Java基础之java8 新特性
- 一、Lambda 表达式
- 二、Stream 初体验
- 三、方法引用
- 四、默认方法
- 五、Optional 类
- 六、Base 64
- 七、字符串拼接
- 八、== equals 与 instanceof
- 九、final
一、Lambda 表达式
Lambda 表达式是在 Java8 中引入的,并号称是 Java8 的最大的特点。Lambda 表达式有利于函数式编程,简化了开发了很多。
语法:parameter -> expression body
操作符 “->” 称为箭头操作符或 Lambda 操作符
箭头操作符将 Lambda 表达式拆分成两部分:
左侧:Lambda 表达式的参数列表
右侧:Lambda 表达式中所需执行的功能, 即 Lambda 体
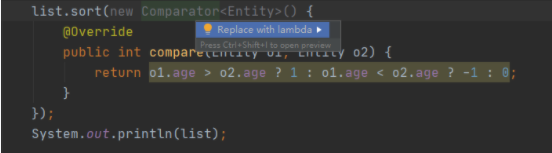
案例:集合排序
public class Demo {public static void main(String[] args) {List<Entity> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add(new Entity("张一", 18));list.add(new Entity("张二", 25));list.add(new Entity("张三", 14));list.add(new Entity("张四", 19));list.add(new Entity("张五", 23));list.sort(new Comparator<Entity>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Entity o1, Entity o2) {return o1.age > o2.age ? 1 : o1.age < o2.age ? -1 : 0;}});System.out.println(list);}
}
class Entity {String name;Integer age;public Entity(String name, Integer age) {this.age = age;this.name = name;}
}
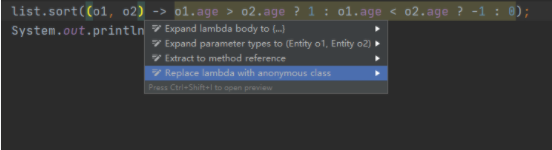
转化后的排序变成一行代码:两个参数一条语句(大括号和 return 可以不写),Lambda 表达式的参数列表的数据类型可以省略不写,因为 JVM 编译器通过上下文推断出,数据类型,即“类型推断”。
list.sort((o1, o2) -> o1.age > o2.age ? 1 : o1.age < o2.age ? -1 : 0);
idea 一般都会自动提示普通写法和 lambda 相互转化,(alt + 回车)一般按照提示转化即可。
案例:Runnable :lambda 表达式一般可以操作加 @FunctionalInterface 注解的接口(函数式接口)
Runnable r = new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("Hello lambda!");}
};
r.run();//变成Runnable r1 = () -> System.out.println("Hello Lambda!");
r1.run();
案例:forEach 遍历 list
List<Entity> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Entity("张一", 18));
list.add(new Entity("张二", 25));
list.add(new Entity("张三", 14));
list.add(new Entity("张四", 19));
list.add(new Entity("张五", 23));
list.forEach(new Consumer<Entity>() {@Overridepublic void accept(Entity entity) {System.out.println(entity);}
});
转化为 Lambda 后,当方法的参数只有一个时前面的括号可以省略。
list.forEach(entity -> System.out.println(entity));
案例:forEach 遍历 map
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("id", 1);
map.put("name", "张三");
map.put("password", "123456");
map.forEach((k, v) -> {System.out.println(k);System.out.println(v);
});
二、Stream 初体验
Java 8 API 添加了一个新的抽象称为流 Stream,可以让你以一种声明的方式处理数据。 Stream 使用一种类似用 SQL 语句从数据库查询数据的直观方式来提供一种对 Java 集合运算和表达的高阶抽象。 Stream API 可以极大提高 Java 程序员的生产力,让程序员写出高效率、干净、简洁的代码。 这种风格将要处理的元素集合看作一种流, 流在管道中传输, 并且可以在管道的节点上进行处理, 比如筛选, 排序,聚合等。

元素流在管道中经过中间操作(intermediate operation)的处理,最后由最终操作(terminal operation)得到前面处理的结果。
流程:
stream of elements -> filter -> sorted -> map -> collect
map
map 方法用于映射每个元素到对应的结果。
案例:使用 map 输出了元素对应的平方数:
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(3, 2, 2, 3, 7, 3, 5);
// 获取对应的平方数
List<Integer> squaresList = numbers.stream().map( i -> i*i).collect(Collectors.toList());
filter
filter 方法用于通过设置的条件过滤出元素。
案例:使用 filter 方法过滤出空字符串:
List<String>strings = Arrays.asList("abc", "", "bc", "efg", "abcd","", "jkl");
// 获取空字符串的数量
long count = strings.stream().filter(string -> string.isEmpty()).count();
limit
limit 方法用于获取指定数量的流。
案例:使用 limit 方法获取前 3 条不为空的数组数据:
List<String>strings = Arrays.asList("abc", "", "bc", "efg", "abcd","", "jkl");
List<String> collect = strings.stream().filter(string -> string != "").limit(3).collect(Collectors.toList());
sorted
sorted 方法用于对流进行排序。
案例:使用 sorted 方法对集合数据进行排序:
List<String>strings = Arrays.asList("abc", "", "bc", "efg", "abcd","", "jkl");
List<String> collect = strings.stream().filter(string -> string != "").sorted().collect(Collectors.toList());
distinct
distinct 方法用于对流进行去重。
案例:
List<String>strings = Arrays.asList("bc", "", "bc", "efg", "abcd","", "jkl");
List<String> collect = strings.stream().filter(string -> string != "").distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
count
count 方法用于对流进行计数。
List<String>strings = Arrays.asList("abc", "", "bc", "efg", "abcd","", "jkl");
long count = strings.stream().filter(string -> string.isEmpty()).count();
扩展案例:
Random random = new Random();
//生成 10 个[0,100] 的随机数
List<Integer> collect = random.ints(0, 101).boxed().limit(10).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(collect);//生成一个从0开始到10的集合
List<Integer> list = IntStream.range(1, 11).boxed().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(list);//计算上面集合的平均值
Double avarage = list.stream().collect(Collectors.averagingInt(item -> item));
System.out.println(avarage);//对列表元素进行统计
IntSummaryStatistics iss = list.stream().collect(Collectors.summarizingInt(value -> value));
System.out.println(iss);
//{count=10, sum=55, min=1, average=5.500000, max=10}//根据 List 创建 Map
Map<Integer, Integer> map = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(p -> p, q->q*3));
System.out.println(map);//获取列表的最大值
Optional<Integer> max = list.stream().reduce(Math::max);
max.ifPresent(value -> System.out.println(value));
注意:
1.boxed 用于将 IntStream 转化成 Stream。
2.Math::max 称为方法引用。
三、方法引用
在 Java8 中,你可以使用 class::methodName 语法引用类或对象的方法。让我们来学习一下 Java 8 中不同类型的方法引用。Java 8 中包含了四种类型的方法引用。
方法引用 描述 例子
静态方法引用 用于引用类的静态方法 Math::max 相当于 Math.max(x,y)
从对象中引用实例方法 使用对象的引用来调用实例方法 System.out::println 相当于 System.out.println(x)
从类中引用实例方法 在上下文提供的对象的引用上调用实例方法 String::length 相当于 str.length()
引用构造函数 引用构造函数 ArrayList::new```相当于new ArrayList()`
引用静态方法 - Class::staticMethodName
一个使用 Math.max() 静态方法的例子。
List<Integer> integers = Arrays.asList(1,12,433,5);
Optional<Integer> max = integers.stream().reduce( Math::max );
max.ifPresent(value -> System.out.println(value));//433
从对象中引用实例方法 - ClassInstance::instanceMethodName
在上面的例子中,我们使用了 System.out.println(value) 打印集合中的最大值,我们可以使用 System.out::println 打印这个值。
List<Integer> integers = Arrays.asList(1,12,433,5);
Optional<Integer> max = integers.stream().reduce( Math::max );
max.ifPresent( System.out::println );//433
引用特定类型的实例方法 - Class::instanceMethodName
在这个例子中 s1.compareTo(s2) 被简写为 String::compareTo。
List<String> strings = Arrays.asList("how", "to", "do", "in", "java", "dot", "com");
List<String> sortedAlt = strings.stream().sorted(String::compareTo).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(sortedAlt);
引用构造函数 - Class::new
使用 lambda 表达式修改第一个例子中的方法,可以非常简单的创建一个从1到100的集合(不包含100)。创建一个新的 ArrayList 实例,我们可以使用 ArrayList::new。
List<Integer> integers = IntStream.range(1, 100).boxed().collect(Collectors.toCollection( ArrayList::new ));
Optional<Integer> max = integers.stream().reduce(Math::max);
max.ifPresent(System.out::println);//99
案例:
public class User {private String username;private Integer age;public User() {}public User(String username, Integer age) {this.username = username;this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "User{" +"username='" + username + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}// Getter&Setter
}
public static void main(String[] args) {// 使用双冒号::来构造静态函数引用Function<String, Integer> fun = Integer::parseInt;Integer value = fun.apply("123");System.out.println(value);// 使用双冒号::来构造非静态函数引用String content = "Hello JDK8";Function<Integer, String> func = content::substring;String result = func.apply(1);System.out.println(result);// 构造函数引用BiFunction<String, Integer, User> biFunction = User::new;User user = biFunction.apply("mengday", 28);System.out.println(user.toString());// 函数引用也是一种函数式接口,所以也可以将函数引用作为方法的参数sayHello(String::toUpperCase, "hello");
}// 方法有两个参数,一个是
private static void sayHello(Function<String, String> func, String parameter){String result = func.apply(parameter);System.out.println(result);
}
四、默认方法
Java 8 新增了接口的默认方法。简单说,默认方法就是接口可以有实现方法,而且不需要实现类去实现其方法。
我们只需在方法名前面加个 default [dɪˈfɔːlt]关键字即可实现默认方法。为什么要有这个特性?
首先,之前的接口是个双刃剑,好处是面向抽象而不是面向具体编程,缺陷是,当需要修改接口时候,需要修改全部实现该接口的类,目前的 java 8 之前的集合框架没有 foreach 方法,通常能想到的解决办法是在 JDK 里给相关的接口添加新的方法及实现。然而,对于已经发布的版本,是没法在给接口添加新方法的同时不影响已有的实现。所以引进的默认方法。他们的目的是为了解决接口的修改与现有的实现不兼容的问题。
案例:
public interface Moveable {default void move(){System.out.println("I am moving");}
}
Moveable 接口定义了一个 move() 方法并且提供了默认的实现。如果任意一个 class 实现这个接口都没有必要去实现这个 move() 方法,能够直接使用 instance.move() 进行调用。
案例:
public class Animal implements Moveable{public static void main(String[] args){Animal tiger = new Animal();tiger.move();}
}
// I am moving
如果该 class 想要自定义一个 move() 也能提供自定义的实现去覆写这个 move 方法。
五、Optional 类
是一个可以为 null 的容器对象。如果值存在则 isPresent() [ˈpreznt , prɪˈzent] 方法会返回 true,调用 get() 方法会返回该对象。
Optional 是个容器:它可以保存类型 T 的值,或者仅仅保存 null。Optional 提供很多有用的方法,这样我们就不用显式进行空值检测。
Optional 类的引入很好的解决空指针异常。
案例:
import java.util.Optional;public class OptionalTester {public static void main(String args[]) {Integer value1 = null;Integer value2 = new Integer(10);// Optional.ofNullable - 允许传递为 null 参数Optional<Integer> a = Optional.ofNullable(value1);// Optional.of - 如果传递的参数是 null,抛出异常 NullPointerExceptionOptional<Integer> b = Optional.of(value2);System.out.println(sum(a, b));}public static Integer sum(Optional<Integer> a, Optional<Integer> b) {// Optional.isPresent - 判断值是否存在System.out.println("第一个参数值存在: " + a.isPresent());System.out.println("第二个参数值存在: " + b.isPresent());// Optional.orElse - 如果值存在,返回它,否则返回默认值 3Integer value1 = a.orElse(new Integer(3));//Optional.get - 获取值,值需要存在Integer value2 = b.get();return value1 + value2;}
}
使用示例:求和时如遇空数字则使用默认值 0 参与运算。
import java.util.Optional;public class OptionalTester {public static void main(String args[]) {Integer value1 = null;Integer value2 = new Integer(10);//同样都是求和,如果数据为空则使用默认值 0 参与计算System.out.println(sum(value1, value2));System.out.println(sum(Optional.ofNullable(value1), Optional.ofNullable(value2)));}public static Integer sum(Optional<Integer> a, Optional<Integer> b) {return a.orElse(0) + b.orElse(0);}public static Integer sum(Integer a, Integer b) {if (a == null && b == null)return 0;if (a == null)return 0 + b;if (b == null)return a + 0;return a + b;}
}
六、Base 64
Base64 是一种用 64 个字符来表示任意二进制数据的方法,有些人也叫 Base64 加密。
用记事本打开 exe、jpg、pdf 这些文件时,我们都会看到一大堆乱码,因为二进制文件包含很多无法显示和打印的字符,所以,如果要让记事本这样的文本处理软件能处理二进制数据,就需要一个二进制到字符串的转换方法。Base64 是一种最常见的二进制解编码方法。
Base64 的原理很简单,首先,准备一个包含 64 个字符的数组:
['A', 'B', 'C', ... 'a', 'b', 'c', ... '0', '1', ... '+', '/']
然后,对二进制数据进行处理,每 3 个字节一组,一共是 3x8=24bit,划为 4 组,每组正好 6 个 bit:
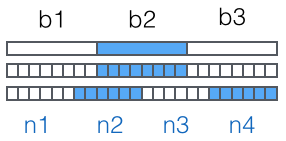
这样我们得到 4 个数字作为索引,然后查表,获得相应的 4 个字符,就是编码后的字符串。
所以,Base64 编码会把 3 字节的二进制数据编码为 4 字节的文本数据,长度增加 33%,好处是编码后的文本数据可以在邮件正文、网页等直接显示。 如果要编码的二进制数据不是 3 的倍数,最后会剩下 1 个或 2 个字节怎么办?Base64 用 \x00 字节在末尾补足后,再在编码的末尾加上 1 个或 2 个 = 号,表示补了多少字节,解码的时候,会自动去掉。
java8 在 Base64 加解码上已经提供一套标准的工具
String base64encodedString = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(byte数组);
byte[] base64decodedBytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(base64字符串);
字符串获取 byte 数组时 .getBytes(“utf-8”); 解决中文乱码问题。
案例:
String string = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString("hello word,你好,世界".getBytes());
System.out.println(string);
byte[] bytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(string);
System.out.println(new String(bytes));
案例:
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Base64;public class Hello {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("c:/下载.png");byte[] bytes = new byte[10240000];int read = inputStream.read(bytes);if (read < 10240000){String base64encodedString = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(Arrays.copyOfRange(bytes,0,read));System.out.println(base64encodedString);}}
}
七、字符串拼接
从 Java7 到目前为止,我们可以通过向 String.split() 方法中传递参数的方式来分割一个字符串,然后把分割后的字符串列表以数组的形式返回。
但是,如果需要连接字符串或者通过分隔符连接的字符串来创建一个 CSV 文件,则必须遍历字符串列表或数组, 然后使用 StringBuilder 或 StringBuffer 对象拼接这些字符串,最后得到 CSV。
在 Java8 中使得字符串拼接任务变得容易。现在你可以使用 String.join() 方法, 其中第一个参数是分隔符,然后可以传递多个字符串或实现了 Iterable 接口的实例作为第二个参数,下面的示例将返回。
import java.time.ZoneId;
public class StringJoinDemo {public static void main(String[] args){String joined = String.join("/","usr","local","bin");System.out.println(joined);String ids = String.join(", ", ZoneId.getAvailableZoneIds());System.out.println(ids);}
}//usr/local/bin
//Asia/Aden, America/Cuiaba, Etc/GMT+9, Etc/GMT+8.....
八、== equals 与 instanceof
== 判断内存地址是否相同(如果是简单类型则比较他们的值是否相等)
equals 调用对象的 equals 方法判断两个对象是否相等,如果对象的类没有重写 equals 方法,则使用 object 的 equals 方法,object 的 equals 方法是比较内存地址。
instanceof:关键字用来确定对象所属的类,或父类。
System.out.println(student instanceof Student);//true
九、final
final 中文意思:最后的,最终的。
final 可以修饰变量、方法或者类
- 当不希望父类的某个方法被子类覆盖(override)时,可以用 final 关键字修饰。
- 当不希望类的某个变量的值被修改,可以用 final 修饰。如果一个变量是 final,则必须赋初值,否则编译出错。
- 当类不希望被继承时,可以在类前面用 final 修饰。
注意:
final 修饰的变量又叫常量,一般用全大写下划线命名。( Integer.MAX_VALUE )
final 修饰的变量在定义时,必须初始化,并且以后不能再赋值。
章节练习:
1.遍历集合:使用 Lambda 表达式遍历如下的集合,代码尽可能精简。
List<Employee> emps = Arrays.asList(new Employee(101, "张三", 18, 9999.99), new Employee(102, "李四", 59, 6666.66),new Employee(103, "王五", 28, 3333.33), new Employee(104, "赵六", 18, 7777.77),new Employee(105, "田七", 38, 5555.55));
2.遍历 map:使用 Lambda 表达式遍历如下的 Map,代码尽可能精简。
Map<String, Employee> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("101", new Employee(101, "张三", 18, 9999.99));
map.put("102", new Employee(102, "李四", 59, 6666.66));
map.put("103", new Employee(103, "王五", 28, 3333.33));
map.put("104", new Employee(104, "赵六", 8, 7777.77));
map.put("105", new Employee(105, "田七", 38, 5555.55));
3.获取集合里面的某属性:使用 Stream 获取第一题里面的全部 id 的集合。
4.字符串的 base64:使用 base64 加密与解密如下字符串:“abcd1234”。
5.文件的 base64:使用 base64 算法获取 C:/Windows/win.ini 的 base64 字符串。
6.乱序集合:创建一个方法 void shuffle(List arr),使其能在代码最精简,且最省内存的情况下完成数组的乱序。
参考代码:
import org.junit.Test;import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;public class Demo {/*** 1.遍历集合*/@Testpublic void t1() {List<Employee> list = Arrays.asList(new Employee(101, "张三", 18, 9999.99),new Employee(102, "李四", 59, 6666.66), new Employee(103, "王五", 28, 3333.33),new Employee(104, "赵六", 18, 7777.77), new Employee(105, "田七", 38, 5555.55));list.forEach(System.out::println);}/*** 2.遍历 map*/@Testpublic void t2() {Map<String, Employee> map = new HashMap<>();map.put("101", new Employee(101, "张三", 18, 9999.99));map.put("102", new Employee(102, "李四", 59, 6666.66));map.put("103", new Employee(103, "王五", 28, 3333.33));map.put("104", new Employee(104, "赵六", 8, 7777.77));map.put("105", new Employee(105, "田七", 38, 5555.55));map.forEach((k, v) -> System.out.println(k + "=" + v));}/*** 3.获取集合里面的某属性*/@Testpublic void t3() {List<Employee> list = Arrays.asList(new Employee(101, "张三", 18, 9999.99),new Employee(102, "李四", 59, 6666.66), new Employee(103, "王五", 28, 3333.33),new Employee(104, "赵六", 18, 7777.77), new Employee(111, "田七", 38, 5555.55));List<Integer> collect = list.stream().map(Employee::getId).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(collect);}/*** 4.字符串的 base64*/@Testpublic void t4() {String s1 = "abcd1234";String string = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(s1.getBytes());System.out.println(string);byte[] decode = Base64.getDecoder().decode(string);System.out.println(new String(decode));}/*** 5.获取文件的 base64*/@Testpublic void t5() throws IOException {InputStream stream = new FileInputStream("C:/Windows/win.ini");byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];int n = stream.read(bytes);String string = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(Arrays.copyOfRange(bytes, 0, n));System.out.println(string);byte[] decode = Base64.getDecoder().decode(string);System.out.println(new String(decode));stream.close();}/*** 6.乱序集合*/@Testpublic void t6() {List<Integer> list = IntStream.range(1, 11).boxed().collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(list);shuffle(list);System.out.println(list);}public void shuffle(List<Integer> arr) {for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) {int index = (int) (Math.random() * arr.size());int temp = arr.get(i);arr.set(i, arr.get(index));arr.set(index, temp);}}
}class Employee {private Integer id;private String name;private Integer age;private Double sal;public Employee(Integer id, String name, Integer age, Double sal) {this.id = id;this.name = name;this.age = age;this.sal = sal;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Employee{" +"id=" + id +", name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +", sal=" + sal +'}';}
}