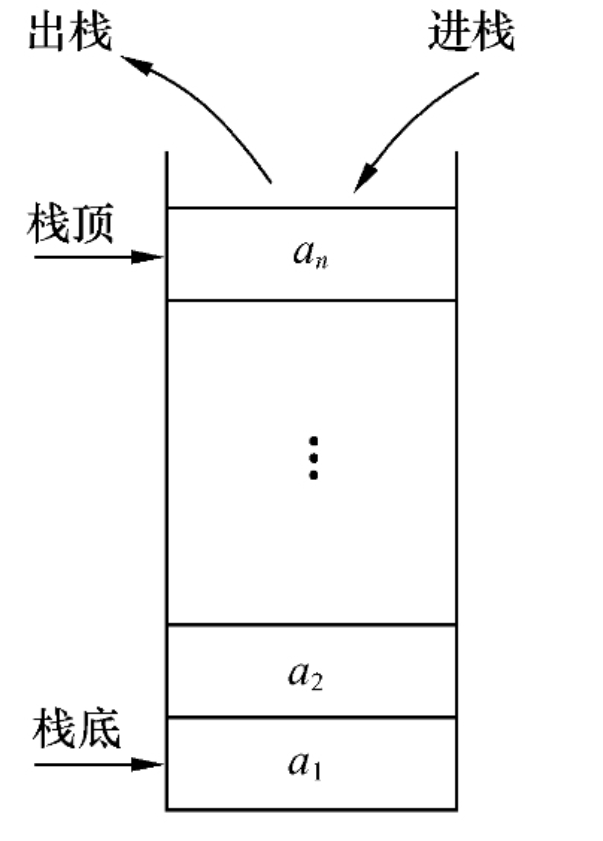
栈的定义:栈是一种特殊的表这种表只在表头进行插入和删除操作。因此,表头对于栈来说具有特殊的意义,称为栈顶。相应地,表尾称为栈底。不含任何元素的栈称为空栈。
栈的逻辑结构:假设一个栈S中的元素为an,an-1,..,a1,则称a1为栈底元素,an为栈顶元 素。栈中的元素按a1 ,a2,..,an-1,an的次序进栈。在任何时候,出栈的元素都是栈顶元素。换句话说,栈的修改是按后进先出的原则进行的.因此,栈又称为后进先出(Last In First Out)表,简称为LIFO表。所以,只要问题满足LIFO原则,就可以使用栈。
notice:换句话说,栈就是可以一个元素进后,可以接着进行输出的表.
java 模拟栈操作:
1 packagecom.zsy.stack;2 /**
3 * 栈 java 实现 先进后出4 *@author偶my耶5 *6 */
7 public classstack {8 privateObject[] stack;9
10 //元素个数;
11 private intsize;12
13 //默认长度为10;
14 publicstack(){15 this(10);16 }17
18 //也可以自己设置长度,即容量;
19 public stack(intlen){20 stack = newObject[len];21 }22
23 //返回元素个数;
24 public intsize(){25 returnsize;26 }27
28 //返回数组长度,即容量;
29 public intcapacity(){30 returnstack.length;31 }32
33 //实现动态的数组;
34 public voidensureCapacity(){35 if(size() ==capacity()){36 Object[] newStack = new Object[size() * 3 / 2 + 1];37 System.arraycopy(stack, 0, newStack, 0, size());38 stack =newStack;39 }40 }41
42 //入栈;
43 public voidpush(Object o){44 size++;45 ensureCapacity();46 stack[size - 1] =o;47 }48
49
50
51 //判空;
52 public booleanisEmpty(){53 return size == 0;54 }55
56 //出栈;
57 publicObject pop(){58 //首先要判空;
59 if(isEmpty()){60 throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("不能为空");61 }62
63 Object o = stack[--size];64 stack[size] = null;65 returno;66 }67
68
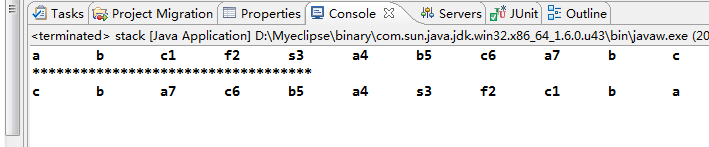
69 public static voidmain(String[] args) {70 stack stack = new stack(3);71 String[] data = new String[] { "a", "b", "c1" ,"f2","s3", "a4", "b5", "c6" , "a7", "b", "c"};72 for(String i:data)73 { stack.push(i);74 System.out.print(i + "\t");75 }76
77 System.out.println("\n***********************************");78 while (!stack.isEmpty()) {79 System.out.print(stack.pop() + "\t");80 }81 //}
82 }83 }
运行效果:
队列
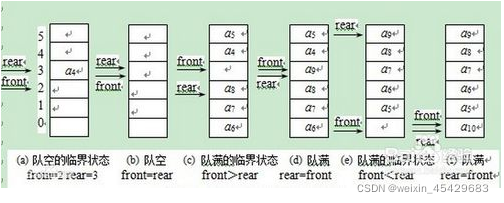
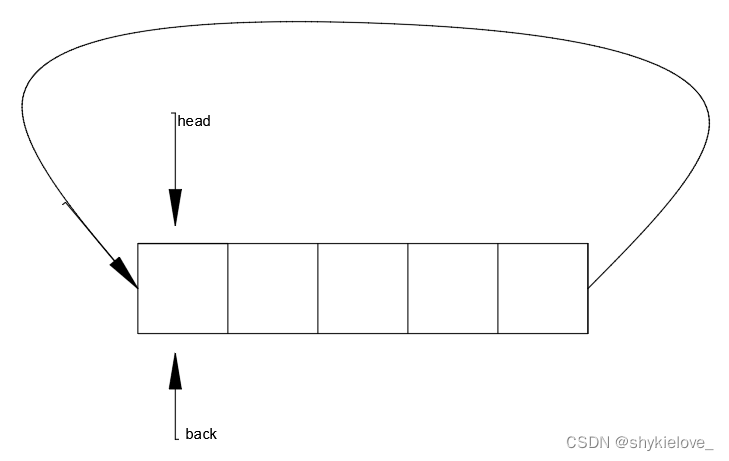
在java5中新增加了java.util.Queue接口,用以支持队列的常见操作。该接口扩展了java.util.Collection接口。
Queue使用时要尽量避免Collection的add()和remove()方法,而是要使用offer()来加入元素,使用poll()来获取并移出元素。它们的优
点是通过返回值可以判断成功与否,add()和remove()方法在失败的时候会抛出异常。 如果要使用前端而不移出该元素,使用
element()或者peek()方法。
值得注意的是LinkedList类实现了Queue接口,因此我们可以把LinkedList当成Queue来用。
java代码模拟:
1 packagecom.zsy.stack;2 /**
3 * java 队列实现 先进先出4 *@author偶my耶5 *6 */
7 public classQueue {8
9 private int maxSize; //队列长度,由构造函数初始化
10 private long[] queArray; //队列
11 private int front; //队头
12 private int rear; //队尾
13 private int nItems; //元素的个数
14
15 public Queue(int s) //构造函数
16 {17 maxSize =s;18 queArray = new long[maxSize];19 front = 0;20 rear = -1;21 nItems = 0;22 }23
24 public void insert(long j) //进队列
25 {26 if(rear == maxSize-1) //处理循环
27 rear = -1;28 queArray[++rear] = j; //队尾指针加1,把值j加入队尾
29 nItems++;30 }31
32 public long remove() //取得队列的队头元素。
33 {34 long temp = queArray[front++]; //取值和修改队头指针
35 if(front == maxSize) //处理循环
36 front = 0;37 nItems--;38 returntemp;39 }40
41 public long peekFront() //取得队列的队头元素。该运算与 remove()不同,后者要修改队头元素指针。
42 {43 returnqueArray[front];44 }45
46 public boolean isEmpty() //判队列是否为空。若为空返回一个真值,否则返回一个假值。
47 {48 return (nItems==0);49 }50
51 public boolean isFull() //判队列是否已满。若已满返回一个真值,否则返回一个假值。
52 {53 return (nItems==maxSize);54 }55
56 public int size() //返回队列的长度
57 {58 returnnItems;59 }60 public static voidmain(String[] args)61 {62 Queue theQueue = new Queue(5); //队列有5个元素
63
64 theQueue.insert(10); //添加4个元素
65 theQueue.insert(20);66 theQueue.insert(30);67 theQueue.insert(40);68
69 theQueue.remove(); //移除3个元素
70 theQueue.remove(); //(10, 20, 30)
71 theQueue.remove();72
73 theQueue.insert(50); //添加4个元素
74 theQueue.insert(60);75 theQueue.insert(70);76 theQueue.insert(90);77 while( !theQueue.isEmpty() ) //遍历队列并移除所有元素
78 {79 long n = theQueue.remove(); //(40, 50, 60, 70, 80)
80 System.out.print(n);81 System.out.print(" ");82 }83 System.out.println("");84 }85 }
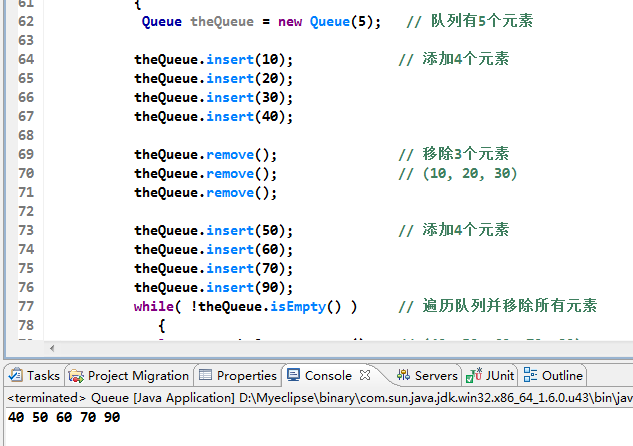
运行效果: