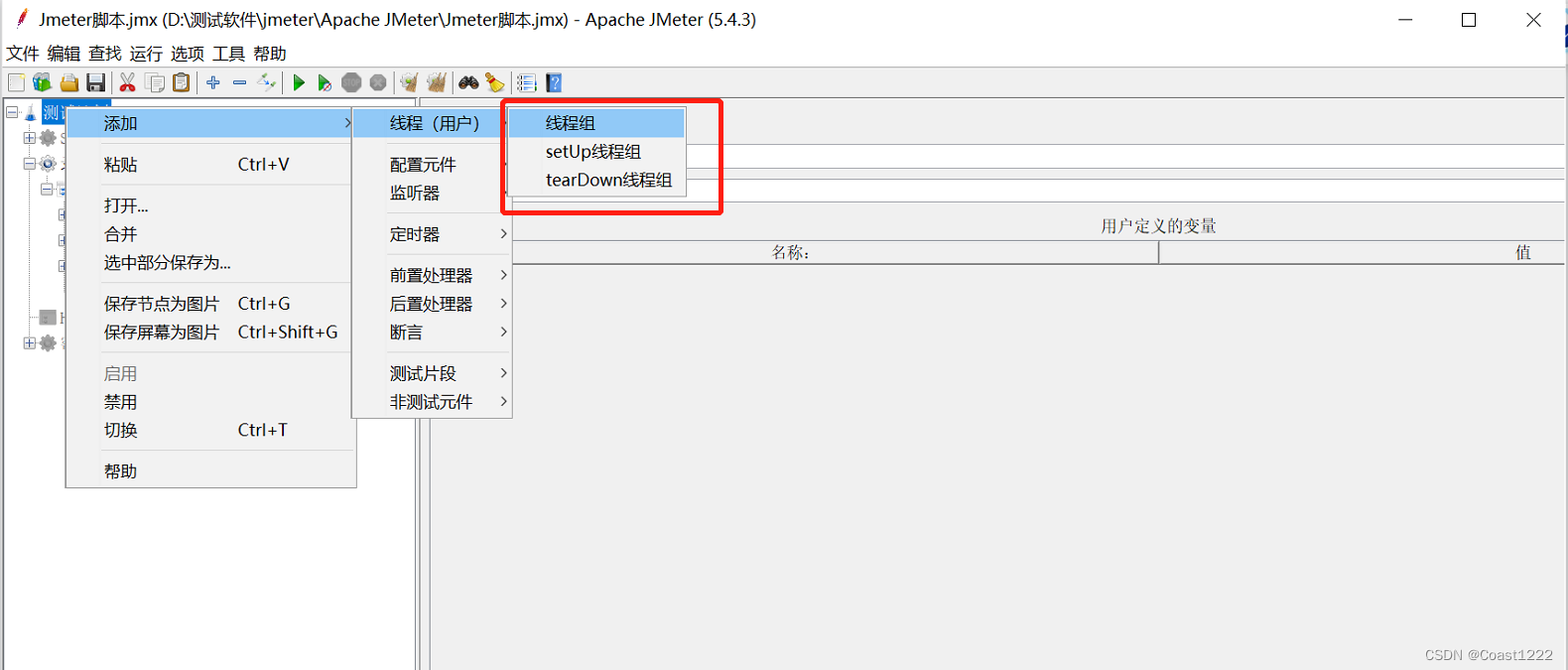
shiro主要内容:
1:SecurityUtils
shiro提供的工具类,主要作用是获取 SecurityManager和Subject
public abstract class SecurityUtils {private static SecurityManager securityManager;//获取Subjectpublic static Subject getSubject() {Subject subject = ThreadContext.getSubject();if (subject == null) {subject = (new Subject.Builder()).buildSubject();ThreadContext.bind(subject);}return subject;}public static void setSecurityManager(SecurityManager securityManager) {SecurityUtils.securityManager = securityManager;}//获取securityManagerpublic static SecurityManager getSecurityManager() throws UnavailableSecurityManagerException {SecurityManager securityManager = ThreadContext.getSecurityManager();if (securityManager == null) {securityManager = SecurityUtils.securityManager;}if (securityManager == null) {String msg = "No SecurityManager accessible to the calling code, either bound to the " +ThreadContext.class.getName() + " or as a vm static singleton. This is an invalid application " +"configuration.";throw new UnavailableSecurityManagerException(msg);}return securityManager;}
}ThreadContext内部使用ThreadLocal来保存Subject

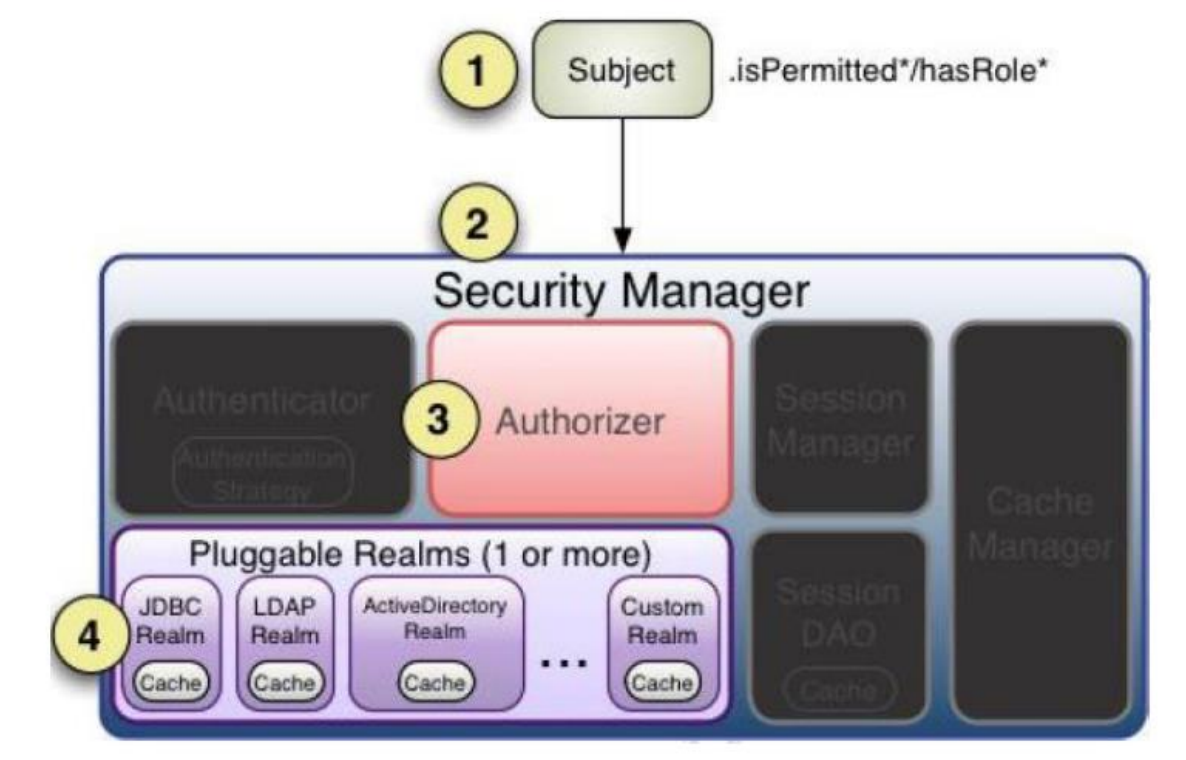
2:SecurityManager 安全管理器
管理 shiro的各个组件实例,提供安全管理的服务,像一个容器
继承了Authenticator(认证器),Authorizer(授权器),SessionManager(会话管理器)三个接口
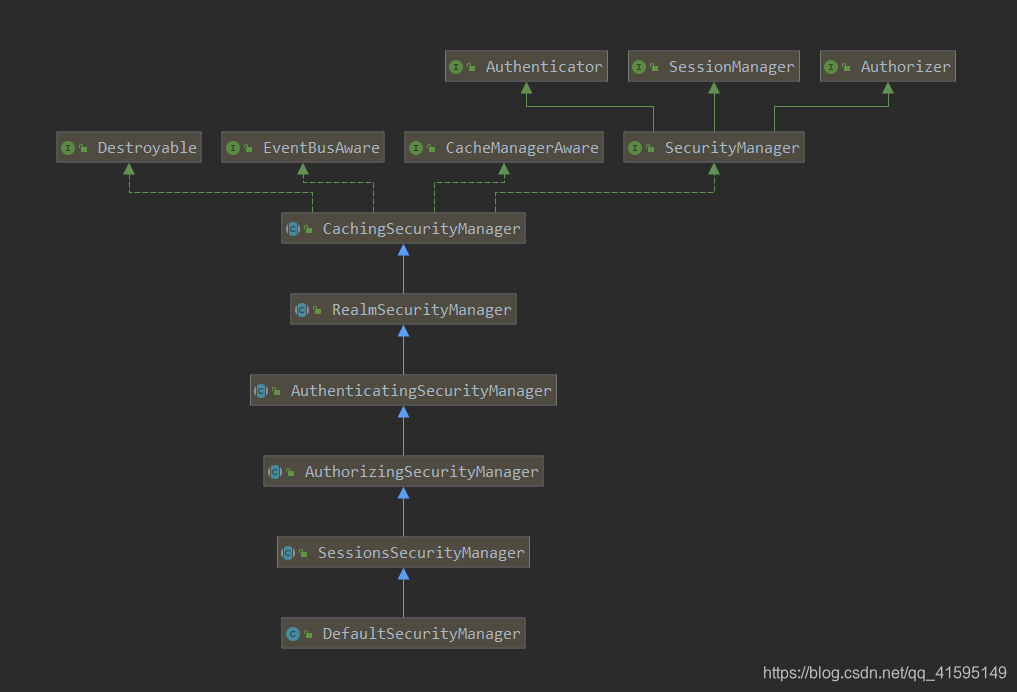
其实现主要有这几个 :
CacheSecurityManager:添加缓存
RealmSecurityManager:添加数据源
AuthenticatingSecurityManager:内部包含一个Authenticator,将验证的操作都委托给该实例
AuthorizingSecurityManager:内部包含一个Authenticator,将授权的操作都委托给该实例
SessionsSecurityManager:内部包含一个SessionManager,将session操作都交给该实例了
DefaultSecurityManger:securityManager的基本实现
3:Authenticator 认证器
只有一个authenticate接口,拿来认证AuthenticationToken是否有效,无效会抛出AuthenticationException异常
public interface Authenticator {/*** 验证失败会抛出的异常* @see ExpiredCredentialsException:凭证过期* @see IncorrectCredentialsException:凭证错误* @see ExcessiveAttemptsException:多次尝试失败* @see LockedAccountException:账户锁定* @see ConcurrentAccessException:并发访问异常* @see UnknownAccountException:账号不存在*/public AuthenticationInfo authenticate(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken)throws AuthenticationException;
}
其实现类:AbstractAuthenticator
public final AuthenticationInfo authenticate(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {if (token == null) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Method argument (authentication token) cannot be null.");}log.trace("Authentication attempt received for token [{}]", token);AuthenticationInfo info;try {info = doAuthenticate(token);if (info == null) {String msg = "No account information found for authentication token [" + token + "] by this " +"Authenticator instance. Please check that it is configured correctly.";throw new AuthenticationException(msg);}} catch (Throwable t) {AuthenticationException ae = null;if (t instanceof AuthenticationException) {ae = (AuthenticationException) t;}if (ae == null) {//Exception thrown was not an expected AuthenticationException. Therefore it is probably a little more//severe or unexpected. So, wrap in an AuthenticationException, log to warn, and propagate:String msg = "Authentication failed for token submission [" + token + "]. Possible unexpected " +"error? (Typical or expected login exceptions should extend from AuthenticationException).";ae = new AuthenticationException(msg, t);if (log.isWarnEnabled())log.warn(msg, t);}try {notifyFailure(token, ae);} catch (Throwable t2) {if (log.isWarnEnabled()) {String msg = "Unable to send notification for failed authentication attempt - listener error?. " +"Please check your AuthenticationListener implementation(s). Logging sending exception " +"and propagating original AuthenticationException instead...";log.warn(msg, t2);}}throw ae;}log.debug("Authentication successful for token [{}]. Returned account [{}]", token, info);notifySuccess(token, info);return info;}
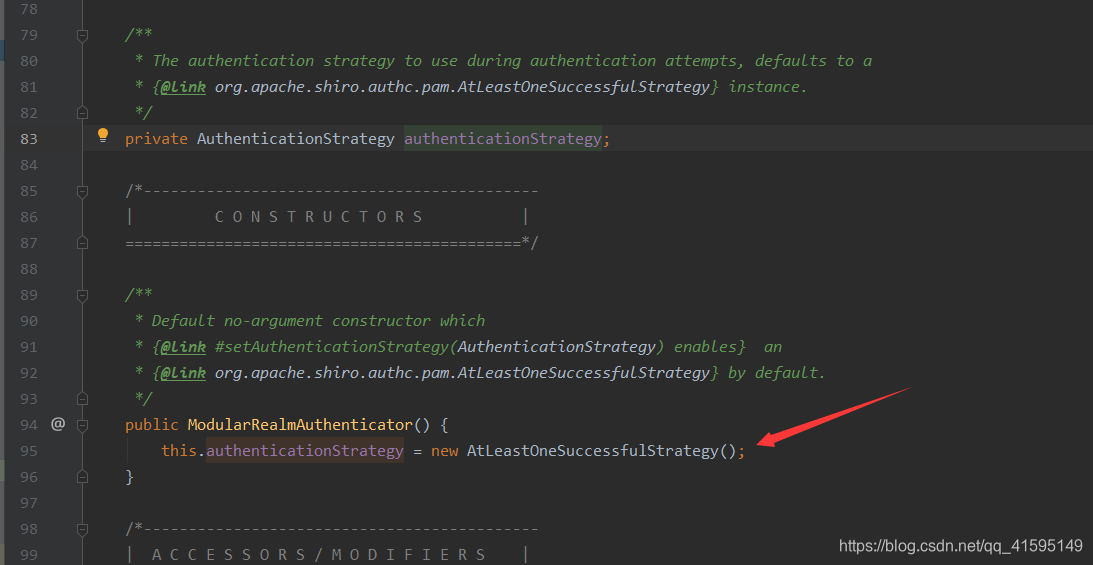
通过上面代码可以看出验证是通过doAuthenticate方法来验证的,成功则返回AuthenticationInfo对象,失败则抛出异常,而doAuthenticate是一个抽象方法,shiro只提供了一个实现类:ModularRealmAuthenticator
protected AuthenticationInfo doAuthenticate(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException {assertRealmsConfigured();Collection<Realm> realms = getRealms();if (realms.size() == 1) {return doSingleRealmAuthentication(realms.iterator().next(), authenticationToken);} else {return doMultiRealmAuthentication(realms, authenticationToken);}}
ModularRealmAuthenticator通过Realm数量来判断使用那种方式获取AuthenticationInfo
只有一个realm时:
protected AuthenticationInfo doSingleRealmAuthentication(Realm realm, AuthenticationToken token) {if (!realm.supports(token)) {String msg = "Realm [" + realm + "] does not support authentication token [" +token + "]. Please ensure that the appropriate Realm implementation is " +"configured correctly or that the realm accepts AuthenticationTokens of this type.";throw new UnsupportedTokenException(msg);}AuthenticationInfo info = realm.getAuthenticationInfo(token);if (info == null) {String msg = "Realm [" + realm + "] was unable to find account data for the " +"submitted AuthenticationToken [" + token + "].";throw new UnknownAccountException(msg);}return info;}
可以看到realm通过getAuthenticationInfo方法进行获取AuthenticationInfo,getAuthenticationInfo方法是一个抽象方法,我们在使用的时候就是通过实现这个方法来完成自定义的用户认证功能,到此如果只有一个relam,认证就结束了
如果有多个realm时:
protected AuthenticationInfo doMultiRealmAuthentication(Collection<Realm> realms, AuthenticationToken token) {//获取身份验证尝试期间使用的身份验证策略,默认为AtLeastOneSuccessfulStrategyAuthenticationStrategy strategy = getAuthenticationStrategy();//获取一个空的SimpleAuthenticationInfo对象AuthenticationInfo aggregate = strategy.beforeAllAttempts(realms, token);if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {log.trace("Iterating through {} realms for PAM authentication", realms.size());}for (Realm realm : realms) {// 认证前处理// AllSuccessfulStrategy - 判断realm.supports(token),如果不支持直接抛异常,返回aggregate// AtLeastOneSuccessfulStrategy - 返回aggregate// FirstSuccessfulStrategy - 返回aggregate,也就是nullaggregate = strategy.beforeAttempt(realm, token, aggregate);if (realm.supports(token)) {log.trace("Attempting to authenticate token [{}] using realm [{}]", token, realm);AuthenticationInfo info = null;Throwable t = null;try {info = realm.getAuthenticationInfo(token);} catch (Throwable throwable) {t = throwable;if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {String msg = "Realm [" + realm + "] threw an exception during a multi-realm authentication attempt:";log.debug(msg, t);}}// AllSuccessfulStrategy - 如果有异常会抛出异常, 如果没有就合并info和aggregate// AtLeastOneSuccessfulStrategy - 如果有异常并不会抛出,只是会合并info和aggregate// FirstSuccessfulStrategy - 如果aggregate存在,则返回aggregate;否则返回infoaggregate = strategy.afterAttempt(realm, token, info, aggregate, t);} else {log.debug("Realm [{}] does not support token {}. Skipping realm.", realm, token);}}aggregate = strategy.afterAllAttempts(token, aggregate);return aggregate;}多个realm比单个realm多了一个合并操作,先获取一种验证策略,在合并的时候验证
AuthenticationStrategy strategy = getAuthenticationStrategy();
默认是AtLeastOneSuccessfulStrategy,至少有一个Realm认证成功。除了AtLeastOneSuccessfulStrategy还有AllSuccessfulStrategy和FirstSuccessfulStrategy,分别是所有realm成功则成功和第一个realm成功则成功
4Authorizer 授权器
Authorizer接口中的方法
/*** 判断是否有指定的权限*/
boolean isPermitted(PrincipalCollection principals, String permission);/*** 判断是否有指定的权限*/
boolean isPermitted(PrincipalCollection subjectPrincipal, Permission permission);/*** 判断是否有指定的权限集合*/
boolean[] isPermitted(PrincipalCollection subjectPrincipal, String... permissions);/*** 判断是否有指定的所有权限集合*/
boolean isPermittedAll(PrincipalCollection subjectPrincipal, String... permissions);/*** 判断是否有指定的所有权限集合*/
boolean isPermittedAll(PrincipalCollection subjectPrincipal, Collection<Permission> permissions);/*** 检测是否存在权限,否则抛异常*/
void checkPermission(PrincipalCollection subjectPrincipal, String permission) throws AuthorizationException;/*** 检测是否存在权限,否则抛异常*/
void checkPermission(PrincipalCollection subjectPrincipal, Permission permission) throws AuthorizationException;/*** 检测是否存在权限,否则抛异常*/
void checkPermissions(PrincipalCollection subjectPrincipal, String... permissions) throws AuthorizationException;/*** 检测是否存在权限,否则抛异常*/
void checkPermissions(PrincipalCollection subjectPrincipal, Collection<Permission> permissions) throws AuthorizationException;/*** 判断是否有指定的角色*/
boolean hasRole(PrincipalCollection subjectPrincipal, String roleIdentifier);/*** 判断是否有指定的角色集合*/
boolean[] hasRoles(PrincipalCollection subjectPrincipal, List<String> roleIdentifiers);/*** 判断是否有指定的所有角色集合*/
boolean hasAllRoles(PrincipalCollection subjectPrincipal, Collection<String> roleIdentifiers);/*** 检测角色*/
void checkRole(PrincipalCollection subjectPrincipal, String roleIdentifier) throws AuthorizationException;/*** 检测角色*/
void checkRoles(PrincipalCollection subjectPrincipal, Collection<String> roleIdentifiers) throws AuthorizationException;/*** 检测角色*/
void checkRoles(PrincipalCollection subjectPrincipal, String... roleIdentifiers) throws AuthorizationException;方法很多,但作用都差不多,检查PrincipalCollection是否含有角色和权限,我们就看一个isPermitted(PrincipalCollection principals, String permission);
它的的实现类是AuthorizingRealm:
public boolean isPermitted(PrincipalCollection principals, String permission) {Permission p = getPermissionResolver().resolvePermission(permission);return isPermitted(principals, p);}
获取一个PermissionResolver对象,将permission字符串转换成Permission对象,PermissionResolver默认是WildcardPermissionResolver
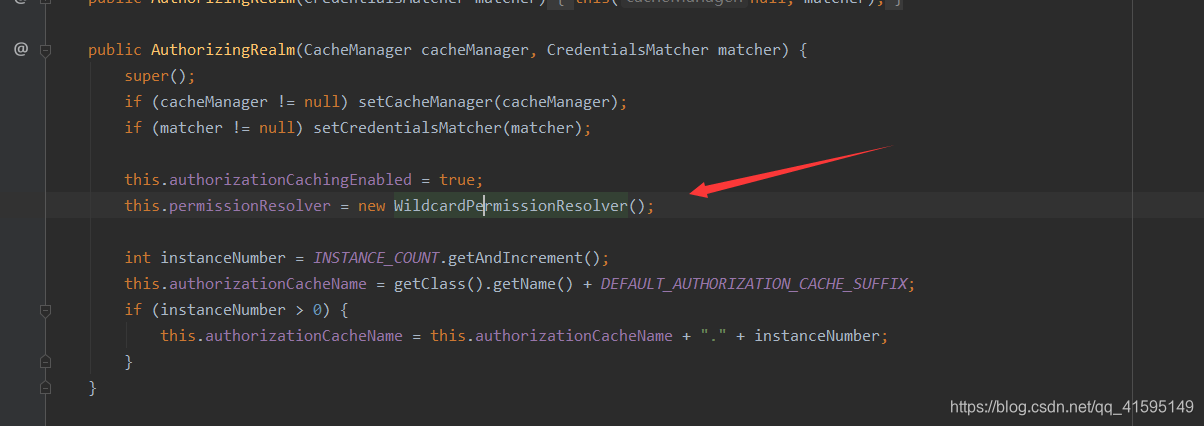
转换的Permission对象默认是WildcardPermission
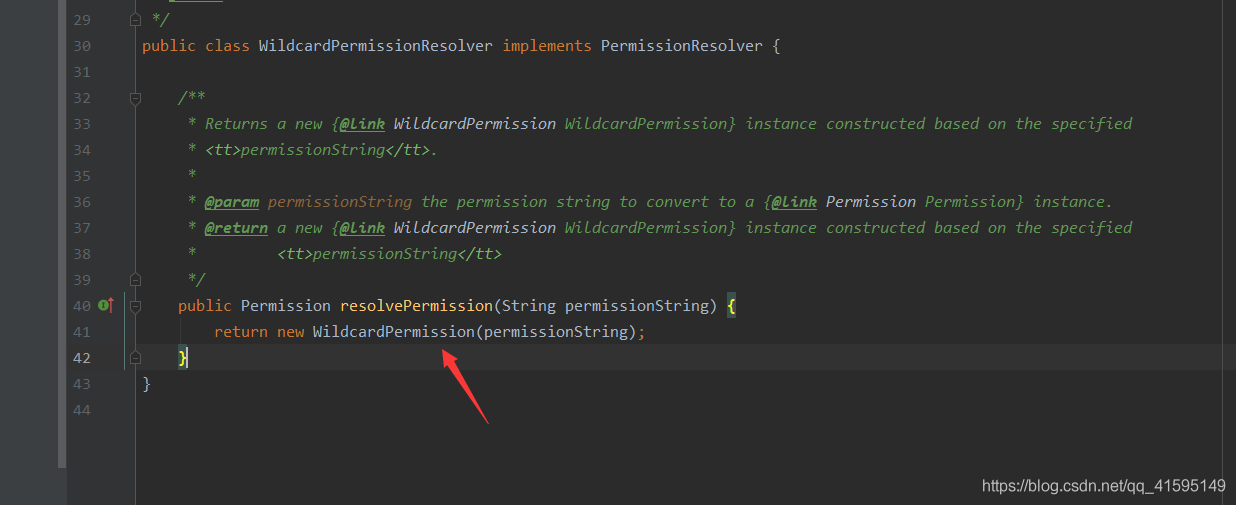
回到上面,获取到了Permission对象后就开始验证了:isPermitted(principals, p)
public boolean isPermitted(PrincipalCollection principals, String permission) {Permission p = getPermissionResolver().resolvePermission(permission);return isPermitted(principals, p);}
先获取用户信息,然后再验证:getAuthorizationInfo(principals);
public boolean isPermitted(PrincipalCollection principals, Permission permission) {AuthorizationInfo info = getAuthorizationInfo(principals);return isPermitted(permission, info);}
先在缓存里面获取,如果为null就通过doGetAuthorizationInfo来获取,而doGetAuthorizationInfo在我们使用shiro的时候一般会重写这个方法,达到自定义的目的
protected AuthorizationInfo getAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {if (principals == null) {return null;}AuthorizationInfo info = null;if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {log.trace("Retrieving AuthorizationInfo for principals [" + principals + "]");}Cache<Object, AuthorizationInfo> cache = getAvailableAuthorizationCache();if (cache != null) {if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {log.trace("Attempting to retrieve the AuthorizationInfo from cache.");}Object key = getAuthorizationCacheKey(principals);info = cache.get(key);if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {if (info == null) {log.trace("No AuthorizationInfo found in cache for principals [" + principals + "]");} else {log.trace("AuthorizationInfo found in cache for principals [" + principals + "]");}}}if (info == null) {// Call template method if the info was not found in a cacheinfo = doGetAuthorizationInfo(principals);// If the info is not null and the cache has been created, then cache the authorization info.if (info != null && cache != null) {if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {log.trace("Caching authorization info for principals: [" + principals + "].");}Object key = getAuthorizationCacheKey(principals);cache.put(key, info);}}return info;}
上面获取到了AuthorizationInfo,下面看一下验证过程
//visibility changed from private to protected per SHIRO-332protected boolean isPermitted(Permission permission, AuthorizationInfo info) {Collection<Permission> perms = getPermissions(info);if (perms != null && !perms.isEmpty()) {for (Permission perm : perms) {if (perm.implies(permission)) {return true;}}}return false;}
先获取Permission集合对象,然后使用implies()方法来检查权限,只要有一个为true就返回true,下面看一下WildcardPermission类的验证方法
public boolean implies(Permission p) {// By default only supports comparisons with other WildcardPermissionsif (!(p instanceof WildcardPermission)) {return false;}WildcardPermission wp = (WildcardPermission) p;List<Set<String>> otherParts = wp.getParts();int i = 0;for (Set<String> otherPart : otherParts) {//otherParts会和getParts()逐一匹配,如果getParts()在匹配过程中比otherParts数量少,就暗指省略可以匹配,返回true// 否则的话需要一一进行比较,在比较的过程中如果part不包含通配符(*),且part不能完全包含otherPart集合,就认为没有权限,返回false。if (getParts().size() - 1 < i) {return true;} else {Set<String> part = getParts().get(i);if (!part.contains(WILDCARD_TOKEN) && !part.containsAll(otherPart)) {return false;}i++;}}for (; i < getParts().size(); i++) {Set<String> part = getParts().get(i);if (!part.contains(WILDCARD_TOKEN)) {return false;}}return true;}
获取List<Set> otherParts集合,如果getParts()在匹配过程中比otherParts数量少,就暗指省略可以匹配,返回true,
否则的话需要一一进行比较,在比较的过程中如果part不包含通配符(*),且part不能完全包含otherPart集合,就认为没有权限,返回false。到此权限验证就结束了
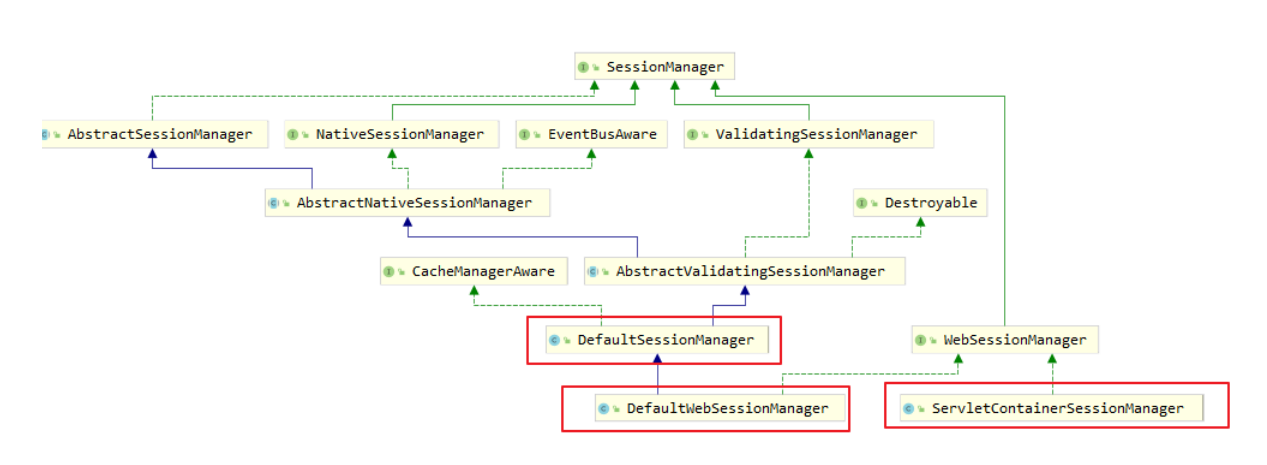
5:SessionManager会话管理器
shiro的session可以不依赖web环境,自己实现了一个企业级session,这表明shiro可以在任何环境使用session,是一个很强大 的功能,一般我们在使用shiro的时候会配置一个sessionManager比如这样:
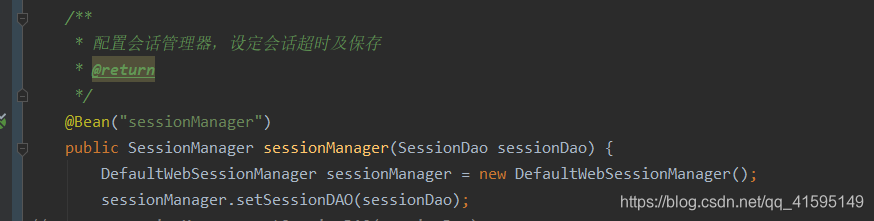
这里配置的是一个DefaultWebSessionManager,看名字就知道是一个支持web环境的sessionManager,下面看一下他默认的构造器
public DefaultWebSessionManager() {Cookie cookie = new SimpleCookie(ShiroHttpSession.DEFAULT_SESSION_ID_NAME);cookie.setHttpOnly(true); //more secure, protects against XSS attacksthis.sessionIdCookie = cookie;this.sessionIdCookieEnabled = true;this.sessionIdUrlRewritingEnabled = true;}
这里需要注意一下ShiroHttpSession.DEFAULT_SESSION_ID_NAME这个参数,它的默认值是JSESSIONID,后面在生成sessionid的时候就是根据这个值来生成的
private String getSessionIdCookieValue(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) {if (!isSessionIdCookieEnabled()) {log.debug("Session ID cookie is disabled - session id will not be acquired from a request cookie.");return null;}if (!(request instanceof HttpServletRequest)) {log.debug("Current request is not an HttpServletRequest - cannot get session ID cookie. Returning null.");return null;}HttpServletRequest httpRequest = (HttpServletRequest) request;return getSessionIdCookie().readValue(httpRequest, WebUtils.toHttp(response));}
根据cookie的值来获取session的id,进入readValue方法
public String readValue(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse ignored) {String name = getName();String value = null;javax.servlet.http.Cookie cookie = getCookie(request, name);if (cookie != null) {// Validate that the cookie is used at the correct place.String path = StringUtils.clean(getPath());if (path != null && !pathMatches(path, request.getRequestURI())) {log.warn("Found '{}' cookie at path '{}', but should be only used for '{}'", new Object[] { name, request.getRequestURI(), path});} else {value = cookie.getValue();log.debug("Found '{}' cookie value [{}]", name, value);}} else {log.trace("No '{}' cookie value", name);}return value;}
第一行就看到了,首先获取一个name,而这个name的值就是初始化的时候传递进去的JSESSIONID,由此可见session和cookie就是通过这个值来关联起来的,接下来看一下他的父类
DefaultSessionManager:
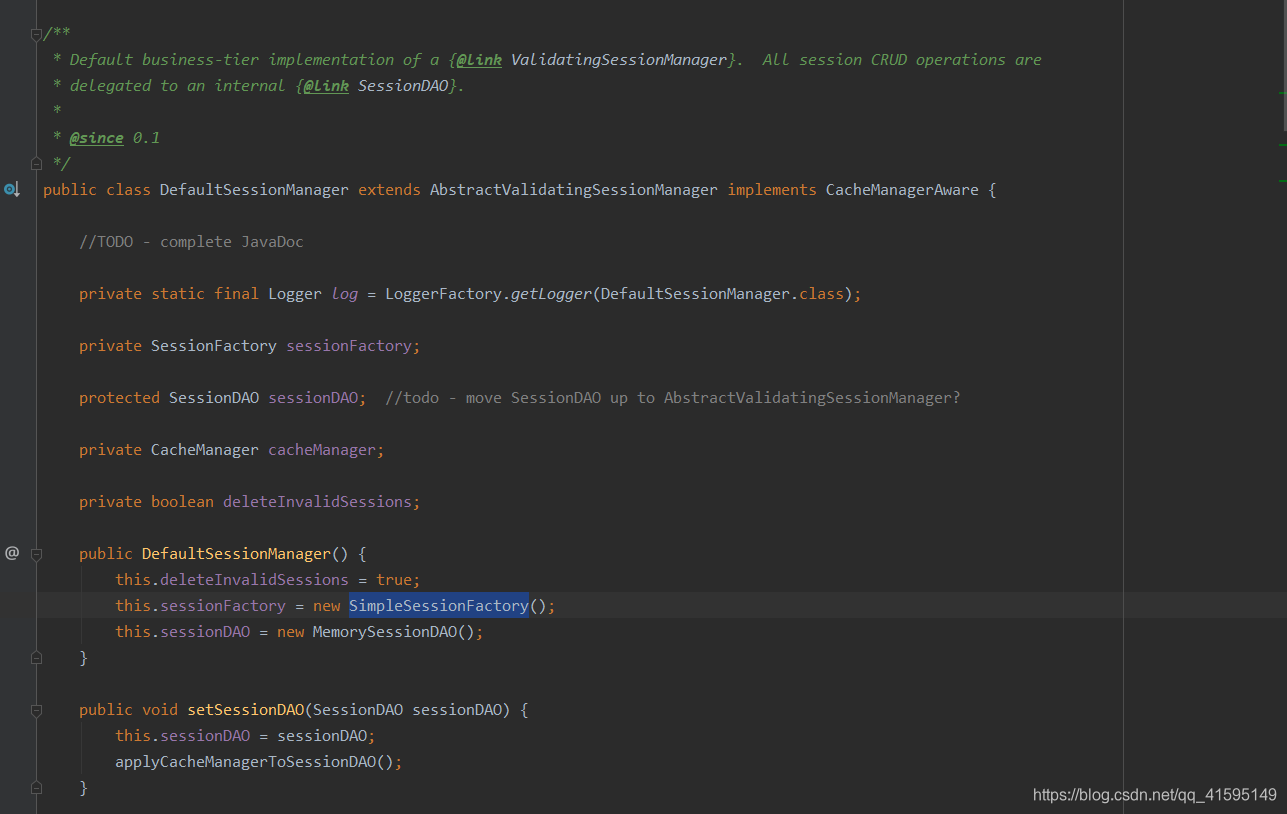
开头注释,所有会话CRUD操作都*委托给内部{@link SessionDAO},通过构造函数可以看出默认是使用MemorySessionDAO来操作session的,如果想要使用我们自己的SessionDAO只需要替换这个就行了,而且还专门提供了一个带有SessionDAO参数的构造器,除了SessionDAO还有两个初始值,一个是deleteInvalidSessions,初始值是true,用来控制当session失效时是否删除session,
一个是SessionFactory,默认是SimpleSessionFactory,用来创建session,下面看一下session的创建过程
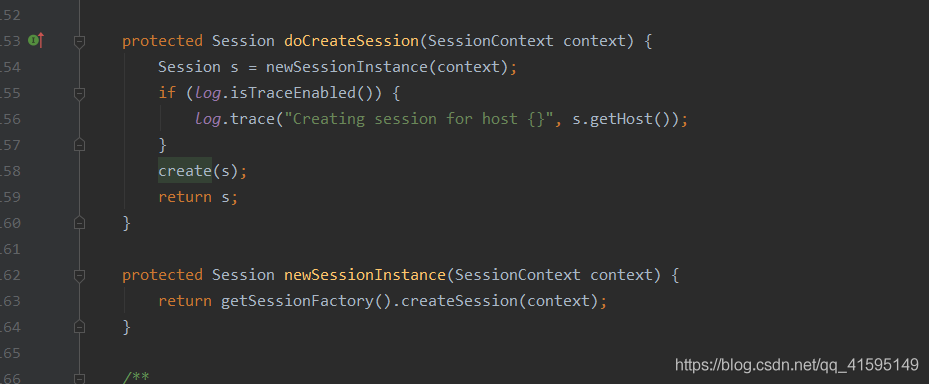
newSessionInstance方法创建session,下面的create是保存到sesssiondao,先看一下newSessionInstance,这个方法先通过getSessionFactory()获取一个创建工厂,上面已经说过初始化了,默认是SimpleSessionFactory工厂,SimpleSessionFactory创建session:
*/
public class SimpleSessionFactory implements SessionFactory {/*** Creates a new {@link SimpleSession SimpleSession} instance retaining the context's* {@link SessionContext#getHost() host} if one can be found.** @param initData the initialization data to be used during {@link Session} creation.* @return a new {@link SimpleSession SimpleSession} instance*/public Session createSession(SessionContext initData) {if (initData != null) {String host = initData.getHost();if (host != null) {return new SimpleSession(host);}}return new SimpleSession();}
}
有host就调用host的构造参数,没有就调用无参构造器
// Serialization reminder:// You _MUST_ change this number if you introduce a change to this class// that is NOT serialization backwards compatible. Serialization-compatible// changes do not require a change to this number. If you need to generate// a new number in this case, use the JDK's 'serialver' program to generate it.private static final long serialVersionUID = -7125642695178165650L;//TODO - complete JavaDocprivate transient static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SimpleSession.class);protected static final long MILLIS_PER_SECOND = 1000;protected static final long MILLIS_PER_MINUTE = 60 * MILLIS_PER_SECOND;protected static final long MILLIS_PER_HOUR = 60 * MILLIS_PER_MINUTE;//serialization bitmask fields. DO NOT CHANGE THE ORDER THEY ARE DECLARED!static int bitIndexCounter = 0;private static final int ID_BIT_MASK = 1 << bitIndexCounter++;private static final int START_TIMESTAMP_BIT_MASK = 1 << bitIndexCounter++;private static final int STOP_TIMESTAMP_BIT_MASK = 1 << bitIndexCounter++;private static final int LAST_ACCESS_TIME_BIT_MASK = 1 << bitIndexCounter++;private static final int TIMEOUT_BIT_MASK = 1 << bitIndexCounter++;private static final int EXPIRED_BIT_MASK = 1 << bitIndexCounter++;private static final int HOST_BIT_MASK = 1 << bitIndexCounter++;private static final int ATTRIBUTES_BIT_MASK = 1 << bitIndexCounter++;// ==============================================================// NOTICE://// The following fields are marked as transient to avoid double-serialization.// They are in fact serialized (even though 'transient' usually indicates otherwise),// but they are serialized explicitly via the writeObject and readObject implementations// in this class.//// If we didn't declare them as transient, the out.defaultWriteObject(); call in writeObject would// serialize all non-transient fields as well, effectively doubly serializing the fields (also// doubling the serialization size).//// This finding, with discussion, was covered here://// http://mail-archives.apache.org/mod_mbox/shiro-user/201109.mbox/%3C4E81BCBD.8060909@metaphysis.net%3E//// ==============================================================private transient Serializable id;private transient Date startTimestamp;private transient Date stopTimestamp;private transient Date lastAccessTime;private transient long timeout;private transient boolean expired;private transient String host;private transient Map<Object, Object> attributes;public SimpleSession() {this.timeout = DefaultSessionManager.DEFAULT_GLOBAL_SESSION_TIMEOUT; //TODO - remove concrete reference to DefaultSessionManagerthis.startTimestamp = new Date();this.lastAccessTime = this.startTimestamp;}public SimpleSession(String host) {this();this.host = host;}
这里主要看一下timeout,startTimestamp,lastAccessTime,分别是超时时间,开始时间,最后一次操作时间,超时时间默认是30分钟

到这里,一个session就创建完成了,返回到上面接着看创建完成之后又干了啥
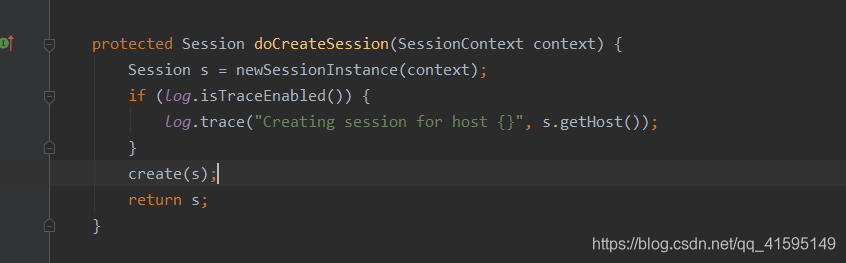
进入create(s);
protected void create(Session session) {if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug("Creating new EIS record for new session instance [" + session + "]");}sessionDAO.create(session);}他把操作交给sessionDao了,而这个sessionDao在初始化的时候默认是MemorySessionDAO,如果我们自己配置了Dao,就进入到我们的Dao了,看一下默认的MemorySessionDAO
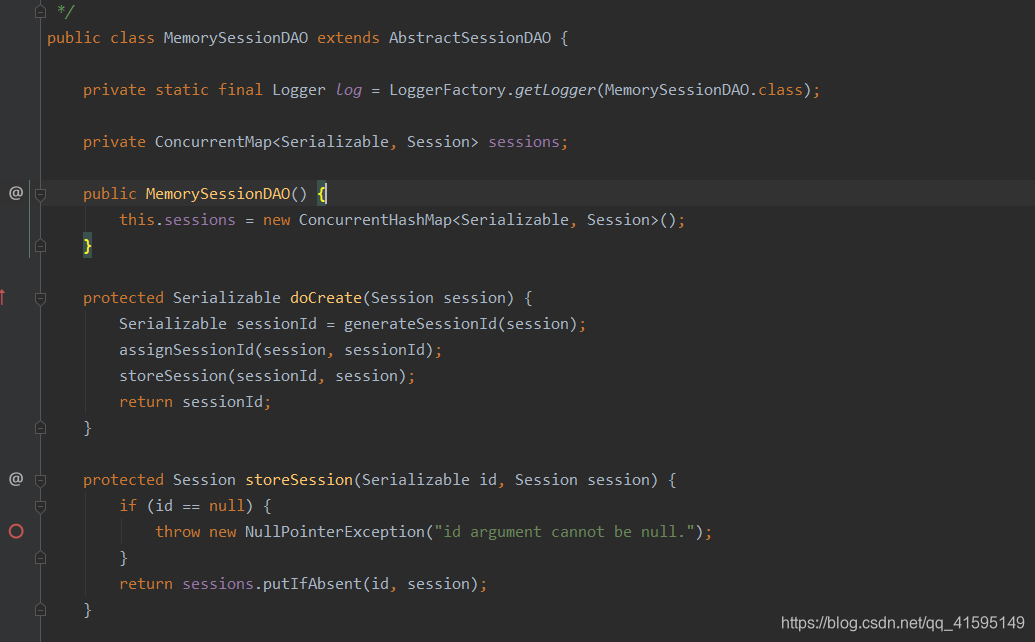
内部有一个 ConcurrentMap<Serializable, Session> sessions;通过storeSession方法可以看出,session最后都是被存在了这里,下面是他的一些CRUD方法,都是在操作这个map
protected Serializable doCreate(Session session) {Serializable sessionId = generateSessionId(session);assignSessionId(session, sessionId);storeSession(sessionId, session);return sessionId;}protected Session storeSession(Serializable id, Session session) {if (id == null) {throw new NullPointerException("id argument cannot be null.");}return sessions.putIfAbsent(id, session);}protected Session doReadSession(Serializable sessionId) {return sessions.get(sessionId);}public void update(Session session) throws UnknownSessionException {storeSession(session.getId(), session);}public void delete(Session session) {if (session == null) {throw new NullPointerException("session argument cannot be null.");}Serializable id = session.getId();if (id != null) {sessions.remove(id);}}public Collection<Session> getActiveSessions() {Collection<Session> values = sessions.values();if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(values)) {return Collections.emptySet();} else {return Collections.unmodifiableCollection(values);}}
到此session的保存就完成了,虽然知道他怎么创建和保存的了,但还不知道他在什么时候创建session,下面开始研究,通过上面的了解,我们知道它最终是创建了一个SimpleSession,那么就在这打个断点,看下调用链就知道了
public SimpleSession() {this.timeout = DefaultSessionManager.DEFAULT_GLOBAL_SESSION_TIMEOUT; //TODO - remove concrete reference to DefaultSessionManagerthis.startTimestamp = new Date();this.lastAccessTime = this.startTimestamp;}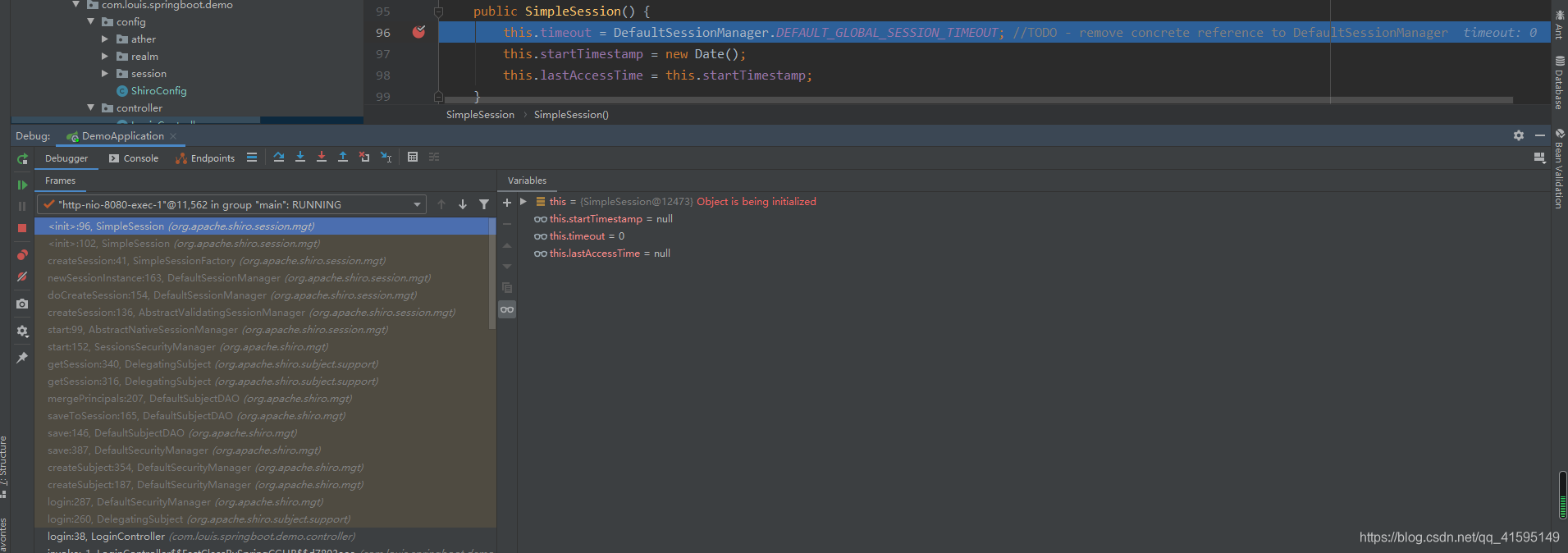
看一下最熟悉的login方法
public Subject login(Subject subject, AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {AuthenticationInfo info;try {info = authenticate(token);} catch (AuthenticationException ae) {try {onFailedLogin(token, ae, subject);} catch (Exception e) {if (log.isInfoEnabled()) {log.info("onFailedLogin method threw an " +"exception. Logging and propagating original AuthenticationException.", e);}}throw ae; //propagate}Subject loggedIn = createSubject(token, info, subject);onSuccessfulLogin(token, info, loggedIn);return loggedIn;}
通过调用链可以看出session是从这里开始创建的(Subject loggedIn = createSubject(token, info, subject)),也就是说sessio是在认证成功之后创建sunject的时候创建的,具体在创建subject的什么时候呢?
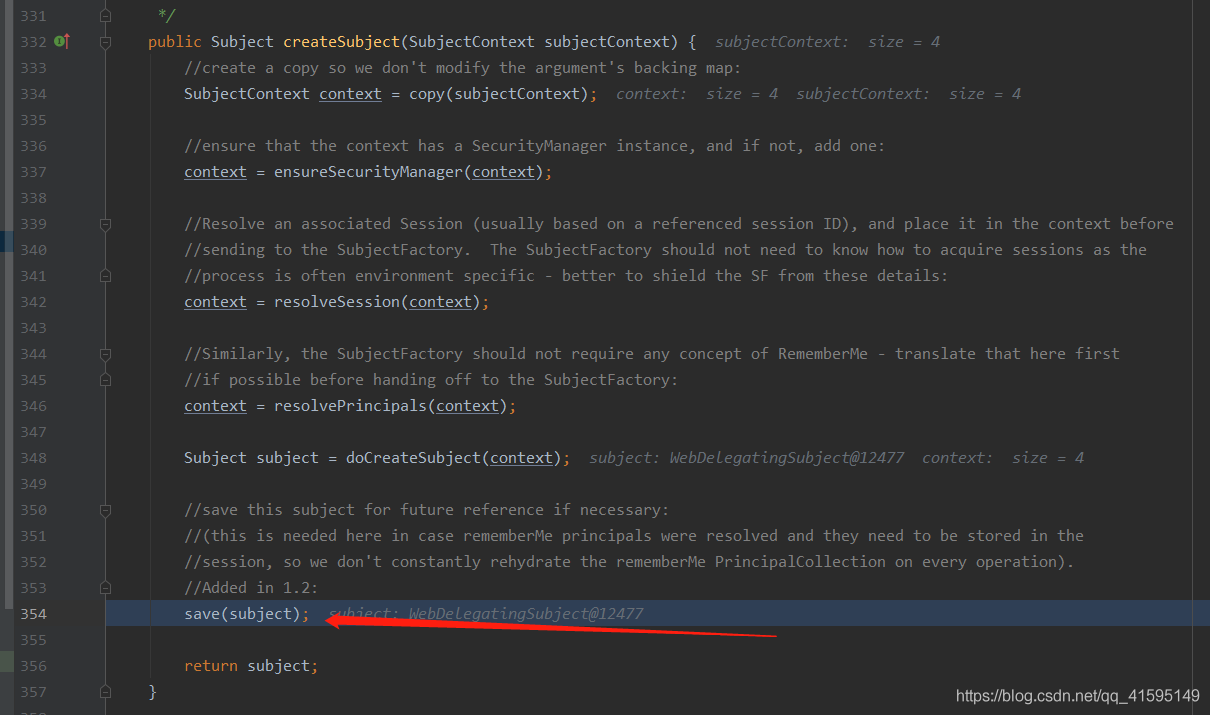
还是通过调用链,可以看出是在保存subject的时候创建的session,这里需要注意一下 doCreateSubject(context);,这个方法并没有真正的创建的session,通过下面这段代码可以看出,在getsession的时候传递的一个false
public Session resolveSession() {Session session = getSession();if (session == null) {//try the Subject if it exists:Subject existingSubject = getSubject();if (existingSubject != null) {session = existingSubject.getSession(false);}}return session;}
回到上面保存subject的方法
public Subject save(Subject subject) {if (isSessionStorageEnabled(subject)) {saveToSession(subject);} else {log.trace("Session storage of subject state for Subject [{}] has been disabled: identity and " +"authentication state are expected to be initialized on every request or invocation.", subject);}return subject;}
这里通过isSessionStorageEnabled方法来判断是否保存session,
protected boolean isSessionStorageEnabled(Subject subject) {return getSessionStorageEvaluator().isSessionStorageEnabled(subject);}
getSessionStorageEvaluator()获取一个SessionStorageEvaluator,默认是DefaultSessionStorageEvaluator
下面是isSessionStorageEnabled方法
public boolean isSessionStorageEnabled(Subject subject) {return (subject != null && subject.getSession(false) != null) || isSessionStorageEnabled();}
可以看出只要subject存在session或者sessionStorageEnabled为true都返回true,而sessionStorageEnabled默认是true
看完什么情况会保存session后,回到上面 saveToSession(subject);
/*** Saves the subject's state (it's principals and authentication state) to its* {@link org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject#getSession() session}. The session can be retrieved at a later time* (typically from a {@link org.apache.shiro.session.mgt.SessionManager SessionManager} to be used to recreate* the {@code Subject} instance.** @param subject the subject for which state will be persisted to its session.*/protected void saveToSession(Subject subject) {//performs merge logic, only updating the Subject's session if it does not match the current state:mergePrincipals(subject);mergeAuthenticationState(subject);}
这一步就是在保存session了
protected void mergePrincipals(Subject subject) {PrincipalCollection currentPrincipals = null;if (subject.isRunAs() && subject instanceof DelegatingSubject) {try {Field field = DelegatingSubject.class.getDeclaredField("principals");field.setAccessible(true);currentPrincipals = (PrincipalCollection)field.get(subject);} catch (Exception e) {throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to access DelegatingSubject principals property.", e);}}if (currentPrincipals == null || currentPrincipals.isEmpty()) {currentPrincipals = subject.getPrincipals();}Session session = subject.getSession(false);if (session == null) {if (!isEmpty(currentPrincipals)) {session = subject.getSession();session.setAttribute(DefaultSubjectContext.PRINCIPALS_SESSION_KEY, currentPrincipals);}// otherwise no session and no principals - nothing to save} else {PrincipalCollection existingPrincipals =(PrincipalCollection) session.getAttribute(DefaultSubjectContext.PRINCIPALS_SESSION_KEY);if (isEmpty(currentPrincipals)) {if (!isEmpty(existingPrincipals)) {session.removeAttribute(DefaultSubjectContext.PRINCIPALS_SESSION_KEY);}// otherwise both are null or empty - no need to update the session} else {if (!currentPrincipals.equals(existingPrincipals)) {session.setAttribute(DefaultSubjectContext.PRINCIPALS_SESSION_KEY, currentPrincipals);}// otherwise they're the same - no need to update the session}}}先获取一下session,(subject.getSession(false)),如果session为null就进入创建session的代码了:session = subject.getSession();