什么是DIKW模型?
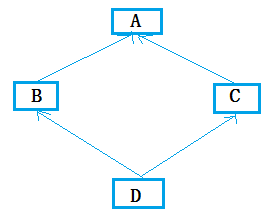
D=Data,表示数据,I=Information,表示信息,K=Knowledge,表示知识,W=Wisdom,表示智慧。DIKW模型将数据、信息、知识、智慧纳入到一种金字塔形的层次体系,每一层比下一层都赋予的一些特质。原始观察及量度获得了数据、分析数据间的关系获得了信息。在行动上应用信息产生了知识。智慧关心未来,它含有暗示及滞后影响的意味。
What is the relationship between Data and Knowledge? (How do you find knowledge from Data?)
1.Information=Data + Contents 2.Knowledge = Valuable Information
∴Data->information->knowledge
通过从数据中发现relations,发现patterns来找knowledge(通过一些技术)
What is Wisdom? The difference between Knowledge and Wisdom?
Wisdom which is integrated knowledge and happens when you understand why the patterns are occurring
Wisdom = Knowledge + Value(experience, insights, deep understanding, actionable knowledge)
Knowledge answers “how” and "know-how“ questions
Wisdom answers “what to do, act or carry out"
How do you apply the concepts of DIKW Model to Big Data and Machine Learning? (If you understand the DIKW Model that will help you study Big Data and Machine Learning more effectively. Why ?)
(没找到标准答案)
Knowledge and Wisdom (Decision) come from the extracting value and insights of Big data.
什么是大数据(Big Data)?
大数据是大量的数据,超出了技术的存储容量,不能有效的管理和加工。Big Data is not about the size of the data, it’s about the value within the data. It uses range of quantitative and investigative techniques to derive value from data(不在于数据量,而在于价值,使用一系列的方法从数据中获取价值)
大数据的特征?
3V:Volume——总量大,Variety——类型多,Velocity——变化快
4V:Volume——总量大,Variety——类型多,Velocity——变化快,Value——有价值
5V:Volume—总量大,Variety—类型多,Velocity—变化快,Value—价值高,Veracity—真实性
大数据的来源?
各种用户,应用,系统,网络,传感器等产生的信息
大数据的真正意义?
大数据关心的不是数据的规模,而是数据中的有用信息,或者说数据的价值所在
What are the major values and benefits that Big Data adds to the business in both Publics and private sectors? (Three most recognized values based the US/China industries surveyed) 在公共或个人因素上,大数据主要价值和益处?(三个公认的价值)
•Cost reduction. Big data technologies such as Hadoop and cloud-based analytics bring significant cost advantages when it comes to storing large amounts of data –plus they can identify more efficient ways of doing business. 降低成本。在存储大量数据时,诸如Hadoop和基于云的分析等大数据技术带来了显著的成本优势,此外,它们还可以确定更高效的经营方式。
•Faster, better decision making. With the speed of Hadoop and in-memory analytics, combined with the ability to analyze new sources of data, businesses are able to analyze information immediately –and make decisions based on what they’ve learned. 更快,更好的决策。借助Hadoop和内存分析的速度,再加上分析新数据源的能力,企业能够立即分析信息,并根据所学知识做出决策。
•New products and services. With the ability to gauge customer needs and satisfaction through analytics comes the power to give customers what they want. Davenport points out that with big data analytics, more companies are creating new products to meet customers’ needs. 新产品和服务。有了通过分析来衡量客户需求和满意度的能力,就有能力满足客户的需求。达文波特指出,随着大数据分析,越来越多的公司正在开发新产品来满足客户的需求。
大数据的结构层次
从底层到顶层:数据源层——数据存储层——数据处理/分析层——数据输出层
大数据分析生命周期
1.发现 2.数据准备 3.模型规划 4.模型构建 5.结果交流 6.实施
什么是数据分析?
数据分析是对数据进行清洗和组织,然后通过模型进行数据剖析,提取数据中有用信息的过程。
Big Data how it works? (How it finds the value from the huge amount of large data ?)如何从大数据中提取价值?
•使用数据挖掘机器学习技术发现数据相关性、隐藏模式、预测和趋势分析
•从数据中提取洞察力,通过操纵大型数据集,使用统计分析方法和基于算法的预测建模,为隐藏的模式和趋势提供可操作的洞察力。
•商业分析和商业智能都依赖于数据和统计分析方法,如数据挖掘、报告、文本挖掘、文本分析、数据可视化、风险分析、预测分析和预测建模。两者都可以驱动即时、自动的决策——比如实时分析交通模式,从而实现实时、自动的交通管理——或者它们可以作为人类决策的输入。
什么是大数据分析?
大数据分析是一个用来提取有意义的见解的过程,如隐藏的模式、未知的相关性、市场趋势和客户偏好。 Big Data analytics provides various advantages—it can be used for better decision making, preventing fraudulent activities, among other thing
大数据分析的类型
发现数据相关性,隐藏模式,使用数据挖掘技术预测分析
•描述性分析——发生了什么?
•诊断分析——为什么会发生?
•预测分析——可能会发生什么?
•说明性分析——应该发生什么。提供最优决定
Among those four Big Data Analytics, which analytics are focused on the analysis of the past events, which analytics their results are for the future decision?(哪一个类型是分析过去的事,哪一个是预测将来的决定)
Descriptive analysis answers the “what happened” by summarizing past data, usually in the form of dashboards
Predictive analysis attempts to answer the question “what is likely to happen”. This type of analytics utilizes previous data to make predictions about future outcomes.
What are the layers that required for Big Data Process ?
Data Analysis Layer. 数据分析层。
When you want to use the data you have stored to find out something useful, you will need to process and analyse it. The analysis layer reads the data digested by the data massaging and store layer. 当你想用你储存的数据来找出有用的东西时,你需要对它进行处理和分析。分析层读取由数据处理和存储层消化的数据。
Four Big Data Analytics models, which model is the most useful for designing Big Data Applications that could benefit the company for decision making ?
Prescriptive Analytics: Recommends actions you can take to affect those outcomes. Tell organizations what they should do in order to achieve a desired result.(为了某个目标推荐你采取某些行动,告诉你应该做什么才能达到你想要的结果)
6种大数据分析技术
1.A/B测试(A/B testing)
2.数据融合与数据集成(Data fusion and data integration)
3.数据挖掘(Data Mining)
4.机器学习(Machine Learning)
5.自然语言处理(Natural Language Processing)
6.统计(Statistics)
什么是大数据技术?
大数据技术可以被定义为一种软件-实用程序,旨在分析、处理和提取极其复杂和庞大的,传统技术无法处理的数据集的信息
大数据技术的类型
两类:1.运营型大数据技术 2.分析型大数据技术
前沿的大数据技术:1.数据存储 2.数据挖掘 3.数据分析 4.数据可视化
什么是机器学习(Machine Learning)?
机器学习是门学科,它致力于研究如何通过计算手段,利用经验来改善系统自身的性能,在计算机系统中,"经验"通常以"数据"的形式存在,因此,机器学习所研究的主要内容,是关于在计算机上从数据中产生"模型"的算法,即"学习算法"。有了学习算法,我们把经验数据提供给它,它就能基于这些数据产生模型;在面对新的情况时,模型会给我们提供相应的判断,可以说机器学习是研究关于"学习算法"的学问。
What is “concepts”?
A concept is a set of objects, symbols, or events grouped together because they share certain characteristics. Such as “Pattern”.概念是一组物体、符号或事件的集合,因为它们具有某些共同的特征。如“模式”。
机器学习是如何从数据中学习的?
•机器学习是一种数据分析技术,它教会计算机做人类和动物天生具备的事情:从经验中学习。
•机器学习算法使用计算方法直接从数据中“学习”信息,而不依赖于预先确定的方程作为模型。
How does machine learning work?机器学习如何工作?
These machine learning algorithms use the patterns contained in the training data to perform classification and future predictions. • Whenever any new input is introduced to the ML model, it applies its learned patterns over the new data to make future predictions. • Based on the final accuracy, one can optimize their models using various standardized approaches. In this way, Machine Learning model learns to adapt to new examples and produce better results
这些机器学习算法使用训练数据中包含的模式来进行分类和未来预测。•每当有新的输入被引入ML模型时,它将其学习到的模式应用于新数据,以做出未来的预测。•基于最终的准确性,可以使用各种标准化方法优化他们的模型。通过这种方式,机器学习模型学习适应新的例子,并产生更好的结果
In general, Machine Learning is used to accomplish two things, What are they?机器学习被用于完成哪两件事?
Generally, Machine Learning are used to accomplish two things: 1. Prediction: make predictions about the future based on data about the past 2. Inference: discover patterns in data.一般情况下,机器学习用于完成两件事:1。预测:根据过去的数据预测未来。推论:在数据中发现模式
The difference between Data Mining and Machine Learning?
1)Machine Learning focuses on prediction, based on known properties learned from the training data.机器学习的重点是基于从训练数据中学习到的已知属性进行预测。
2)focused on improving performance of a learning agent专注于提高学习主体的表现
3)also looks at real-time learning and robotics – areas not part of data mining还关注了实时学习和机器人技术——这些领域不是数据挖掘的一部分
Data Mining
1)integrates theory and heuristics整合理论和启发式
2)Data Mining focuses on the discovery of previously unknown properties in the data. This is the analysis step of knowledge discovery in Database looking for Patterns and Trends on prediction数据挖掘专注于发现数据中先前未知的属性。这是数据库中知识发现的分析步骤,寻找预测的模式和趋势
What is a Model?
Model is a mathematical object describing the relationship between the features and the target.模型是描述特征与目标之间关系的数学对象。
何时使用机器学习?
1. 它们涉及到你想要自动化的重复决策或评估,并且需要一致的结果。
2. 很难或不能明确描述决策背后的解决方案或标准
3.您已经标记了数据或现有的示例,可以在这些示例中描述情况并将其映射到正确的结果
为什么说机器学习是重要的?
- 有些任务不能被很好的定义
- 关系和相关性被隐藏在大量的数据中,机器学习或数据挖掘或许能发现这些关系
- 设计师设计的机器经常在他们的工作环境中不能像他们期望的那样工作
- 关于某些任务的可用知识数量可能太大,无法由人类进行显式编码(例如,医疗诊断)。
- 环境会随着时间而变化
-
关于任务的新知 识不断被人类发现。“手工”不断地重新设计系统可能是困难的。
机器学习的类别
- Supervised Learning(监督学习,指导性的学习)
- Unsupervised Learning(无监督学习,非指导性的学习)
- Semi-Supervised Learning (半监督学习,半指导性的学习)
- Reinforcement Learning (强化学习)
什么是Supervised Learning(监督学习,指导性的学习)?
监督学习算法采用已知的输入数据集(训练集)和已知的数据响应(输出),并训练模型生成对新输入数据的输出的合理预测。
1.已知训练数据的正确类别2.使用带标签的训练数据来学习数据的模型3.随后使用学到的模型来预测测试数据。4.学习从一组输入到目标变量的映射
预测性,包括classification分类(knn,贝叶斯,决策树),regression回归(线性,逻辑)
How to Work: This algorithm consist of a target / outcome variable(or dependent variable) which is to be predictedfrom a given set of predictors (independent variables).
• Using these set of variables, we generate a function that map inputs to desired outputs.
• The training process continues until the model achieves a desired level of accuracy on the training data. Examples of Supervised Learning: Regression, Decision Tree, Random Forest, KNN, Logistic Regression etc.
该算法由一个目标/结果变量(或因变量)组成,该变量将由一组给定的预测器(自变量)来预测。
•使用这些变量集,我们生成一个将输入映射到所需输出的函数。
•继续训练过程,直到模型在训练数据上达到期望的精度水平。监督学习的例子:回归、决策树、随机森林、KNN、Logistic回归等。
什么是Unsupervised Learning(无监督学习,非指导性的学习)?
使用机器学习算法去分析和聚类无标签的数据集。不需要人工干预就能发现隐藏的模式,不用训练集指导,相反,模型本身能从被给的数据中找到隐藏的模式
描述性,包括clustering聚类,关联规则,模式识别
How to Work: In this algorithm, we do not have any target or outcome variable to predict / estimate.在这个算法中,我们没有任何目标或结果变量来预测/估计。
• It is used for clustering population in different groups, which is widely used for segmenting customers in different groups for specific intervention.•用于对不同群体的人群进行聚类,广泛用于对不同群体的客户进行细分,进行具体干预。
• Examples of Unsupervised Learning: Apriori algorithm, K-means.•无监督学习的例子:Apriori算法,K-means。
什么是强化学习(Reinforcement machine learning)?
强化学习是一种通过产生动作和发现错误或奖励与环境交互的学习方法。
试错搜索和延迟奖励是强化学习最相关的特征。
这种方法允许机器和软件代理在特定的环境中自动确定理想的行为,以最大化其性能。
需要简单的奖励反馈,以便了解哪个行动是最好的;这就是所谓的强化信号
什么是半监督学习(Semi-Supervised machine learning)?
介于监督学习和非监督学习之间,他们在训练中同时使用有标记和无标记的数据——通常是少量有标记的数据和大量无标记的数据。
使用这种方法的系统能够大大提高学习的准确性。
通常,当获取的标签数据需要技能和相关资源来训练/学习时,选择半监督学习。否则,获取未标记数据通常不需要额外的资源。
许多机器学习研究人员发现,当将未标记数据与少量标记数据结合使用时,可以显著提高学习准确性。
What is the key difference between supervised vs. unsupervised ML?监督学习和无监督学习的关键区别
两者的关键不同,核心是有无先验知识
1. 机器学习算法在大数据中发现模式。这些不同的算法可以根据它们“学习”数据进行预测的方式分为两类。这就是监督学习和无监督学习。
2. 在监督学习中,科学家充当向导,教算法得出什么结论或预测。在无监督学习中,没有正确答案,没有老师,算法只能自己去发现和呈现数据中有趣的隐藏结构。
3.监督学习模型将使用训练数据来学习输入和输出之间的链接.
4. 无监督学习不使用输出数据。在无监督学习中,它们不会是任何标注的先验知识,而在监督学习中,它们可以访问标签,并拥有关于数据集的先验知识
5. 监督学习:其思想是训练可以被一般化,并且模型可以用在新数据上,具有一定的准确性。
6. 有监督学习算法:支持向量机、线性和logistic回归、神经网络、分类树和随机森林等。
7. 无监督算法可以分为不同的类别:聚类算法、K-means、层次聚类、降维算法、异常检测等。
8. 分类和回归算法在有监督学习中得到了广泛的应用。支持向量机(SVM)是具有相关学习算法的有监督的机器学习模型,可用于分类和回归,但主要用于分类问题。
9. 在SVM模型中,我们将每个数据项绘制为n维空间中的一个点(其中n是我们拥有的特征),每个特征的值是特定坐标的值。然后通过寻找区分这两类的超平面来进行分类。
10. 回归算法的主要目标是预测离散值或连续值。在某些情况下,预测值可以用来识别属性之间的线性关系。基于这些问题,可以使用差分回归算法。一些基本的回归算法是线性回归、多项式回归等
11.聚类在无监督学习中得到广泛应用。聚类是将数据点分成若干组,使相同的特征点以聚类的形式聚在一起。聚类算法比较多;其中包括连接性模型、质心模型、分布模型和密度模型
12. 层次聚类属于无监督学习。层次聚类,顾名思义,是一种构建集群层次结构的算法。该算法首先将所有数据点分配到自己的集群中。然后两个最近的簇合并成同一个簇。最后,当只剩下一个聚类时,该算法终止
13.KMeans采用无监督聚类方法。数据将根据其特征被划分为k个集群。每个簇都用它的质心来表示,质心定义为簇中各点的中心。KMeans是简单和快速的,但它每次运行的结果不一定相同

What is training Data ? What is test Data ? What are the ratio when using both data in Supervised model. (What do you receive the results after testing Model ?)
第一问:To help us train the model, we simply use the data from the training set to determine the parameters of the fitting curve.帮助我们训练模型,简单的说就是通过训练集的数据让我们确定拟合曲线的参数。
第二问: To test the accuracy of the model that has been trained.Of course, test set does not guarantee the correctness of the model, it just says that similar data in this model will produce similar results.Because we are training model, the parameters are all according to the existing in the training set of data modification, fitting, fitting, is likely to be seen that this parameter is only for the data fitting is accurate in the training set, this time again need to use a data model predicted results, the accuracy may be very poor.为了测试已经训练好的模型的精确度。当然,test set这并不能保证模型的正确性,他只是说相似的数据用此模型会得出相似的结果。因为我们在训练模型的时候,参数全是根据现有训练集里的数据进行修正、拟合,有可能会出现过拟合的情况,即这个参数仅对训练集里的数据拟合比较准确,这个时候再有一个数据需要利用模型预测结果,准确率可能就会很差。
第三问:3:7
(留出法,交叉验证法,自助法)
机器学习建模过程
1.准备数据 2.建立并训练模型 3.实施和预测
机器学习的生命周期
1.获取数据 2.数据准备 3.数据整理 4.分析数据 5.训练模型 6.测试模型 7.实施
What is Data Mining ?什么是数据挖掘?
Data mining is looking for hidden, valid, and potentially useful patterns in huge data sets. It is all about discovering unsuspected/ previously unknown relationships amongst the data.数据挖掘是在巨大的数据集中寻找隐藏的、有效的和可能有用的模式。这一切都是关于发现数据之间未被怀疑或之前未知的关系。
What kind of information that Data Mining is looking for and try to discover and identify from the massive amount of Data ?数据挖掘在海量数据中寻找并试图发现和识别什么样的信息?
patterns that have not previously been discovered and trends that exist in data.These patterns cannot be discovered by traditional data exploration because the relationships are too complex or because there is too much data.以前没有发现的模式和数据中存在的趋势。由于关系太复杂或数据太多,传统的数据探索无法发现这些模式。
What are the two categories of Data Mining Functions / Tasks ? Explain their purposes ?数据挖掘的两个功能或任务是什么?解释其目的
Descriptive mining tasks characterize the general properties of the data in the database. Find humaninterpretable patterns that describe the data.描述性挖掘任务描述了数据库中数据的一般属性。找到人们可以理解的描述数据的模式
Predictive mining tasks perform inference on the current data in order to make predictions. Use some variables to predict unknown or future values of other variables.预测挖掘任务对当前数据进行推理,以便进行预测。用一些变量来预测其他变量的未知值或未来值。
What is Predictive Data Mining?How it works(Prediction), in general?
Predictive data mining is data mining that is done for the purpose of using business intelligence or other data to forecast or predict trends.预测数据挖掘是为了使用商业智能或其他数据来预测或预测趋势而进行的数据挖掘。
it works by utilizing a few variables of the present to predict the future not known data values for other variables.and The methods come under this type of mining category are called classification, time-series analysis and regression.它的工作原理是利用当前的一些变量来预测未知的未来其他变量的数据值。这类挖掘的方法有分类、时间序列分析和回归。
Explain how Predictive Model works? (tasks sequence)

What is ML Algorithm?
A set of rules used to make a calculation or solve a problem.
There are many ML algorithms, how to select the right algorithm?
1. Understand Your Data
1-1 Know your data
1-2 Clean your data
2. Categorize the problem
2-1 Categorize by input
2-2. Categorize by output.
3. Understand your constraints
4. Find the available algorithms
Model Evaluation, what is ML Model Evaluation Accuracy?
• True Positive (TP) — A true positive is an outcome where the model correctly predicts the positive class.
• True Negative (TN)—A true negative is an outcome where the model correctly predicts the negative class.
• False Positive (FP)—A false positive is an outcome where the model incorrectly predicts the positive class.
• False Negative (FN)—A false negative is an outcome where the model incorrectly predicts the negative class.
Accuracy - Accuracy is the most intuitive performance measure and it is simply a ratio of correctly predicted observation to the total observations.
Model accuracy in terms of classification models can be defined as the ratio of correctly classified samples to the total number of samples:
Accuracy = TP+TN/TP+FP+FN+TN
Accuracy = (TP+TN)/total
What is ML Model Precision?
What is ML model Precision?
Precision is the ratio of system generated results that correctly predicted positive observations (True Positives) to the system’s total predicted positive observations, both correct (True Positives) and incorrect (False Positives). Precision = TP/TP+FP
What is Recall?
The recall is the measure of our model correctly identifying True Positives.
Recall tells us how many we correctly identified as having a heart disease.
In this context, recall is defined as the number of true positives divided by the total number of elements that actually elong to the positive class (/*i.e. the sum of true positives and false negatives, which are items which were not labeled as belonging to the positive class but should have been*/).
(召回是我们模型正确识别“真实肯定”的度量。召回率告诉我们有多少我们正确地识别为患有心脏病。在这种情况下,召回率定义为真实阳性的数量除以实际属于阳性类别的元素的总数)
What is Deep Learning ?
(1)Deep learning is a machine learning technique that learns featuresand tasks directly from data. Data can be images, text, or sound.(深度学习是一种直接从数据中学习特征和任务的机器学习技术。 数据可以是图像,文本或声音。)
(2)Deep learning is a subset of machine learning in artificial intelligence that has networks capable of learning unsupervised from data that is unstructured or unlabeled. Also known as deep neural learning or deep neural network.(深度学习是人工智能机器学习的一个子集,它具有能够从非结构化或未标记的数据中不受监督地学习的网络。 也称为深度神经学习或深度神经网络。)
The term “deep” refers to the number of layers in the network—the more layers, the deeper the network. Neural networks contain a series of neurons, or nodes, which are interconnected and process input.(术语“深度”是指网络中的层数-层越多,网络越深。 神经网络包含一系列神经元或节点,它们相互连接并进行过程输入。)
What is the difference between Machine Learning and Deep Learning?
(1)Machine learning covers deep learning. (机器学习包括深度学习。)
(2)Features are given machine learning manually. (特征是机器学习手动给出的。)
(3)On the other hand, deep learning learns features directly from data.(另一方面,深度学习直接从数据中学习特征。)

| Machine Learning | Deep Learning |
| 使机器能够根据过去的数据自己做出决定。 只需要少量的训练数据 在低端系统上运行良好 大多数功能需要提前识别并手动编码 问题被分成几个部分,分别解决,然后结合起来 测试需要更长的时间 Crip规则解释了为什么会做出某个决定 | 使机器在人工神经网络的帮助下作出决定 需要大量的培训数据 需要高端系统工作 机器从提供的数据中学习特征,将原始图像直接输入一个自动学习特征的深度神经网络。 以端到端的方式解决问题 测试花费的时间更少 因为系统根据自己的逻辑做出决策。其原因可能难以解释 |