1.MapReduce简介
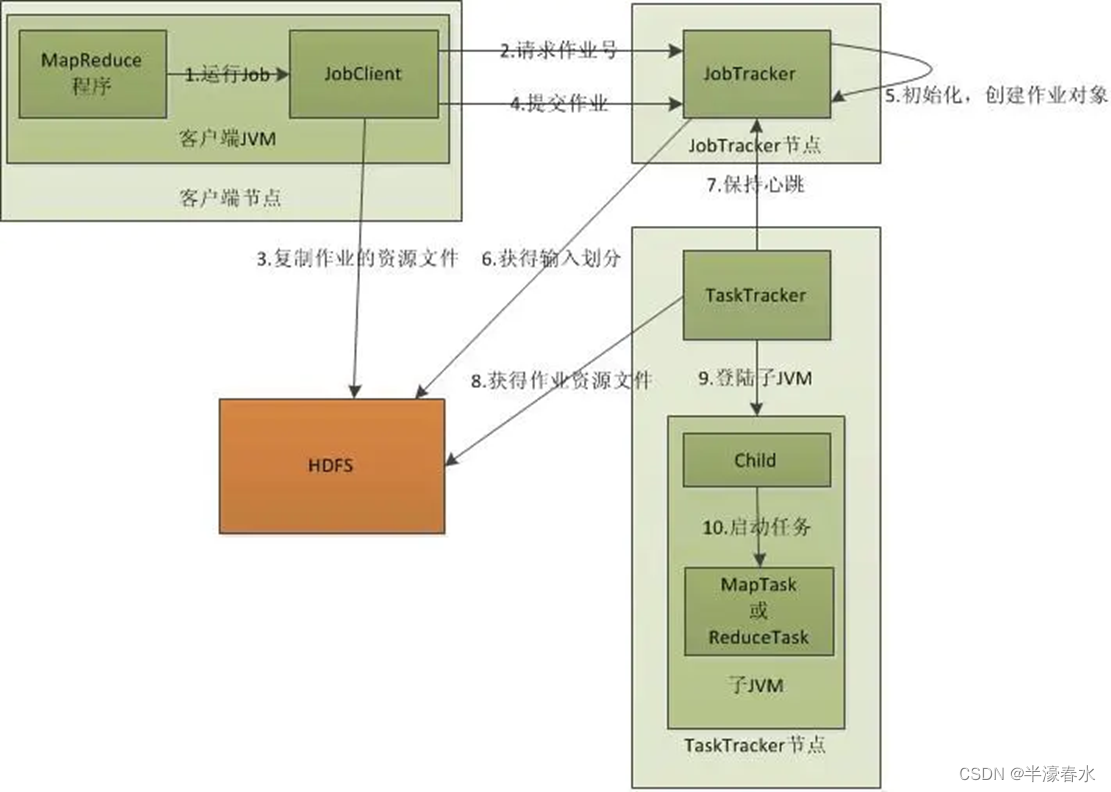
MapReduce是一个分布式运算程序的编程框架,核心功能是将用户编写的业务逻辑代码和自带默认组件整合成一个完整的分布式运算程序,并发运行在Hadoop集群上。
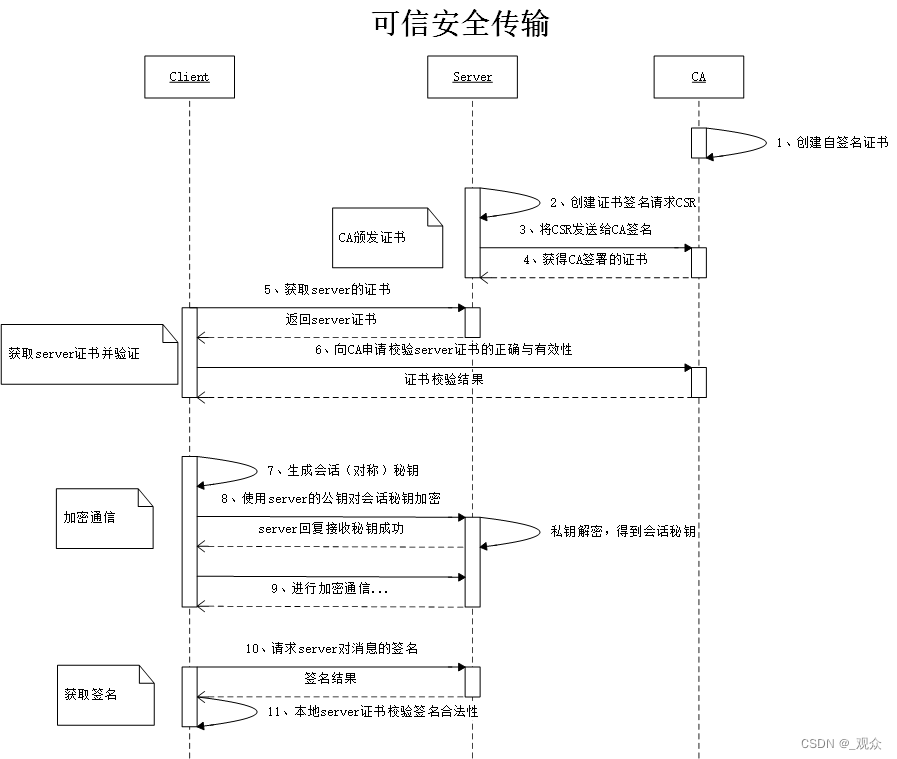
一个完整的mapreduce程序在分布式运行时有三类实例进程:
MRAppMaster 负责整个程序的过程调度及状态协调
MapTask 负责map阶段的整个数据处理流程
ReduceTask 负责reduce阶段的整个数据处理流程
2.MapReduce核心编程思想

1)分布式的运算程序往往需要分成至少2个阶段。
2)第一个阶段的maptask并发实例,完全并行运行,互不相干。
3)第二个阶段的reduce task并发实例互不相干,但是他们的数据依赖于上一个阶段的所有maptask并发实例的输出。
4)MapReduce编程模型只能包含一个map阶段和一个reduce阶段,如果用户的业务逻辑非常复杂,那就只能多个mapreduce程序,串行运行。
3.MapReduce编程规范

用户需要编写的代码分成三个部分:Mapper,Reducer,Driver(提交运行mr程序的客户端)
1)Mapper阶段
(1)用户自定义的Mapper要继承自己的父类
(2)Mapper的输入数据是KV对的形式(KV的类型可自定义)
(3)Mapper中的业务逻辑写在map()方法中
(4)Mapper的输出数据是KV对的形式(KV的类型可自定义)
(5)map()方法(maptask进程)对每一个<K,V>调用一次
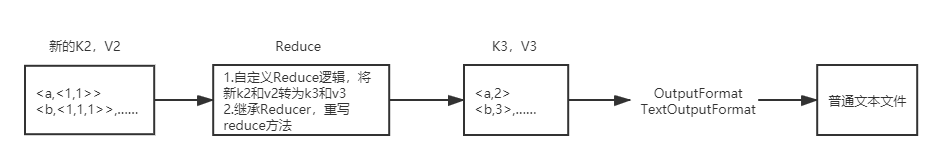
2)Reducer阶段
(1)用户自定义的Reducer要继承自己的父类
(2)Reducer的输入数据类型对应Mapper的输出数据类型,也是KV
(3)Reducer的业务逻辑写在reduce()方法中
(4)Reducetask进程对每一组相同k的<k,v>组调用一次reduce()方法
3)Driver阶段
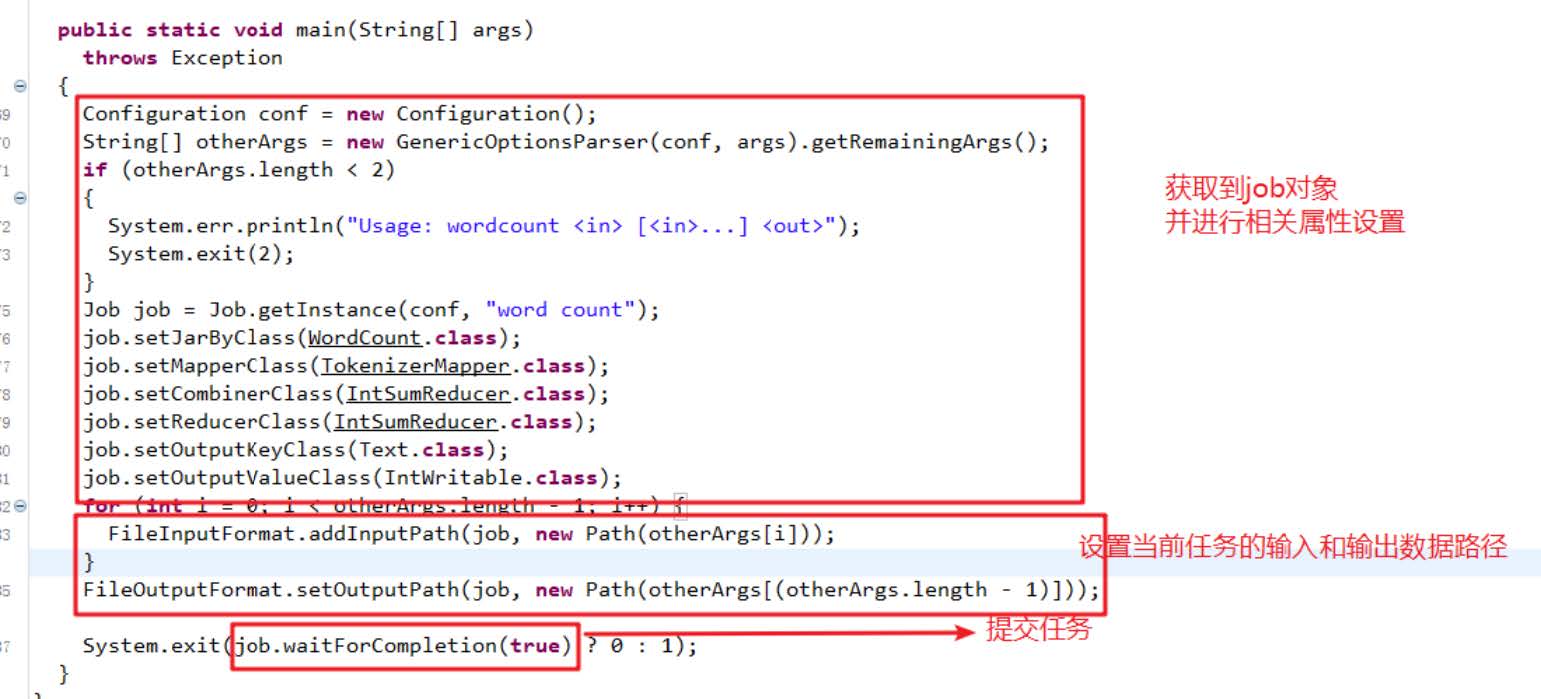
整个程序需要一个Drvier来进行提交,提交的是一个描述了各种必要信息的job对象
4.实操案例
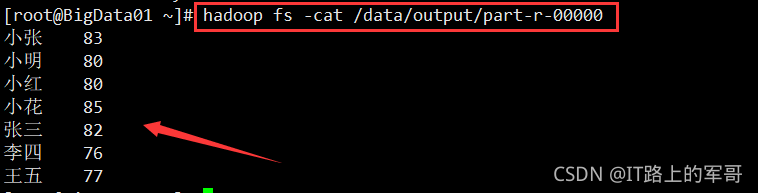
需求:统计某个文本文件中每个单词出现的次数并输出到文件
4.1编写Mapper类
public class WordCountMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable,Text,Text,LongWritable> {@Overridepublic void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {String line = value.toString();String[] split = line.split(",");for (String word : split) {context.write(new Text(word),new LongWritable(1));}}
}
4.2编写Reduce类
public class WordCountReducer extends Reducer<Text,LongWritable,Text,LongWritable> {/*** 自定义我们的reduce逻辑* 所有的key都是我们的单词,所有的values都是我们单词出现的次数* @param key* @param values* @param context* @throws IOException* @throws InterruptedException*/@Overrideprotected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<LongWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {long count = 0;for (LongWritable value : values) {count += value.get();}context.write(key,new LongWritable(count));}
}
4.3编写Driver类即是主方法main的类
public class JobMain extends Configured implements Tool {@Overridepublic int run(String[] args) throws Exception {Job job = Job.getInstance(super.getConf(), JobMain.class.getSimpleName());//打包到集群上面运行时候,必须要添加以下配置,指定程序的main函数job.setJarByClass(JobMain.class);//第一步:读取输入文件解析成key,value对job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);TextInputFormat.addInputPath(job,new Path("hdfs://node1:8020/wordcount"));//第二步:设置我们的mapper类job.setMapperClass(WordCountMapper.class);//设置我们map阶段完成之后的输出类型job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);job.setMapOutputValueClass(LongWritable.class);//第三步,第四步,第五步,第六步,省略//第七步:设置我们的reduce类job.setReducerClass(WordCountReducer.class);//设置我们reduce阶段完成之后的输出类型job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);job.setOutputValueClass(LongWritable.class);//第八步:设置输出类以及输出路径job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);TextOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,new Path("hdfs://node1:8020/wordcount_out"));boolean b = job.waitForCompletion(true);return b?0:1;}/*** 程序main函数的入口类* @param args* @throws Exception*/public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {Configuration configuration = new Configuration();Tool tool = new JobMain();int run = ToolRunner.run(configuration, tool, args);System.exit(run);}
}
关于这个最后的主类还有另外一种写法
public class WordMain {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException,InterruptedException {args = new String[]{"E:\\mapreduce\\hello.txt","E:\\mapreduce\\20200712"};Configuration conf = new Configuration();Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);job.setJarByClass(WordMain.class);job.setMapperClass(WordCountMapper.class);job.setReducerClass(WordCountReducer.class);job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);job.setMapOutputValueClass(LongWritable.class);job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);job.setOutputValueClass(LongWritable.class);FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job,new Path(args[0]));FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,new Path(args[1]));job.waitForCompletion(true);}
}
两种方式任君选择,需要注意的是输出路径一定不能存在否则会报错的。其实也很好理解。毕竟这是要在集群中运行的如果两个不同的mapreduce任务输出路径是同一个那么结果就无法分清楚了。关于基本的MapReduce就介绍到这里,后续的省略的第3456步会在后面文章中更新的。