日常开发中,我们可能会遇到需要监听EditText输入,比如判断输入是否为电话号码,获取输入的数据长度来限定字数等。这就需要监听EditText的输入状态。EditText使用TextWatcher实现类似按钮监听事件:
使用方法
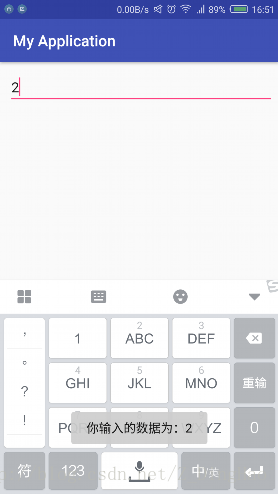
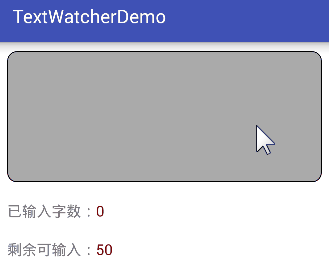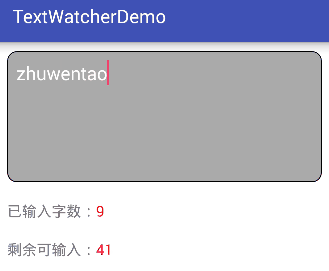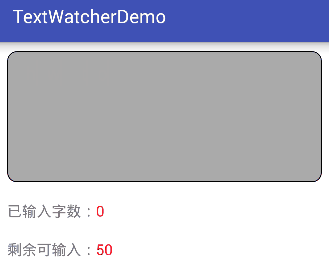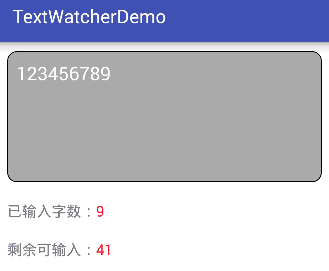
效果图:
MainActivity.java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {private EditText mNumber;@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);mNumber = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.phone_number);//为EditText设置监听,注意监听类型为TextWatchermNumber.addTextChangedListener(new TextWatcher() {@Overridepublic void beforeTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int count, int after) {}@Overridepublic void onTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int before, int count) {toast("您输入的数据为:"+s.toString());}@Overridepublic void afterTextChanged(Editable s) {}});}private void toast(String s){Toast.makeText(getApplication(),s,Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();}
}Activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"android:padding="10dp"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"tools:context="com.alphathink.myapplication.MainActivity"><EditText
android:id="@+id/phone_number"android:layout_width="368dp"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:hint="@string/number"android:inputType="number"tools:layout_editor_absoluteY="0dp"tools:layout_editor_absoluteX="8dp" /></LinearLayout>
TextWatcher详解
注意:
CharSequence是一个接口,比较常见的String、StringBuilder、StringBuffer都实现了这个接口。当我们看到一个API里面有CharSequence的时候,它也是可以被其子类代替的,一般用String代替即可。
我们看到TextWatcher监听里覆写了3个方法:
void beforeTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int count, int after); void onTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int before, int count); void afterTextChanged(Editable s); 执行顺序来说是:beforeTextChanged()>>>onTextChanged()>>>afterTextChanged()
请勿在afterTextChanged();内加入代码进行验证,这个会进入死循环的,后边讲原因。
关于beforeTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int count, int after);
官方文档解释:
void beforeTextChanged (CharSequence s, int start, int count, int after)This method is called to notify you that, within s, the count characters beginning at start are about to be replaced by new text with length after. It is an error to attempt to make changes to s from this callback. 意思大概是:
这个方法用来通知你,在字符串s里,光标start开始处的count个字符将要被after长的字符代替,禁止在这个回调里改字符串s。可以理解成提醒你你做了什么操作。
操作》》》系统提醒你做了什么事(还没做)》》》》系统开始做@Overridepublic void beforeTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int count, int after) {toast("s字符串为:"+s+"开始处:"+start+",替换体的长度:"+count+"后替换体长度"+after);}@Overridepublic void onTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int before, int count) {}@Overridepublic void afterTextChanged(Editable s) {}分别输入一个字符、二个字符、删除一个字符的截图



这样理解:
这个方法执行获取的状态是在你输入前光标所在位置:
输入一个字符:s字符串也就是当前EditText中的内容为空,所以输出空;开始处:0,司空见惯,从0计数;替换长度:0,这个怎么理解呢?理解成将被替换长度即可,你要在光标处往后替换然而往后并没有字符;后替换体长度:1,虽然他光标没动,这里表示他将要改变的长度,等于你输入字符长度1。输入二个字符:s字符串是什么?我们刚刚输入的你字是不是还在,这就是s的内容;开始处:光标所在位置1;替换长度:0,为什么还是0?实话说这个是一直为0的,因为在你输入前执行,你所做的操作时一直往后增加,而增加操作相当于用输入字符替换了一个长度为0的字符,也就是空,所以一直为0;后替换体长度:等于替换字符长度。删除一个字符:删除前执行,所以内容为“你你好”;开始处:2,光标所在位;替换体长度:1,这个这里就变了,为什么变了呢?因为我们做了删除操作,被替换的长度是删除的那个字符长度也就是1;后替换体的长度:0,这个又是一直为0的,为什么呢,和前边那个一直为0的原因一样,我们做删除操作等于用空来替换一个字符,所以替换的长度为空的长度,也就是0;这个原理理解了的话,对于void onTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int before, int count); 和这个类似,官方文档如下:
void onTextChanged (CharSequence s, int start, int before, int count)This method is called to notify you that, within s, the count characters beginning at start have just replaced old text that had length before. It is an error to attempt to make changes to s from this callback. 意思大概是:这个方法是用来告诉你,在字符串s里,光标start开始处的count个字符刚刚把原来的before长度的字符替换。理解为通知你刚刚做,或正在做,主要与后边afterTextChanged()方法区分;代码更改如下:
@Override
public void beforeTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int count, int after) {}@Override
public void onTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int before, int count) {toast("s字符串为:"+s+",开始处:"+start+",替换体长度:"+count+",前替换体长度"+before);
}@Override
public void afterTextChanged(Editable s) {}分别输入一个字符、二个字符、删除一个字符的截图:


结合第一个理解:这个方法在你刚刚操作后提示你:
输入一个字符:s替换后后执行此方法,所以可以读取到字符串“你”;开始处0:下标位,接下来不说了这个。替换体:也就是你输入的字符长度,“你”的长度为1;前替换体:0,你用“你”这个字符替换了长度为0的字符。
输入二个字符:替换体为你输入的“你好”的长度2;前替换体:0,同上。
删除一个字符:s字符为“你你”;替换体长度:0,好比你用长度为0的字符代替了“你”字;前替换体:1,“你”的长度。对于 void afterTextChanged(Editable s):
官方解释:
This method is called to notify you that, somewhere within s, the text has been changed. It is legitimate to make further changes to s from this callback, but be careful not to get yourself into an infinite loop, because any changes you make will cause this method to be called again recursively. (You are not told where the change took place because other afterTextChanged() methods may already have made other changes and invalidated the offsets. But if you need to know here, you can use setSpan(Object, int, int, int) in onTextChanged(CharSequence, int, int, int) to mark your place and then look up from here where the span ended up.意思是:这个方法告诉你,在字符串s内的某处,一些地方已经改变了,在这个方法里可以对s做一些改变,但是注意别让你陷入反复调用它的问题上,因为可能你做的任何改变会让他递归调用本身。(这个方法没有告诉你哪里改变了,或许其他afterTextChanged()可能已经改变它了并使这个改变失效,但是如果你确定知道他是否起作用了,你可以在onTextChanged()里调用setSpan(Object, int, int, int)方法去标记并在此验证是否在这结束了))
来吧我们来验证一下这个方法做了什么事:
修改代码:
@Overridepublic void beforeTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int count, int after) {}@Overridepublic void onTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int before, int count) {}@Overridepublic void afterTextChanged(Editable s) {s.append("hello");toast(s.toString());}假如我们输入“你”字,预测结果是不是:
你hello然而结果是:
.......竟然ANR了。也就是程序无响应了 -_-!修改EditText的输入长度为15再试试:
android:maxLength="15"运行截图:
达到最大长度才显示了一下,我们可以推测到,他竟然递归调用了。。。所以文档中说到谨慎一点,小心陷入递归自身的问题。所以这个方法是在你输入完后才调用的,你输入一个字符,然后以后是不是一直处于输入完成状态,所以他一直在调用这个方法。
总结
一般我们在onTextChanged();方法里做一些自己要做的事,比如监听输入的字符长度,或者应用在验证输入一个手机号就设置按钮可点击等等。
beforeTextChanged();在View改变之前执行,好比你输入了字符,系统先统计你输入的信息,在这里可以提前获取你的动机。
onTextChanged();在View改变之后短时间内执行,也就是区别afterTextChanged();的一直执行状态,他只调用一次。我们做自己的操作一般在这里;
afterTextChanged();在你输入完成后执行,我们输入完后处于完成状态,他就监测到完成了就不断的执行,因为我们不操作,是不是一直处于完成状态?所以就处于死循环了。切记在此做操作。
好了,关于监控EditText就说到这里,看了后会不会更清晰怎么用了呢?