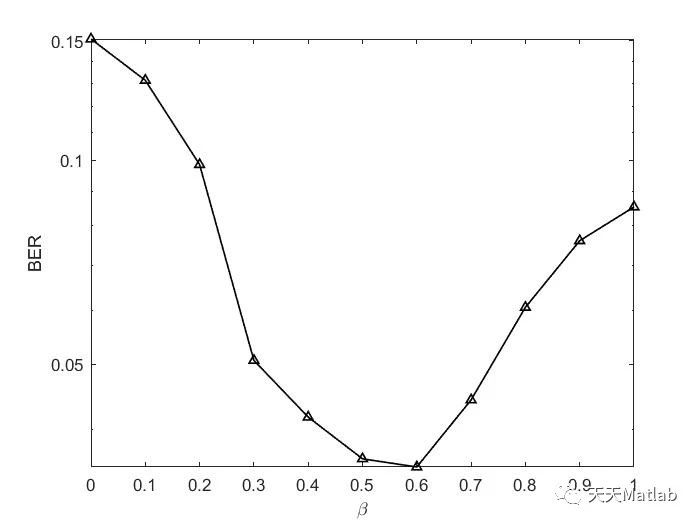
ldpc编码针对的是上下行数据的编码,也是5G最重要的一种编码。
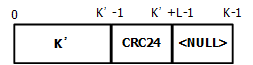
1 TB块添加CRC
这个是和UCI POLAR区别的一个地方,UCI是对每个cb块添加crc.

% Get transport block size after CRC attachment according to 38.212% 6.2.1 and 7.2.1, and assign CRC polynomial to CRC field of output% structure infoif A > 3824L = 24;info.CRC = '24A';elseL = 16;info.CRC = '16';end
**此处会对TB块进行crc的添加,具体添加crc的过程已经在上一篇文章
《UCI和数据复用在pusch上传输(第五部分)---polar编码》分享过了,
这里就不在做复述。**
2 graph选择

% LDPC base graph selectionif A <= 292 || (A <= 3824 && R <= 0.67) || R <= 0.25bgn = 2;elsebgn = 1;end
3 cb块分段和cb块添加crc






具体添加crc的过程已经在上一篇文章
《UCI和数据复用在pusch上传输(第五部分)—polar编码》分享过了,
这里就不在做复述。
% Get the maximum code block sizeif bgn == 1Kcb = 8448;elseKcb = 3840;end% Get number of code blocks and length of CB-CRC coded blockif B <= KcbL = 0;C = 1;Bd = B;elseL = 24; % Length of the CRC bits attached to each code blockC = ceil(B/(Kcb-L));Bd = B+C*L;end% Obtain the number of bits per code block (excluding CB-CRC bits)cbz = ceil(B/C);% Get number of bits in each code block (excluding filler bits)Kd = ceil(Bd/C);% Find the minimum value of Z in all sets of lifting sizes in 38.212% Table 5.3.2-1, denoted as Zc, such that Kb*Zc>=Kdif bgn == 1Kb = 22;elseif B > 640Kb = 10;elseif B > 560Kb = 9;elseif B > 192Kb = 8;elseKb = 6;endendZlist = [2:16 18:2:32 36:4:64 72:8:128 144:16:256 288:32:384];Zc = min(Zlist(Kb*Zlist >= Kd));% Get number of bits (including <NULL> filler bits) to be input to the LDPC% encoderif bgn == 1K = 22*Zc; %这块为啥一定要是Zc的倍数,这个是个问题?elseK = 10*Zc;end
4 UL_SCH的通道编码(这是编码最难的部分需要进一步搞清楚)





% Get lifting set numberZSets = {[2 4 8 16 32 64 128 256],... % Set 1[3 6 12 24 48 96 192 384],... % Set 2[5 10 20 40 80 160 320],... % Set 3[7 14 28 56 112 224],... % Set 4[9 18 36 72 144 288],... % Set 5[11 22 44 88 176 352],... % Set 6[13 26 52 104 208],... % Set 7[15 30 60 120 240]}; % Set 8for setIdx = 1:8 % LDPC lifting size set indexif any(Zc==ZSets{setIdx})break;endend% Pre-stored H types for each BGN and setIdx pair% 这个是怎么来的不知道,需要进一步看看Htype = {3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 2, 3;4, 4, 4, 1, 4, 4, 4, 1};% Get the matrix with base graph number 'bgn' and set number 'setIdx'.% The element of matrix V in the following is H_BG(i,j)*V(i,j), where% H_BG(i,j) and V(i,j) are defined in TS 38.212 5.3.2; if V(i,j) is not% defined in Table 5.3.2-2 or Table 5.3.2-3, the elements are -1.% %这个就是协议中的v_ijswitch bgncase 1switch setIdxcase 1V = bgs.BG1S1;case 2V = bgs.BG1S2;case 3V = bgs.BG1S3;case 4V = bgs.BG1S4;case 5V = bgs.BG1S5;case 6V = bgs.BG1S6;case 7V = bgs.BG1S7;otherwise % 8V = bgs.BG1S8;endNplus2Zc = Zc*(66+2);otherwise % bgn = 2switch setIdxcase 1V = bgs.BG2S1;case 2V = bgs.BG2S2;case 3V = bgs.BG2S3;case 4V = bgs.BG2S4;case 5V = bgs.BG2S5;case 6V = bgs.BG2S6;case 7V = bgs.BG2S7;otherwise % 8V = bgs.BG2S8;end Nplus2Zc = Zc*(50+2);%为啥要求这和?endP = nr5g.internal.ldpc.calcShiftValues(V,Zc);%根据V和Zc得到P P=mod(V,Zc)% The element of matrix P in the following is P(i,j) in TS 38.212 5.3.2% when V(i,j) are defined in Table 5.3.2-2 or Table 5.3.2-3. If not% defined, the elements are -1.P = zeros(size(V));for i = 1:size(V,1)for j = 1:size(V,2)if V(i,j) == -1P(i,j) = -1;elseP(i,j) = mod(V(i,j),Z);endendendP1 = P(:,1:(size(P,2) - size(P,1)));%取了P的前面(52-42)或者(67-45)行,为啥要取这个?C = size(infoBits,2); %获取层数 codewords = zeros(Nplus2Zc,C);% Get shift values matrixP = nr5g.internal.ldpc.calcShiftValues(V,Zc);P1 = P(:,1:(size(P,2) - size(P,1)));C = size(infoBits,2);codewords = zeros(Nplus2Zc,C);for r = 1:C% Per code-block processing onlyinfoVec = reshape(infoBits(:,r),Zc,[]);%将信息bit(协议中的C_k)变成Zc行,K/Zc列。d = blockMultiply(P1,infoVec);d0 = d(:,1:4);% Solve 4 equations for Htype * m = d0switch Htype{bgn,setIdx}case 1% H1 = [ 1 0 -1 -1;% -1 0 0 -1;% 0 -1 0 0;% 1 -1 -1 0 ];m1 = sum(d0, 2);m2 = d0(:,1) + m1([2:end 1]);m3 = d0(:,2) + m2;m4 = d0(:,3) + m1 + m3;case 2% H2 = [ 0 0 -1 -1;% 105 0 0 -1;% -1 -1 0 0;% 0 -1 -1 0 ];m1 = sum(d0, 2);shift = mod(105, Zc);if shift > 0m1 = m1([(end-shift+1):end 1:(end-shift)]);endm2 = d0(:,1) + m1;m4 = d0(:,4) + m1;m3 = d0(:,3) + m4;case 3% H3 = [ 1 0 -1 -1;% 0 0 0 -1;% -1 -1 0 0;% 1 -1 -1 0 ];m1 = sum(d0, 2);m2 = d0(:,1) + m1([2:end 1]);m3 = d0(:,2) + m1 + m2;m4 = d0(:,3) + m3;otherwise % == 4% H4 = [ 0 0 -1 -1;% -1 0 0 -1;% 1 -1 0 0;% 0 -1 -1 0 ];m1 = sum(d0, 2);m1 = m1([end 1:(end-1)]);m2 = d0(:,1) + m1;m3 = d0(:,2) + m2;m4 = d0(:,4) + m1;end% Get other parity bitsP3 = P(5:end,size(P1,2)+(1:4));p = blockMultiply(P3, [m1 m2 m3 m4]) + d(:,5:end);% Form codeword and assign to outputcodewords(:,r) = [infoBits(:,r); mod([m1; m2; m3; m4; p(:)],2)]; end
end
5 速率匹配






% Get code block soft buffer sizeif ~isempty(Nref)fcnName = 'nrRateMatchLDPC';validateattributes(Nref, {'numeric'}, ...{'scalar','integer','positive'},fcnName,'NREF');Ncb = min(N,Nref);else % No limit on buffer sizeNcb = N;end% Get starting position in circular bufferif bgn == 1if rv == 0k0 = 0;elseif rv == 1k0 = floor(17*Ncb/N)*Zc;elseif rv == 2k0 = floor(33*Ncb/N)*Zc;else % rv is equal to 3k0 = floor(56*Ncb/N)*Zc;endelseif rv == 0k0 = 0;elseif rv == 1k0 = floor(13*Ncb/N)*Zc;elseif rv == 2k0 = floor(25*Ncb/N)*Zc;else % rv is equal to 3k0 = floor(43*Ncb/N)*Zc;endend% Get rate matching output for all scheduled code blocks and perform% code block concatenation according to Section 5.4.2 and 5.5out = [];for r = 0:C-1if r <= C-mod(outlen/(nlayers*Qm),C)-1E = nlayers*Qm*floor(outlen/(nlayers*Qm*C));elseE = nlayers*Qm*ceil(outlen/(nlayers*Qm*C));endout = [out; cbsRateMatch(in(:,r+1),E,k0,Ncb,Qm)]; %#ok<AGROW>endendfunction e = cbsRateMatch(d,E,k0,Ncb,Qm)
% Rate match a single code block segment as per TS 38.212 Section 5.4.2% Bit selection, Section 5.4.2.1k = 0;j = 0;e = zeros(E,1,class(d));while k < Eif d(mod(k0+j,Ncb)+1) ~= -1 % Filler bitse(k+1) = d(mod(k0+j,Ncb)+1);k = k+1;endj = j+1;end% Bit interleaving, Section 5.4.2.2e = reshape(e,E/Qm,Qm);e = e.';e = e(:);end