最近在复习Spring的面试题,关于Spring Bean的生命周期一直没有很深入的理解,自己结合源码参考了网上的几篇文章,写了一点东西,方便理解。
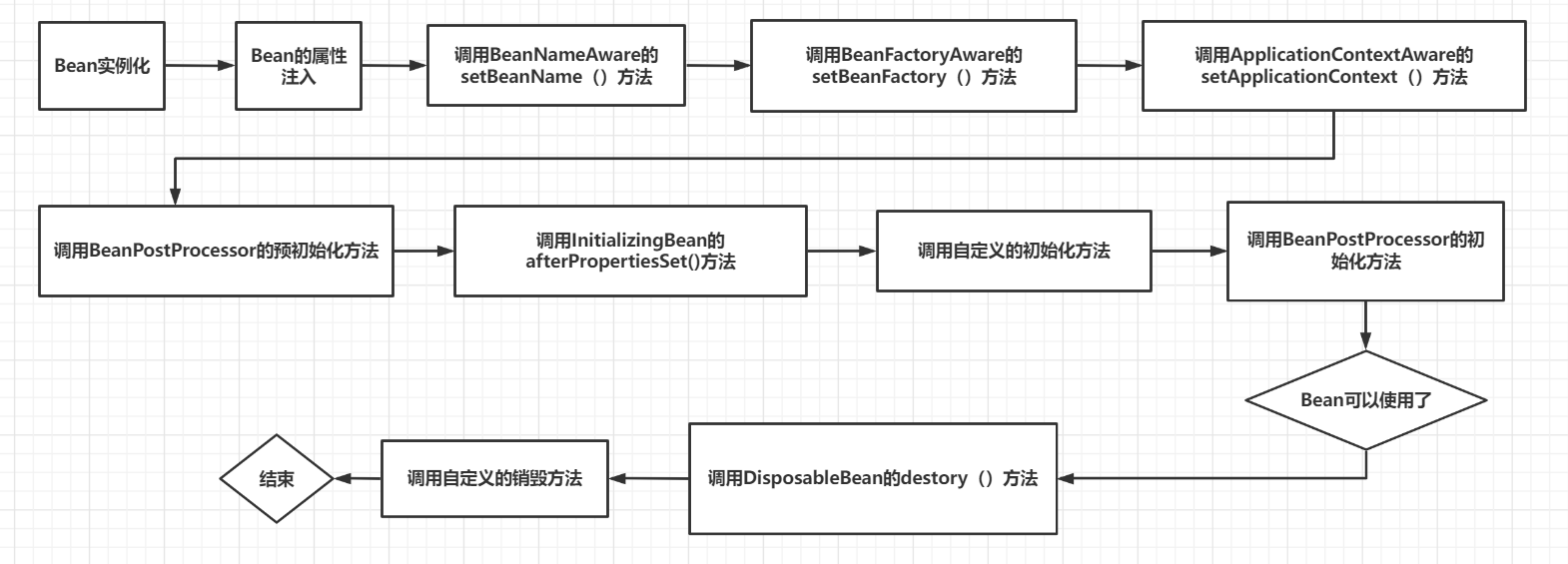
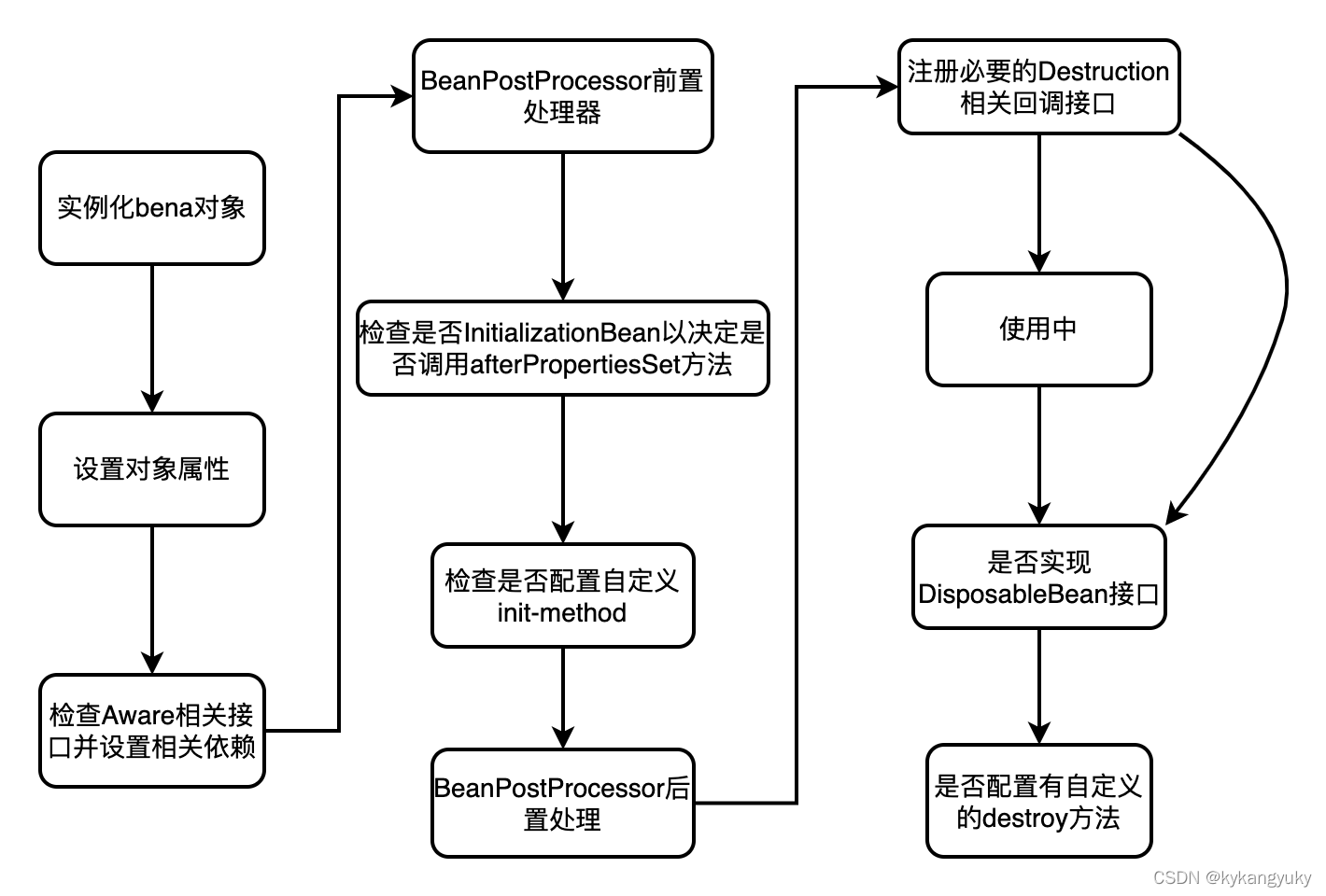
- Spring 启动,查找并加载需要被 Spring 管理的 Bean,进行 Bean 的实例化;
- Bean 实例化后,对 Bean 的引入和值注入到 Bean 的属性中;
- 如果 Bean 实现了 BeanNameAware 接口的话,Spring 将 Bean 的 Id 传递给 setBeanName() 方法;
- 如果 Bean 实现了 BeanFactoryAware 接口的话,Spring 将调用 setBeanFactory() 方法,将 BeanFactory 容器实例传入;
- 如果 Bean 实现了 ApplicationContextAware 接口的话,Spring 将调用 Bean 的 setApplicationContext() 方法,将 Bean 所在应用上下文引用传入进来;
- 如果 Bean 实现了 BeanPostProcessor 接口,Spring 就将调用它们的postProcessBeforeInitialization() 方法;
- 如果 Bean 实现了 InitializingBean 接口,Spring 将调用它们的 afterPropertiesSet() 方法。类似地,如果 Bean 使用 init-method 声明了初始化方法,该方法也会被调用;
- 如果 Bean 实现了 BeanPostProcessor 接口,Spring 就将调用它们的 postProcessAfterInitialization() 方法;
- 此时,Bean 已经准备就绪,可以被应用程序使用了。它们将一直驻留在应用上下文中,直到应用上下文被销毁;
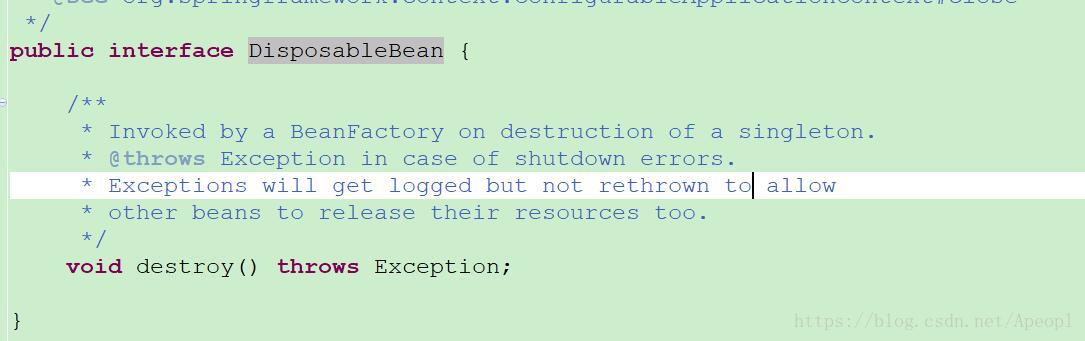
- 如果 Bean 实现了 DisposableBean 接口,Spring 将调用它的 destory() 接口方法,同样,如果 Bean 使用了 destory-method 声明销毁方法,该方法也会被调用。
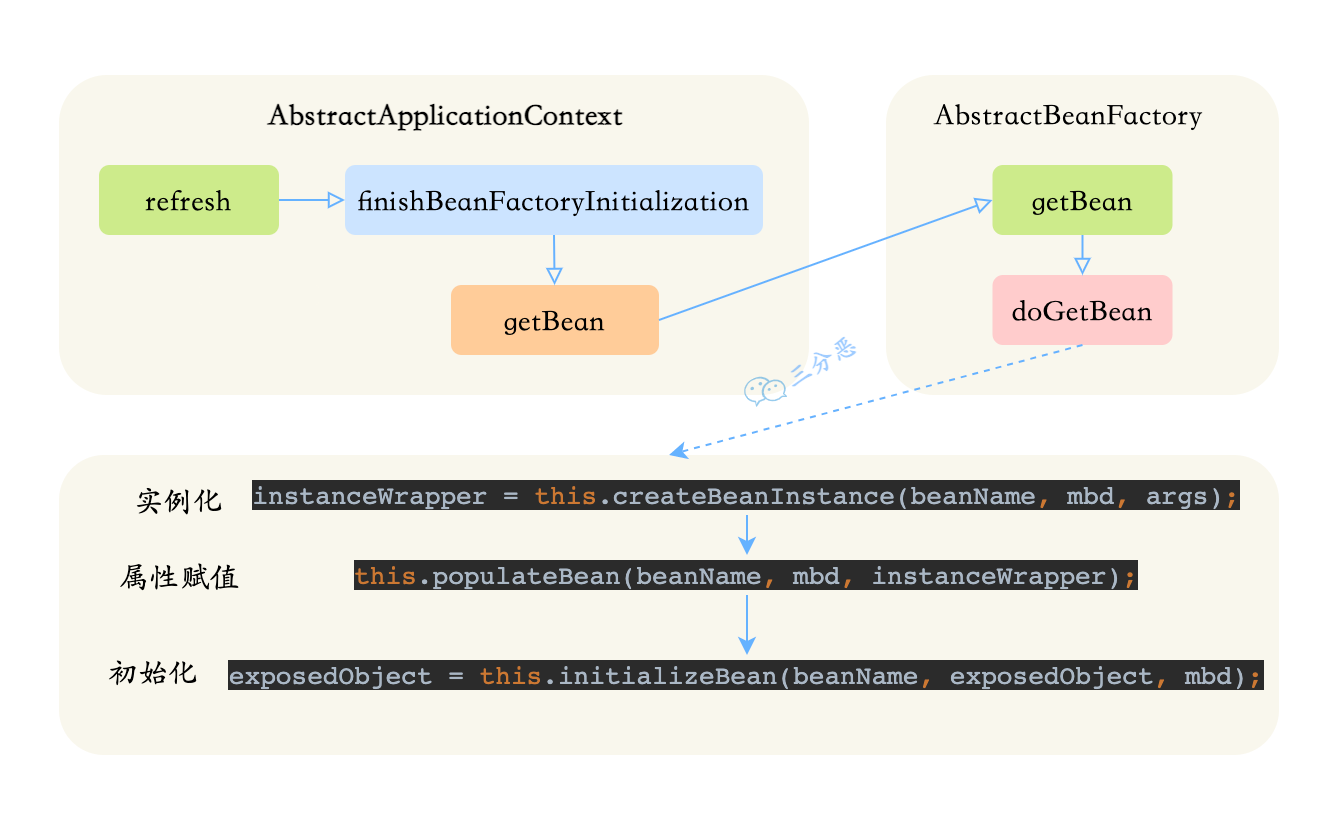
让我们结合源码捋一遍这个过程,主要的过程在org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java这个类中
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java initializeBean()方法protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);return null;}, getAccessControlContext());}else {/*** 调用Bean实现的Aware接口的方法,主要包括下面三个接口* BeanNameAware ----> setBeanName()* BeanClassLoaderAware ----> setBeanClassLoader()* BeanFactoryAware ----> setBeanFactory()*/invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);}Object wrappedBean = bean;if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {/** 调用Bean对象的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法,此处会执行标注@PostConstruct注解的方法 */// 此处会调用ApplicationContextAwareProcessor执行其他的aware方法.wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);}try {/*** 执行Bean的初始化方法:** 1.先判断Bean是否实现了InitializingBean接口,如果实现了InitializingBean接口,则调用Bean对象的afterPropertiesSet方法;* 2.然后判断Bean是否有指定init-method方法,如果指定了init-method方法,则调用bean对象的init-method指定的方法.*/invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);}catch (Throwable ex) {throw new BeanCreationException((mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);}if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {/*** 调用Bean对象的postProcessAfterInitialization方法** 如果需要创建代理,在该步骤中执行postProcessAfterInitialization方法的时候会去创建代理* 调用AbstractAutoProxyCreator类的postProcessAfterInitialization方法,然后调用wrapIfNecessary方法去创建代理.*** 另外还有一些Aware接口,也会在该步骤中执行,例如:ApplicationContextAwareProcessor后置处理器,对应的setApplicationContext方法会被执行.*/wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);}return wrappedBean;}
- 如果 Bean 实现了 BeanNameAware 接口的话,Spring 将 Bean 的 Id 传递给 setBeanName() 方法;
- 如果 Bean 实现了 BeanFactoryAware 接口的话,Spring 将调用 setBeanFactory() 方法,将 BeanFactory 容器实例传入;
- 如果 Bean 实现了 ApplicationContextAware 接口的话,Spring 将调用 Bean 的 setApplicationContext() 方法,将 Bean 所在应用上下文引用传入进来;
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java/*** 执行所有的Aware接口中的方法* @param beanName bean的名称* @param bean bean对象*/private void invokeAwareMethods(final String beanName, final Object bean) {// 如果Bean实现了Aware接口if (bean instanceof Aware) {// 如果实现了BeanNameAware接口,则调用Bean的setBeanName方法if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) {((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName);}// 如果实现了BeanClassLoaderAware接口,则调用Bean的setBeanClassLoader方法if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) {ClassLoader bcl = getBeanClassLoader();if (bcl != null) {((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(bcl);}}// 如果实现了BeanFactoryAware接口,则调用Bean的setBeanFactory方法if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this);}}}ApplicationContextAwareProcessor.javaprivate void invokeAwareInterfaces(Object bean) {if (bean instanceof Aware) {//....////如果 Bean 实现了 ApplicationContextAware 接口的话,Spring 将调用 Bean 的 setApplicationContext() 方法,//将 Bean 所在应用上下文引用传入进来;if (bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware) {((ApplicationContextAware) bean).setApplicationContext(this.applicationContext);}}}
- 如果 Bean 实现了 BeanPostProcessor 接口,Spring 就将调用它们的postProcessBeforeInitialization() 方法;
public interface BeanPostProcessor {// 该方法是Spring后置处理器中的方法// 该方法是在Bean实例化(new)之后,初始化(设置各种属性)之前会被调用// 在调用afterPropertiesSet方法之前会被调用@Nullabledefault Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {return bean;}// 在bean初始化之后会被调用// 在调用InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet方法或者init-method指定的方法执行之后调用.@Nullabledefault Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {return bean;}}
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java@Overridepublic Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)throws BeansException {Object result = existingBean;for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {/** 调用InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor来处理标注有@PostConstruct注解的方法. *//** 执行ApplicationContextAwareProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization*/Object current = processor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName);if (current == null) {return result;}result = current;}return result;}
- 如果 Bean 实现了 InitializingBean 接口,Spring 将调用它们的 afterPropertiesSet() 方法。类似地,如果 Bean 使用 init-method 声明了初始化方法,该方法也会被调用;
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.javaprotected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd)throws Throwable {// 判断bean对象是否为InitializingBean的实例// 如果实现了InitializingBean接口,则只掉调用bean的afterPropertiesSet方法boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean);if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) {if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");}if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {try {AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () -> {((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();return null;}, getAccessControlContext());}catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) {throw pae.getException();}}else {((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();}}// 判断是否指定了init-method方法,如果指定了init-method方法,而且初始化方法不是afterPropertiesSet// 则通过反射执行指定的初始化方法if (mbd != null && bean.getClass() != NullBean.class) {// 获取初始化方法的名称String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName();if (StringUtils.hasLength(initMethodName) &&!(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) &&!mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) {// 调用init-method方法时也是通过反射实现invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd);}}}
- 如果 Bean 实现了 BeanPostProcessor 接口,Spring 就将调用它们的 postProcessAfterInitialization() 方法;
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
调用Bean对象的postProcessAfterInitialization方法@Overridepublic Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)throws BeansException {Object result = existingBean;for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {// 该步骤中会创建代理类.// 在bean初始化之后会被调用// 在调用InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet方法或者init-method指定的方法执行之后调用.Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);if (current == null) {return result;}result = current;}return result;}
- 此时,Bean 已经准备就绪,可以被应用程序使用了。它们将一直驻留在应用上下文中,直到应用上下文被销毁;
- 如果 Bean 实现了 DisposableBean 接口,Spring 将调用它的 destory() 接口方法,同样,如果 Bean 使用了 destory-method 声明销毁方法,该方法也会被调用。
DisposableBeanAdapter.java@Overridepublic void destroy() {//...//if (this.invokeDisposableBean) {if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Invoking destroy() on bean with name '" + this.beanName + "'");}try {// 9. 若实现 DisposableBean 接口,则执行 destory()方法if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () -> {((DisposableBean) bean).destroy();return null;}, acc);}else {((DisposableBean) bean).destroy();}}catch (Throwable ex) {//...//}}// 10. 若配置自定义的 detory-method 方法,则执行if (this.destroyMethod != null) {invokeCustomDestroyMethod(this.destroyMethod);}else if (this.destroyMethodName != null) {Method methodToCall = determineDestroyMethod(this.destroyMethodName);if (methodToCall != null) {invokeCustomDestroyMethod(methodToCall);}}}
总结:
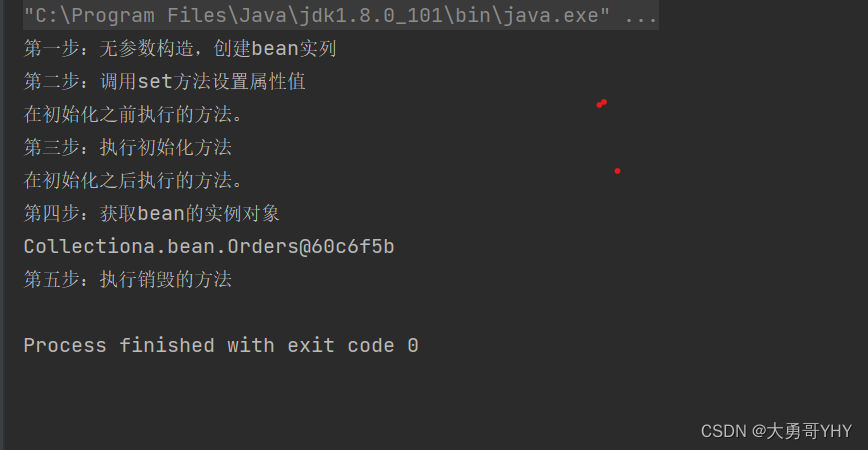
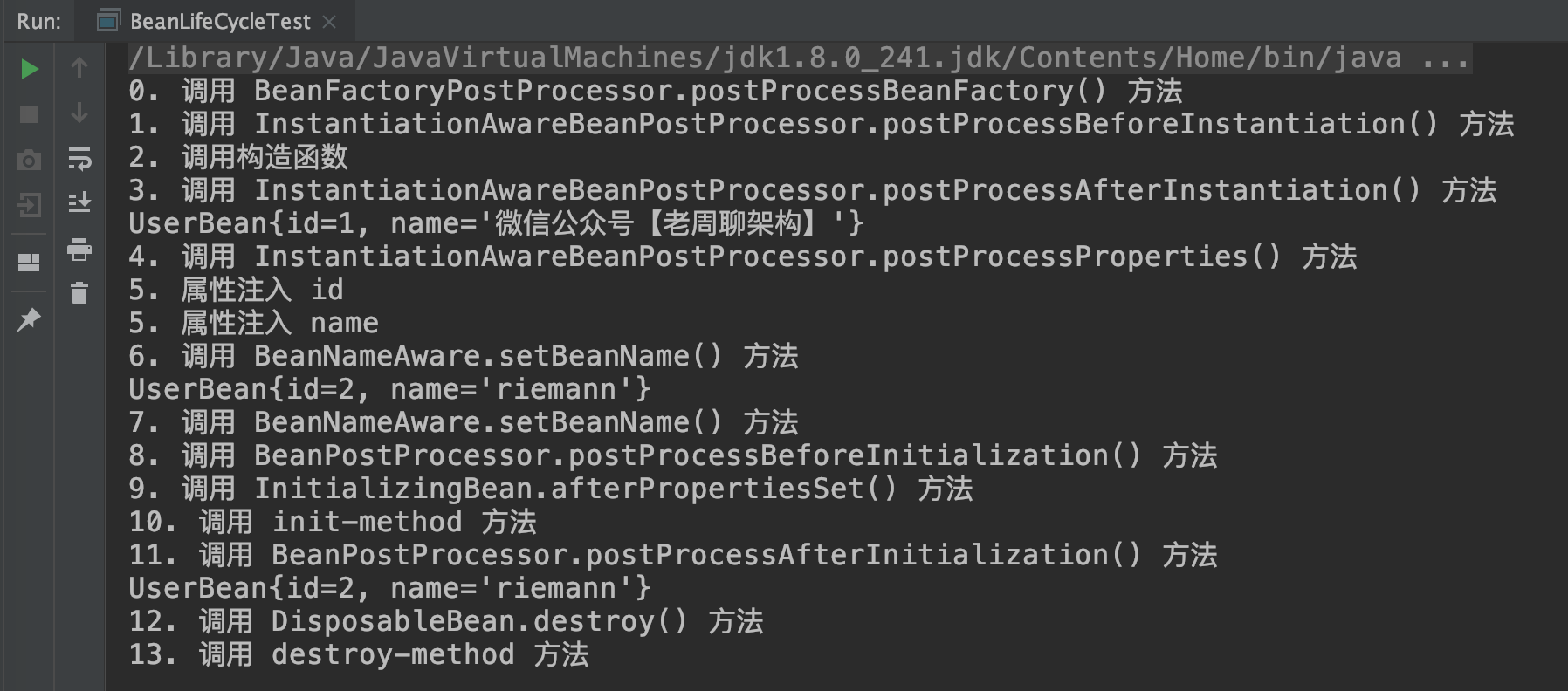
- 首先是实例化、属性赋值、初始化、销毁这 4 个大阶段;
- 再是初始化的具体操作,有 Aware 接口的依赖注入、BeanPostProcessor 在初始化前后的处理以及 InitializingBean 和 init-method 的初始化操作;
- 销毁的具体操作,有注册相关销毁回调接口,最后通过DisposableBean 和 destory-method 进行销毁。







![[Linux]Ubuntu 换源 20.04 阿里源](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20200927113617756.png#)