Imagine that one model is displayed at time t0 and we wish it to change into another model by time t1. For all times between t0 and t1, a continuous “mixed” model is obtained, using some kind of interpolation. An example of morphing is shown in Figure 4.14.
假设在时间t0显示一个模型,我们希望它在时间t1变成另一个模型。对于t0和t1之间的所有时间,使用某种插值获得连续的“混合”模型。变形的一个例子如图4.14所示。

顶点变形。为每个顶点定义了两个位置和法线。在每一帧中,顶点着色器对中间位置和法线进行线性插值。(图片由英伟达公司提供。)
Morphing involves solving two major problems, namely, the vertex correspondence problem and the interpolation problem.
变形涉及解决两个主要问题,即顶点对应问题和插值问题。
To compute a morphed vertex for time t ∈ [t0, t1], we first compute s = (t−t0)/(t1 −t0), and then the linear vertex blend,where p0 and p1 correspond to the same vertex but at different times, t0 and t1.
为了计算时间t ∈ [t0,t1]的变形顶点,我们首先计算s =(t-t0)/(t1-t0),然后计算线性顶点混合,其中p0和p1对应于相同的顶点,但是在不同的时间t0和t1。

A variant of morphing where the user has more intuitive control is referred to as morph targets or blend shapes. The basic idea can be explained using Figure 4.15.
用户可以更直观地控制的变形的变体被称为变形目标或混合形状。基本思想可以用图4.15来解释。
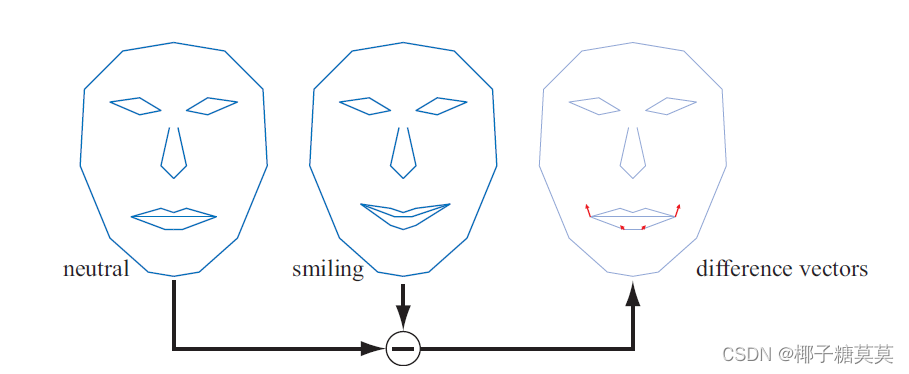
Figure 4.15. Given two mouth poses, a set of difference vectors is computed to control interpolation,or even extrapolation. In morph targets, the difference vectors are used to “add” movements onto the neutral face. With positive weights for the difference vectors, we get a smiling mouth, while negative weights can give the opposite effect.
图4.15。给定两个嘴部姿态,计算一组差向量来控制内插,或者甚至外插。在变形目标中,差异向量用于将运动“添加”到中性面上。对于差值向量的正权重,我们得到一个微笑的嘴,而负权重会产生相反的效果。
At this point, we have a neutral model, N, and a set of difference poses, Di. A morphed model M can then be obtained using the following formula:
此时,我们有一个中性模型N和一组差分姿势Di。然后可以使用下面的公式获得变形的模型M:

Lewis et al. introduce pose-space deformation, which combines vertex blending and morph targets. Senior uses precomputed vertex textures to store and retrieve displacements between target poses. Hardware supporting stream-out and the ID of each vertex allow many more targets to be used in a single model and the effects to be computed exclusively on the GPU. Using a lowresolution mesh and then generating a high-resolution mesh via the tessellation stage and displacement mapping avoids the cost of skinning every vertex in a highly detailed model .
Lewis等人引入了姿态空间变形,它结合了顶点混合和变形目标。Senior 使用预先计算的顶点纹理来存储和检索目标姿势之间的位移。支持流输出和每个顶点的ID的硬件允许在单个模型中使用更多的目标,并且只在GPU上计算效果。使用低分辨率网格,然后通过镶嵌阶段和置换贴图生成高分辨率网格,避免了在高度详细的模型中为每个顶点蒙皮的成本