JPQL全称Java Persistence Query Language
这是JPA提供的复杂查询
sql:查询的是表和表中的字段
jpql:查询的是实体类和类中的属性
jpql和sql语句的语法相似
进行sql查询的步骤
1.创建query查询对象
2.对参数进行赋值
3.查询,并得到返回结果
1. 查询全部
/*** 查询全部* jpql:from cn.yy.domain.Customer* sql:select * from cst_customer*/@Testpublic void testFindAll(){//1.通过工具类获取entityManagerEntityManager entityManager = JpaUtils.getEntityManager();//2.开启事务EntityTransaction tx = entityManager.getTransaction();tx.begin();//3.查询全部String sql = "from cn.yy.domain.Customer";//直接写Customer也可以Query query = entityManager.createQuery(sql);//创建Query查询对象,query对象才是执行jpql的对象//发送查询并封装结果集List list = query.getResultList();for(Object obj:list){System.out.println(obj);}//4.提交事务tx.commit();//5.释放资源entityManager.close();}
运行结果
2.分页查询
/*** 使用jpql查询,分页查询* sql:select * from cst_customer limit ?,?* jpql:from Customer*/@Testpublic void testPage(){//1.通过工具类获取entityManagerEntityManager entityManager = JpaUtils.getEntityManager();//2.开启事务EntityTransaction tx = entityManager.getTransaction();tx.begin();//3.查询全部//这里面的order by之后的内容可以修改为其他字段的String sql = "from Customer";//根据注解id倒序查询Query query = entityManager.createQuery(sql);//创建Query查询对象,query对象才是执行jpql的对象//对参数进行赋值:分页参数//起始索引query.setFirstResult(0);//从0开始查,不包含0//每页查询的条数query.setMaxResults(3);//每页显示两条//发送查询并封装结果集/*** getResultList:直接将查询结果封装为list集合* getSingleResult:获得唯一的结果集*/List list = query.getResultList();for(Object obj:list){System.out.println(obj);}//4.提交事务tx.commit();//5.释放资源entityManager.close();}
运行结果:
3.统计查询
/*** 使用jpql查询,查询客户的总数* sql:select count(cust_id) from cst_customer* jpql:select count(custId) from Customer*/@Testpublic void testCount(){//1.通过工具类获取entityManagerEntityManager entityManager = JpaUtils.getEntityManager();//2.开启事务EntityTransaction tx = entityManager.getTransaction();tx.begin();//3.查询全部//这里面的order by之后的内容可以修改为其他字段的String sql = "select count(custId) from Customer";//根据注解id倒序查询Query query = entityManager.createQuery(sql);//创建Query查询对象,query对象才是执行jpql的对象//发送查询并封装结果集/*** getResultList:直接将查询结果封装为list集合* getSingleResult:获得唯一的结果集*/Object singleResult = query.getSingleResult();System.out.println(singleResult);//4.提交事务tx.commit();//5.释放资源entityManager.close();}
运行结果:
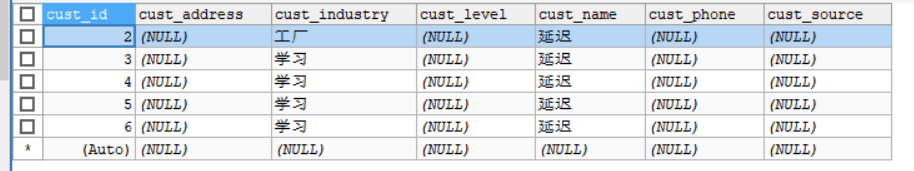
4.条件查询
/*** 使用jpql查询,根据条件查询:查询industry以学开头的* sql:select * from cst_customer where cust_industry like ?* jpql:from Customer where custIndustry like ?*/@Testpublic void testCondition(){//1.通过工具类获取entityManagerEntityManager entityManager = JpaUtils.getEntityManager();//2.开启事务EntityTransaction tx = entityManager.getTransaction();tx.begin();//3.查询全部//这里面的order by之后的内容可以修改为其他字段的String sql = "from Customer where custIndustry like ?";//根据注解id倒序查询Query query = entityManager.createQuery(sql);//创建Query查询对象,query对象才是执行jpql的对象//对参数进行赋值:占位符参数//第一个参数:占位符的索引位置(从1开始),第二个参数:取值query.setParameter(1,"学%");//发送查询并封装结果集/*** getResultList:直接将查询结果封装为list集合* getSingleResult:获得唯一的结果集*/List list = query.getResultList();for(Object obj:list){System.out.println(obj);}//4.提交事务tx.commit();//5.释放资源entityManager.close();}
运行结果:
5.排序
/*** 排序查询:倒序查询全部客户 (根据id倒序)* sql:select * from cst_customer order by cust_id DESC;* jpql:from Customer order by custId desc*/@Testpublic void testOrder(){//1.通过工具类获取entityManagerEntityManager entityManager = JpaUtils.getEntityManager();//2.开启事务EntityTransaction tx = entityManager.getTransaction();tx.begin();//3.查询全部//这里面的order by之后的内容可以修改为其他字段的String sql = "from Customer order by custId desc";//根据注解id倒序查询Query query = entityManager.createQuery(sql);//创建Query查询对象,query对象才是执行jpql的对象//发送查询并封装结果集List list = query.getResultList();for(Object obj:list){System.out.println(obj);}//4.提交事务tx.commit();//5.释放资源entityManager.close();}
运行结果: