> enumerable = (EnumerablePropertySource<?>) source;Map<String, Object> properties = new LinkedHashMap<String, Object>();for (String name : enumerable.getPropertyNames()) {Object property = source.getProperty(name);Object resolved = property instanceof String? resolver.resolvePlaceholders((String) property) : property;properties.put(name, sanitize(name, resolved));}// 4.2 后置处理,该方法的实现是直接返回原始值,可以通过覆写的方式进行扩展properties = postProcessSourceProperties(sourceName, properties);if (properties != null) {// 4.3 如果不为空,则添加到result中result.put(sourceName, properties);}}}return result; }- 将spring boot 中激活的profile 放入result中,key –> profile
获得PlaceholderSanitizingPropertyResolver –> 处理占位符,处理敏感数据.代码如下:
public PropertyResolver getResolver() { // 1. 实例化PlaceholderSanitizingPropertyResolver --> 处理占位符,处理敏感数据 PlaceholderSanitizingPropertyResolver resolver = new PlaceholderSanitizingPropertyResolver(getPropertySources(), this.sanitizer); // 2. 设置ignoreUnresolvableNestedPlaceholders 为true resolver.setIgnoreUnresolvableNestedPlaceholders(true); return resolver; }- 实例化PlaceholderSanitizingPropertyResolver –> 处理占位符,处理敏感数据
- 设置ignoreUnresolvableNestedPlaceholders 为true
PlaceholderSanitizingPropertyResolver继承了PropertySourcesPropertyResolver,这样就能对占位符进行处理了,又因为其内部持有Sanitizer(用于敏感数据脱敏),复写了getPropertyAsRawString,这样就能处理占位符,敏感数据了.代码如下:
protected String getPropertyAsRawString(String key) {String value = super.getPropertyAsRawString(key);return (String) this.sanitizer.sanitize(key, value); }遍历environment 配置的PropertySource,依次处理之
- 只针对EnumerablePropertySource 类型的PropertySource 进行处理–> 依次将属性添加到properties中,如果属性值为string,则在添加前进行占位符,数据脱敏的处理
- 后置处理(postProcessSourceProperties),该方法的实现是直接返回原始值,可以通过覆写的方式进行扩展
- 如果不为空,则添加到result中
属性配置,由于EnvironmentEndpoint被@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “endpoints.env”)注解,因此可通过如下配置进行个性化配置:
endpoints.env.id=env endpoints.env.sensitive=true endpoints.env.enabled=true同时,又因为其声明了如下方法:
public void setKeysToSanitize(String... keysToSanitize) {this.sanitizer.setKeysToSanitize(keysToSanitize); }因此可以通过endpoints.env.keys-to-sanitize=xx,xx 来配置对指定的数据进行脱敏
自动化装配:
EnvironmentEndpoint的自动化装配是在EndpointAutoConfiguration中,代码如下:
@Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public EnvironmentEndpoint environmentEndpoint() {return new EnvironmentEndpoint(); }- @Bean –> 注册1个id为environmentEndpoint,类型为EnvironmentEndpoint的bean
- @ConditionalOnMissingBean –> 当beanFactory中不存在EnvironmentEndpoint类型的bean时注册
InfoEndpoint
InfoEndpoint–>暴露应用信息,继承自AbstractEndpoint.
其字段和构造器如下:
private final List<InfoContributor> infoContributors; public InfoEndpoint(List<InfoContributor> infoContributors) {super("info", false);Assert.notNull(infoContributors, "Info contributors must not be null");this.infoContributors = infoContributors; }其内部持有了BeanFactory中所有InfoContributor类型的bean,其通过构造器注入
invoke 实现如下:
public Map<String, Object> invoke() {Info.Builder builder = new Info.Builder();for (InfoContributor contributor : this.infoContributors) {contributor.contribute(builder);}Info build = builder.build();return build.getDetails(); }通过遍历其内部的持有infoContributors,因此调用其contribute将info的数据添加到Info.Builder中,最后通过Info.Builder构建出Info,返回Info持有的details(建造者模式). Info中的details为Map. 这里的代码比较简单,读者可自行阅读.
InfoContributor接口用于向Info$Builder添加信息,关于这部分的内容,我们后续文章有分析.这里就不在赘述了.
属性配置:
InfoEndpoint由于有@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “endpoints.info”)注解,因此可通过如下进行配置:
endpoints.info.id=info endpoints.info.sensitive=true endpoints.info.enabled=true自动化装配–>在EndpointAutoConfiguration中,代码如下:
@Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public InfoEndpoint infoEndpoint() throws Exception {return new InfoEndpoint(this.infoContributors == null? Collections.<InfoContributor>emptyList() : this.infoContributors); }- @Bean –> 注册1个id为infoEndpoint,类型为InfoEndpoint的bean
- @ConditionalOnMissingBean –> 当beanFactory中不存在InfoEndpoint类型的bean时注册
RequestMappingEndpoint
RequestMappingEndpoint 实现了ApplicationContextAware接口,因此,在初始化该类时会注入applicationContext.
RequestMappingEndpoint,构造器如下:
public RequestMappingEndpoint() {super("mappings"); }因此, RequestMappingEndpoint的id为 mappings,默认为敏感
invoke 实现如下:
public Map<String, Object> invoke() {Map<String, Object> result = new LinkedHashMap<String, Object>();// 1. 从handlerMappings中获取HandlerMapping,默认情况下handlerMappings是不存在数据的extractHandlerMappings(this.handlerMappings, result);// 2. 从applicationContext中获取AbstractUrlHandlerMapping类型的bean,依次将其注册的handler 添加进去.extractHandlerMappings(this.applicationContext, result);// 3. 从methodMappings中获取HandlerMapping,默认情况下methodMappings是不存在数据的extractMethodMappings(this.methodMappings, result);// 3. 从applicationContext中获取AbstractUrlHandlerMapping类型的bean,依次获得其持有的HandlerMethods,进行处理.extractMethodMappings(this.applicationContext, result);return result; }- 从handlerMappings中获取HandlerMapping,默认情况下handlerMappings是不存在数据的
从applicationContext中获取AbstractUrlHandlerMapping类型的bean,依次将其注册的handler 添加进去.代码如下:
protected void extractHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext applicationContext,Map<String, Object> result) { if (applicationContext != null) {Map<String, AbstractUrlHandlerMapping> mappings = applicationContext.getBeansOfType(AbstractUrlHandlerMapping.class);for (Entry<String, AbstractUrlHandlerMapping> mapping : mappings.entrySet()) {Map<String, Object> handlers = getHandlerMap(mapping.getValue());for (Entry<String, Object> handler : handlers.entrySet()) {result.put(handler.getKey(),Collections.singletonMap("bean", mapping.getKey()));}} } }获得AbstractUrlHandlerMapping类型的bean,此时有4个:
- beanNameHandlerMapping=org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping
- resourceHandlerMapping=org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleUrlHandlerMapping
- faviconHandlerMapping=org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleUrlHandlerMapping
- welcomePageHandlerMapping=org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.WebMvcAutoConfiguration$WelcomePageHandlerMapping
依次遍历mappings:
- 获得AbstractUrlHandlerMapping中注册的handler,key–> path,value–>handler
- 依次遍历handlerss,存入结果集中,存入的key–>AbstractUrlHandlerMapping的id,value={bean=AbstractUrlHandlerMapping中注册的handler的路径}
- 从methodMappings中获取HandlerMapping,默认情况下methodMappings是不存在数据的
从applicationContext中获取AbstractUrlHandlerMapping类型的bean,依次获得其持有的HandlerMethods,进行处理.代码如下:
protected void extractMethodMappings(ApplicationContext applicationContext,Map<String, Object> result) { if (applicationContext != null) {for (Entry<String, AbstractHandlerMethodMapping> bean : applicationContext.getBeansOfType(AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.class).entrySet()) {@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")Map<?, HandlerMethod> methods = bean.getValue().getHandlerMethods();for (Entry<?, HandlerMethod> method : methods.entrySet()) {Map<String, String> map = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>();map.put("bean", bean.getKey());map.put("method", method.getValue().toString());result.put(method.getKey().toString(), map);}} } }- 获得AbstractUrlHandlerMapping类型的bean
- 依次遍历AbstractUrlHandlerMapping中注册的handler,添加至结果集中,key–> Handler 映射路径 ,value = {bean = AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的id,method=HandlerMethod}
属性配置–>可通过如下属性配置(因为有@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “endpoints.mappings”)注解):
endpoints.mappings.enabled= # Enable the endpoint. endpoints.mappings.id= # Endpoint identifier. endpoints.mappings.sensitive= # Mark if the endpoint exposes sensitive information.自动装配–>在EndpointAutoConfiguration$RequestMappingEndpointConfiguration中:
代码如下:
@Configuration @ConditionalOnClass(AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.class) protected static class RequestMappingEndpointConfiguration {@Bean@ConditionalOnMissingBeanpublic RequestMappingEndpoint requestMappingEndpoint() {RequestMappingEndpoint endpoint = new RequestMappingEndpoint();return endpoint;}}当满足如下条件时生效,注册1个id为requestMappingEndpoint,类型为RequestMappingEndpoint的bean:
- @ConditionalOnClass(AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.class) –> 在beanFactory中存在AbstractHandlerMethodMapping类型的bean时生效
- @ConditionalOnMissingBean–>在beanFactory中不存在RequestMappingEndpoint类型的bean时生效
DumpEndpoint
- DumpEndpoint–> 打印出线程的堆栈信息.id为dump,默认为敏感
invoke 实现:
@Override public List<ThreadInfo> invoke() {return Arrays.asList(ManagementFactory.getThreadMXBean().dumpAllThreads(true, true)); }调用了ThreadMXBean的dumpAllThreads来返回所有活动线程的线程信息,并带有堆栈跟踪和同步信息。 当此方法返回时,返回数组中包含的一些线程可能已经终止。其中两个参数指的意义如下:
- 第1个–>如果为 true,则转储所有锁定的监视器。
- 第2个–>如果为 true,则转储所有锁定的可拥有同步器。
可参考如下链接:
接口 ThreadMXBean 一个很好用的线程管理接口类可通过如下属性进行配置(因为有@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “endpoints.dump”)注解):
endpoints.dump.enabled= # Enable the endpoint. endpoints.dump.id= # Endpoint identifier. endpoints.dump.sensitive= # Mark if the endpoint exposes sensitive information.自动化装配:
在EndpointAutoConfiguration中声明,代码如下:
@Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public DumpEndpoint dumpEndpoint() {return new DumpEndpoint(); }- @Bean –> 注册1个id为dumpEndpoint,类型为DumpEndpoint的bean
- @ConditionalOnMissingBean –> 当beanFactory中不存在DumpEndpoint类型的Bean时生效
FlywayEndpoint
没有启用,列在这里是为了做个提示
ShutdownEndpoint
ShutdownEndpoint 实现了ApplicationContextAware.其构造器如下:
public ShutdownEndpoint() {super("shutdown", true, false); }调用:
public AbstractEndpoint(String id, boolean sensitive, boolean enabled) {setId(id);this.sensitiveDefault = sensitive;this.enabled = enabled; }因此,其id为shutdown,默认敏感,默认不启用.
如何启用ShutdownEndpoint呢?
因为ShutdownEndpoint在类上声明了@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “endpoints.shutdown”)的注解,因此可以通过endpoints.shutdown.enabled = true的方式来在ShutdownEndpoint 实例化后进行配置(在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization方法中,会调用ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor实现属性注入).关于这部分的原理我们在 spring boot 源码解析13-@ConfigurationProperties是如何生效的 中有详解.
invoke 实现:
public Map<String, Object> invoke() {if (this.context == null) {return NO_CONTEXT_MESSAGE;}try {return SHUTDOWN_MESSAGE;}finally {Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {Thread.sleep(500L);}catch (InterruptedException ex) {Thread.currentThread().interrupt();}ShutdownEndpoint.this.context.close();}});thread.setContextClassLoader(getClass().getClassLoader());thread.start();} }- 如果context 等于null,则返回{message=No context to shutdown.}, 2. 否则,返回{message=Shutting down, bye…},然后启动一个线程,在该线程中,先sleep 5秒后,然后调用了ShutdownEndpoint中持有的context的close方法进行关闭.
属性配置(因为有@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “endpoints.shutdown”)注解):
endpoints.shutdown.enabled= # Enable the endpoint. endpoints.shutdown.id= # Endpoint identifier. endpoints.shutdown.sensitive= # Mark if the endpoint exposes sensitive information.自动装配:
在EndpointAutoConfiguration中配置,代码如下:
@Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public ShutdownEndpoint shutdownEndpoint() {return new ShutdownEndpoint(); }- @Bean –> 注册1个id为shutdownEndpoint,类型为ShutdownEndpoint的bean
- @ConditionalOnMissingBean –> 当beanFactory中不存在ShutdownEndpoint类型的Bean时生效
AutoConfigurationReportEndpoint
AutoConfigurationReportEndpoint 构造器如下:
public AutoConfigurationReportEndpoint() {super("autoconfig"); }因此其id为autoconfig,默认为敏感
其内部持有ConditionEvaluationReport,会在实例化的时候进行注入.
invoke 实现:
public Report invoke() {return new Report(this.autoConfigurationReport); }Report类上声明了如下注解:
@JsonPropertyOrder({ "positiveMatches", "negativeMatches", "exclusions" }) @JsonInclude(Include.NON_EMPTY)- @JsonPropertyOrder–>作用在类上,被用来指明当序列化时需要对属性做排序,它有2个属性:一个是alphabetic:布尔类型,表示是否采用字母拼音顺序排序,默认是为false,即不排序
- @JsonInclude–> Report中的属性值为空集合则不进行展示
Report 有如下字段:
// 匹配的 private final MultiValueMap<String, MessageAndCondition> positiveMatches;// 不匹配的 private final Map<String, MessageAndConditions> negativeMatches;// 去除的 private final List<String> exclusions;// 一般为null private final Report parent;其中MessageAndCondition封装了ConditionAndOutcome中的condition,message以进行更好的展示(json友好).其类上声明了如下注解:
@JsonPropertyOrder({ "condition", "message" })因此在进行输出的时候,先输出condition,再输出message.
构造器如下:
public MessageAndCondition(ConditionAndOutcome conditionAndOutcome) {Condition condition = conditionAndOutcome.getCondition();ConditionOutcome outcome = conditionAndOutcome.getOutcome();this.condition = ClassUtils.getShortName(condition.getClass());if (StringUtils.hasLength(outcome.getMessage())) {this.message = outcome.getMessage();}else {this.message = (outcome.isMatch() ? "matched" : "did not match");} }- 赋值condition为ConditionAndOutcome中的Condition的短类名.
- 赋值message:如果ConditionAndOutcome中的Message有值则直接赋值,否则,如果对应的Condition匹配,则赋值为matched,否则赋值为did not match。
构造器如下:
public Report(ConditionEvaluationReport report) {this.positiveMatches = new LinkedMultiValueMap<String, MessageAndCondition>();this.negativeMatches = new LinkedHashMap<String, MessageAndConditions>();// 1. 通过report#getExclusions 获得不进行加载的beanthis.exclusions = report.getExclusions();// 2. for (Map.Entry<String, ConditionAndOutcomes> entry : report.getConditionAndOutcomesBySource().entrySet()) {// 2.1 如果该配置生效条件都匹配,则加入到positiveMatches,否则,加入到negativeMatchesif (entry.getValue().isFullMatch()) {add(this.positiveMatches, entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());}else {add(this.negativeMatches, entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());}}// 3. 如果report存在父report,则进行初始化Report 赋值为当前类的parent 属性boolean hasParent = report.getParent() != null;this.parent = (hasParent ? new Report(report.getParent()) : null); }- 通过ConditionEvaluationReport#getExclusions 获得不进行加载的bean,赋值为exclusions
- 调用ConditionEvaluationReport#getConditionAndOutcomesBySource 获得ConditionEvaluationReport中持有匹配信息,返回的map中,key–> 匹配类名,ConditionAndOutcomes–> 匹配结果.
依次遍历第2步的返回值–>如果该配置生效条件都匹配,则加入到positiveMatches,否则,加入到negativeMatches.其中add 代码如下:
private void add(MultiValueMap<String, MessageAndCondition> map, String source,ConditionAndOutcomes conditionAndOutcomes) { String name = ClassUtils.getShortName(source); for (ConditionAndOutcome conditionAndOutcome : conditionAndOutcomes) {map.add(name, new MessageAndCondition(conditionAndOutcome)); } }因此positiveMatches,negativeMatches 中的key为配置类的简单类名.
- 如果report存在父report,则进行初始化Report 赋值为当前类的parent 属性.一般来说,是不存在父report的
属性配置(因为有@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “endpoints.autoconfig”) 注解):
endpoints.autoconfig.enabled= # Enable the endpoint. endpoints.autoconfig.id= # Endpoint identifier. endpoints.autoconfig.sensitive= # Mark if the endpoint exposes sensitive information.自动装配:
同样还是在EndpointAutoConfiguration中,代码如下:
@Bean @ConditionalOnBean(ConditionEvaluationReport.class) @ConditionalOnMissingBean(search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT) public AutoConfigurationReportEndpoint autoConfigurationReportEndpoint() {return new AutoConfigurationReportEndpoint(); }- @Bean –> 注册1个id为autoConfigurationReportEndpoint,类型为AutoConfigurationReportEndpoint的bean
- @ConditionalOnBean(ConditionEvaluationReport.class)–>beanFactory中存在ConditionEvaluationReport类型的bean时生效
- @ConditionalOnMissingBean(search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)–> 在当前上下文中不存在AutoConfigurationReportEndpoint类型的bean时生效
ConditionEvaluationReport
AutoConfigurationReportEndpoint 是通过ConditionEvaluationReport 来进行暴露信息.
ConditionEvaluationReport 字段如下:
private static final String BEAN_NAME = "autoConfigurationReport";// 如果一个配置类中内部配置类不匹配,则在其外部类的所对应的ConditionAndOutcomes中添加1个AncestorsMatchedCondition private static final AncestorsMatchedCondition ANCESTOR_CONDITION = new AncestorsMatchedCondition();// key-->配置类类名,ConditionAndOutcomes-->匹配条件结果的封装 private final SortedMap<String, ConditionAndOutcomes> outcomes = new TreeMap<String, ConditionAndOutcomes>();// 是否添加AncestorsMatchedCondition,默认为false private boolean addedAncestorOutcomes;// 父ConditionEvaluationReport,一般为null private ConditionEvaluationReport parent;// 去除加载的配置 private List<String> exclusions = Collections.emptyList();// 在ConditionEvaluationReportAutoConfigurationImportListener#onAutoConfigurationImportEvent 添加,用于保存还没有 // 执行判断的class private Set<String> unconditionalClasses = new HashSet<String>();ConditionEvaluationReport 实例化过程如下:
在SpringApplication#run中会调用AbstractApplicationContext#refresh,在refresh会调用PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors,在该方法中最终会调用到AutoConfigurationImportSelector#selectImports方法.在该方法中会调用fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents,代码如下:
private void fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(List<String> configurations,Set<String> exclusions) {List<AutoConfigurationImportListener> listeners = getAutoConfigurationImportListeners();if (!listeners.isEmpty()) {AutoConfigurationImportEvent event = new AutoConfigurationImportEvent(this,configurations, exclusions);for (AutoConfigurationImportListener listener : listeners) {invokeAwareMethods(listener);listener.onAutoConfigurationImportEvent(event);}} }- 会加载/META-INF/spring.factories 中配置的org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportListener,实例化后,依次调用其onAutoConfigurationImportEvent 方法. spring.factories 配置如下:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportListener=\ org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionEvaluationReportAutoConfigurationImportListener因此此处会调用ConditionEvaluationReportAutoConfigurationImportListener#onAutoConfigurationImportEvent.代码如下:
public void onAutoConfigurationImportEvent(AutoConfigurationImportEvent event) {if (this.beanFactory != null) {ConditionEvaluationReport report = ConditionEvaluationReport.get(this.beanFactory);report.recordEvaluationCandidates(event.getCandidateConfigurations());report.recordExclusions(event.getExclusions());} }实例化ConditionEvaluationReport,代码如下:
public static ConditionEvaluationReport get(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { synchronized (beanFactory) {ConditionEvaluationReport report;// 1. 如果当前beanFactory包含autoConfigurationReport定义的话,就从beanFactory中获取,if (beanFactory.containsSingleton(BEAN_NAME)) {report = beanFactory.getBean(BEAN_NAME, ConditionEvaluationReport.class);}else {// 否则就实例化一个,然后进行注册report = new ConditionEvaluationReport();beanFactory.registerSingleton(BEAN_NAME, report);}// 2. 如果存在父容器的话,就从父容器中获取。locateParent(beanFactory.getParentBeanFactory(), report);return report; } }- 如果当前beanFactory包含autoConfigurationReport定义的话,就从beanFactory中获取,否则就实例化一个,然后进行注册
如果存在父容器的话,就从父容器中获取,并将其赋值为当前context中获得的ConditionEvaluationReport的父ConditionEvaluationReport.代码如下:
private static void locateParent(BeanFactory beanFactory, ConditionEvaluationReport report) { if (beanFactory != null && report.parent == null&& beanFactory.containsBean(BEAN_NAME)) { report.parent = beanFactory.getBean(BEAN_NAME,ConditionEvaluationReport.class); } }一般都是null,不会执行的
- 设置unconditionalClasses为event#getCandidateConfigurations的返回值
- 设置exclusions为event#getExclusions的返回值
在AutoConfigurationReportEndpoint中是通过Report来进行暴露信息的,而在其构造器中,调用了ConditionEvaluationReport#getConditionAndOutcomesBySource方法,代码如下:
public Map<String, ConditionAndOutcomes> getConditionAndOutcomesBySource() {if (!this.addedAncestorOutcomes) {// 1. 如果addedAncestorOutcomes 设为false,则依次遍历outcomes,如果一个配置类中内部配置类不匹配,则在其外部类的所对应的ConditionAndOutcomes中添加1个AncestorsMatchedConditionfor (Map.Entry<String, ConditionAndOutcomes> entry : this.outcomes.entrySet()) {if (!entry.getValue().isFullMatch()) {addNoMatchOutcomeToAncestors(entry.getKey());}}this.addedAncestorOutcomes = true;}return Collections.unmodifiableMap(this.outcomes); }如果addedAncestorOutcomes 设为false,则依次遍历outcomes,如果一个配置类中内部配置类不匹配,则在其外部类的所对应的ConditionAndOutcomes中添加1个AncestorsMatchedCondition
返回outcomes.
问题来了, outcomes 中的数据是如何添加的?
答案: 有2处.
还是在AutoConfigurationImportSelector#selectImports中,会调用其filter方法.代码如下
private List<String> filter(List<String> configurations,AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata) { long startTime = System.nanoTime(); String[] candidates = configurations.toArray(new String[configurations.size()]); boolean[] skip = new boolean[candidates.length]; boolean skipped = false; // 1. 获取META-INFspring.factories/中配置的org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportFilter,.OnClassCondition.依次进行遍历之 // 此时获得的是org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition for (AutoConfigurationImportFilter filter : getAutoConfigurationImportFilters()) {// 1.1 进行属性注入invokeAwareMethods(filter);// 1.2 调用AutoConfigurationImportFilter#match 进行判断,依次遍历其返回值,如果返回的是false,则说明该配置为跳过,并将skipped设置为true// 获得AutoConfigurationMetadata中配置的ConditionalOnClass,如果不会空,则依次遍历之,看是否在当前类路径下存在// 如果不匹配的话,则调用ConditionEvaluationReport.#ecordConditionEvaluation 进行记录// 由于此时AutoConfigurationMetadata 什么都没有配置,因此此步骤相当于空操作,最终会在第2步返回boolean[] match = filter.match(candidates, autoConfigurationMetadata);for (int i = 0; i < match.length; i++) {if (!match[i]) {skip[i] = true;skipped = true;}} } // 2. 如果skipped 等于false,则直接返回configurations,说明没有配置是需要跳过的 if (!skipped) {return configurations; } // 3. 依次遍历candidates,如果该配置是不进行跳过的,则添加至result中进行返回 List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>(candidates.length); for (int i = 0; i < candidates.length; i++) {if (!skip[i]) {result.add(candidates[i]);} } return new ArrayList<String>(result); }获取META-INFspring.factories/中配置的org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportFilter,.OnClassCondition.依次进行遍历之.此时获得的是org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition
- 进行属性注入
- 调用AutoConfigurationImportFilter#match 进行判断,依次遍历其返回值,如果返回的是false,则说明该配置为跳过,并将skipped设置为true.由于此时调用的是OnClassCondition,其判断逻辑为获得AutoConfigurationMetadata中配置的ConditionalOnClass,如果不会空,则依次遍历之,看是否在当前类路径下存在.如果不匹配的话,则调用ConditionEvaluationReport#ecordConditionEvaluation 进行记录.由于此时AutoConfigurationMetadata 什么都没有配置,因此此步骤相当于空操作,最终会在第2步返回
如果skipped 等于false,则直接返回configurations,说明没有配置是需要跳过的
- 依次遍历candidates,如果该配置是不进行跳过的,则添加至result中进行返回
在ConfigurationClassParser#processConfigurationClass进行解析加载配置类时,会调用ConditionEvaluator#shouldSkip,在该方法中,会因此遍历配置类配置的@Conditional所对应的处理类.此时,如果处理类是SpringBootCondition的子类的话,就会调用ConditionEvaluationReport进行记录匹配结果. 代码如下:
private void recordEvaluation(ConditionContext context, String classOrMethodName,ConditionOutcome outcome) { if (context.getBeanFactory() != null) {ConditionEvaluationReport.get(context.getBeanFactory()).recordConditionEvaluation(classOrMethodName, this, outcome); } }
LiquibaseEndpoint
默认不生效,这里就不进行分析了
BeansEndpoint
- BeansEndpoint的作用 –> 暴露关于beans的json视图.如果Environment 中设置了spring.liveBeansView.mbeanDomain,则所有spring 上下文的bean都会展示.否则只会展示当前的上下文中的bean.默认是没有配置的
BeansEndpoint,构造器如下:
public BeansEndpoint() {super("beans"); }id为beans,默认为敏感
BeansEndpoint的字段如下:
// 继承自LiveBeansView,用于生成json格式的数据 private final HierarchyAwareLiveBeansView liveBeansView = new HierarchyAwareLiveBeansView();// json 解析器对象 private final JsonParser parser = JsonParserFactory.getJsonParser();由于BeansEndpoint实现了ApplicationContextAware接口,因此当前初始化时,会调用其setApplicationContext方法,代码如下:
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext context) throws BeansException {if (context.getEnvironment().getProperty(LiveBeansView.MBEAN_DOMAIN_PROPERTY_NAME) == null) {this.liveBeansView.setLeafContext(context);} }如果没有设置spring.liveBeansView.mbeanDomain的属性,则将HierarchyAwareLiveBeansView中的leafContext设置为传入的ApplicationContext(通常是当前应用所对应的上下文)
invoke实现如下:
public List<Object> invoke() {return this.parser.parseList(this.liveBeansView.getSnapshotAsJson()); }调用HierarchyAwareLiveBeansView#getSnapshotAsJson 生成json串.代码如下:
public String getSnapshotAsJson() {if (this.leafContext == null) {return super.getSnapshotAsJson();}// 2. 将leafContext的整个继承关系都添加到contexts中,即:如果给定的leafContext 存在父context,则一直递归的添加至contexts// 直至顶级容器,然后调用LiveBeansView#generateJson 来生成json串return generateJson(getContextHierarchy()); }- 如果leafContext 等于null,则调用LiveBeansView#getSnapshotAsJson来生成json串.一般都会执行第2步
将leafContext的整个继承关系都添加到contexts中,即:如果给定的leafContext 存在父context,则一直递归的添加至contexts.代码如下:
private Set<ConfigurableApplicationContext> getContextHierarchy() { Set<ConfigurableApplicationContext> contexts = new LinkedHashSet<ConfigurableApplicationContext>(); ApplicationContext context = this.leafContext; while (context != null) {contexts.add(asConfigurableContext(context));context = context.getParent(); } return contexts; }将leafContext的整个继承关系都添加到contexts中,即:如果给定的leafContext 存在父context,则一直递归的添加至contexts直至顶级容器
调用LiveBeansView#generateJson 来生成json串.在该方法中没有使用第3方的json解析库的目的是为了避免对其进行依赖.返回的格式为数组格式.代码如下:
protected String generateJson(Set<ConfigurableApplicationContext> contexts) { StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder("[\n"); for (Iterator<ConfigurableApplicationContext> it = contexts.iterator(); it.hasNext();) { // 1. context和parent属性来标识该数据是属于哪个context的 ConfigurableApplicationContext context = it.next(); result.append("{\n\"context\": \"").append(context.getId()).append("\",\n"); if (context.getParent() != null) {result.append("\"parent\": \"").append(context.getParent().getId()).append("\",\n"); } else {result.append("\"parent\": null,\n"); } // 2.构造beans的数组格式的字符串,含有bean,aliases,scope,type,resource,dependencies 属性 result.append("\"beans\": [\n"); ConfigurableListableBeanFactory bf = context.getBeanFactory(); String[] beanNames = bf.getBeanDefinitionNames(); boolean elementAppended = false; for (String beanName : beanNames) {BeanDefinition bd = bf.getBeanDefinition(beanName);if (isBeanEligible(beanName, bd, bf)) {// 如果该BeanDefinition的角色不是ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE 并且(不是延迟初始化|| 该bean是1个单例)if (elementAppended) {result.append(",\n");}result.append("{\n\"bean\": \"").append(beanName).append("\",\n");result.append("\"aliases\": ");appendArray(result, bf.getAliases(beanName));result.append(",\n");String scope = bd.getScope();if (!StringUtils.hasText(scope)) {scope = BeanDefinition.SCOPE_SINGLETON;}result.append("\"scope\": \"").append(scope).append("\",\n");Class<?> beanType = bf.getType(beanName);if (beanType != null) {result.append("\"type\": \"").append(beanType.getName()).append("\",\n");}else {result.append("\"type\": null,\n");}result.append("\"resource\": \"").append(getEscapedResourceDescription(bd)).append("\",\n");result.append("\"dependencies\": ");appendArray(result, bf.getDependenciesForBean(beanName));result.append("\n}");elementAppended = true;} } result.append("]\n"); result.append("}"); if (it.hasNext()) {result.append(",\n"); } } result.append("]"); return result.toString(); }依次遍历给定的contexts
- 构建context和parent属性来标识该数据是属于哪个context的和继承关系
- 构造beans的数组格式的字符串,依次遍历该上下文中注册的bean的id,如果该id所对应的BeanDefinition的角色不是ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE 并且(不是延迟初始化|| 该bean是1个单例),则进行拼接json串
进行json串的反序列化
由于BeansEndpoint声明了@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “endpoints.beans”),因此可以通过如下属性来配置:
endpoints.beans.id endpoints.beans.sensitive endpoints.beans.enabled自动化配置:
beansEndpoint 是在EndpointAutoConfiguration 中进行配置的,代码如下:
@Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public BeansEndpoint beansEndpoint() {return new BeansEndpoint(); }- @Bean –> 注册1个id为 beansEndpoint,类型为BeansEndpoint的bean
- @ConditionalOnMissingBean–> 当beanFactory中不存在BeansEndpoint类型的bean时生效
ConfigurationPropertiesReportEndpoint
作用:–>暴露被@ConfigurationProperties 注解的bean的属性.为了保护数据,将敏感数据进行了脱敏
字段:
private static final String CONFIGURATION_PROPERTIES_FILTER_ID = "configurationPropertiesFilter";// 数据脱敏 private final Sanitizer sanitizer = new Sanitizer();// 通过实现ApplicationContextAware 进行自动注入 private ApplicationContext context;public ConfigurationPropertiesReportEndpoint() {super("configprops"); }invoke 实现:
public Map<String, Object> invoke() {return extract(this.context); }调用:
protected Map<String, Object> extract(ApplicationContext context) {// Serialize beans into map structure and sanitize valuesObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();// 1. 配置ObjectMapper的属性configureObjectMapper(mapper);// 2. 抽取数据return extract(context, mapper); }对ObjectMapper 进行配置:
代码如下:
protected void configureObjectMapper(ObjectMapper mapper) { mapper.configure(SerializationFeature.FAIL_ON_EMPTY_BEANS, false); mapper.configure(SerializationFeature.WRITE_NULL_MAP_VALUES, false); applyConfigurationPropertiesFilter(mapper); applySerializationModifier(mapper); }- SerializationFeature.FAIL_ON_EMPTY_BEANS –> 设置当对于给定的类型无法访问时如何处理,true–> 抛出异常,false–> 返回null
- SerializationFeature.WRITE_NULL_MAP_VALUES –> 设置当map对于的value为null时如何处理,treu–>序列化,false–> 跳过
applyConfigurationPropertiesFilter 代码如下:
private void applyConfigurationPropertiesFilter(ObjectMapper mapper) { mapper.setAnnotationIntrospector(new ConfigurationPropertiesAnnotationIntrospector()); mapper.setFilterProvider(new SimpleFilterProvider().setDefaultFilter(new ConfigurationPropertiesPropertyFilter())); }设置AnnotationIntrospector为ConfigurationPropertiesAnnotationIntrospector.该类的作用是:获得@JsonFilter注解的值,如果获取不到,则返回configurationPropertiesFilter.代码如下:
private static class ConfigurationPropertiesAnnotationIntrospector extends JacksonAnnotationIntrospector { @Override public Object findFilterId(Annotated a) { // 1. 获得@JsonFilter注解的值,如果获取不到,则返回configurationPropertiesFilter Object id = super.findFilterId(a); if (id == null) { id = CONFIGURATION_PROPERTIES_FILTER_ID; } return id; } }设置默认的过滤器为ConfigurationPropertiesPropertyFilter,该类的作用是进行如下规则的过滤:
- 类名以$$开头的被过滤掉
- 自我引用的字段被过滤掉
- 当在序列化时抛出异常时过滤掉
代码如下:
public void serializeAsField(Object pojo, JsonGenerator jgen, SerializerProvider provider, PropertyWriter writer) throws Exception { if (writer instanceof BeanPropertyWriter) { try {// 1. 自我引用的字段被过滤掉if (pojo == ((BeanPropertyWriter) writer).get(pojo)) {if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Skipping '" + writer.getFullName() + "' on '"+ pojo.getClass().getName()+ "' as it is self-referential");}return;} } catch (Exception ex) {// 2. 当在序列化时抛出异常时过滤掉if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Skipping '" + writer.getFullName() + "' on '"+ pojo.getClass().getName() + "' as an exception "+ "was thrown when retrieving its value", ex);}return; } } // 3. 序列化字段 super.serializeAsField(pojo, jgen, provider, writer); }
设置序列化工厂中的方法序列化器为GenericSerializerModifier.代码如下:
public List<BeanPropertyWriter> changeProperties(SerializationConfig config,BeanDescription beanDesc, List<BeanPropertyWriter> beanProperties) { List<BeanPropertyWriter> result = new ArrayList<BeanPropertyWriter>(); for (BeanPropertyWriter writer : beanProperties) {boolean readable = isReadable(beanDesc, writer);if (readable) {result.add(writer);} } return result; }依次遍历beanProperties,如果可读的话,则添加至result中.可读的判断逻辑如下:
- 根据bean 的类型和属性的类型 找出对应的set方法
- 如果set方法 存在或者是同一包下的类或者是map或者集合的子类,则返回true
调用extract方法抽取数据.代码如下:
private Map<String, Object> extract(ApplicationContext context, ObjectMapper mapper) { Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<String, Object>(); // 1. 获得beanFactory中ConfigurationBeanFactoryMetaData类型的bean ConfigurationBeanFactoryMetaData beanFactoryMetaData = getBeanFactoryMetaData(context); // 2. 获得被@ConfigurationProperties注解的bean,key--> bean的id,value --> bean Map<String, Object> beans = getConfigurationPropertiesBeans(context,beanFactoryMetaData); // 3. 依次遍历beans for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : beans.entrySet()) {String beanName = entry.getKey();Object bean = entry.getValue();Map<String, Object> root = new HashMap<String, Object>();String prefix = extractPrefix(context, beanFactoryMetaData, beanName, bean);// 3.1 获得@ConfigurationProperties注解的前缀,添加至root中,key-->prefix,value-->@ConfigurationProperties注解的前缀root.put("prefix", prefix);// 3.2 root.put("properties", sanitize(prefix, safeSerialize(mapper, bean, prefix)));// 3.3 添加至result中,key--> bean id,value-->map{prefix=xx,properties=xx}result.put(beanName, root); } // 4. 如果ApplicationContext存在父容器的,则递归调用extract提取数据,key为parent. if (context.getParent() != null) {result.put("parent", extract(context.getParent(), mapper)); } return result; }- 获得beanFactory中ConfigurationBeanFactoryMetaData类型的bean
- 获得被@ConfigurationProperties注解的bean,key–> bean的id,value –> bean
依次遍历beans
- 获得@ConfigurationProperties注解的前缀,添加至root中,key–>prefix,value–>@ConfigurationProperties注解的前缀
对数据进行脱敏.代码如下:
private Map<String, Object> sanitize(String prefix, Map<String, Object> map) { for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : map.entrySet()) { String key = entry.getKey(); String qualifiedKey = (prefix.isEmpty() ? prefix : prefix + ".") + key; Object value = entry.getValue(); if (value instanceof Map) { // 1. 如果对应的属性值为Map,List 则递归调用sanitize 进行数据脱敏 map.put(key, sanitize(qualifiedKey, (Map<String, Object>) value)); } else if (value instanceof List) { map.put(key, sanitize(qualifiedKey, (List<Object>) value)); } else { // 2. 如果属性名包含password", "secret", "key", "token", ".*credentials.*", "vcap_services,则将其替换为****** value = this.sanitizer.sanitize(key, value); value = this.sanitizer.sanitize(qualifiedKey, value); map.put(key, value); } } return map; }- 如果对应的属性值为Map,List 则递归调用sanitize 进行数据脱敏
- 否则如果属性名包含password, secret, key, token, .*credentials.*, vcap_services,则将其替换为**
- 添加至result中,key–> bean id,value–>map{prefix=xx,properties=xx}
如果ApplicationContext存在父容器的,则递归调用extract提取数据,key为parent.
由于ConfigurationPropertiesReportEndpoint 被@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “endpoints.configprops”)注解,因此可通过如下属性配置:
endpoints.configprops.id=configprops endpoints.configprops.sensitive=true endpoints.configprops.enabled=true endpoints.configprops.keys-to-sanitize=password,secret之所以可以通过 endpoints.configprops.keys-to-sanitize 进行配置,是因为ConfigurationPropertiesReportEndpoint声明了如下方法:
public void setKeysToSanitize(String... keysToSanitize) {this.sanitizer.setKeysToSanitize(keysToSanitize); }自动化配置(在EndpointAutoConfiguration中配置):
代码如下:
@Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public ConfigurationPropertiesReportEndpoint configurationPropertiesReportEndpoint() {return new ConfigurationPropertiesReportEndpoint(); }- @Bean –> 注册1个id为configurationPropertiesReportEndpoint,类型为ConfigurationPropertiesReportEndpoint的Bean
- @ConditionalOnMissingBean –> beanFactory中不存在ConfigurationPropertiesReportEndpoint类型的bean时生效
TraceEndpoint
作用:–> 该端点用来返回基本的HTTP跟踪信息。默认情况下,跟踪信息的存储采用org.springframework.boot.actuate.trace.InMemoryTraceRepository实现的内存方式,始终保留最近的100条请求记录.其中,返回的Trace定义如下:
public final class Trace {// 时间戳 private final Date timestamp;// 保存用于分析上下文信息,例如HTTP头 private final Map<String, Object> info;public Trace(Date timestamp, Map<String, Object> info) {super();Assert.notNull(timestamp, "Timestamp must not be null");Assert.notNull(info, "Info must not be null");this.timestamp = timestamp;this.info = info; }public Date getTimestamp() {return this.timestamp; }public Map<String, Object> getInfo() {return this.info; } }字段:
private final TraceRepository repository;这里我们有必要说明一下TraceRepository:
TraceRepository 是用来保存Trace的. 接口定义如下:
public interface TraceRepository {// 返回保存的Trace List<Trace> findAll();// 进行添加 void add(Map<String, Object> traceInfo); }TraceRepository 只要1个实现–>InMemoryTraceRepository.其字段如下:
// 容量为100 private int capacity = 100; // 是否倒序展示,默认为false private boolean reverse = true; // 容器,用于保存Trace private final List<Trace> traces = new LinkedList<Trace>();findAll只需简单的返回保存的traces即可.实现如下:
public List<Trace> findAll() { synchronized (this.traces) {return Collections.unmodifiableList(new ArrayList<Trace>(this.traces)); } }add,代码如下:
public void add(Map<String, Object> map) { // 1. 实例化Trace,时间戳为当前时间 Trace trace = new Trace(new Date(), map); synchronized (this.traces) {// 2. 如果traces中的容量大于等于了阈值,则进行删除.如果reverse等于true 则删除最后1个,否则,删除第1个while (this.traces.size() >= this.capacity) {this.traces.remove(this.reverse ? this.capacity - 1 : 0);}// 3. 进行添加,如果reverse等于true 则添加至第1个,否则,添加至最后if (this.reverse) {this.traces.add(0, trace);}else {this.traces.add(trace);} } }- 实例化Trace,时间戳为当前时间
- 如果traces中的容量大于等于了阈值,则进行删除.如果reverse等于true 则删除最后1个,否则,删除第1个
- 进行添加,如果reverse等于true 则添加至第1个,否则,添加至最后
TraceRepository 是在何处配置的呢?
在TraceRepositoryAutoConfiguration中,代码如下:
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(TraceRepository.class) @Bean public InMemoryTraceRepository traceRepository() { return new InMemoryTraceRepository(); }- @Bean –> 注册1个id为traceRepository,类型为InMemoryTraceRepository的bean
- @ConditionalOnMissingBean(TraceRepository.class)–> 当beanFactory中不存在TraceRepository类型的bean时生效
invoke 实现:
@Override public List<Trace> invoke() {return this.repository.findAll(); }只需调用TraceRepository# findAll,返回保存的Trace即可.
属性配置,因此其被@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “endpoints.trace”)注解,因此可以通过如下属性进行配置:
endpoints.trace.id=trace endpoints.trace.sensitive=true endpoints.trace.enabled=true自动装配:
在EndpointAutoConfiguration中进行了装配,代码如下:
@Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public TraceEndpoint traceEndpoint() {return new TraceEndpoint(this.traceRepository == null? new InMemoryTraceRepository() : this.traceRepository); }- @Bean–> 注册1个id为traceEndpoint,类型为TraceEndpoint的bean
- @ConditionalOnMissingBean–> 当beanFactory中不存在TraceEndpoint类型的bean时生效
这里提1个问题,TraceEndpoint 是通过TraceRepository获取Trace,那么TraceRepository中的Trace是如何保存的呢?
答案:
通过WebRequestTraceFilter(Filter)来实现. WebRequestTraceFilter实现了Ordered接口,指定了其在过滤器链中的顺序,代码如下:
private int order = Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE - 10;public int getOrder() {return this.order; }WebRequestTraceFilter中的字段如下:
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(WebRequestTraceFilter.class);// debug时使用.如果启用的话,并且log的trace级别可用的话,则打印请求头信息,默认为false private boolean dumpRequests = false;// Not LOWEST_PRECEDENCE, but near the end, so it has a good chance of catching all // enriched headers, but users can add stuff after this if they want to private int order = Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE - 10;private final TraceRepository repository;private ErrorAttributes errorAttributes;private final TraceProperties properties;其中TraceProperties的定义如下:
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "management.trace") public class TraceProperties {private static final Set<Include> DEFAULT_INCLUDES;static {Set<Include> defaultIncludes = new LinkedHashSet<Include>();defaultIncludes.add(Include.REQUEST_HEADERS);defaultIncludes.add(Include.RESPONSE_HEADERS);defaultIncludes.add(Include.COOKIES);defaultIncludes.add(Include.ERRORS);defaultIncludes.add(Include.TIME_TAKEN);DEFAULT_INCLUDES = Collections.unmodifiableSet(defaultIncludes);}private Set<Include> include = new HashSet<Include>(DEFAULT_INCLUDES);public Set<Include> getInclude() {return this.include;}public void setInclude(Set<Include> include) {this.include = include;} }默认配置的是Include.REQUEST_HEADERS, Include.RESPONSE_HEADERS, Include.COOKIES ,Include.ERRORS, Include.TIME_TAKEN. 可以通过如下进行配置
management.trace.include=REQUEST_HEADERS,RESPONSE_HEADERS可选值为org.springframework.boot.actuate.trace.TraceProperties.Include.这里就不在贴出了
WebRequestTraceFilter 继承了OncePerRequestFilter,因此只需实现doFilterInternal即可,代码如下:
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)throws ServletException, IOException {long startTime = System.nanoTime();// 1. 获得traceMap<String, Object> trace = getTrace(request);// 2. 打印日志-->如果log的trace级别可用的话并且dumpRequests等于true,则打印请求头信息,默认为falselogTrace(request, trace);int status = HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value();try {// 3. 继续过滤器链的过滤,最后获得响应状态filterChain.doFilter(request, response);status = response.getStatus();}finally {// 4. 添加Http请求耗时统计-->如果TraceProperties中配置了Include#TIME_TAKEN(默认配置了),则添加到trace中,key为timeTaken,value-->当前时间-开始时间的毫秒值addTimeTaken(trace, startTime);// 5. 添加响应头信息enhanceTrace(trace, status == response.getStatus() ? response: new CustomStatusResponseWrapper(response, status));// 6. 添加至TraceRepository 中this.repository.add(trace);} }- 记录开始时间
获得trace.代码如下:
protected Map<String, Object> getTrace(HttpServletRequest request) { // 1. 获得HttpSession HttpSession session = request.getSession(false); // 2. 获得javax.servlet.error.exception,所对应的异常--> 当spring mvc 出现异常时,会加入到javax.servlet.error.exception中 Throwable exception = (Throwable) request.getAttribute("javax.servlet.error.exception"); // 3. 获得Principal,如果返回null,说明没有该请求没有进行验证 Principal userPrincipal = request.getUserPrincipal(); Map<String, Object> trace = new LinkedHashMap<String, Object>(); Map<String, Object> headers = new LinkedHashMap<String, Object>(); // 4. 添加请求方法,请求路径,请求头到trace中 trace.put("method", request.getMethod()); trace.put("path", request.getRequestURI()); trace.put("headers", headers); if (isIncluded(Include.REQUEST_HEADERS)) {headers.put("request", getRequestHeaders(request)); } // 省略掉默认不执行的代码.... // 5. 如果有异常并且errorAttributes不等于null,则记录error if (isIncluded(Include.ERRORS) && exception != null&& this.errorAttributes != null) {trace.put("error", this.errorAttributes.getErrorAttributes(new ServletRequestAttributes(request), true)); } return trace; }- 继续过滤器链的过滤,最后获得响应状态
添加Http请求耗时统计–>如果TraceProperties中配置了Include#TIME_TAKEN(默认配置了),则添加到trace中,key为timeTaken,value–>当前时间-开始时间的毫秒值.代码如下:
private void addTimeTaken(Map<String, Object> trace, long startTime) { long timeTaken = System.nanoTime() - startTime; add(trace, Include.TIME_TAKEN, "timeTaken","" + TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(timeTaken)); }添加响应头信息.代码如下:
protected void enhanceTrace(Map<String, Object> trace, HttpServletResponse response) { if (isIncluded(Include.RESPONSE_HEADERS)) {Map<String, Object> headers = (Map<String, Object>) trace.get("headers");headers.put("response", getResponseHeaders(response)); } }getResponseHeaders 代码如下:
private Map<String, String> getResponseHeaders(HttpServletResponse response) { Map<String, String> headers = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>(); // 1. 依次遍历响应头,添加至headers 中,key--> 响应头名,value-->响应头对应的值 for (String header : response.getHeaderNames()) {String value = response.getHeader(header);headers.put(header, value); } // 2. 如果TraceProperties中没有配置Include#COOKIES,则在headers中删除key为Set-Cookie的值.默认是配置了的,因此不会删除 if (!isIncluded(Include.COOKIES)) {headers.remove("Set-Cookie"); } // 3. 向headers 中添加 key--> status,value-->响应状态码 headers.put("status", "" + response.getStatus()); return headers; }- 遍历响应头,添加至headers 中,key–> 响应头名,value–>响应头对应的值
- 如果TraceProperties中没有配置Include#COOKIES,则在headers中删除key为Set-Cookie的值.默认是配置了的,因此不会删除
- 向headers 中添加 key–> status,value–>响应状态码
- 添加至TraceRepository中
WebRequestTraceFilter 是如何配置的呢?
答案: 在TraceWebFilterAutoConfiguration中.代码如下:
@Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public WebRequestTraceFilter webRequestLoggingFilter(BeanFactory beanFactory) {WebRequestTraceFilter filter = new WebRequestTraceFilter(this.traceRepository,this.traceProperties);if (this.errorAttributes != null) {filter.setErrorAttributes(this.errorAttributes);}return filter; }- @Bean–> 注册1个id为webRequestLoggingFilter,类型为WebRequestTraceFilter的bean
- @ConditionalOnMissingBean–> 当beanFactory中不存在WebRequestTraceFilter类型的bean时生效
同时由于TraceWebFilterAutoConfiguration声明了如下注解:
@Configuration @ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, ServletRegistration.class }) @AutoConfigureAfter(TraceRepositoryAutoConfiguration.class) @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "endpoints.trace.filter", name = "enabled", matchIfMissing = true) @EnableConfigurationProperties(TraceProperties.class)- @Configuration–> 配置类
- @ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, ServletRegistration.class })–> 在当前的类路径下存在Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, ServletRegistration.class时生效
- @AutoConfigureAfter(TraceRepositoryAutoConfiguration.class)–> 在TraceRepositoryAutoConfiguration之后进行自动装配,这样就可以自动注入TraceRepository
- @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = “endpoints.trace.filter”, name = “enabled”, matchIfMissing = true)–> 当配置有endpoints.trace.filter.enabled 等于true时生效,如果没有配置,默认生效
- @EnableConfigurationProperties(TraceProperties.class)–> 可以通过management.trace.include 进行配置.