FemPosDeviation参考线平滑方法是离散点平滑方法,Fem是Finite element estimate的意思。
1. 优化目标

1.1 平滑性
参考线平滑的首要目标当然是平滑性,使用向量的模 ∣ P 2 P 2 ′ ⃗ ∣ | \vec{P_2 P^{\prime}_2}| ∣P2P2′∣来表示,显然 ∣ P 2 P 2 ′ ⃗ ∣ | \vec{P_2 P^{\prime}_2}| ∣P2P2′∣越小,三个点 P 1 , P 2 , P 3 P_1,P_2,P_3 P1,P2,P3越接近一条直线,越平滑。
J s m o o t h = ∣ P 2 P 2 ′ ⃗ ∣ 2 = ∣ P 2 P 1 ⃗ + P 2 P 3 ⃗ ∣ 2 = ( x 1 − x 2 , y 1 − y 2 ) 2 + ( x 3 − x 2 , y 3 − y 2 ) 2 (1-1) J_{smooth} = | \vec{P_2 P^{\prime}_2}| ^ 2 = | \vec{P_2 P_1} + \vec{P_2 P_3} | ^ 2 = (x_1 - x_2, y_1 - y_2) ^ 2 + (x_3 - x_2, y_3 - y_2) ^ 2 \tag{1-1} Jsmooth=∣P2P2′∣2=∣P2P1+P2P3∣2=(x1−x2,y1−y2)2+(x3−x2,y3−y2)2(1-1)
J s m o o t h = [ x 1 , y 1 , x 2 , y 2 , x 3 , y 3 ] [ 1 0 − 2 0 1 0 0 1 0 − 2 0 1 − 2 0 4 0 − 2 0 0 − 2 0 4 0 − 2 1 0 − 2 0 1 0 0 1 0 − 2 0 1 ] [ x 1 , y 1 , x 2 , y 2 , x 3 , y 3 ] T (1-2) J_{smooth} = [x_1, y_1, x_2, y_2, x_3, y_3] \left[\begin{matrix} 1 & 0 & -2 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 & -2 & 0 & 1 \\ -2 & 0 & 4 & 0 & -2 & 0 \\ 0 & -2 & 0 & 4 & 0 & -2 \\ 1 & 0 & -2 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 & -2 & 0 & 1 \end{matrix}\right] [x_1, y_1, x_2, y_2, x_3, y_3]^T \tag{1-2} Jsmooth=[x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3]⎣ ⎡10−2010010−201−2040−200−2040−210−2010010−201⎦ ⎤[x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3]T(1-2)
1.2 几何性
平滑后的参考线,希望能够保留原始道路的几何信息,不会把弯道的处的参考线平滑成一条直线。使用平滑后点与原始点的距离来表示。
J d e v i a t i o n = ∣ P r , 1 P 1 ⃗ ∣ 2 + ∣ P r , 2 P 2 ⃗ ∣ 2 + ∣ P r , 3 P 3 ⃗ ∣ 2 = ( x 1 − x 1 , r ) 2 + ( y 1 − y 1 , r ) 2 + ( x 2 − x 2 , r ) 2 + ( y 2 − y 2 , r ) 2 + ( x 3 − x 3 , r ) 2 + ( y 3 − y 3 , r ) 2 (1-3) J_{deviation} = | \vec{P_{r,1} P_1}|^ 2 + | \vec{P_{r,2} P_2}|^ 2 + | \vec{P_{r,3} P_3}| ^ 2 = (x_1 - x_{1,r})^ 2 + (y_1 - y_{1,r})^ 2 + (x_2 - x_{2,r})^ 2 + (y_2 - y_{2,r})^ 2 + (x_3 - x_{3,r})^ 2 + (y_3 - y_{3,r})^ 2 \tag{1-3} Jdeviation=∣Pr,1P1∣2+∣Pr,2P2∣2+∣Pr,3P3∣2=(x1−x1,r)2+(y1−y1,r)2+(x2−x2,r)2+(y2−y2,r)2+(x3−x3,r)2+(y3−y3,r)2(1-3)
J d e v i a t i o n = [ x 1 , y 1 , x 2 , y 2 , x 3 , y 3 ] [ 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 ] [ x 1 , y 1 , x 2 , y 2 , x 3 , y 3 ] T − 2 [ x 1 , r , y 1 , r , x 2 , r , y 2 , r , x 3 , r , y 3 , r ] [ x 1 , y 1 , x 2 , y 2 , x 3 , y 3 ] T (1-4) J_{deviation} = [x_1, y_1, x_2, y_2, x_3, y_3] \left[\begin{matrix} 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1 \end{matrix}\right] [x_1, y_1, x_2, y_2, x_3, y_3]^T \\ -2[x_{1,r}, y_{1,r}, x_{2,r}, y_{2,r}, x_{3,r}, y_{3,r}] [x_1, y_1, x_2, y_2, x_3, y_3]^T \tag{1-4} Jdeviation=[x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3]⎣ ⎡100000010000001000000100000010000001⎦ ⎤[x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3]T−2[x1,r,y1,r,x2,r,y2,r,x3,r,y3,r][x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3]T(1-4)
1.3 均匀性
平滑后的参考线的每两个相邻点之间的长度尽量均匀一直。
J l e n g t h = ∣ P 1 P 2 ⃗ ∣ 2 + ∣ P 2 P 3 ⃗ ∣ 2 = ( x 2 − x 1 ) 2 + ( y 2 − y 1 ) 2 + ( x 3 − x 2 ) 2 + ( y 3 − y 2 ) 2 (1-5) J_{length} = | \vec{P_1 P_2}|^2 + | \vec{P_2 P_3}|^2 = (x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2 + (x_3 - x_2)^2 + (y_3 - y_2)^2 \tag{1-5} Jlength=∣P1P2∣2+∣P2P3∣2=(x2−x1)2+(y2−y1)2+(x3−x2)2+(y3−y2)2(1-5)
J l e n g t h = [ x 1 , y 1 , x 2 , y 2 , x 3 , y 3 ] [ 1 0 − 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 − 1 0 0 − 1 0 2 0 − 1 0 0 − 1 0 2 0 − 1 0 0 − 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 − 1 0 1 ] [ x 1 , y 1 , x 2 , y 2 , x 3 , y 3 ] T (1-6) J_{length} = [x_1, y_1, x_2, y_2, x_3, y_3] \left[\begin{matrix} 1 & 0 & -1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 & -1 & 0 & 0 \\ -1 & 0 & 2 & 0 & -1 & 0 \\ 0 & -1 & 0 & 2 & 0 & -1 \\ 0 & 0 & -1 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & -1 & 0 & 1 \end{matrix}\right] [x_1, y_1, x_2, y_2, x_3, y_3]^T \tag{1-6} Jlength=[x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3]⎣ ⎡10−1000010−100−1020−100−1020−100−1010000−101⎦ ⎤[x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3]T(1-6)
因此,参考线平滑的优化目标可以定义为:
J = w s m o o t h ∗ J s m o o t h + w d e v i a t i o n ∗ J d e v i a t i o n + w l e n g t h ∗ J l e n g t h (1-7) J = w_{smooth} * J_{smooth} + w_{deviation} * J_{deviation} + w_{length} * J_{length} \tag{1-7} J=wsmooth∗Jsmooth+wdeviation∗Jdeviation+wlength∗Jlength(1-7)
上述是按照 3 3 3个点进行举例的,当平滑点的数目为 N ≥ 3 N \geq 3 N≥3时,同时为了简化公式表达,令 X i = [ x i , y i ] , I = [ 1 , 0 ; 0 , 1 ] , O = [ 0 , 0 ; 0 , 0 ] X_i = [x_i, y_i],I = [1,0;0,1],O=[0,0;0,0] Xi=[xi,yi],I=[1,0;0,1],O=[0,0;0,0]可得:
J s m o o t h = [ X 1 , X 2 , X 3 , ⋯ , X N ] [ I − 2 I I O ⋯ O O O − 2 I 5 I − 4 I I ⋯ O O O I − 4 I 6 I − 4 I ⋯ O O O O I − 4 I 6 I ⋯ O O O ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋱ ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ O O O O ⋯ 6 I − 4 I I O O O O ⋯ − 4 I 5 I − 2 I O O O O ⋯ O − 2 I I ] [ X 1 , X 2 , X 3 , ⋯ , X N ] T (1-8) J_{smooth} = [X_1, X_2, X_3, \cdots, X_N] \left[\begin{matrix} I & -2I & I & O & \cdots & O & O & O \\ -2I & 5I & -4I & I & \cdots & O & O & O \\ I & -4I & 6I & -4I & \cdots & O & O & O \\ O & I & -4I & 6I & \cdots & O & O & O \\ \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots \\ O & O & O & O & \cdots & 6I & -4I & I \\ O & O & O & O & \cdots & -4I & 5I &-2I \\ O & O & O & O & \cdots & O & -2I &I \end{matrix}\right] [X_1, X_2, X_3, \cdots, X_N]^T \tag{1-8} Jsmooth=[X1,X2,X3,⋯,XN]⎣ ⎡I−2IIO⋮OOO−2I5I−4II⋮OOOI−4I6I−4I⋮OOOOI−4I6I⋮OOO⋯⋯⋯⋯⋱⋯⋯⋯OOOO⋮6I−4IOOOOO⋮−4I5I−2IOOOO⋮I−2II⎦ ⎤[X1,X2,X3,⋯,XN]T(1-8)
J d e v i a t i o n = [ X 1 , X 2 , X 3 , ⋯ , X N ] [ I O ⋯ O O I ⋯ O ⋮ ⋮ ⋱ ⋮ O O O I ] [ X 1 , X 2 , X 3 , ⋯ , X N ] T − 2 [ X 1 , r , X 2 , r , X 3 , r , ⋯ , X N , r ] [ X 1 , X 2 , X 3 , ⋯ , X N ] T (1-9) J_{deviation} = [X_1, X_2, X_3, \cdots, X_N] \left[\begin{matrix} I & O & \cdots & O \\ O & I & \cdots & O \\ \vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots\\ O & O & O & I \end{matrix}\right] [X_1, X_2, X_3, \cdots, X_N]^T -2 [X_{1,r}, X_{2,r}, X_{3,r}, \cdots, X_{N,r}] [X_1, X_2, X_3, \cdots, X_N]^T \tag{1-9} Jdeviation=[X1,X2,X3,⋯,XN]⎣ ⎡IO⋮OOI⋮O⋯⋯⋱OOO⋮I⎦ ⎤[X1,X2,X3,⋯,XN]T−2[X1,r,X2,r,X3,r,⋯,XN,r][X1,X2,X3,⋯,XN]T(1-9)
J l e n g t h = [ X 1 , X 2 , X 3 , ⋯ , X N ] [ I − I O ⋯ O O − I 2 I − I ⋯ O O O − I 2 I ⋯ O O ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ ⋱ ⋮ ⋮ O O O ⋯ 2 I − I O O O ⋯ − I I ] [ X 1 , X 2 , X 3 , ⋯ , X N ] T (1-10) J_{length} = [X_1, X_2, X_3, \cdots, X_N] \left[\begin{matrix} I & -I & O & \cdots & O & O\\ -I & 2I & -I & \cdots & O & O\\ O & -I & 2I & \cdots & O & O\\ \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots & \vdots\\ O & O & O &\cdots & 2I & -I \\ O & O & O &\cdots & -I & I \end{matrix}\right] [X_1, X_2, X_3, \cdots, X_N]^T \tag{1-10} Jlength=[X1,X2,X3,⋯,XN]⎣ ⎡I−IO⋮OO−I2I−I⋮OOO−I2I⋮OO⋯⋯⋯⋱⋯⋯OOO⋮2I−IOOO⋮−II⎦ ⎤[X1,X2,X3,⋯,XN]T(1-10)
2. 约束条件
2.1 边界约束
只考虑边界约束,即:
x i , l o w e r ≤ x i ≤ x i , u p p e r y i , l o w e r ≤ y i ≤ y i , u p p e r (2-1) x_{i,lower} \leq x_i \leq x_{i,upper} \\ y_{i,lower} \leq y_i \leq y_{i,upper} \tag{2-1} xi,lower≤xi≤xi,upperyi,lower≤yi≤yi,upper(2-1)
可以转化为:
x i , r − b o u n d ≤ x i ≤ x i , r + b o u n d y i , r − b o u n d ≤ y i ≤ y i , r + b o u n d (2-2) x_{i,r} - bound \leq x_i \leq x_{i,r} + bound \\ y_{i,r} - bound \leq y_i \leq y_{i,r} + bound \tag{2-2} xi,r−bound≤xi≤xi,r+boundyi,r−bound≤yi≤yi,r+bound(2-2)
对参考线的起点和终点进行约束,令其等于原始参考线上的点:
x 1 , r ≤ x 1 ≤ x 1 , r y 1 , r ≤ y 1 ≤ y 1 , r (2-3) x_{1,r} \leq x_1 \leq x_{1,r} \\ y_{1,r} \leq y_1 \leq y_{1,r} \tag{2-3} x1,r≤x1≤x1,ry1,r≤y1≤y1,r(2-3)
2.2 曲率约束
( x i − 1 + x i + 1 − 2 x i ) 2 + ( y i − 1 + y i + 1 − 2 y i ) 2 − ε κ , i ≤ ( Δ s 2 × κ m a x ) 2 , i = 1 , 2 , ⋯ , N − 1 ε κ , i ≥ 0 , i = 1 , 2 , ⋯ , N − 1 (2-4) (x_{i-1} + x_{i+1} - 2x_i)^2 + (y_{i-1} + y_{i+1} - 2y_i)^2 - \varepsilon_{\kappa, i} \leq ( \Delta s^2 \times \kappa_{max} ) ^ 2, i = 1, 2, \cdots, N-1 \\ \varepsilon_{\kappa, i} \geq 0, i = 1, 2, \cdots, N-1 \tag{2-4} (xi−1+xi+1−2xi)2+(yi−1+yi+1−2yi)2−εκ,i≤(Δs2×κmax)2,i=1,2,⋯,N−1εκ,i≥0,i=1,2,⋯,N−1(2-4)
曲率约束是非线性的,可以使用一阶泰勒展开在平衡点 X ˉ \bar{X} Xˉ(参考点)处进行线性化。令 f = ( x i − 1 + x i + 1 − 2 x i ) 2 + ( y i − 1 + y i + 1 − 2 y i ) 2 f = (x_{i-1} + x_{i+1} - 2x_i)^2 + (y_{i-1} + y_{i+1} - 2y_i)^2 f=(xi−1+xi+1−2xi)2+(yi−1+yi+1−2yi)2, f f f的梯度向量函数为:
∇ f = [ ∂ f ∂ x i − 1 ∂ f ∂ y i − 1 ∂ f ∂ x i ∂ f ∂ y i ∂ f ∂ x i + 1 ∂ f ∂ y i + 1 ] = [ 2 ( x i − 1 + x i + 1 − 2 x i ) 2 ( y i − 1 + y i + 1 − 2 y i ) − 4 ( x i − 1 + x i + 1 − 2 x i ) − 4 ( y i − 1 + y i + 1 − 2 y i ) 2 ( x i − 1 + x i + 1 − 2 x i ) 2 ( y i − 1 + y i + 1 − 2 y i ) ] (2-5) \nabla f = \begin{bmatrix} \frac{\partial f}{\partial x_{i-1}} \\ \frac{\partial f}{\partial y_{i-1}} \\ \frac{\partial f}{\partial x_{i}} \\ \frac{\partial f}{\partial y_{i}} \\ \frac{\partial f}{\partial x_{i+1}} \\ \frac{\partial f}{\partial y_{i+1}} \\ \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 2(x_{i-1} + x_{i+1} - 2x_i) \\ 2(y_{i-1} + y_{i+1} - 2y_i) \\ -4(x_{i-1} + x_{i+1} - 2x_i) \\ -4(y_{i-1} + y_{i+1} - 2y_i) \\ 2(x_{i-1} + x_{i+1} - 2x_i) \\ 2(y_{i-1} + y_{i+1} - 2y_i) \\ \end{bmatrix} \tag{2-5} ∇f=⎣ ⎡∂xi−1∂f∂yi−1∂f∂xi∂f∂yi∂f∂xi+1∂f∂yi+1∂f⎦ ⎤=⎣ ⎡2(xi−1+xi+1−2xi)2(yi−1+yi+1−2yi)−4(xi−1+xi+1−2xi)−4(yi−1+yi+1−2yi)2(xi−1+xi+1−2xi)2(yi−1+yi+1−2yi)⎦ ⎤(2-5)
则 f f f的一阶泰勒展开式为:
f = f ( X ˉ ) + ∇ f X = X ˉ T ( X − X ˉ ) (2-6) f = f(\bar{X}) + \nabla f_{X=\bar{X}} ^T (X - \bar{X}) \tag{2-6} f=f(Xˉ)+∇fX=XˉT(X−Xˉ)(2-6)
所以,非线性约束 ( 2 − 4 ) (2-4) (2−4)可以转化为线性约束。
3. SQP
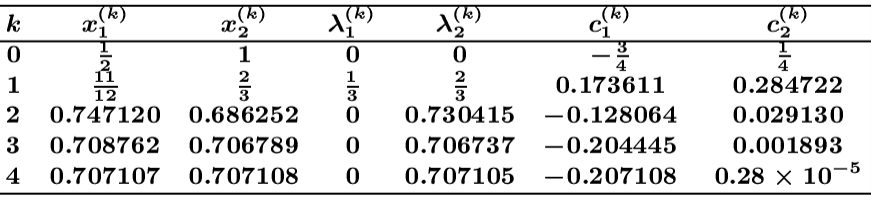
通过一阶泰勒展开可以将非线性约束转化为线性约束,然后使用二次规划求解。但是泰勒展开的精度只能保证在平衡点的邻域内,因此当平衡点选取不合适时(可以理解为 ∣ X − X ˉ ∣ |X-\bar{X}| ∣X−Xˉ∣较大时),线性化会有较大误差,而序列二次规划(Sequential quadratic programming, SQP)可以解决此问题。序列二次规划将复杂的非线性约束最优化问题转化为一个或者多个二次规划子问题,然后依次迭代求解,在求解二次规划子问题时,会使用上一个二次规划的结果作为非线性约束泰勒展开线性化时的平衡点,使线性化结果逐渐逼近非线性约束,直至求解结果收敛或者达到最大迭代次数。其伪代码可以表示为:
| Input: | Reference line: r r r |
|---|---|
| Output: | An optimal trajectory: τ \tau τ |
| parameters: | SQP max iteration: i t e r m a x iter_{max} itermax, SQP max tolerance: ϵ m a x \epsilon_{max} ϵmax |
| 1. 1. 1. | Set i t e r = 0 iter=0 iter=0; |
| 2. 2. 2. | Set τ l a s t = r \tau_{last} = r τlast=r |
| 3. 3. 3. | while i t e r < i t e r m a x iter < iter_{max} iter<itermax, do |
| 4. 4. 4. | τ \tau τ = QP( r , τ l a s t r, \tau_{last} r,τlast); |
| 5. 5. 5. | if Converge( τ , τ l a s t \tau, \tau_{last} τ,τlast), then |
| 6. 6. 6. | break; |
| 7. 7. 7. | End if |
| 8. 8. 8. | τ l a s t = τ \tau_{last} = \tau τlast=τ; |
| 9. 9. 9. | i t e r = i t e r + 1 ; iter = iter + 1; iter=iter+1; |
| 10. 10. 10. | End while |
| 11. 11. 11. | Return with τ \tau τ |
在Apollo的代码中,可以看到其求解流程是符合上述伪代码的,其有二点不同,一是会先进行一次 Q P QP QP求解后再进入while循环中,这么做是使用了 O S Q P OSQP OSQP求解器的updata相关函数接口,对每次迭代时线性化后的约束进行更新,以避免过多的 Q P QP QP问题构造,以优化时耗;二是在每次迭代时,会对松弛因子的权重逐渐增大,使曲率约束越来越严格,但其仍然是软约束,所以在迭代结束后会进行曲率校核。
bool FemPosDeviationSqpOsqpInterface::Solve() {// Sanity Checkif (ref_points_.empty()) {AERROR << "reference points empty, solver early terminates";return false;}if (ref_points_.size() != bounds_around_refs_.size()) {AERROR << "ref_points and bounds size not equal, solver early terminates";return false;}if (ref_points_.size() < 3) {AERROR << "ref_points size smaller than 3, solver early terminates";return false;}if (ref_points_.size() > std::numeric_limits<int>::max()) {AERROR << "ref_points size too large, solver early terminates";return false;}// Calculate optimization states definitionsnum_of_points_ = static_cast<int>(ref_points_.size());num_of_pos_variables_ = num_of_points_ * 2;num_of_slack_variables_ = num_of_points_ - 2;num_of_variables_ = num_of_pos_variables_ + num_of_slack_variables_;num_of_variable_constraints_ = num_of_variables_;num_of_curvature_constraints_ = num_of_points_ - 2;num_of_constraints_ =num_of_variable_constraints_ + num_of_curvature_constraints_;// Set primal warm startstd::vector<c_float> primal_warm_start;SetPrimalWarmStart(ref_points_, &primal_warm_start);// Calculate kernelstd::vector<c_float> P_data;std::vector<c_int> P_indices;std::vector<c_int> P_indptr;CalculateKernel(&P_data, &P_indices, &P_indptr);// Calculate offsetstd::vector<c_float> q;CalculateOffset(&q);// Calculate affine constraintsstd::vector<c_float> A_data;std::vector<c_int> A_indices;std::vector<c_int> A_indptr;std::vector<c_float> lower_bounds;std::vector<c_float> upper_bounds;CalculateAffineConstraint(ref_points_, &A_data, &A_indices, &A_indptr,&lower_bounds, &upper_bounds);// Load matrices and vectors into OSQPDataOSQPData* data = reinterpret_cast<OSQPData*>(c_malloc(sizeof(OSQPData)));data->n = num_of_variables_;data->m = num_of_constraints_;data->P = csc_matrix(data->n, data->n, P_data.size(), P_data.data(),P_indices.data(), P_indptr.data());data->q = q.data();data->A = csc_matrix(data->m, data->n, A_data.size(), A_data.data(),A_indices.data(), A_indptr.data());data->l = lower_bounds.data();data->u = upper_bounds.data();// Define osqp solver settingsOSQPSettings* settings =reinterpret_cast<OSQPSettings*>(c_malloc(sizeof(OSQPSettings)));osqp_set_default_settings(settings);settings->max_iter = max_iter_;settings->time_limit = time_limit_;settings->verbose = verbose_;settings->scaled_termination = scaled_termination_;settings->warm_start = warm_start_;settings->polish = true;settings->eps_abs = 1e-5;settings->eps_rel = 1e-5;settings->eps_prim_inf = 1e-5;settings->eps_dual_inf = 1e-5;// Define osqp workspaceOSQPWorkspace* work = nullptr;// osqp_setup(&work, data, settings);work = osqp_setup(data, settings);// Initial solutionbool initial_solve_res = OptimizeWithOsqp(primal_warm_start, &work);if (!initial_solve_res) {AERROR << "initial iteration solving fails";osqp_cleanup(work);c_free(data->A);c_free(data->P);c_free(data);c_free(settings);return false;}// Sequential solutionint pen_itr = 0;double ctol = 0.0;double original_slack_penalty = weight_curvature_constraint_slack_var_;double last_fvalue = work->info->obj_val;while (pen_itr < sqp_pen_max_iter_) {int sub_itr = 1;bool fconverged = false;while (sub_itr < sqp_sub_max_iter_) {SetPrimalWarmStart(opt_xy_, &primal_warm_start);CalculateOffset(&q);CalculateAffineConstraint(opt_xy_, &A_data, &A_indices, &A_indptr,&lower_bounds, &upper_bounds);osqp_update_lin_cost(work, q.data());osqp_update_A(work, A_data.data(), OSQP_NULL, A_data.size());osqp_update_bounds(work, lower_bounds.data(), upper_bounds.data());bool iterative_solve_res = OptimizeWithOsqp(primal_warm_start, &work);if (!iterative_solve_res) {AERROR << "iteration at " << sub_itr<< ", solving fails with max sub iter " << sqp_sub_max_iter_;weight_curvature_constraint_slack_var_ = original_slack_penalty;osqp_cleanup(work);c_free(data->A);c_free(data->P);c_free(data);c_free(settings);return false;}double cur_fvalue = work->info->obj_val;double ftol = std::abs((last_fvalue - cur_fvalue) / last_fvalue);if (ftol < sqp_ftol_) {ADEBUG << "merit function value converges at sub itr num " << sub_itr;ADEBUG << "merit function value converges to " << cur_fvalue<< ", with ftol " << ftol << ", under max_ftol " << sqp_ftol_;fconverged = true;break;}last_fvalue = cur_fvalue;++sub_itr;}if (!fconverged) {AERROR << "Max number of iteration reached";weight_curvature_constraint_slack_var_ = original_slack_penalty;osqp_cleanup(work);c_free(data->A);c_free(data->P);c_free(data);c_free(settings);return false;}ctol = CalculateConstraintViolation(opt_xy_);ADEBUG << "ctol is " << ctol << ", at pen itr " << pen_itr;if (ctol < sqp_ctol_) {ADEBUG << "constraint satisfied at pen itr num " << pen_itr;ADEBUG << "constraint voilation value drops to " << ctol<< ", under max_ctol " << sqp_ctol_;weight_curvature_constraint_slack_var_ = original_slack_penalty;osqp_cleanup(work);c_free(data->A);c_free(data->P);c_free(data);c_free(settings);return true;}weight_curvature_constraint_slack_var_ *= 10;++pen_itr;}ADEBUG << "constraint not satisfied with total itr num " << pen_itr;ADEBUG << "constraint voilation value drops to " << ctol<< ", higher than max_ctol " << sqp_ctol_;weight_curvature_constraint_slack_var_ = original_slack_penalty;osqp_cleanup(work);c_free(data->A);c_free(data->P);c_free(data);c_free(settings);return true;
}