# 四十六、百万骰子投掷统计模拟器
原文:http://inventwithpython.com/bigbookpython/project46.html

当你掷出两个六面骰子时,有 17%的机会掷出 7。这比掷出 2 的几率好得多:只有 3%。这是因为只有一种掷骰子的组合给你 2(当两个骰子都掷出 1 时发生的组合),但许多组合加起来是 7:1 和 6,2 和 5,3 和 4,等等。
但是当你掷出三个骰子呢?还是四个?还是 1000?你可以用数学方法计算理论概率,或者你可以让计算机掷骰子一百万次,凭经验算出它们。这个程序采用了后一种方法。在这个程序中,你告诉计算机掷骰子一百万次并记住结果。然后,它显示每笔金额的百分比机会。
这个程序做了大量的计算,但是计算本身并不难理解。
运行示例
当您运行milliondicestats.py时,输出将如下所示:
Million Dice Roll Statistics Simulator
By Al Sweigart email@protectedEnter how many six-sided dice you want to roll:
> 2
Simulating 1,000,000 rolls of 2 dice...
36.2% done...
73.4% done...
TOTAL - ROLLS - PERCENTAGE2 - 27590 rolls - 2.8%3 - 55730 rolls - 5.6%4 - 83517 rolls - 8.4%5 - 111526 rolls - 11.2%6 - 139015 rolls - 13.9%7 - 166327 rolls - 16.6%8 - 139477 rolls - 13.9%9 - 110268 rolls - 11.0%10 - 83272 rolls - 8.3%11 - 55255 rolls - 5.5%12 - 28023 rolls - 2.8%
工作原理
我们通过在第 30 行调用random.randint(1, 6)来模拟单个六面骰子的滚动。这将返回一个介于1和6之间的随机数,无论掷出多少骰子,该随机数都会被添加到累计总数中。random.randint()函数具有均匀分布,这意味着每个数字都像其他数字一样有可能被返回。
程序用results字典存储这次掷骰的结果。这个字典的关键字是每个可能的掷骰子总数,值是这个总数遇到的次数。为了获得频率百分比,我们将总数遇到的次数除以 1,000,000(在该模拟中掷骰子的次数)并乘以 100(以获得 0.0 和 100.0 之间的百分比,而不是 0.0 和 1.0)。通过做一些代数运算,我们可以算出,这与我们在第 37 行所做的将遭遇次数除以 10,000 是一样的。
"""Million Dice Roll Statistics Simulator
By Al Sweigart email@protected
A simulation of one million dice rolls.
This code is available at https://nostarch.com/big-book-small-python-programming
Tags: tiny, beginner, math, simulation"""import random, timeprint('''Million Dice Roll Statistics Simulator
By Al Sweigart email@protectedEnter how many six-sided dice you want to roll:''')
numberOfDice = int(input('> '))# Set up a dictionary to store the results of each dice roll:
results = {}
for i in range(numberOfDice, (numberOfDice * 6) + 1):results[i] = 0# Simulate dice rolls:
print('Simulating 1,000,000 rolls of {} dice...'.format(numberOfDice))
lastPrintTime = time.time()
for i in range(1000000):if time.time() > lastPrintTime + 1:print('{}% done...'.format(round(i / 10000, 1)))lastPrintTime = time.time()total = 0for j in range(numberOfDice):total = total + random.randint(1, 6)results[total] = results[total] + 1# Display results:
print('TOTAL - ROLLS - PERCENTAGE')
for i in range(numberOfDice, (numberOfDice * 6) + 1):roll = results[i]percentage = round(results[i] / 10000, 1)print(' {} - {} rolls - {}%'.format(i, roll, percentage))
在输入源代码并运行几次之后,尝试对其进行实验性的修改。你也可以自己想办法做到以下几点:
- 尝试掷出 8 面、10 面、12 面或 20 面骰子。
- 尝试模拟双面抛硬币。
探索程序
试着找出下列问题的答案。尝试对代码进行一些修改,然后重新运行程序,看看这些修改有什么影响。
- 如果把第 24 行的
lastPrintTime + 1改成lastPrintTime + 2会怎么样? - 如果删除或注释掉第 31 行的
results[total] = results[total] + 1,会导致什么 bug? - 如果用户键入字母而不是数字来表示要掷出的六面骰子的数量,会出现什么错误?
四十七、蒙德里安艺术生成器
原文:http://inventwithpython.com/bigbookpython/project47.html

皮耶·蒙德里安是 20 世纪的荷兰画家,也是抽象艺术运动“新塑料主义”的创始人之一。他最具标志性的画作依赖于原色(蓝、黄、红)、黑色和白色。他采用极简主义的方法,用水平和垂直的元素将这些颜色分开。
这个程序随机生成遵循蒙德里安风格的绘画。你可以在en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Piet_Mondrian找到更多关于皮特·蒙德里安的信息。
运行示例
bext模块允许我们的 Python 程序在文本输出中显示明亮的原色,尽管这本书只显示黑白图像。图 47-1 显示了运行mondrian.py时的输出。

图 47-1 :蒙德里安艺术程序的计算机生成艺术。程序每次运行都会生成不同的图像。
工作原理
该算法通过创建一个带有随机间隔的垂直线和水平线的数据结构(canvas字典)来工作,如图图 47-2 。
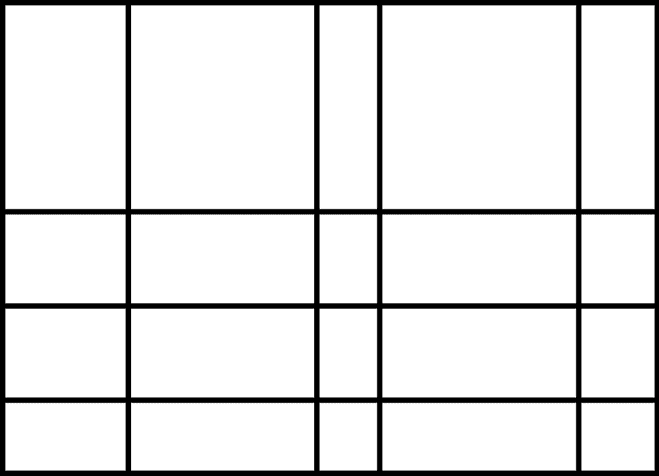
:蒙德里安艺术算法的第一步是创建一个网格。
接下来,它移除一些线段来创建更大的矩形,如图图 47-3 所示。
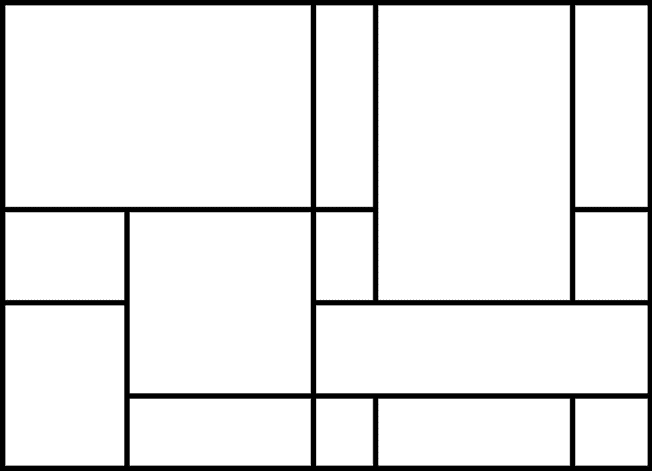
:蒙德里安艺术算法的第二步随机去掉一些线条。
最后,算法用黄色、红色、蓝色或黑色随机填充一些矩形,如图图 47-4 。
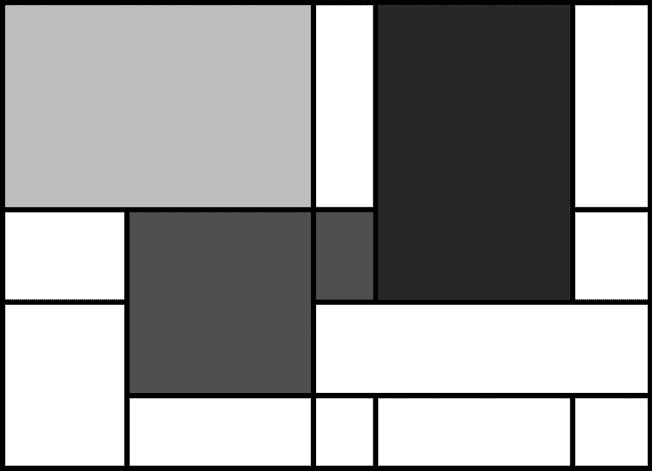
:蒙德里安艺术算法第三步随机选择矩形填充颜色。
你可以在github.com/asweigart/mondrian_art_generator找到这个蒙德里安艺术生成器的另一个版本,还有一些样本图片。
"""Mondrian Art Generator, by Al Sweigart email@protected
Randomly generates art in the style of Piet Mondrian.
More info at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Piet_Mondrian
This code is available at https://nostarch.com/big-book-small-python-programming
Tags: large, artistic, bext"""import sys, randomtry:import bext
except ImportError:print('This program requires the bext module, which you')print('can install by following the instructions at')print('https://pypi.org/project/Bext/')sys.exit()# Set up the constants:
MIN_X_INCREASE = 6
MAX_X_INCREASE = 16
MIN_Y_INCREASE = 3
MAX_Y_INCREASE = 6
WHITE = 'white'
BLACK = 'black'
RED = 'red'
YELLOW = 'yellow'
BLUE = 'blue'# Setup the screen:
width, height = bext.size()
# We can't print to the last column on Windows without it adding a
# newline automatically, so reduce the width by one:
width -= 1height -= 3while True: # Main application loop.# Pre-populate the canvas with blank spaces:canvas = {}for x in range(width):for y in range(height):canvas[(x, y)] = WHITE# Generate vertical lines:numberOfSegmentsToDelete = 0x = random.randint(MIN_X_INCREASE, MAX_X_INCREASE)while x < width - MIN_X_INCREASE:numberOfSegmentsToDelete += 1for y in range(height):canvas[(x, y)] = BLACKx += random.randint(MIN_X_INCREASE, MAX_X_INCREASE)# Generate horizontal lines:y = random.randint(MIN_Y_INCREASE, MAX_Y_INCREASE)while y < height - MIN_Y_INCREASE:numberOfSegmentsToDelete += 1for x in range(width):canvas[(x, y)] = BLACKy += random.randint(MIN_Y_INCREASE, MAX_Y_INCREASE)numberOfRectanglesToPaint = numberOfSegmentsToDelete - 3numberOfSegmentsToDelete = int(numberOfSegmentsToDelete * 1.5)# Randomly select points and try to remove them.for i in range(numberOfSegmentsToDelete):while True: # Keep selecting segments to try to delete.# Get a random start point on an existing segment:startx = random.randint(1, width - 2)starty = random.randint(1, height - 2)if canvas[(startx, starty)] == WHITE:continue# Find out if we're on a vertical or horizontal segment:if (canvas[(startx - 1, starty)] == WHITE andcanvas[(startx + 1, starty)] == WHITE):orientation = 'vertical'elif (canvas[(startx, starty - 1)] == WHITE andcanvas[(startx, starty + 1)] == WHITE):orientation = 'horizontal'else:# The start point is on an intersection,# so get a new random start point:continuepointsToDelete = [(startx, starty)]canDeleteSegment = Trueif orientation == 'vertical':# Go up one path from the start point, and# see if we can remove this segment:for changey in (-1, 1):y = startywhile 0 < y < height - 1:y += changeyif (canvas[(startx - 1, y)] == BLACK andcanvas[(startx + 1, y)] == BLACK):# We've found a four-way intersection.breakelif ((canvas[(startx - 1, y)] == WHITE andcanvas[(startx + 1, y)] == BLACK) or(canvas[(startx - 1, y)] == BLACK andcanvas[(startx + 1, y)] == WHITE)):# We've found a T-intersection; we can't# delete this segment:canDeleteSegment = Falsebreakelse:pointsToDelete.append((startx, y))elif orientation == 'horizontal':# Go up one path from the start point, and# see if we can remove this segment:for changex in (-1, 1):x = startxwhile 0 < x < width - 1:x += changexif (canvas[(x, starty - 1)] == BLACK andcanvas[(x, starty + 1)] == BLACK):# We've found a four-way intersection.breakelif ((canvas[(x, starty - 1)] == WHITE andcanvas[(x, starty + 1)] == BLACK) or(canvas[(x, starty - 1)] == BLACK andcanvas[(x, starty + 1)] == WHITE)):# We've found a T-intersection; we can't# delete this segment:canDeleteSegment = Falsebreakelse:pointsToDelete.append((x, starty))if not canDeleteSegment:continue # Get a new random start point.break # Move on to delete the segment.# If we can delete this segment, set all the points to white:for x, y in pointsToDelete:canvas[(x, y)] = WHITE# Add the border lines:for x in range(width):canvas[(x, 0)] = BLACK # Top border.canvas[(x, height - 1)] = BLACK # Bottom border.for y in range(height):canvas[(0, y)] = BLACK # Left border.canvas[(width - 1, y)] = BLACK # Right border.# Paint the rectangles:for i in range(numberOfRectanglesToPaint):while True:startx = random.randint(1, width - 2)starty = random.randint(1, height - 2)if canvas[(startx, starty)] != WHITE:continue # Get a new random start point.else:break# Flood fill algorithm:colorToPaint = random.choice([RED, YELLOW, BLUE, BLACK])pointsToPaint = set([(startx, starty)])while len(pointsToPaint) > 0:x, y = pointsToPaint.pop()canvas[(x, y)] = colorToPaintif canvas[(x - 1, y)] == WHITE:pointsToPaint.add((x - 1, y))if canvas[(x + 1, y)] == WHITE:pointsToPaint.add((x + 1, y))if canvas[(x, y - 1)] == WHITE:pointsToPaint.add((x, y - 1))if canvas[(x, y + 1)] == WHITE:pointsToPaint.add((x, y + 1))# Draw the canvas data structure:for y in range(height):for x in range(width):bext.bg(canvas[(x, y)])print(' ', end='')print()# Prompt user to create a new one:try:input('Press Enter for another work of art, or Ctrl-C to quit.')except KeyboardInterrupt:sys.exit()
在输入源代码并运行几次之后,尝试对其进行实验性的修改。你也可以自己想办法做到以下几点:
- 用不同的调色板创建程序。
- 使用
Pillow模块制作蒙德里安艺术的图像文件。你可以从《Python 自动化指南》第 19 章了解这个模块,automatetheboringstuff.com/2e/chapter19。
探索程序
试着找出下列问题的答案。尝试对代码进行一些修改,然后重新运行程序,看看这些修改有什么影响。
- 如果把第 41 行的
canvas[(x, y)] = WHITE改成canvas[(x, y)] = RED会出现什么错误? - 如果把 176 行的
print(' ', end='')改成print('A', end='')会怎么样?
四十八、蒙蒂霍尔问题
原文:http://inventwithpython.com/bigbookpython/project48.html

蒙蒂霍尔问题说明了一个令人惊讶的概率事实。这个问题大致基于老游戏节目《让我们做个交易》和它的主持人蒙蒂·霍尔。在蒙蒂大厅问题中,你可以选择三扇门中的一扇门。一扇门后有一个奖品:一辆新车。另外两扇门都通向一只没用的山羊。假设你选了 1 号门。在你选择的门打开之前,主人打开了另一扇门(2 号或 3 号),这导致了一只山羊。您可以选择打开您最初选择的门,或者切换到另一扇未打开的门。
看起来你是否换门并不重要,但是如果你换了门,你的机会就会增加!这个程序通过让你重复做实验来演示蒙蒂霍尔问题。
为了理解为什么你的机会增加了,考虑一个有一千个门而不是三个门的蒙蒂大厅问题的版本。你挑一扇门,然后主持人打开 998 扇门,里面都是山羊。仅有的两个未打开的门是您选择的门和另一个门。如果你一开始就选对了车门(1/1000 的概率),那么主人会让一个随机的山羊车门关着。如果你选了一个山羊车门(1000 分之 999 的概率),主人会特别选择车门保持关闭。选择打开哪扇门不是随机的;主人知道让车门关着。几乎可以肯定的是,你一开始就没有选车门,所以你应该换另一个车门。
另一种想法是,你有 1000 个盒子,一个盒子里装着奖品。你猜猜奖品在哪个盒子里,主持人把它放到你手里。你认为奖品在你的盒子里还是在其他 999 个盒子里?你不需要主持人打开 999 个不含奖品的盒子中的 998 个;选择的数量与 1000 扇门相同。你一开始猜对的几率是 1/1000,而猜错的几率(奖品在其他盒子里)几乎是 999/1000。
更多关于蒙蒂霍尔问题的信息可以在en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Monty_Hall_problem找到。
运行示例
当您运行montyhall.py时,输出将如下所示:
The Monty Hall Problem, by Al Sweigart email@protected
`--snip--`
+------+ +------+ +------+
| | | | | |
| 1 | | 2 | | 3 |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
+------+ +------+ +------+
Pick a door 1, 2, or 3 (or "quit" to stop):
> 1+------+ +------+ +------+
| | | | | (( |
| 1 | | 2 | | oo |
| | | | | /_/|_|
| | | | | | |
| | | | |GOAT|||
+------+ +------+ +------+
Door 3 contains a goat!
Do you want to swap doors? Y/N
> y+------+ +------+ +------+
| (( | | CAR! | | (( |
| oo | | __| | oo |
| /_/|_| | _/ | | /_/|_|
| | | | /_ __| | | |
|GOAT||| | O | |GOAT|||
+------+ +------+ +------+
Door 2 has the car!
You won!Swapping: 1 wins, 0 losses, success rate 100.0%
Not swapping: 0 wins, 0 losses, success rate 0.0%Press Enter to repeat the experiment...
`--snip--`
工作原理
ASCII 艺术画门的多行字符串存储在几个常量变量中,比如ALL_CLOSED、FIRST_GOAT和FIRST_CAR_OTHERS_GOAT。使用这些常量的代码,比如第 125 行的print(FIRST_GOAT),即使我们更新了图形也保持不变。通过将多行字符串一起放在源代码文件的顶部,我们将更容易比较它们,以确保图形是一致的。
"""The Monty Hall Problem, by Al Sweigart email@protected
A simulation of the Monty Hall game show problem.
More info at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Monty_Hall_problem
This code is available at https://nostarch.com/big-book-small-python-programming
Tags: large, game, math, simulation"""import random, sysALL_CLOSED = """
+------+ +------+ +------+
| | | | | |
| 1 | | 2 | | 3 |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
+------+ +------+ +------+"""FIRST_GOAT = """
+------+ +------+ +------+
| (( | | | | |
| oo | | 2 | | 3 |
| /_/|_| | | | |
| | | | | | |
|GOAT||| | | | |
+------+ +------+ +------+"""SECOND_GOAT = """
+------+ +------+ +------+
| | | (( | | |
| 1 | | oo | | 3 |
| | | /_/|_| | |
| | | | | | |
| | |GOAT||| | |
+------+ +------+ +------+"""THIRD_GOAT = """
+------+ +------+ +------+
| | | | | (( |
| 1 | | 2 | | oo |
| | | | | /_/|_|
| | | | | | |
| | | | |GOAT|||
+------+ +------+ +------+"""FIRST_CAR_OTHERS_GOAT = """
+------+ +------+ +------+
| CAR! | | (( | | (( |
| __| | oo | | oo |
| _/ | | /_/|_| | /_/|_|
| /_ __| | | | | | |
| O | |GOAT||| |GOAT|||
+------+ +------+ +------+"""SECOND_CAR_OTHERS_GOAT = """
+------+ +------+ +------+
| (( | | CAR! | | (( |
| oo | | __| | oo |
| /_/|_| | _/ | | /_/|_|
| | | | /_ __| | | |
|GOAT||| | O | |GOAT|||
+------+ +------+ +------+"""THIRD_CAR_OTHERS_GOAT = """
+------+ +------+ +------+
| (( | | (( | | CAR! |
| oo | | oo | | __|
| /_/|_| | /_/|_| | _/ |
| | | | | | | /_ __|
|GOAT||| |GOAT||| | O |
+------+ +------+ +------+"""print('''The Monty Hall Problem, by Al Sweigart email@protectedIn the Monty Hall game show, you can pick one of three doors. One door
has a new car for a prize. The other two doors have worthless goats:
{} 77\. Say you pick Door #1.
Before the door you choose is opened, another door with a goat is opened:
{} 80\. You can choose to either open the door you originally picked or swap
to the other unopened door.It may seem like it doesn't matter if you swap or not, but your odds
do improve if you swap doors! This program demonstrates the Monty Hall
problem by letting you do repeated experiments.You can read an explanation of why swapping is better at
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Monty_Hall_problem
'''.format(ALL_CLOSED, THIRD_GOAT))input('Press Enter to start...')swapWins = 0
swapLosses = 0
stayWins = 0
stayLosses = 0
while True: # Main program loop.# The computer picks which door has the car:doorThatHasCar = random.randint(1, 3)# Ask the player to pick a door:print(ALL_CLOSED)while True: # Keep asking the player until they enter a valid door.print('Pick a door 1, 2, or 3 (or "quit" to stop):')response = input('> ').upper()if response == 'QUIT':# End the game.print('Thanks for playing!')sys.exit()if response == '1' or response == '2' or response == '3':breakdoorPick = int(response)# Figure out which goat door to show the player:while True:# Select a door that is a goat and not picked by the player:showGoatDoor = random.randint(1, 3)if showGoatDoor != doorPick and showGoatDoor != doorThatHasCar:break# Show this goat door to the player:if showGoatDoor == 1:print(FIRST_GOAT)elif showGoatDoor == 2:print(SECOND_GOAT)elif showGoatDoor == 3:print(THIRD_GOAT)print('Door {} contains a goat!'.format(showGoatDoor))# Ask the player if they want to swap:while True: # Keep asking until the player enters Y or N.print('Do you want to swap doors? Y/N')swap = input('> ').upper()if swap == 'Y' or swap == 'N':break# Swap the player's door if they wanted to swap:if swap == 'Y':if doorPick == 1 and showGoatDoor == 2:doorPick = 3elif doorPick == 1 and showGoatDoor == 3:doorPick = 2elif doorPick == 2 and showGoatDoor == 1:doorPick = 3elif doorPick == 2 and showGoatDoor == 3:doorPick = 1elif doorPick == 3 and showGoatDoor == 1:doorPick = 2elif doorPick == 3 and showGoatDoor == 2:doorPick = 1# Open all the doors:if doorThatHasCar == 1:print(FIRST_CAR_OTHERS_GOAT)elif doorThatHasCar == 2:print(SECOND_CAR_OTHERS_GOAT)elif doorThatHasCar == 3:print(THIRD_CAR_OTHERS_GOAT)print('Door {} has the car!'.format(doorThatHasCar))# Record wins and losses for swapping and not swapping:if doorPick == doorThatHasCar:print('You won!')if swap == 'Y':swapWins += 1elif swap == 'N':stayWins += 1else:print('Sorry, you lost.')if swap == 'Y':swapLosses += 1elif swap == 'N':stayLosses += 1# Calculate success rate of swapping and not swapping:totalSwaps = swapWins + swapLossesif totalSwaps != 0: # Prevent zero-divide error.swapSuccess = round(swapWins / totalSwaps * 100, 1)else:swapSuccess = 0.0totalStays = stayWins + stayLossesif (stayWins + stayLosses) != 0: # Prevent zero-divide.staySuccess = round(stayWins / totalStays * 100, 1)else:staySuccess = 0.0print()print('Swapping: ', end='')print('{} wins, {} losses, '.format(swapWins, swapLosses), end='')print('success rate {}%'.format(swapSuccess))print('Not swapping: ', end='')print('{} wins, {} losses, '.format(stayWins, stayLosses), end='')print('success rate {}%'.format(staySuccess))print()input('Press Enter repeat the experiment...')
探索程序
试着找出下列问题的答案。尝试对代码进行一些修改,然后重新运行程序,看看这些修改有什么影响。
- 如果把第 100 行的
doorThatHasCar = random.randint(1, 3)改成doorThatHasCar = 1会怎么样? - 如果把第 124 到 129 行换成
print([FIRST_GOAT, SECOND_GOAT, THIRD_GOAT][showGoatDoor - 1])会怎么样?
四十九、乘法表
原文:http://inventwithpython.com/bigbookpython/project49.html

这个程序生成一个从0 × 0到12 × 12的乘法表。虽然简单,但它提供了嵌套循环的有用演示。
运行示例
当您运行multiplicationtable.py时,输出将如下所示:
Multiplication Table, by Al Sweigart email@protected| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
--+---------------------------------------------------0| 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 01| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 122| 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 243| 0 3 6 9 12 15 18 21 24 27 30 33 364| 0 4 8 12 16 20 24 28 32 36 40 44 485| 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 606| 0 6 12 18 24 30 36 42 48 54 60 66 727| 0 7 14 21 28 35 42 49 56 63 70 77 848| 0 8 16 24 32 40 48 56 64 72 80 88 969| 0 9 18 27 36 45 54 63 72 81 90 99 108
10| 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120
11| 0 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 110 121 132
12| 0 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96 108 120 132 144
工作原理
第 9 行打印表格的第一行。请注意,它在数字之间设置了足够大的距离,以容纳最大长度为三位数的产品。由于这是一个12 × 12的乘法表,这个间距可以装下最大的积,144。如果您想创建一个更大的表格,您可能还需要增加列的间距。请记住,标准的终端窗口是 80 列宽,24 行高,所以如果不在窗口的右边换行,就无法创建更大的乘法表。
"""Multiplication Table, by Al Sweigart email@protected
Print a multiplication table.
This code is available at https://nostarch.com/big-book-small-python-programming
Tags: tiny, beginner, math"""print('Multiplication Table, by Al Sweigart email@protected')# Print the horizontal number labels:
print(' | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12')
print('--+---------------------------------------------------')# Display each row of products:
for number1 in range(0, 13):# Print the vertical numbers labels:print(str(number1).rjust(2), end='')# Print a separating bar:print('|', end='')for number2 in range(0, 13):# Print the product followed by a space:print(str(number1 * number2).rjust(3), end=' ')print() # Finish the row by printing a newline.
探索程序
试着找出下列问题的答案。尝试对代码进行一些修改,然后重新运行程序,看看这些修改有什么影响。
- 如果把第 13 行的
range(0, 13)改成range(0, 80)会怎么样? - 如果把第 13 行的
range(0, 13)改成range(0, 100)会怎么样?
五十、九十九瓶
原文:http://inventwithpython.com/bigbookpython/project50.html

《九十九瓶》是一首来历不明的民歌,以其长度和反复性著称。歌词是这样的,“九十九瓶牛奶在墙上,九十九瓶牛奶。拿一个下来,传一传,墙上九十八瓶奶。”正如歌词所重复的,瓶子的数量从九十八降到九十七,再从九十七降到九十六,直到零:“墙上一瓶牛奶,一瓶牛奶。拿下来,传来传去,墙上已经没有牛奶瓶了!”
对我们来说幸运的是,计算机擅长执行重复性的任务,这个程序以编程的方式再现了所有的歌词。这个程序的一个扩展版本在项目 51 中,“90 分钟启动”
运行示例
当您运行ninetyninebottles.py时,输出将如下所示:
Ninety-Nine Bottles, by Al Sweigart email@protected(Press Ctrl-C to quit.)
99 bottles of milk on the wall,
99 bottles of milk,
Take one down, pass it around,
98 bottles of milk on the wall!98 bottles of milk on the wall,
98 bottles of milk,
Take one down, pass it around,
97 bottles of milk on the wall!
`--snip--`
工作原理
这首歌中的重复很容易使用一个for循环(从第 20 行到第 30 行)来显示前 98 节。然而,最后一节有一些小的不同,需要单独的代码来显示(第 33 到 39 行)。这是因为最后一行'No more bottles of milk on the wall!'偏离了循环中重复的那一行,也是因为单词bottle是单数而不是复数。
"""Ninety-Nine Bottles of Milk on the Wall
By Al Sweigart email@protected
Print the full lyrics to one of the longest songs ever! Press
Ctrl-C to stop.
This code is available at https://nostarch.com/big-book-small-python-programming
Tags: tiny, beginner, scrolling"""import sys, timeprint('Ninety-Nine Bottles, by Al Sweigart email@protected')
print()
print('(Press Ctrl-C to quit.)')time.sleep(2)bottles = 99 # This is the starting number of bottles.
PAUSE = 2 # (!) Try changing this to 0 to see the full song at once.try:while bottles > 1: # Keep looping and display the lyrics.print(bottles, 'bottles of milk on the wall,')time.sleep(PAUSE) # Pause for PAUSE number of seconds.print(bottles, 'bottles of milk,')time.sleep(PAUSE)print('Take one down, pass it around,')time.sleep(PAUSE)bottles = bottles - 1 # Decrease the number of bottles by one.print(bottles, 'bottles of milk on the wall!')time.sleep(PAUSE)print() # Print a newline.# Display the last stanza:print('1 bottle of milk on the wall,')time.sleep(PAUSE)print('1 bottle of milk,')time.sleep(PAUSE)print('Take it down, pass it around,')time.sleep(PAUSE)print('No more bottles of milk on the wall!')
except KeyboardInterrupt:sys.exit() # When Ctrl-C is pressed, end the program.
在输入源代码并运行几次之后,尝试对其进行实验性的修改。你也可以自己想办法做到以下几点:
- 为重复的歌曲“圣诞节的十二天”创建一个程序
- 为其他累积歌曲创建程序。你可以在
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cumulative_song找到他们的名单。
探索程序
试着找出下列问题的答案。尝试对代码进行一些修改,然后重新运行程序,看看这些修改有什么影响。
- 如果把第 27 行的
bottles = bottles - 1改成bottles = bottles - 2会怎么样? - 如果把第 20 行的
while bottles > 1:改成while bottles < 1:会怎么样?